China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Top 5 Chinese Online Consumer Trends After Single’s Day Sales
The world’s biggest online sale of the year, China’s Single’s Day, took place on November 11. What’s on Weibo gives an overview of the latest trends and biggest brands, showing how China’s middle-class online consumer habits are undergoing drastic changes.
Published
7 years agoon

WHAT’S ON WEIBO ARCHIVE | PREMIUM CONTENT ARTICLE
The world’s biggest online sale of the year, China’s Single’s Day, took place on November 11. Some Chinese consumer trends have become especially visible after the big sales. What’s on Weibo gives an overview of the latest trends and biggest brands, showing how China’s middle-class online consumer habits are undergoing drastic changes. [Premium Content by What’s on Weibo].
China’s 11/11 Single’s Day, the world’s biggest online shopping event of the year, has once again exceeded the sale figures of previous years.
The 8th edition of China’s Online Single’s Day Shopping Festival, that was initiated by e-commerce giant Alibaba in 2009, broke all previous sales records with a 24-hour sales volume of $17.6 billion (120.7 billion RMB) on Alibaba’s Tmall (天猫) on November 11. Online shopping mall JD.com also had 60% more sales than the previous year.
With so much success, many e-commerce platforms have extended the shopping festival until November 18. Time to see which Chinese online consumer trends are especially apparent during this year’s Single Day’s sales.
[blendlebutton]
1. Smartphone & Tablets: Made-in-China Wins
Together with fashion and health and beauty products, electronics are among the top-selling products of China’s biggest annual online sale. This year’s Single’s Day has shown that the iPhone7 is still very popular among Chinese consumers, despite the subdued reactions in China to its release in September.
The Gome e-commerce chain (国美在线) revealed that the iPhone7, which was priced at 4888 RMB (±719 US$), was the store’s number one best-seller of November 11. Gome sold 22000 devices within 24 hours.
Despite the surge in iPhone sales, made-in-China smartphones were the undeniable winner of the Single’s Day smartphone sales. Overall, netizens bought more Chinese smartphone brands than international ones. According to the Single’s Day sales numbers of JD.com, no less than 8 of the top 10 best-selling smartphones were domestically produced mobile phones. China’s Huawei and Xiaomi brands did especially well on Alibaba’s Tmall.

The surge in sales of Chinese smartphones is also promising for the international market: Huawei aims to become the world’s second-largest maker of smartphones within two years.
The growth of Chinese brand popularity is not just noticeable on the smartphone market – Chinese brands are also winning over tablet buyers. Apple is no longer the only big player on the Chinese tablet market, with brands such as Lenovo and Huawei seeing considerable growth in tablet sales.
2. Good for the Baby
Of the non-electronic products, it is especially baby products that did well on China’s Single’s Day. Anything from milk powder to baby wipes or diapers were popular during the 11/11 sales. Vastly different from the electronic market, it is especially foreign brands such as Friso (Friesland Campina, Dutch) and Moony (Japanese) that are most popular among Chinese consumers.
As China’s consumer trust in made-in-China baby brands has been damaged through various safety scandals over previous years, foreign brands are leading the market.
What is remarkable about this year’s sales, as revealed by China’s e-commerce platform Beibei (贝贝网, focused on maternal and infant products) is that the children’s clothing market is more booming than ever. Together with the surge in other baby- and mother-related products, the shift to bigger sales of these non-traditional products shows that China’s ‘Mummy Economy’ (妈妈经济) is becoming more relevant.

According to Beibei, there are over 50 million Chinese mothers registered as e-commerce users on their platform. Their data shows that there are different consumer trends within this group in China.
Mothers from the northeast of China, for example, will buy more baby’s clothes and shoes, as it gets colder in those regions than the more southern parts of China. The mothers in the Yangtze River Delta area (Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang) are known to buy many baby snacks and foodstuff. In the south of China, nearer to Hong Kong, consumers mainly buy baby necessities such as diapers and baby wipes.
3. Fashion: Individual Style over Traditional Brands
Despite the popularity of electronics and baby products, clothing and lifestyle goods are still the number one best-selling products in China’s online sales. According to sales numbers released by JD.com, 40% of all their 11/11 sales were in the apparel & lifestyle category.
Noteworthy non-Chinese brand names are Lee, TUMI and Guess, which respectively sold 43 times, 20 times, and 70 times more clothes this year than in previous years.
Although traditional international luxury brands such as Burberry and MaxMara remain popular, new sales data shows that Chinese consumers now, for the first time, pursue more non-mainstream brands for their style than the established luxury brands.
A good example is the growing popularity of the Canadian apparel brand Canada Goose, which completely sold out on Chinese fashion e-commerce site Xiu.com (走秀网) on November 11. The brand is known for its warm and stylish outerwear. Another non-mainstream popular brand is the Italian designer clothes & accessories label Mr & Mrs Italy, which was only recently introduced on fashion platform Xiu.com and became hot selling on 11/11.

