China Arts & Entertainment
The Comeback of Calligraphy in China
In the digital age, calligraphy has not just maintained its relevancy in China; it has made a comeback. Calligraphy researcher Laura Vermeeren talks about the power of calligraphy and the status quo of this ancient art in modern China.
Published
8 years agoon

In the digital age, calligraphy has not just maintained its relevancy in China; it has made a comeback. Calligraphy researcher Laura Vermeeren talks about the power of calligraphy and the status quo of this ancient art in modern China.
This interview with Laura Vermeeren, sinologist and Ph.D. researcher in Chinese calligraphy, was conducted and condensed by Manya Koetse in Beijing.
The word ‘calligraphy’ comes from the ancient Greek kallos “beauty” and graphein “writing”, referring to the visual art of decorative writing by pen or brush. In China, it is known as shufa (书法), literally meaning the method or law of writing. Calligraphy was the main form of art in traditional China, and it was appreciated as a fine art long before painting became more common.
Calligraphy has seen a boom in recent years, as part of the surge in popularity of guoxue (国学), the learning of traditional Chinese culture. It was partly fuelled by President Xi Jinping promoting Chinese traditions, which is seen by some as a way for the Communist Party to legimitize their ruling power, reinventing themselves as the “inheritor and savior of a 5000-year-old civilization”.
Dutch sinologist Laura Vermeeren moved to Beijing this year to dive into the world of Chinese calligraphy. The research is part of a larger project by University of Amsterdam on creativity in China, a 5-year programme where ten researchers collaborately research China’s shift from a “made in China” towards a “created in China” country.
What’s on Weibo sat down with Laura to ask her about her love for calligraphy, its status quo in Chinese society, and its link to the digital era.
MORE THAN PAPER AND INK
“Calligraphy is entwined with Chinese language and history.”
“Calligraphy is a very honest form of art. Many forms of western art are about redoing, resculpting, and repainting until something is right. Painters can spend months on end working on one oil painting. But in calligraphy, it has to be right at once. You only get one chance to put your character on paper. Any hesitation in the calligrapher will reflect in the calligraphy. You can see by the strokes of the characters if it was done fast or slow, how the ink was used, how the paper is filled up. It is virtually always done with black on white, so every little drop of ink is noticeable. There is no way to hide.”
“Calligraphy is an art with so many layers. There are millions of things written about it, there are thousands of years of history behind it. You cannot separate the art from its history. It might seem like a simple form of art, that just needs the right paper, ink and brush, but the entire tradition and culture around it makes it deep and complex. It is entwined with Chinese language and history.”
“One of my favorite calligraphers is Mi Fu [米芾, Chinese calligrapher who lived from 1051–1107]. I cannot explain why – it is a feeling. It always makes me realize that there is so much to calligraphy; it is beautifully written, and there is an actual message. It is visual art with textual content.”
ALIVE AND KICKING
“It is often said that calligraphy has revived, but it has actually never been dead.”
“It is often said that Chinese calligraphy has been revived, but it has actually never been dead. I would prefer saying it went into some sort of hibernation mode for some time.”
“Unlike other forms of art, calligraphy was not abolished during the Mao years because Mao Zedong loved calligraphy. He has done quite a lot of famous calligraphy, just think about the People’s Daily logo (Renmin Ribao) – those are Mao’s characters. During the Mao years, calligraphy was indeed practiced, but mainly by higher officials. There were no lessons in calligraphy at the time for the common people.”

