China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
“Support Xinjiang MianHua!” – China’s Social Media Storm over Xinjiang Cotton Ban
The hashtag “Wo Zhichi Xinjiang Mianhua” – “I Support Xinjiang Cotton” – received over 6 billion views on Weibo.
Published
3 years agoon

Western brands faced heavy criticism in China this week when a social media storm erupted over the Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) and its brand members for no longer sourcing from China’s Xinjiang region. The ‘Xinjiang cotton ban’ led to a major ‘Xinjiang cotton support’ campaign on Weibo, and a boycott for those brands siding with BCI.
In 2019, an extensive brand ‘witch hunt’ took place on Weibo and other Chinese social media networks in light of the protests in Hong Kong, with international fashion and luxury brands, from Versace to Swarovski, getting caught in the crossfire for listing Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan as separate countries or regions – not part of China – on their official websites or brand T-shirts.
Now, another brand ‘witch hunt’ is taking place on Chinese social media. This time, it is not about Hong Kong, but about Xinjiang and its cotton industry.
H&M, Uniqlo, Nike, Adidas and other international brands have caused public outrage for the stand they’ve taken against the alleged use of forced labor involving the Muslim Uyghur minority to produce cotton in China’s western region of Xinjiang.
The social media storm started earlier this week on Wednesday, March 24, and is linked to H&M and the ‘BCI’ (Better Cotton Initiative), a Swiss NGO that aims to promote better standards in cotton farming.
In October 2020, H&M shared a statement on its site in which the Swedish retailer said it was “deeply concerned” over reports of forced labor in the production of cotton in Xinjiang, officially Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR).
H&M stated that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang, following the BCI decision to suspend licensing of BCI cotton in the region.
BCI and its Suspension of Activities in Xinjiang
The Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) is the largest cotton sustainability program in the world. It practices across 23 countries and accounts for 22% of global cotton production. The governance group was established in 2005 in cooperation with WWF and leading retailers, with the aim of promoting the widespread use of improved farm practices.