Other upcoming trendy brands such as the Scandinavian Acne Studios and & Other Stories (by the same fashion heads as H&M) were also surprising best-selling names that are all about style.

With Chinese middle-class consumers now gradually attaching more importance to style, originality, and quality of a label than its fame, somewhat more low-key designer brands like Brunello Cucinelli or Loro Piana are starting to replace classic Louis Vuitton or Burberry brands.
According to Xiu.com representatives, these new developments show that China’s middle-class consumer habits are now undergoing dramatic changes. People are no longer pursuing a bag only because it has an LV logo – they want a bag that suits their own style and needs.
4. China’s New Online Consumers: The Rise of Smaller Towns
Although first- and second-tier cities are still the most important consumer markets for online e-commerce platforms, this year’s sales data point out that consumers in third-tier cities and provincial level towns are becoming an important target group.
E-commerce giant JD.com saw a substantial growth in orders from prefectural cities and smaller towns from provinces such as Guizhou, Jiangxi, Hubei, Henan, and Yunnan.
In 2011, “the rise of China’s 2nd and 3rd tier cities” was a hot topic in the media. Five years later, this trend has shifted to China’s rural areas, where the new consumers are located.

Earlier this year, Bloomberg reported that 77.14 million rural Chinese shopped online in 2015, which was already a 40.6 percent increase from 2014. On average, rural Chinese spend more online than their urban counterparts, and their online spending is growing faster.
According to Economics Daily, drastic increases in sales to consumers from smaller towns and villages shows the improving living standards in these areas. High-end products like refrigerators and air-conditionings are among their top-selling products for this consumer group.
The rise of China’s more third-tier and rural consumers is closely connected to China’s booming and readily available e-commerce, that has made rural consumer demand strong. With China’s online population now exceeding 700 million people, China’s rural netizens are growing steadily – that new tablet or heater is now just a few clicks away.
5. The Power of the Post-1990s Generation
The sales data from this year’s Single’s Day as provided by the Gome (国美) e-commerce platform have pointed out that the majority of orders (which had a staggering growth of 268% compared to last year) were placed by consumers below the age of 40. Of all online customers on Single’s Day, 85% were below the age of 40.
Within this group, 47% of people are of the 16-29 age category and 34% aged between 30-39. Young women are more active online consumers than the men; 67% of all purchases were done by women.