Logo of People’s Daily, by Mao Zedong.
“After Mao’s death, in the 1980s, contemporary calligraphy emerged. It was brought to life by a group of modern calligraphers who did not want to return to previous styles. They wanted to define what Chinese calligraphy should look like in the new age, and created their own style. They were influenced by modern abstract art forms from America. People like Gu Wenda and Xu Bing belong to this group of calligraphers. Xu Bing is especially famous for his square characters.”
 Xu Bing. Square Word Calligraphy, 2011, Columbia University.
Xu Bing. Square Word Calligraphy, 2011, Columbia University.
“One of the reasons why calligraphy is experiencing a comeback now is because Xi Jinping is pushing for a revival of Chinese traditions. Calligraphy is an easy tradition to implement, and a relevant one: it is said that calligraphy is the source of all art in China.”
“The government will soon implement the teaching of calligraphy in schools. Because there are not enough teachers in the country, there will also be government-funded schools to train people to become calligraphy teachers. So that is one part of the ‘revival’.”
“The other part has to do with the times we live in. In the digital era, you see more and more people who turn to basic activities that are not related to their computer screens. In Europe, I have noticed that gardening is becoming a popular activity again, with some people getting busy with rooftop farming. Coloring books for adults have even become a hype. In that way, calligraphy is also part of this global movement where people turn their attention to things, from farming to knitting, that have nothing to do with the digital age.”
WILL THE REAL CALLIGRAPHER PLEASE STAND UP?
“There is an entire world behind Chinese calligraphy that will remain a mystery to me.”
“There is an entire world behind Chinese calligraphy that will remain a mystery to me. What is good or bad calligraphy? When is somebody really a calligrapher? Most people I have encountered during my interviews and research do not call themselves that, they mostly say they are doing it as a hobby. They sometimes say you have to study calligraphy for a century before you can really be good at it, and understand it. The people I spoke to who call themselves a calligrapher actually have a university degree in it – it implies that there always has to be a theoretical background to being a ‘calligrapher’. But in the Netherlands, anyone could call themselves ‘an artist’ without having done any studies for it. It is not the same with calligraphy.”
“I have spoken to calligraphy students at Renmin University here, who argue that getting up at 5.00 am is the best way to really get into the habit of practicing their brush strokes. Their teacher urges them to practice at least 4 hours a day. In the morning, your head is still ‘empty’, so you can focus. You have to practice calligraphy for years before you can give a personal touch to it.”
“Thinking of calligraphers, the cliché image of the old Chinese wise man with a beard might pop up, but there are actually many trendy twenty-somethings who practice it, both men and women. They study the theory and practice the brush. But it is not just a fashion craze: calligraphy is something they take very seriously.”
WHEN WEIBO MEETS CALLIGRAPHY
“Calligraphy brings some spirituality to the digital age.”
“In China’s digitized society, most people are on their phones and computers all the time. Calligraphy is meaningful in the digital age in multiple ways. It can reach many people through social media, so the bigger calligraphy centers have their own accounts on Weixin and Weibo so people can follow them and stay updated on any events.”
“But it is also a powerful art form in another way, which is that people are writing and less and less now that everything can be done through phone. They then tend to forget how to actually write characters, and practicing calligraphy helps with this. New media can help people practicing their calligraphy. There are even apps now where people can train calligraphy.”
“Big brands also want to tie their name to calligraphy. Take Apple for example; they used the calligraphy of Wang Dongling for the opening of their flagship store in Hangzhou. It shows that calligraphy is, actually, very modern again.”
“In a rushed society, practicing calligraphy is very meditative. You have to rewrite the same characters again and again, you have to focus and mind your breathing. Calligraphy brings some spirituality to the digital age.”
THE POWER OF CALLIGRAPHY
“Practicing calligraphy requires you to dare and be impulsive, but at the same time, be in complete control of your impulses.”
“The more I know about calligraphy, the more I realize how complicated it is. There are so many sides to it. The way a piece is composed, how close the characters stand next to each other, how much space it takes up on the paper, the paper and ink you use, the style you choose, the way you hold your wrist. But those are just practicalities, there is also the mindset that goes with it.”
“Doing calligraphy is actually very exciting. You can fail within seconds, possibly messing up a very expensive piece of paper. Practicing calligraphy requires you to dare and be impulsive, but at the same time, be in complete control of your impulses.”
“Calligraphy is everywhere in Chinese society. If you pay attention to the streets, you will notice its influences from adverts using calligraphy fonts to people gathering in parks to do calligraphy; it is all around. Now that there are more and more schools teaching calligraphy, it is really becoming part of people’s lives again. That means that China is still continuing to build on the thousands of years of calligraphy history- it is history in motion. It makes calligraphy a very powerful phenomenon, and a very Chinese one.”
To stay updated on Laura’s research, check out her blog on the Power of Social Calligraphy, and like her page on Facebook.
– By Manya Koetse
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
featured image by Laura Vermeeren.
©2015 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Arts & Entertainment
“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng
Online reactions to the news of Fan’s marriage to Xu Meng, his fourth wife, reveal that the renowned artist is not particularly well-liked among Chinese netizens.
Published
6 hours agoon
April 18, 2024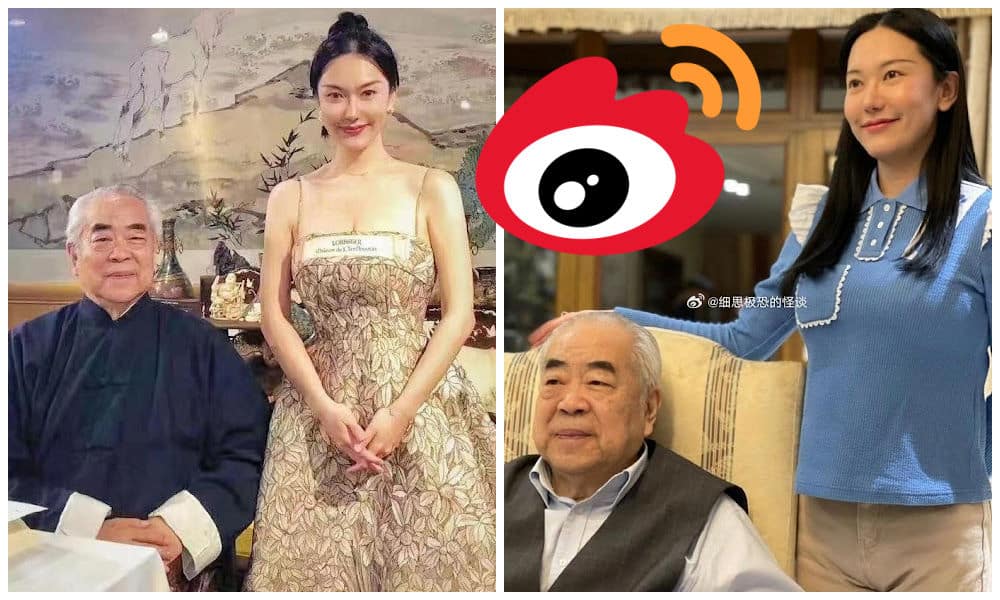
The recent marriage announcement of the renowned Chinese calligrapher/painter Fan Zeng and Xu Meng, a Beijing TV presenter 50 years his junior, has sparked online discussions about the life and work of the esteemed Chinese artist. Some netizens think Fan lacks the integrity expected of a Chinese scholar-artist.
Recently, the marriage of a 86-year-old Chinese painter to his bride, who is half a century younger, has stirred conversations on Chinese social media.
The story revolves around renowned Chinese artist, calligrapher, and scholar Fan Zeng (范曾, 1938) and his new spouse, Xu Meng (徐萌, 1988). On April 10, Fan announced their marriage through an online post accompanied by a picture.
In the picture, Fan is seen working on his announcement in calligraphic form.

Fan Zeng announces his marriage on Chinese social media.
In his writing, Zeng shares that the passing of his late wife, three years ago, left him heartbroken, and a minor stroke also hindered his work. He expresses gratitude for Xu Meng’s care, which he says led to his physical and mental recovery. Zeng concludes by expressing hope for “everlasting harmony” in their marriage.
Fan Zeng is a calligrapher and poet, but he is primarily recognized as a contemporary master of traditional Chinese painting. Growing up in a well-known literary family, his journey in art began at a young age. Fan studied under renowned mentors at the Academy of Fine Arts in Beijing, including Wu Zuoren, Li Keran, Jiang Zhaohe, and Li Kuchan.
Fan gained global acclaim for his simple yet vibrant painting style. He resided in France, showcased his work in numerous exhibitions worldwide, and his pieces were auctioned at Sotheby’s and Christie’s in the 1980s.[1] One of Fan’s works, depicting spirit guardian Zhong Kui (钟馗), was sold for over 6 million yuan (828,000 USD).