While H&M is a ‘top member’ of the Better Cotton Initiative (link), many others brands such as IKEA, Gap, Adidas, Nike, Levi’s, and C&A are also brand members.
January 2020
In January of 2020, the BCI was slammed by Dr Adrian Zenz, a senior fellow with the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation in Washington DC, for its refusal to pull out of the Xinjiang region. At the time, 20 percent of its ‘better cotton’ was sourced from Xinjiang, which is China’s largest cotton growing area.
According to a 2020 report by EcoTextile, the BCI maintained that its implicated council member, the yarn producer Huafu, denied the allegations and that an independent audit of the company’s Aksu facility in Xinjiang had failed to identify any instances of forced labor. An earlier report by Adidas from 2019 also stated that their independent investigations found no evidence of forced labor.
March 2020
In late March of 2020, the BCI reportedly did suspend activities with licensed farmers in the Xinjiang region for the 2020/21 cotton season while also contracting a global expert to conduct an external review of the Xinjiang situation. Chinese state media Global Times later reported that despite suspending its licensing activities, the BCI would remain committed to cotton farming communities in Xinjiang and would continue to engage in activities in the region.
July 2020
The pressure on BCI and other brands to stop sourcing from Xinjiang was heightened when a coalition of civil society groups raised concerns over the treatment of the Uyghur Muslim minority in China and the “grave risk of forced labor.” Reuters reported that more than 180 organizations urged brands from Adidas to Amazon to end sourcing of cotton and clothing from the region and cut ties with any suppliers in China that would benefit from the alleged forced labour of Uyghur other Muslim groups.
October 2020
In October of 2020, the Better Cotton Initiative announced it would cease all field-level activities in Xinjiang with immediate effect because the region had reportedly become “an increasingly untenable operating environment.” The aforementioned statement by H&M came out in the same month.
March 2021
By late March 2021, various Chinese state media reported on the BCI suspension. These reports came days after a coordinated effort by the United States, the European Union, Britain and Canada to impose sanctions on Chinese officials over China’s alleged human rights violations and abuses in Xinjiang, something which was called a “concerted effort to slander China’s policies in its Xinjiang region” by Global Times. The news outlet linked these “anti-China forces’ efforts” to the BCI decision to suspend its Xinjiang activities.
A Social Media Storm over Xinjiang Cotton
The news developments were followed by a wave of social media boycott movements and Chinese brand ambassadors cutting ties with international brands, with H&M being the main target over its Xinjiang statement.
Chinese e-commerce platforms Taobao, JD.com, Pinduoduo, Suning.com, and Meituan’s Dianping on Thursday all removed H&M from their platforms, with Chinese Android app stores also removing H&M. On Thursday, a search for “H&M” came up with no results on these sites (see images below).
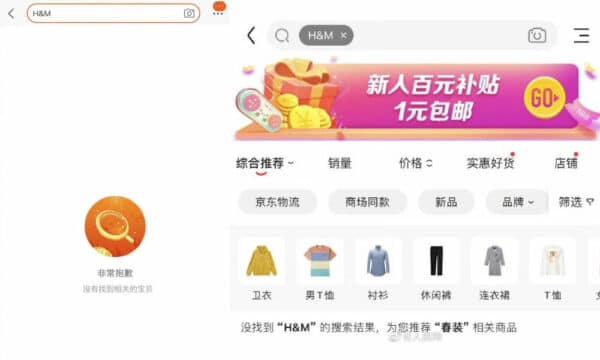
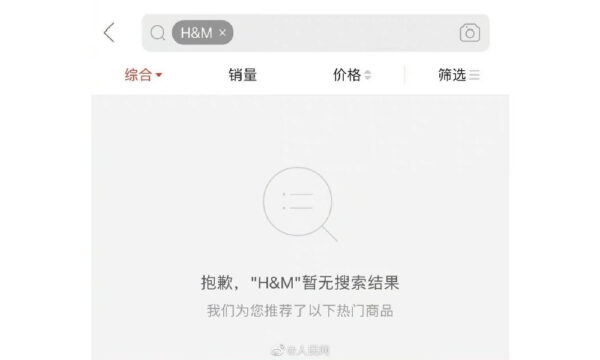
Two of China’s largest online maps also removed H&M from its systems.
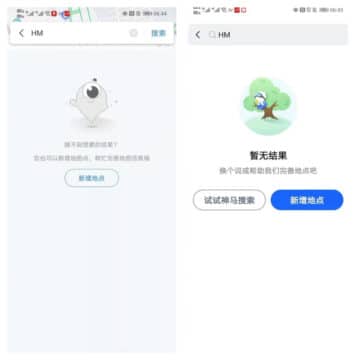
No H&M on these maps.
On Thursday, virtually all topics in Weibo’s top trending lists related to the Xinjiang cotton ban (see image below), with Chinese famous influencers and celebrities one by one announcing they would terminate their contracts with international brands related to the Xinjiang cotton ban.

The storm became so big this week that some people on social media even commented that “if you’re a Chinese celebrity and you don’t have any contracts to terminate now, you’re not doing so well.”
After H&M, an entire list of brands was targeted, including Adidas, Nike, Calvin Klein, New Balance, Tommy Hilfiger, Uniqlo, Converse, Puma, Burberry, and Lacoste.
In light of the heated discussions and calls for boycotts, there was also another hashtag that popped up on Weibo, namely that of “don’t make it hard for the workers” (不要为难打工人). The hashtag came up after some Chinese staff members at Nike and Adidas stores were scolded on a live stream, with netizens calling on people to stay rational and not let the boycott turn into personal attacks on people. But another popular video showed a man in Chongqing calling customers out in an H&M store for buying their “trash.”
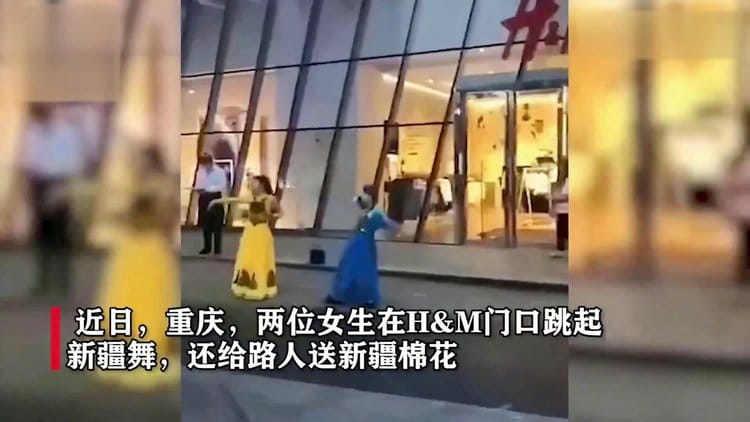
Another hashtag gaining many views, 520 million in total, was that of two ‘girls from Xinjiang dancing outside H&M’ (#新疆小姐姐在HM门店外跳新疆舞#) – it was linked to a video that showed two women performing outside of a H&M store in Chongqing.
Meanwhile, some brands, including Chinese company Anta Sports and the Japanese Asics, reportedly announced they would leave the Better Cotton Initiative in order to continue sourcing cotton from Xinjiang.
The discussions on Xinjiang as Weibo saw this week are unprecedented, as ‘Xinjiang’ was previously a sensitive topic on Chinese social media and was barely discussed in political contexts. The last time Xinjiang became a big topic of discussion on Chinese social media was in 2018, when CCTV aired a program on the region’s “vocational education programs” in Xinjiang. That media moment triggered mixed reactions on Weibo, with some commenters wondering what the difference between a ‘re-education center’ and a ‘prison’ is.
Chinese State Media and the ‘Xinjiang Cotton Ban’
While Chinese netizens and celebrities play a major role in the storm that erupted over BCI, H&M, and Xinjiang cotton, the role of Chinese state media is pivotal.
Over the past week, various state media outlets posted strong messages regarding the ban in various ways, the most noteworthy one being People’s Daily‘s “I Support Xinjiang Cotton” (#我支持新疆棉花#) hashtag, which had garnered six billion views by the weekend. “The H&M Group released a statement that sparked outrage among netizens. Let’s pass it on together: Support Xinjiang Cotton,” the tagline of the hashtag page said.