The Gome data shows the power of the post-1990s consumer. People of the generation born after 1990, often referred to as the ‘Post 90s’ or ‘jiulinghou‘ (九零后) are also called “marketers’ dream consumers” for their impulsiveness in buying goods, and their general pursuit of products that improve their happiness; they are the ultimate consumers, much more willing to spend money than the generations before them.
With a new young generation of eager online consumers, the rise of rural e-shoppers and a thriving ‘mummy economy’, China’s e-commerce companies having something to look forward to for their next year’s Single’s Day. The biggest online shopping event in the world is only about to get bigger.
– By Manya Koetse
Follow on Twitter or Like on Facebook
Sources:
Part of this article on based on the 14 November article by Zhao Chenting (赵陈婷) originally published on http://www.yicai.com/..
Other sources are linked to within the article.
©2016 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
[/blendlebutton]
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron
Who’s gonna buy this Zara dress in China? “I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”
Published
6 hours agoon
April 19, 2024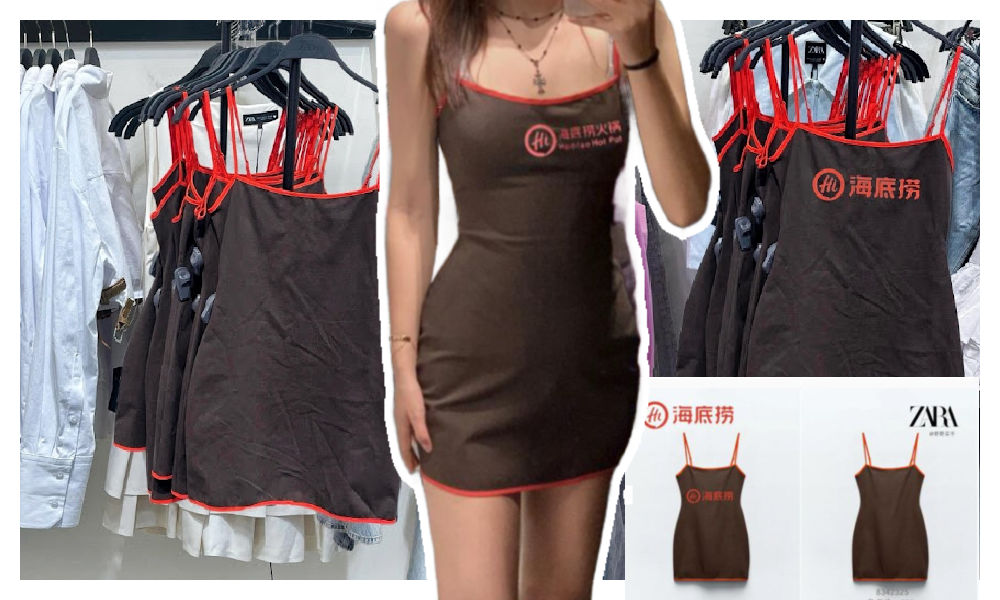
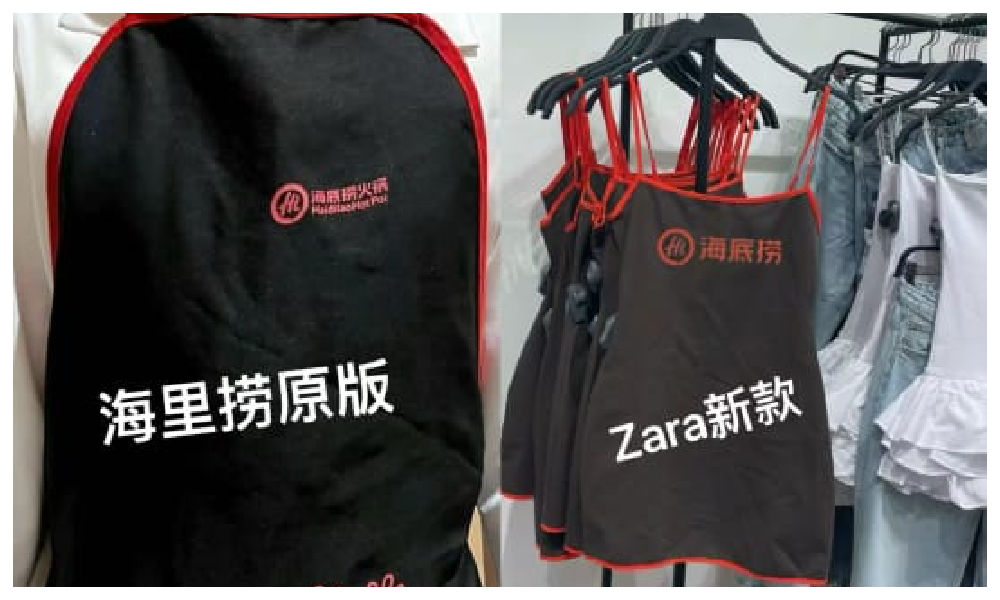
A short dress sold by Zara has gone viral in China for looking like the aprons used by the popular Chinese hotpot chain Haidilao.
“I really thought it was a Zara x Haidialo collab,” some customers commented. Others also agree that the first thing they thought about when seeing the Zara dress was the Haidilao apron.

The “original” vs the Zara dress.
The dress has become a popular topic on Xiaohongshu and other social media, where some images show the dress with the Haidilao logo photoshopped on it to emphasize the similarity.