Zhong Kui in works by Fan Zeng.
In his later years, Fan Zeng transitioned to academia, serving as a lecturer at Nankai University in Tianjin. At the age of 63, he assumed the role of head of the Nankai University Museum of Antiquities, as well as holding various other positions from doctoral supervisor to honorary dean.
By now, Fan’s work has already become part of China’s twentieth-century art history. Renowned contemporary scholar Qian Zhongshu once remarked that Fan “excelled all in artistic quality, painting people beyond mere physicality.”
A questionable “role model”
Fan’s third wife passed away in 2021. Later, he got to know Xu Meng, a presenter at China Traffic Broadcasting. Allegedly, shortly after they met, he gifted her a Ferrari, sparking the beginning of their relationship.

A photo of Xu and her Hermes Birkin 25 bag has also been making the rounds on social media, fueling rumors that she is only in it for the money (the bag costs more than 180,000 yuan / nearly 25,000 USD).
On Weibo, reactions to the news of Fan’s marriage to Xu Meng, his fourth wife, reveal that the renowned artist is not particularly well-liked among netizens. Despite Fan’s reputation as a prominent philanthropist, many perceive his recent marriage as yet another instance of his lack of integrity and shamelessness.
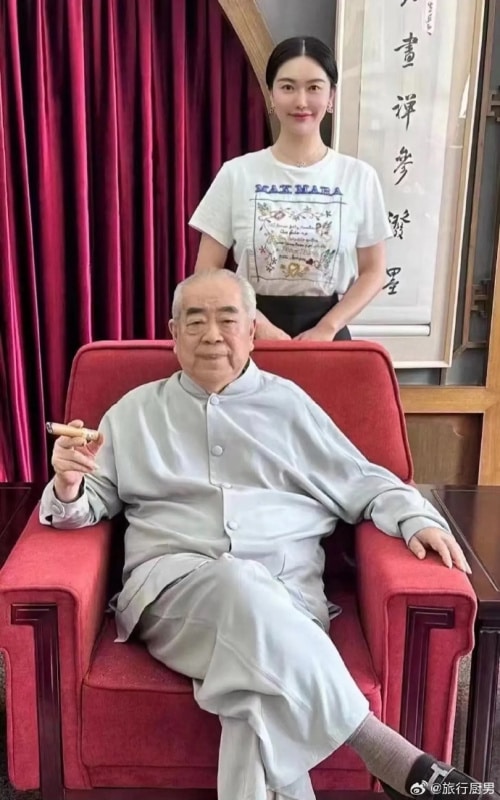

Fan Zeng and Xu Meng. Image via Weibo.
One popular blogger (@好时代见证记录者) sarcastically wrote:
“Warm congratulations to the 86-year-old renowned contemporary erudite scholar and famous calligrapher Fan Zeng, born in 1938, on his marriage to Ms Xu Meng, a 50 years younger 175cm tall woman who is claimed to be China’s number one golden ratio beauty. Mr Fan Zeng really is a role model for us middle-aged greasy men, as it makes us feel much less uncomfortable when we’re pursuing post-90s youngsters as girlfriends and gives us an extra shield! Because if contemporary Confucian scholars [like yourself] are doing this, then we, as the inheritors of Confucian culture, can surely do the same!“
Various people criticize the fact that Xu Meng is essentially just an aide to Fan, as she can often be seen helping him during his work. One commenter wrote: “Couldn’t he have just hired an assistant? There’s no need to turn them into a bed partner.”
Others think it’s strange for a supposedly scholarly man to be so superficial: “He just wants her for her body. And she just wants him for his inheritance.”
“It’s so inappropriate,” others wrote, labeling Fan as “an old bull grazing on young grass” (lǎoniú chī nèncǎo 老牛吃嫩草).
Fan is not the only well-known Chinese scholar to ‘graze on young grass.’ The famous Chinese theoretical physicist Yang Zhenning (杨振宁, 1922), now 101 years old, also shares a 48-year age gap with his wife Weng Fen (翁帆). Fan, who is a friend of Yang’s, previously praised the love between Yang and Weng, suggesting that she kept him youthful.
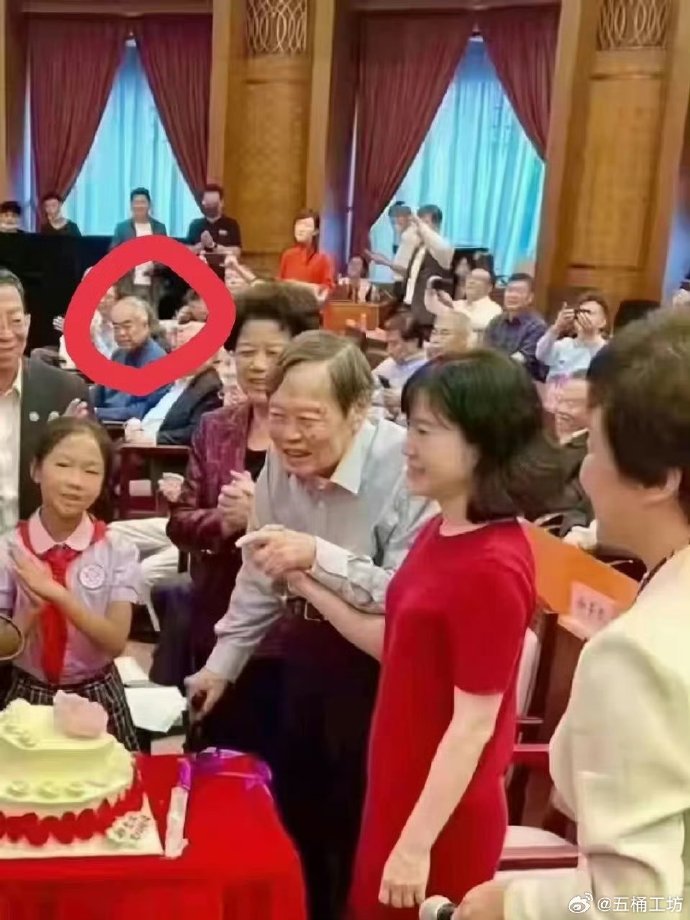

Older photo posted on social media, showing Fan attending the wedding ceremony of Yang Zhenning and his 48-year-younger partner Weng Fen.
Some speculate that Fan took inspiration from Yang in marrying a significantly younger woman. Others view him as hypocritical, given his expressions of heartbreak over his previous wife’s passing, and how there’s only one true love in his lifetime, only to remarry a few years later.
Many commenters argue that Fan Zeng’s conduct doesn’t align with that of a “true Confucian scholar,” suggesting that he’s undeserving of the praise he receives.
“Mr. Wang from next door”
In online discussions surrounding Fan Zeng’s recent marriage, more reasons emerge as to why people dislike him.
Many netizens perceive him as more of a money-driven businessman rather than an idealistic artist. They label him as arrogant, critique his work, and question why his pieces sell for so much money. Some even allege that the only reason he created a calligraphy painting of his marriage announcement is to profit from it.
Others cast doubt on his status as a Chinese calligraphy ‘grandmaster,’ noting that his calligraphy style is not particularly impressive and may contain typos or errors. His wedding announcement calligraphy appears to blend traditional and simplified characters.