The message came with an image saying “Xinjiang Mianhua” (Xinjiang cotton) in a similar font to the H&M logo, the “H” and “M” within ‘mianhua‘ being identical to the H&M letters.


The image and post by People’s Daily was shared over 36 million times.

A message by People’s Daily: those who slander China are not welcome.
Another image by People’s Daily published on March 25 said that the Chinese market does not welcome those who slander China.
The Communist Youth League also contributed to the online storm by posting about H&M, writing: “On the one hand they are starting rumors and boycotting Xinjiang cotton, on the other hand they want to make money in China. Dream on, H&M!” That post received around 430,000 likes.
Various official media, including Global Times and China Daily, posted about cotton production in Xinjiang. Besides refuting the forced labor accusations and accusing Western players of hypocrisy and ulterior motives, a recurring issue stressed is how 42 percent of Xinjiang’s cotton is harvested by machines. Ministry of Commerce spokesman Gao Feng was quoted as saying that “the so-called forced labor in Xinjiang is nonexistent and entirely imaginary. The spotless white Xinjiang cotton brooks no slander.”

This image was posted by China Daily USA.
On March 27, People’s Daily posted a rap video by ‘Xinjiang Youth’ (新疆青年) on its official Weibo channel (video below) that included some tough lines attacking Western powers, companies, and media.
Chinese state media are now posting this rap song on social media about the “Western forces slandering Xinjiang cotton.” pic.twitter.com/piouahMf80
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) March 27, 2021
Also noteworthy in this propaganda campaign is how the Canadian YouTuber Daniel Dumbrill got caught up, as what he said in one of his videos was quoted by Foreign Ministry spokesperson Hua Chunying (华春莹) on March 27 during a press conference, with his video being screened before the conference.
In this video, that was part of a larger panel on Xinjiang, Dumbrill responded to the decision-making process on how China’s treatment of Uyghurs is called a “genocide.”
Recently, a number of countries and parliaments including the U.S., Canada and the Netherlands have declared that China’s crackdown on the Muslim minorities amounts to “genocide” in violation of the U.N. Genocide Convention. Dumbrill talks about why the Xinjiang narratives matter to both the foreign and domestic politics of the US and other Western countries, with Dumbril claiming it “isn’t really about human rights and a care for overseas Muslims” but about other political goals. Dumbrill’s video was praised by authorities, state media, and by Chinese netizens.
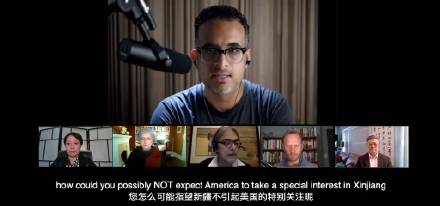
“We have to push for the truth to come out,” some netizens commented. Others wrote: “But we’re only allowed to discuss it from within [the country].”
Meanwhile, while many companies are seeing sales falling, there are also many who are benefiting from the current developments. Some sellers on Taobao have found another way to attract customers, promoting their products as being made with “100% Xinjiang Cotton!”