One post on Xiaohongshu discussing the dress, with the caption “Curious about the inspiration behind Zara’s design,” garnered over 28,000 replies.
Haidilao, with its numerous restaurants across China, is renowned for its hospitality and exceptional customer service. Anyone who has ever dined at their restaurants is familiar with the Haidilao apron provided to diners for protecting their clothes from food or oil stains while enjoying hotpot.
These aprons are meant for use during the meal and should be returned to the staff afterward, rather than taken home.
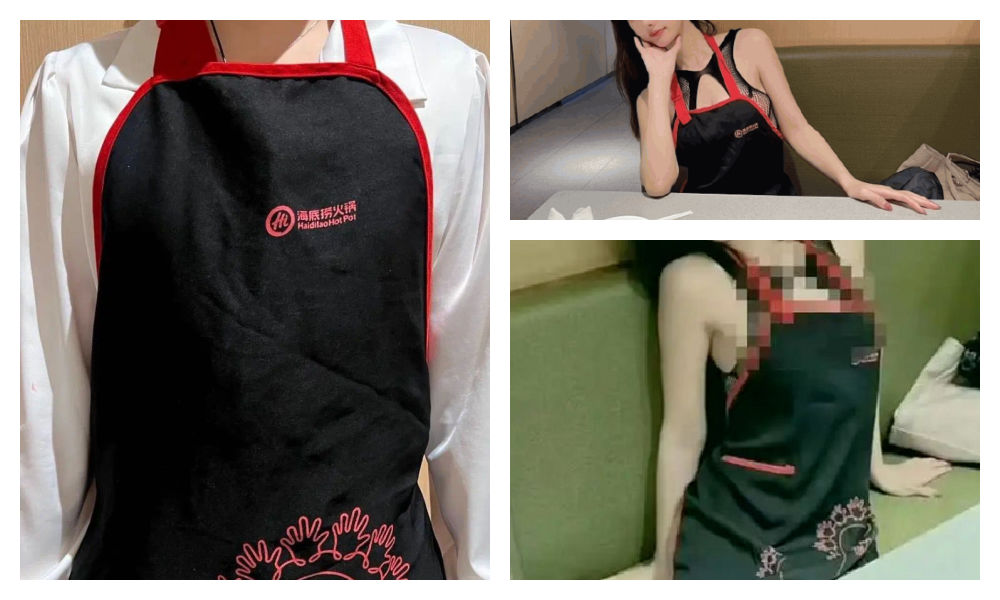

The Haidilao apron.
However, many people who have dined at Haidilao may have encountered the following scenario: after indulging in drinks and hotpot, they realize they are still wearing a Haidilao apron upon leaving the restaurant. Consequently, many hotpot enthusiasts may have an ‘accidental’ Haidilao apron tucked away at home somewhere.
This only adds to the humor of the latest Zara dress looking like the apron. The similarity between the Zara dress and the Haidilao apron is actually so striking, that some people are afraid to be accused of being a thief if they would wear it.
One Weibo commenter wrote: “The most confusing item of this season from Zara has come out. It’s like a Zara x Haidilao collaboration apron… This… I can’t wear it: I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”

Funnily enough, the Haidilao apron similarity seems to have set off a trend of girls trying on the Zara dress and posting photos of themselves wearing it.