Netizens have pointed out what looks like errors or typos in Fan’s calligraphy.
Another source of dislike stems from his history of disloyalty and his feud with another prominent Chinese painter, Huang Yongyu (黄永玉). Huang, who passed away in 2023, targeted Fan Zeng in some of his satirical paintings, including one titled “When Others Curse Me, I Also Curse Others” (“人骂我,我亦骂人”). He also painted a parrot, meant to mock Fan Zeng’s unoriginality.
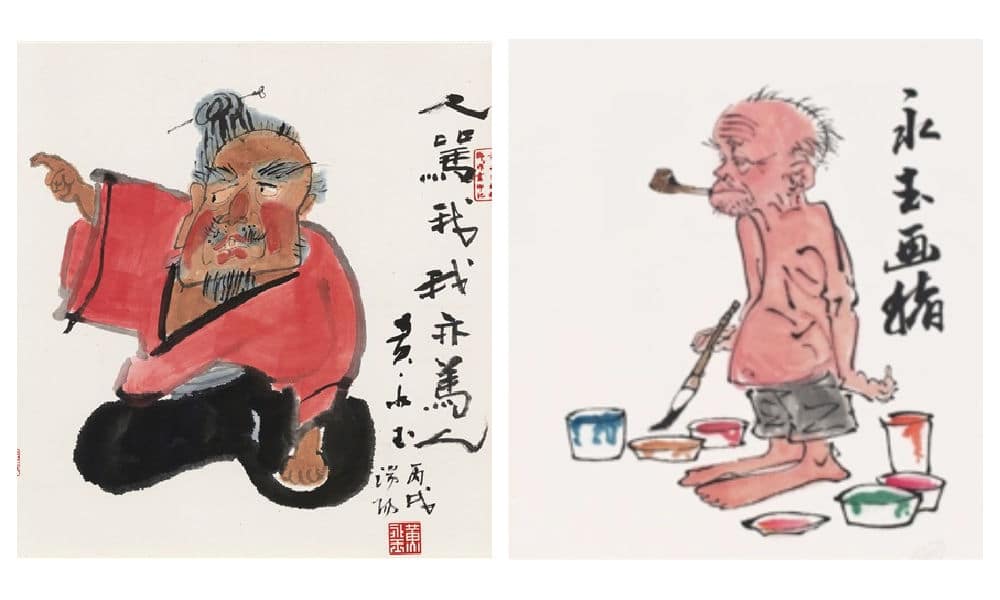

Huang Yongyu made various works targeting Fan Zeng.
In retaliation, Fan produced his own works mocking Huang, sparking an infamous rivalry in the Chinese art world. The two allegedly almost had a physical fight when they ran into each other at the Beijing Hotel.

Fan Zeng mocked Huang Yongyu in some of his works.
Fan and Huang were once on good terms though, with Fan studying under Huang at the Central Academy of Fine Arts in Beijing. Through Huang, Fan was introduced to the renowned Chinese novelist Shen Congwen (沈从文, 1902-1988), Huang’s first cousin and lifelong friend. As Shen guided Fan in his studies and connected him with influential figures in China’s cultural circles, their relationship flourished.
However, during the Cultural Revolution, when Shen was accused of being a ‘reactionary,’ Fan Zeng turned against him, even going as far as creating big-character posters to criticize his former mentor.[2] This betrayal not only severed the bond between Shen and Fan but also ended Fan’s friendship with Huang, and it is still remembered by people today.
Fan Zeng’s behavior towards another former mentor, the renowned painter Li Kuchan (李苦禪, 1899-1983), was also controversial. Once Fan gained fame, he made it clear that he no longer respected Li as his teacher. Li later referred to Fan as “a wolf in sheep’s clothes,” and apparently never forgave him. Although the exact details of their falling out remain unclear, some blame Fan for exploiting Li to further his own career.
There are also some online commenters who call Fan Zeng a “Mr Wang from next door” (隔壁老王), a term jokingly used to refer to the untrustworthy neighbor who sleeps with one’s wife. This is mostly because of the history of how Fan Zeng met his third wife.
Fan’s first wife was the Chinese female calligrapher Lin Xiu (林岫), who came from a wealthy family. During this marriage, Fan did not have to worry about money and focused on his artistic endeavours. The two had a son, but the marriage ended in divorce after a decade. Fan’s second wife was fellow painter Bian Biaohua (边宝华), with whom he had a daughter. It seems that Bian loved Fan much more than he loved her.
It is how he met his third wife that remains controversial to this day. Nan Li (楠莉), formerly named Zhang Guiyun (张桂云), was married to performer Xu Zunde (须遵德). Xu was a close friend of Fan, and helped him out when Fan was still poor and trying to get by while living in Beijing’s old city center.
Wanting to support Fan’s artistic talent, Xu let Fan Zeng stay over, supported him financially, and would invite him for meals. Little did he know that while Xu was away to work, Fan enjoyed much more than meals alone; Fan and Xu’s wife engaged in a secret decade-long affair.
When the affair was finally exposed, Xu Zunde divorced his wife. Still, they would use his house to meet and often locked him out. Three years later, Nan Li officially married Fan Zeng. Xu not only lost his wife and friend but also ended up finding his house emptied, his two sons now bearing Fan’s surname.
When Nan Li passed away in 2021, Fan Zeng published an obituary that garnered criticism. Some felt that the entire text was actually more about praising himself than focusing on the life and character of his late wife, with whom he had been married for forty years.