As this is an ongoing topic, we will report more later. Meanwhile, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2021 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron
Who’s gonna buy this Zara dress in China? “I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”
Published
4 days agoon
April 19, 2024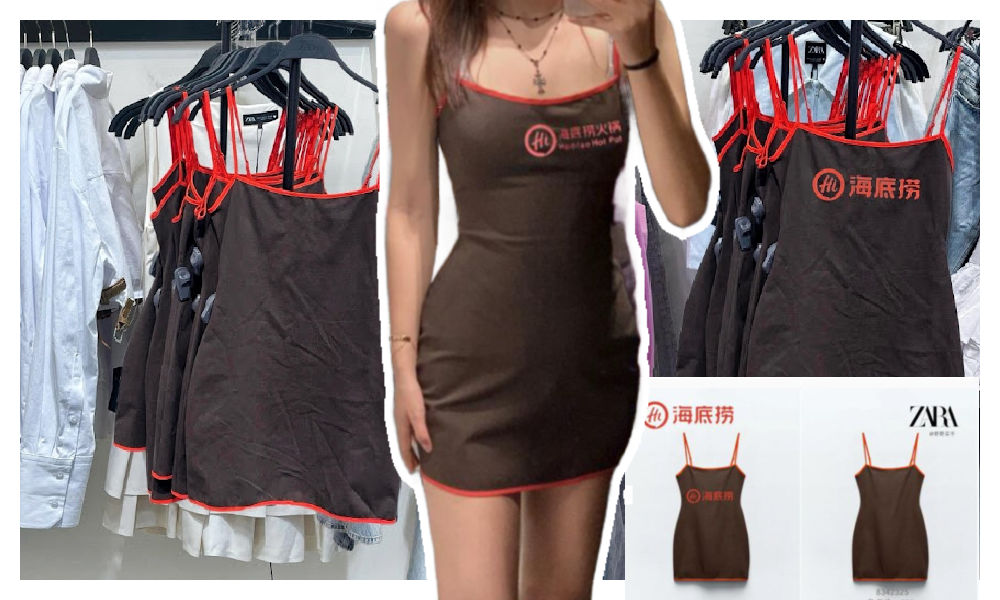
A short dress sold by Zara has gone viral in China for looking like the aprons used by the popular Chinese hotpot chain Haidilao.
“I really thought it was a Zara x Haidialo collab,” some customers commented. Others also agree that the first thing they thought about when seeing the Zara dress was the Haidilao apron.
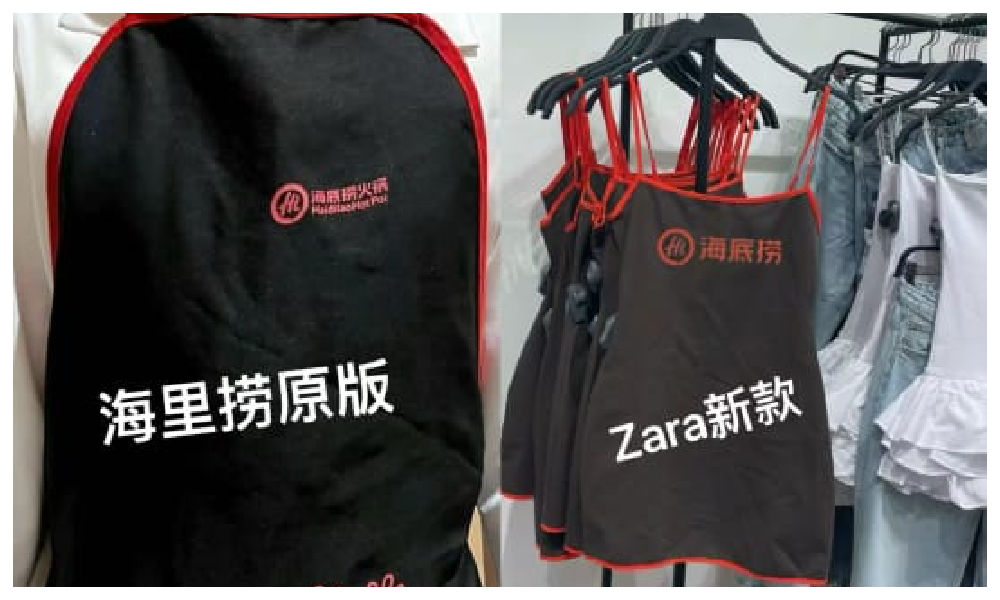

The “original” vs the Zara dress.
The dress has become a popular topic on Xiaohongshu and other social media, where some images show the dress with the Haidilao logo photoshopped on it to emphasize the similarity.