Fan Zeng and his four wives
An ‘old pervert’, a ‘traitor’, a ‘disgrace’—there are a lot of opinions circulating about Fan that have come up this week.
Despite the negativity, a handful of individuals maintain a positive outlook. A former colleague of Xu Meng writes: “If they genuinely like each other, age shouldn’t matter. Here’s to wishing them a joyful marriage.”
By Manya Koetse
[1]Song, Yuwu. 2014. Biographical Dictionary of the People’s Republic of China. United Kingdom: McFarland & Company, 76.
[2]Xu, Jilin. 2024. “Xu Jilin: Are Shen Congwen’s Tears Related to Fan Zeng?” 许纪霖:沈从文的泪与范曾有关系吗? The Paper, April 15. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_27011031. Accessed April 17, 2024.
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Memes & Viral
Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China
How a senior activity park in Chengdu was ‘Disneyfied’ and became a viral hotspot.
Published
6 days agoon
April 12, 2024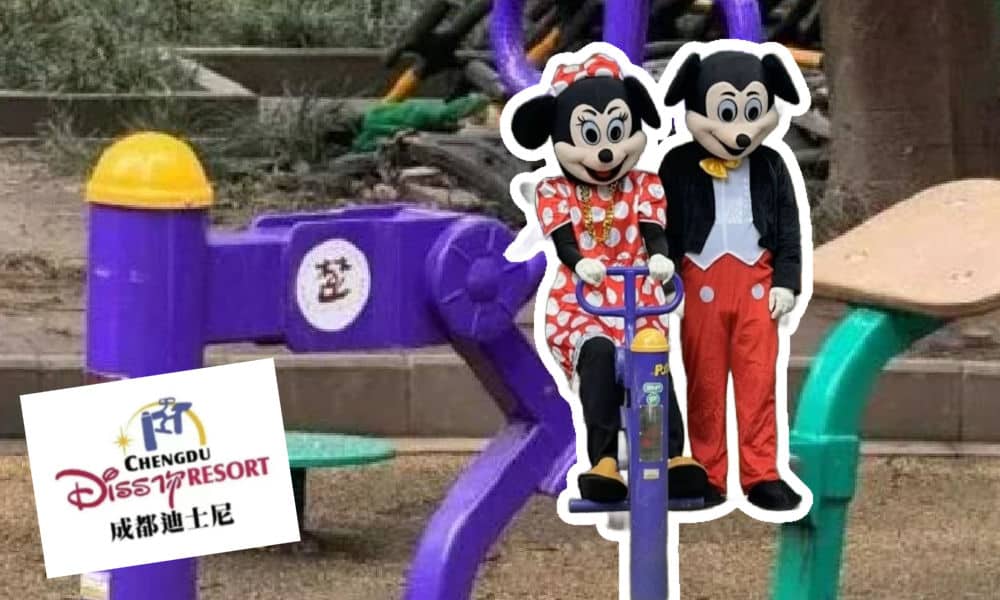
How did a common park turn into a buzzing hotspot? By mixing online trends with real-life fun, blending foreign styles with local charm, and adding a dash of humor and absurdity, Chengdu now boasts its very own ‘Chengdu Disney’. We explain the trend.
– By Manya Koetse, co-authored by Ruixin Zhang
Have you heard about Chengdu Disney yet? If not, it’s probably unlike anything you’d imagine. It’s not actually a Disney theme park opening up in Chengdu, but it’s one of the city’s most viral hotspots these days.
What is now known as ‘Chengdu Disney’ all over the Chinese internet is actually a small outdoor park in a residential area in Chengdu’s Yulin area, which also serves as the local senior fitness activity center.
Crowds of young people are coming to this area to take photos and videos, hang out, sing songs, cosplay, and be part of China’s internet culture in an offline setting.
Once Upon a Rap Talent Show
The roots of ‘Chengdu Disney’ can be traced back to the Chinese hip-hop talent show The Rap of China (中国新说唱), where a performer named Nuomi (诺米), also known as Lodmemo, was eliminated by Chinese rapper Boss Shady (谢帝 Xièdì), one of the judges on the show.
Nuomi felt upset about the elimination and a comment made by his idol mentor, who mistakenly referred to a song Nuomi made for his ‘grandma’ instead of his grandfather. His frustration led to a viral livestream where he expressed his anger towards his participation in The Rap of China and Boss Shady.
However, it wasn’t only his anger that caught attention; it was his exaggerated way of speaking and mannerisms. Nuomi, with his Sichuan accent, repeatedly inserted English phrases like “y’know what I’m saying” and gestured as if throwing punches.
His oversized silver chain, sagging pants, and urban streetwear only reinforce the idea that Nuomi is trying a bit too hard to emulate the fashion style of American rappers from the early 2000s, complete with swagger and street credibility.
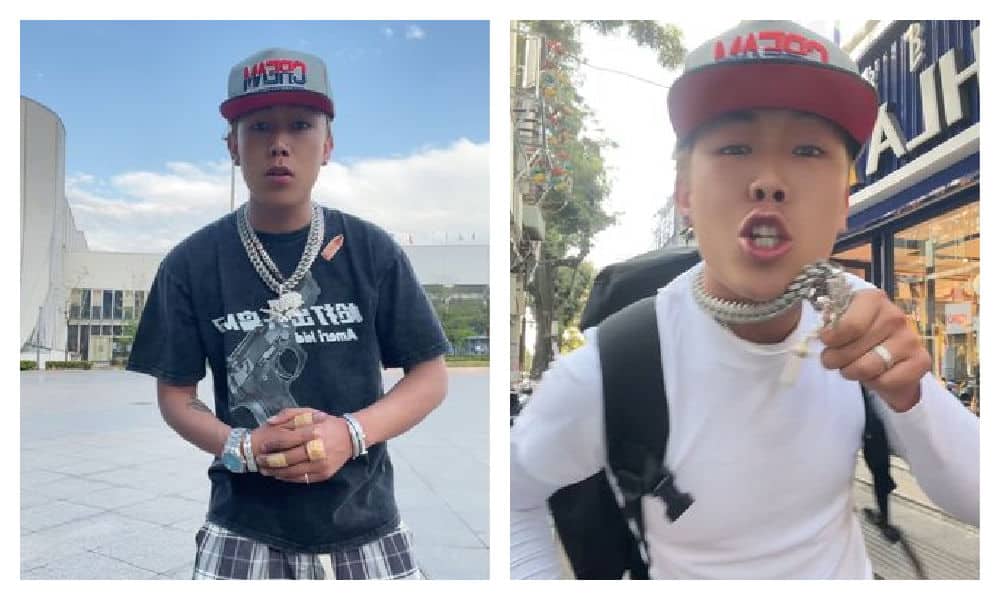

Lodmemo emulates the style of American rappers in the early 2000s, and he has made it his brand.
Although people mocked him for his wannabe ‘gangsta’ style, Nuomi embraced the teasing and turned it into an opportunity for fame.
He decided to create a diss track titled Xiè Tiān Xièdì 谢天谢帝, “Thank Heaven, Thank Emperor,” a word joke on Boss Shady’s name, which sounds like “Shady” but literally means ‘Thank the Emperor’ in Chinese. A diss track is a hip hop or rap song intended to mock someone else, usually a fellow musician.
In the song, when Nuomi disses Boss Shady (谢帝 Xièdì), he raps in Sichuan accent: “Xièdì Xièdì wǒ yào diss nǐ [谢帝谢帝我要diss你].” The last two words, namely “diss nǐ” actually means “to diss you” but sounds exactly like the Chinese word for ‘Disney’: Díshìní (迪士尼). This was soon picked up by netizens, who found humor in the similarity; it sounded as if the ‘tough’ rapper Nuomi was singing about wanting to go to Disney.
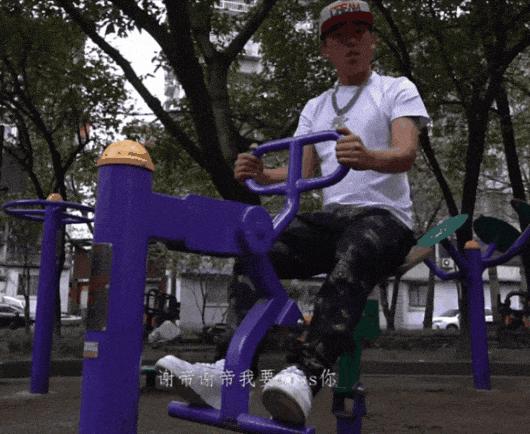

Nuomi and his diss track, from the music video.
Nuomi filmed the music video for this diss track at a senior activity park in Chengdu’s Yulin subdistrict. The music video went viral in late March, and led to the park being nicknamed the ‘Chengdu Disney.’
The particular exercise machine on which Nuomi performed his rap quickly became an iconic landmark on Douyin, as everyone eagerly sought to visit, sit on the same see-saw-style exercise machine, and repeat the phrase, mimicking the viral video.
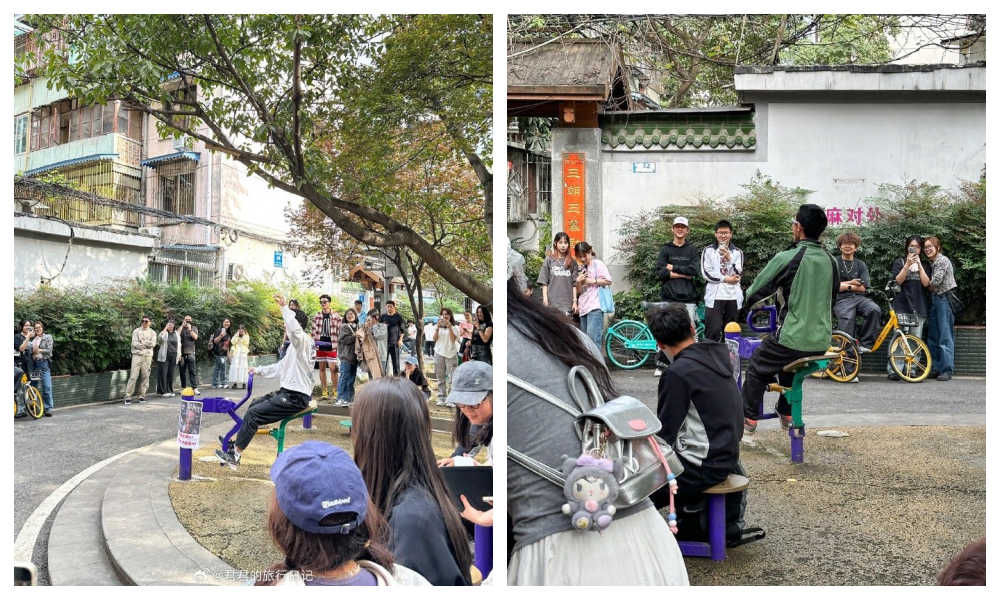

What began as a homonym led to people ‘Disneyfying’ the park itself, with crowds of visitors flocking to the park, some dressed in Disney-related costumes.
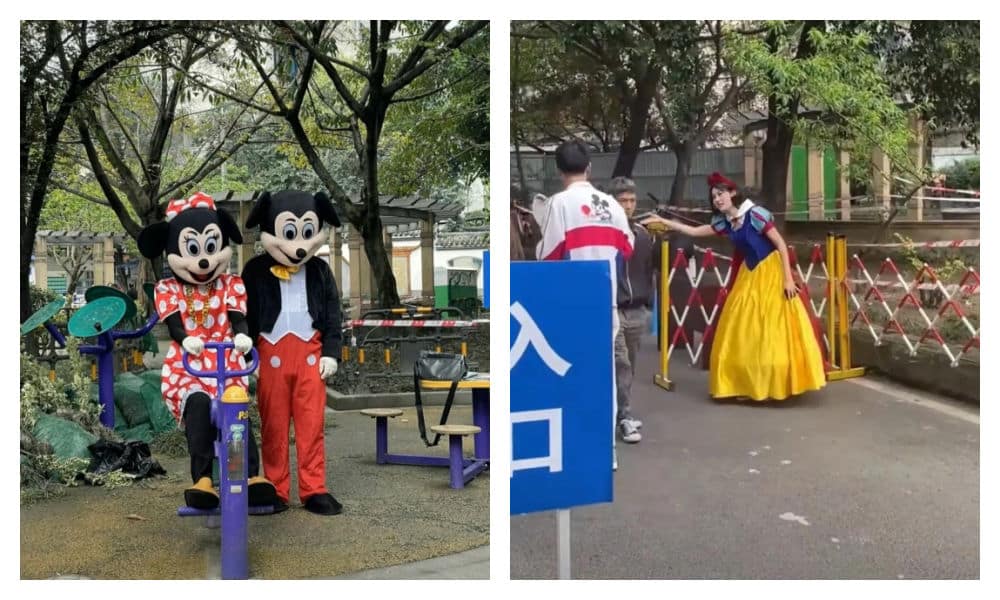