One post on Xiaohongshu discussing the dress, with the caption “Curious about the inspiration behind Zara’s design,” garnered over 28,000 replies.
Haidilao, with its numerous restaurants across China, is renowned for its hospitality and exceptional customer service. Anyone who has ever dined at their restaurants is familiar with the Haidilao apron provided to diners for protecting their clothes from food or oil stains while enjoying hotpot.
These aprons are meant for use during the meal and should be returned to the staff afterward, rather than taken home.
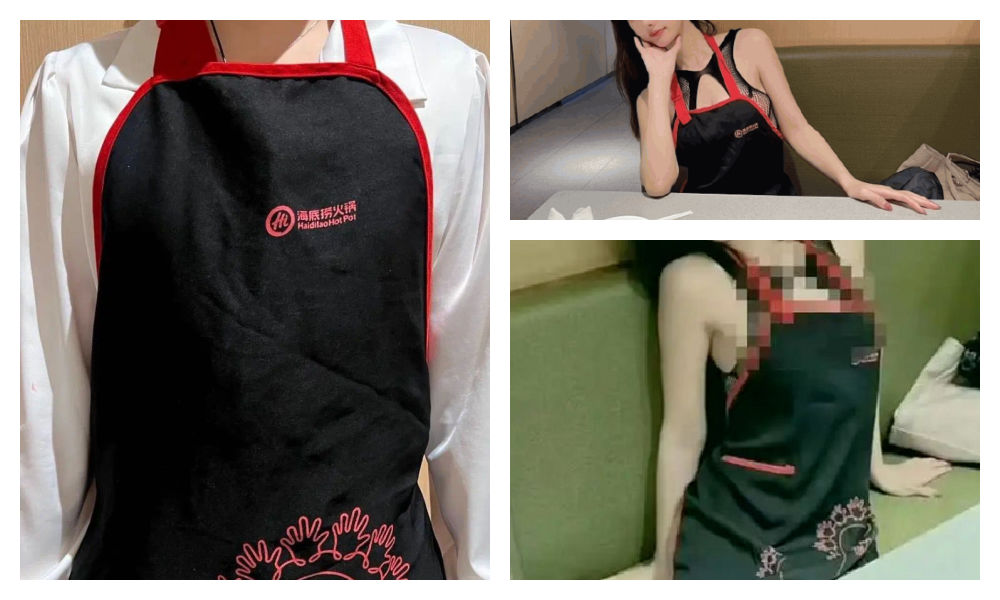

The Haidilao apron.
However, many people who have dined at Haidilao may have encountered the following scenario: after indulging in drinks and hotpot, they realize they are still wearing a Haidilao apron upon leaving the restaurant. Consequently, many hotpot enthusiasts may have an ‘accidental’ Haidilao apron tucked away at home somewhere.
This only adds to the humor of the latest Zara dress looking like the apron. The similarity between the Zara dress and the Haidilao apron is actually so striking, that some people are afraid to be accused of being a thief if they would wear it.
One Weibo commenter wrote: “The most confusing item of this season from Zara has come out. It’s like a Zara x Haidilao collaboration apron… This… I can’t wear it: I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”

Funnily enough, the Haidilao apron similarity seems to have set off a trend of girls trying on the Zara dress and posting photos of themselves wearing it.