This further developed the concept of a Chengdu ‘Disney’ destination, turning the park playground into the happiest place in Yulin.
Chengdu: China’s Most Relaxed Hip Hop Hotspot
Chengdu holds a special place in China’s underground hip-hop scene, thanks to its vibrant music culture and the presence of many renowned Chinese hip-hop artists who incorporate the Sichuan dialect into their songs and raps.
This is one reason why this ‘Disney’ meme happened in Chengdu and not in any other Chinese city. But beyond its musical significance, the playful spirit of the meme also aligns with Chengdu’s reputation for being an incredibly laid-back city.
In recent years, the pursuit of a certain “relaxed feeling” (sōngchígǎn 松弛感) has gained popularity across the Chinese internet. Sōngchígǎn is a combination of the word for “relaxed,” “loose” or “lax” (松弛) and the word for “feeling” (感). Initially used to describe a particular female aesthetic, the term evolved to represent a lifestyle where individuals strive to maintain a relaxed demeanor, especially in the face of stressful situations.
🌟 Attention!
For 11 years, What’s on Weibo has remained a 100% independent blog, fueled by my passion to write about China’s digital culture and online trends. Over a year ago, we introduced a soft paywall to ensure the sustainability of this platform. I’m grateful to all our loyal readers who’ve subscribed since 2022. Your support has been invaluable. But we need more subscribers to continue our work. If you appreciate our content and want to support independent China reporting, please consider becoming a subscriber. Your support keeps What’s on Weibo going strong!
The concept gained traction online in mid-2022 when a Weibo user shared a story of a family remaining composed when their travel plans were unexpectedly disrupted due to passport issues. Their calm and collected response inspired the adoption of the “relaxed feeling” term (also read here).
Central to embodying this sense of relaxation is being unfazed by others’ opinions and avoiding unnecessary stress or haste out of fear of judgment.
Nowadays, Chinese cities aim to foster this sense of sōngchígǎn. Not too long ago, there were many hot topics suggesting that Chengdu is the most sōngchí 松弛, the most relaxed city in China.
This sentiment is reflected in the ‘Chengdu Disney’ trend, which both pokes fun at a certain hip-hop aesthetic deemed overly relaxed—like the guys who showed up with sagging pants—and embraces a carefree, childlike silliness that resonates with the city’s character and its people.
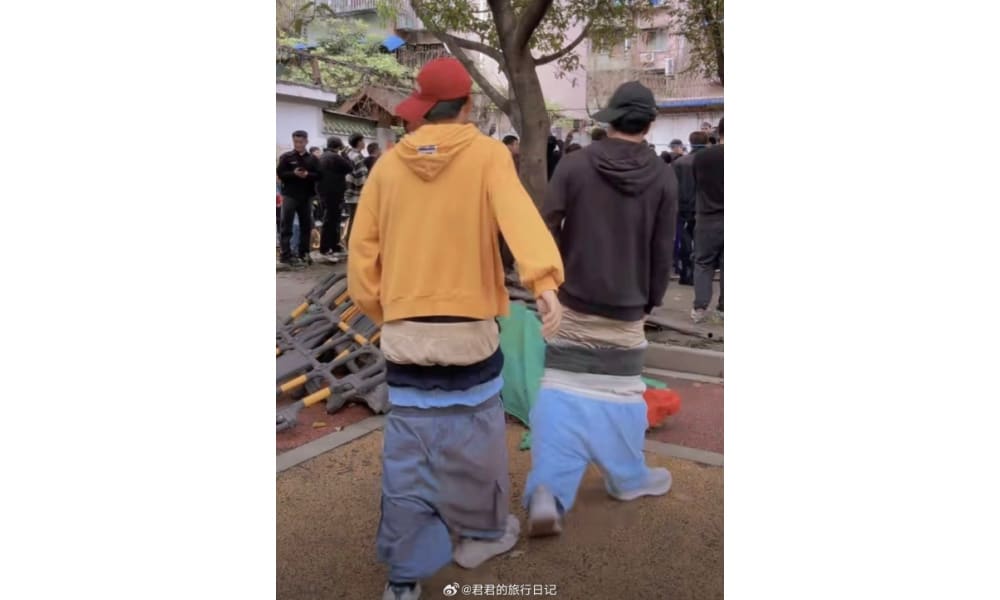

Mocking sagging pants at ‘Chengdu Disney.’
Despite the influx of visitors to the Chengdu Disney area, authorities have not yet significantly intervened. Community notices urging respect for nearby residents and the presence of police officers to maintain order indicate a relatively hands-off approach. For now, it seems most people are simply enjoying the relaxed atmosphere.
Being Part of the Meme
An important aspect that contributes to the appeal of Chengdu Disney is its nature as an online meme, allowing people to actively participate in it.
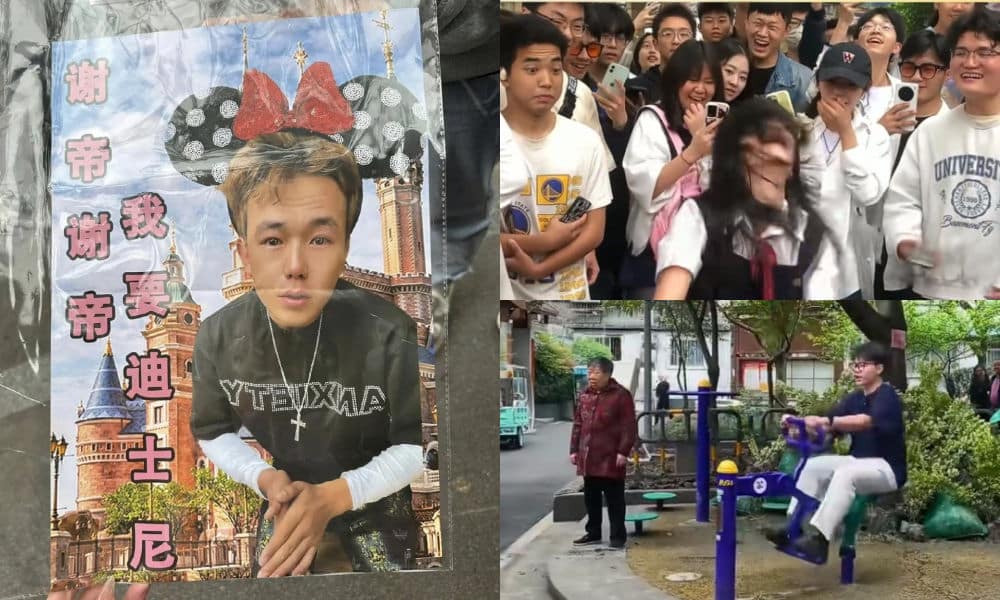

Scenes from Chengdu Disney, images via Weibo.
China has a very strong meme culture. Although there are all kinds of memes, from visual to verbal, many Chinese memes incorporate wordplay. In part, this has to do with the nature of Chinese language, as it offers various opportunities for puns, homophones, and linguistic creativity thanks to its tones and characters.
The use of homophones on Chinese social media is as old as Chinese social media itself. One of the most famous examples is the phrase ‘cǎo ní mǎ’ (草泥马), which literally means ‘grass mud horse’, but is pronounced in the same way as the vulgar “f*ck your mother” (which is written with three different characters).
In the case of the Chengdu Disney trend, it combines a verbal meme—stemming from the ‘diss nǐ’ / Díshìní homophone—and a visual meme, where people gather to pose for videos/photos in the same location, repeating the same phrase.
Moreover, the trend bridges the gap between the online and offline worlds, as people come together at the Chengdu playground, forming a tangible community through digital culture.
The fact that this is happening at a residential exercise park for the elderly adds to the humor: it’s a Chengdu take on what “urban” truly means. These colorful exercise machines are a common sight in Chinese parks nationwide and are actually very mundane. Transforming something so normal into something extraordinary is part of the meme.
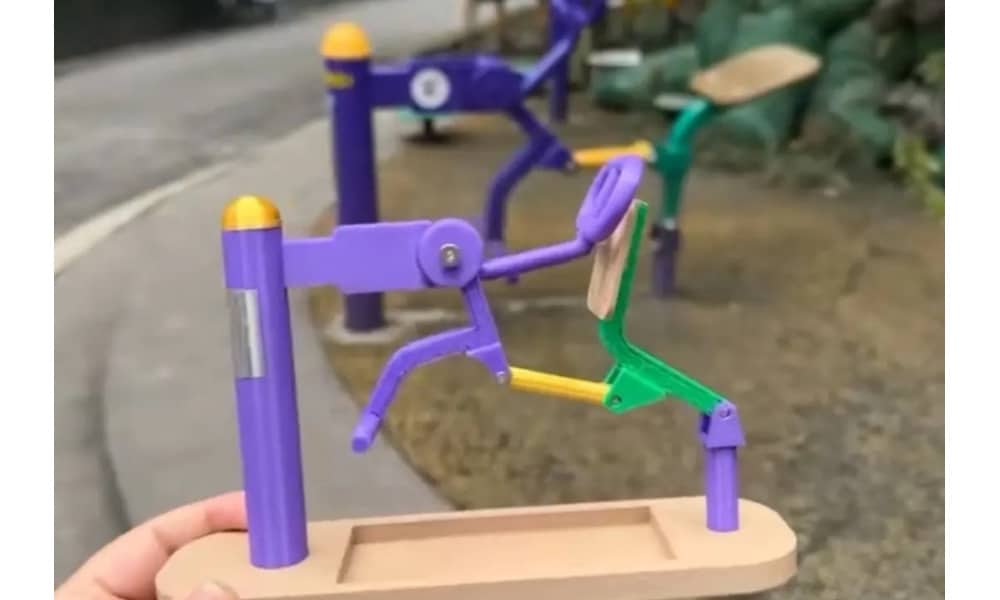

A 3D-printed model version of the exercise equipment featured in Nuomi’s music video.
Lastly, the incorporation of the Disney element adds a touch of whimsy to the trend. By introducing characters like Snow White and Mickey Mouse, the trend blends American influences (hip-hop, Disney) with local Chengdu culture, creating a captivating and absurd backdrop for a viral phenomenon.
For some people, the pace in which these trends develop is just too quick. On Weibo, one popular tourism blogger (@吴必虎) wrote: “The viral hotspots are truly unpredictable these days. We’re still seeing buzz around the spicy hot pot in Gansu’s Tianshui, meanwhile, a small seesaw originally meant for the elderly in a residential community suddenly turns into “Chengdu Disneyland,” catching the cultural and tourism authorities of Sichuan and even Shanghai Disneyland off guard. Netizens are truly powerful, even making it difficult for me, as a professional cultural tourism researcher, to keep up with them.”
By Manya Koetse, co-authored by Ruixin Zhang
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Where to Eat and Drink in Beijing: Yellen’s Picks

Weibo Watch: Burning BMWs

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

A Snowball Effect: How Cold Harbin Became the Hottest Place in China

Jia Ling Returns to the Limelight with New “YOLO” Movie and 110-Pound Weight Loss Announcement

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Weibo Watch: Frogs in Wells

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight1 month ago
China Insight1 month agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoA Snowball Effect: How Cold Harbin Became the Hottest Place in China
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 months agoJia Ling Returns to the Limelight with New “YOLO” Movie and 110-Pound Weight Loss Announcement
-

 China Arts & Entertainment2 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment2 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday






keltan
August 17, 2017 at 6:04 pm
Wow great post thank you for sharing this. my opinion is an intense artistic expression in another way, which is that individuals are composing and less and less now that everything should be possible through telephone. They at that point have a tendency to overlook how to really compose characters, and rehearsing calligraphy assists with this. New media can help individuals rehearsing their calligraphy.
Ref: https://essayjaguar.com/
certificate errors
July 2, 2018 at 4:02 pm
You will be glad to know that here we are having one of the best portal to fix error certificate internet explorer and will also come to know more about advanced features. These all solutions you will find out online.