It’s doubtful that they’re actually purchasing the dress. Although some commenters say the dress is not bad, most people associate it too closely with the Haidilao brand: it just makes them hungry for hotpot.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Zibo had its BBQ moment. Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine with its special take on malatang. Tourism marketing in China will never be the same again.
Published
3 weeks agoon
April 1, 2024
Since the early post-pandemic days, Chinese cities have stepped up their game to attract more tourists. The dynamics of Chinese social media make it possible for smaller, lesser-known destinations to gain overnight fame as a ‘celebrity city.’ Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine.
During this Qingming Festival holiday, there is one Chinese city that will definitely welcome more visitors than usual. Tianshui, the second largest city in Gansu Province, has emerged as the latest travel hotspot among domestic tourists following its recent surge in popularity online.
Situated approximately halfway along the Lanzhou-Xi’an rail line, this ancient city wasn’t previously a top destination for tourists. Most travelers would typically pass through the industrial city to see the Maiji Shan Grottoes, the fourth largest Buddhist cave complex in China, renowned for its famous rock carvings along the Silk Road.
But now, there is another reason to visit Tianshui: malatang.
Gansu-Style Malatang
Málàtàng (麻辣烫), which literally means ‘numb spicy hot,’ is a popular Chinese street food dish featuring a diverse array of ingredients cooked in a soup base infused with Sichuan pepper and dried chili pepper. There are multiple ways to enjoy malatang.
When dining at smaller street stalls, it’s common to find a selection of skewered foods—ranging from meats to quail eggs and vegetables—simmering in a large vat of flavorful spicy broth. This communal dining experience is affordable and convenient for solo diners or smaller groups seeking a hotpot-style meal.
In malatang restaurants, patrons can usually choose from a selection of self-serve skewered ingredients. You have them weighed, pay, and then have it prepared and served in a bowl with a preferred soup base, often with the option to choose the level of spiciness, from super hot to mild.
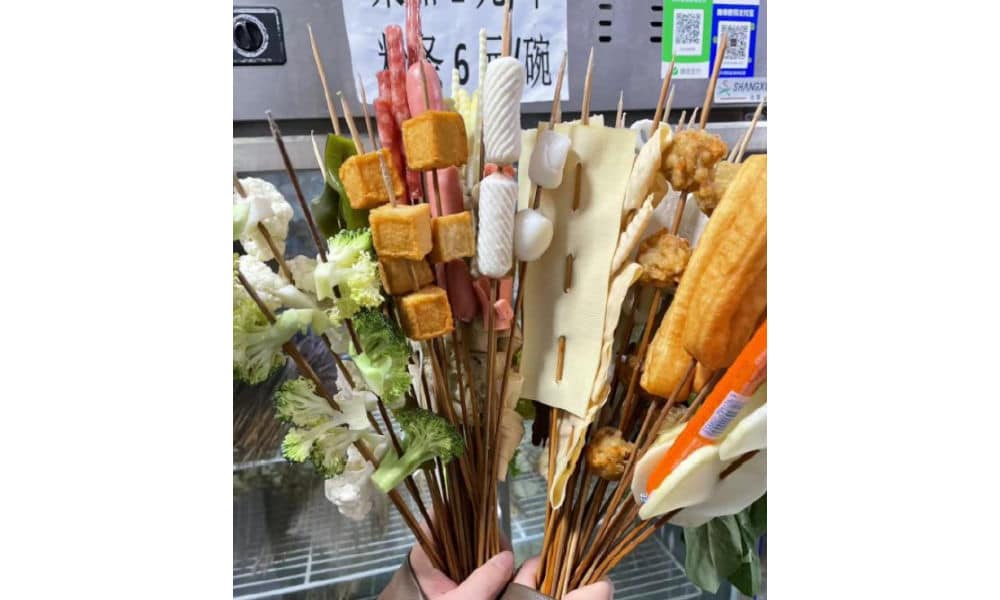

Although malatang originated in Sichuan, it is now common all over China. What makes Tianshui malatang stand out is its “Gansu-style” take, with a special focus on hand-pulled noodles, potato, and spicy oil.
An important ingredient for the soup base is the somewhat sweet and fragrant Gangu chili, produced in Tianshui’s Gangu County, known as “the hometown of peppers.”
Another ingredient is Maiji peppercorns (used in the sauce), and there are more locally produced ingredients, such as the black fungi from Qingshui County.
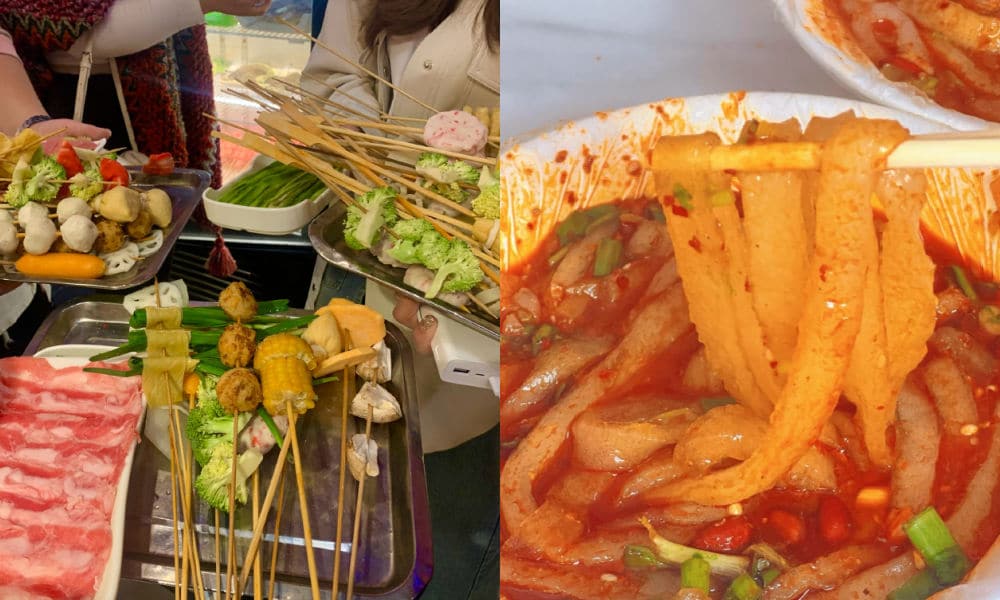

One restaurant that made Tianshui’s malatang particularly famous is Haiying Malatang (海英麻辣烫) in the city’s Qinzhou District. On February 13, the tiny restaurant, which has been around for three decades, welcomed an online influencer (@一杯梁白开) who posted about her visit.
The vlogger was so enthusiastic about her taste of “Gansu-style malatang,” that she urged her followers to try it out. It was the start of something much bigger than she could have imagined.
Replicating Zibo
Tianshui isn’t the first city to capture the spotlight on Chinese social media. Cities such as Zibo and Harbin have previously surged in popularity, becoming overnight sensations on platforms like Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin.
This phenomenon of Chinese cities transforming into hot travel destinations due to social media frenzy became particularly noteworthy in early 2023.
During the Covid years, various factors sparked a friendly competition among Chinese cities, each competing to attract the most visitors and to promote their city in the best way possible.
The Covid pandemic had diverse impacts on the Chinese domestic tourism industry. On one hand, domestic tourism flourished due to the pandemic, as Chinese travelers opted for destinations closer to home amid travel restrictions. On the other hand, the zero-Covid policy, with its lockdowns and the absence of foreign visitors, posed significant challenges to the tourism sector.
Following the abolition of the zero-Covid policy, tourism and marketing departments across China swung into action to revitalize their local economy. China’s social media platforms became battlegrounds to capture the attention of Chinese netizens. Local government officials dressed up in traditional outfits and created original videos to convince tourists to visit their hometowns.
Zibo was the first city to become an absolute social media sensation in the post-Covid era. The old industrial and mining city was not exactly known as a trendy tourist destination, but saw its hotel bookings going up 800% in 2023 compared to pre-Covid year 2019. Among others factors contributing to its success, the city’s online marketing campaign and how it turned its local BBQ culture into a unique selling point were both critical.

Zibo crowds, image via 163.com.
Since 2023, multiple cities have tried to replicate the success of Zibo. Although not all have achieved similar results, Harbin has done very well by becoming a meme-worthy tourist attraction earlier in 2024, emphasizing its snow spectacle and friendly local culture.
By promoting its distinctive take on malatang, Tianshui has emerged as the next city to captivate online audiences, leading to a surge in visitor numbers.
Like with Zibo and Harbin, one particular important strategy used by these tourist offices is to swiftly respond to content created by travel bloggers or food vloggers about their cities, boosting the online attention and immediately seizing the opportunity to turn online success into offline visits.
A Timeline
What does it take to become a Chinese ‘celebrity city’? Since late February and early March of this year, various Douyin accounts started posting about Tianshui and its malatang.
They initially were the main reason driving tourists to the city to try out malatang, but they were not the only reason – city marketing and state media coverage also played a role in how the success of Tianshui played out.
Here’s a timeline of how its (online) frenzy unfolded:
- July 25, 2023: First video on Douyin about Tianshui’s malatang, after which 45 more videos by various accounts followed in the following six months.
- Feb 5, 2024: Douyin account ‘Chuanshuo Zhong de Bozi’ (传说中的波仔) posts a video about malatang streetfood in Gansu
- Feb 13, 2024: Douyin account ‘Yibei Liangbaikai’ (一杯梁白开) posts a video suggesting the “nationwide popularization of Gansu-style malatang.” This video is an important breakthrough moment in the success of Tianshui as a malatang city.
- Feb – March ~, 2024: The Tianshui Culture & Tourism Bureau is visiting sites, conducting research, and organizing meetings with different departments to establish the “Tianshui city + malatang” brand (文旅+天水麻辣烫”品牌) as the city’s new “business card.”
- March 11, 2024: Tianshui city launches a dedicated ‘spicy and hot’ bus line to cater to visitors who want to quickly reach the city’s renowned malatang spots.
- March 13-14, 2024: China’s Baidu search engine witnesses exponential growth in online searches for Tianshui malatang.
- March 14-15, 2024: The boss of Tianshui’s popular Haiying restaurant goes viral after videos show him overwhelmed and worried he can’t keep up. His facial expression becomes a meme, with netizens dubbing it the “can’t keep up-expression” (“烫不完表情”).

The worried and stressed expression of this malatang diner boss went viral overnight.
- March 17, 2024: Chinese media report about free ‘Tianshui malatang’ wifi being offered to visitors as a special service while they’re standing in line at malatang restaurants.
- March 18, 2024: Tianshui opens its first ‘Malatang Street’ where about 40 stalls sell malatang.
- March 18, 2024: Chinese local media report that one Tianshui hair salon (Tony) has changed its shop into a malatang shop overnight, showing just how big the hype has become.
- March 21, 2024: A dedicated ‘Tianshui malatang’ train started riding from Lanzhou West Station to Tianshui (#天水麻辣烫专列开行#).
- March 21, 2024: Chinese actor Jia Nailiang (贾乃亮) makes a video about having Tianshui malatang, further adding to its online success.
- March 30, 2024: A rare occurrence: as the main attraction near Tianshui, the Maiji Mountain Scenic Area announces that they’ve reached the maximum number of visitors and don’t have the capacity to welcome any more visitors, suspending all ticket sales for the day.
- April 1, 2024: Chinese presenter Zhang Dada was spotted making malatang in a local Tianshui restaurant, drawing in even more crowds.
A New Moment to Shine
Fame attracts criticism, and that also holds true for China’s ‘celebrity cities.’
Some argue that Tianshui’s malatang is overrated, considering the richness of Gansu cuisine, which offers much more than just malatang alone.
When Zibo reached hype status, it also faced scrutiny, with some commenters suggesting that the popularity of Zibo BBQ was a symptom of a society that’s all about consumerism and “empty social spectacle.”
There is a lot to say about the downsides of suddenly becoming a ‘celebrity city’ and the superficiality and fleetingness that comes with these kinds of trends. But for many locals, it is seen as an important moment as they see their businesses and cities thrive.
Even after the hype fades, local businesses can maintain their success by branding themselves as previously viral restaurants. When I visited Zibo a few months after its initial buzz, many once-popular spots marketed themselves as ‘wanghong’ (网红) or viral celebrity restaurants.
For the city itself, being in the spotlight holds its own value in the long run. Even after the hype has peaked and subsided, the gained national recognition ensures that these “trendy” places will continue to attract visitors in the future.
According to data from Ctrip, Tianshui experienced a 40% increase in tourism spending since March (specifically from March 1st to March 16th). State media reports claim that the city saw 2.3 million visitors in the first three weeks of March, with total tourism revenue reaching nearly 1.4 billion yuan ($193.7 million).
There are more ripple effects of Tianshui’s success: Maiji Shan Grottoes are witnessing a surge in visitors, and local e-commerce companies are experiencing a spike in orders from outside the city. Even when they’re not in Tianshui, people still want a piece of Tianshui.
By now, it’s clear that tourism marketing in China will never be the same again. Zibo, Harbin, and Tianshui exemplify a new era of destination hype, requiring a unique selling point, social media success, strong city marketing, and a friendly and fair business culture at the grassroots level.
While Zibo’s success was largely organic, Harbin’s was more orchestrated, and Tianshui learned from both. Now, other potential ‘celebrity’ cities are preparing to go viral, learning from the successes and failures of their predecessors to shine when their time comes.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Where to Eat and Drink in Beijing: Yellen’s Picks

Weibo Watch: Burning BMWs

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

In Hot Water: The Nongfu Spring Controversy Explained

The Benz Guy from Baoding and the Granny Xu Line-Cutting Controversy

Weibo Watch: Stealing the Show
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight2 months ago
China Insight2 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Arts & Entertainment2 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment2 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday
-

 China Media1 month ago
China Media1 month agoParty Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”
-

 China World2 months ago
China World2 months agoFrom Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)





Michael Gordon
April 8, 2021 at 5:39 pm
we support the Xinjiang people!