It’s doubtful that they’re actually purchasing the dress. Although some commenters say the dress is not bad, most people associate it too closely with the Haidilao brand: it just makes them hungry for hotpot.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Zibo had its BBQ moment. Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine with its special take on malatang. Tourism marketing in China will never be the same again.
Published
3 weeks agoon
April 1, 2024
Since the early post-pandemic days, Chinese cities have stepped up their game to attract more tourists. The dynamics of Chinese social media make it possible for smaller, lesser-known destinations to gain overnight fame as a ‘celebrity city.’ Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine.
During this Qingming Festival holiday, there is one Chinese city that will definitely welcome more visitors than usual. Tianshui, the second largest city in Gansu Province, has emerged as the latest travel hotspot among domestic tourists following its recent surge in popularity online.
Situated approximately halfway along the Lanzhou-Xi’an rail line, this ancient city wasn’t previously a top destination for tourists. Most travelers would typically pass through the industrial city to see the Maiji Shan Grottoes, the fourth largest Buddhist cave complex in China, renowned for its famous rock carvings along the Silk Road.
But now, there is another reason to visit Tianshui: malatang.
Gansu-Style Malatang
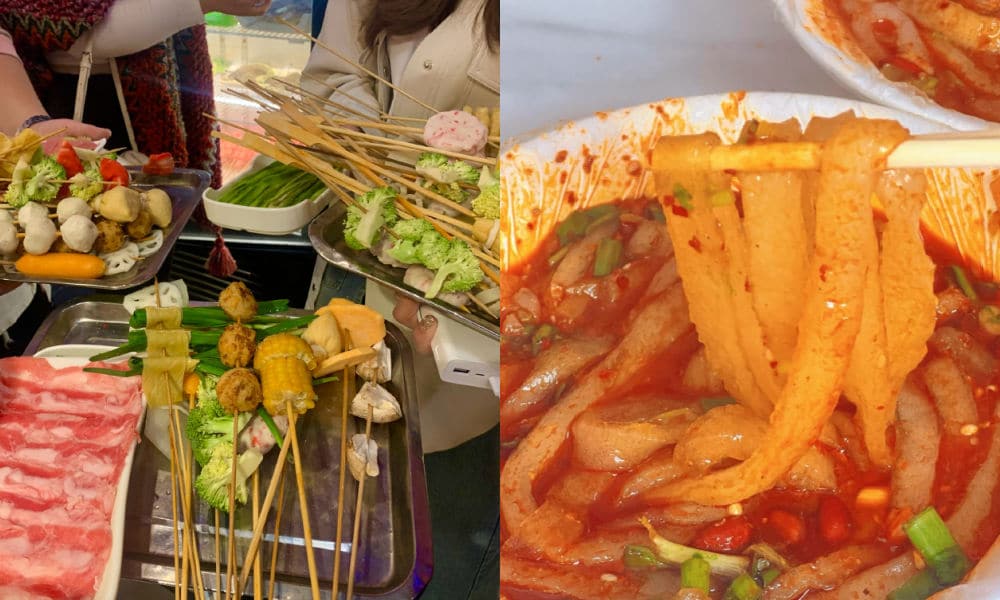
Málàtàng (麻辣烫), which literally means ‘numb spicy hot,’ is a popular Chinese street food dish featuring a diverse array of ingredients cooked in a soup base infused with Sichuan pepper and dried chili pepper. There are multiple ways to enjoy malatang.
When dining at smaller street stalls, it’s common to find a selection of skewered foods—ranging from meats to quail eggs and vegetables—simmering in a large vat of flavorful spicy broth. This communal dining experience is affordable and convenient for solo diners or smaller groups seeking a hotpot-style meal.
In malatang restaurants, patrons can usually choose from a selection of self-serve skewered ingredients. You have them weighed, pay, and then have it prepared and served in a bowl with a preferred soup base, often with the option to choose the level of spiciness, from super hot to mild.
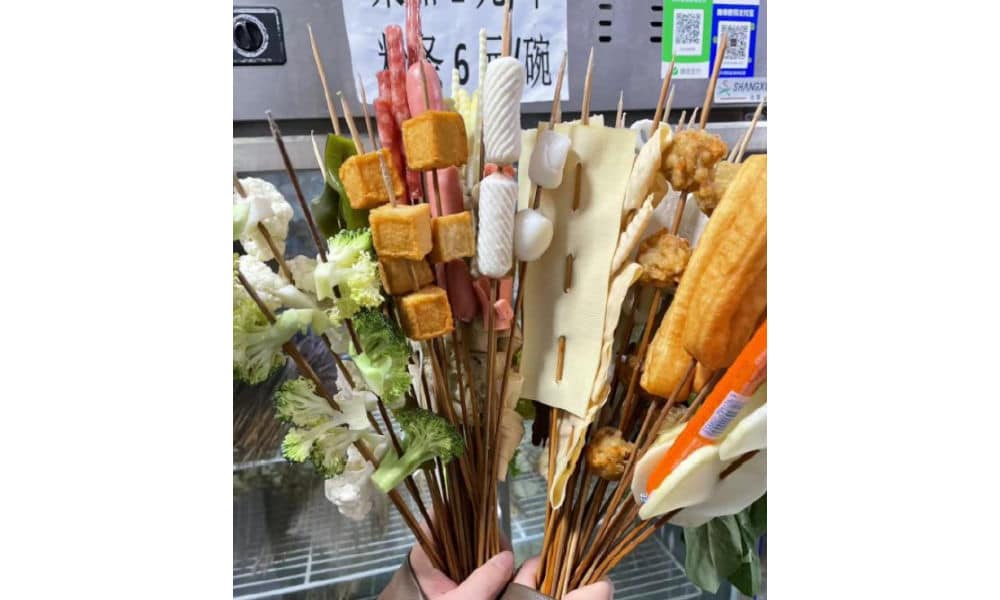

Although malatang originated in Sichuan, it is now common all over China. What makes Tianshui malatang stand out is its “Gansu-style” take, with a special focus on hand-pulled noodles, potato, and spicy oil.
An important ingredient for the soup base is the somewhat sweet and fragrant Gangu chili, produced in Tianshui’s Gangu County, known as “the hometown of peppers.”
Another ingredient is Maiji peppercorns (used in the sauce), and there are more locally produced ingredients, such as the black fungi from Qingshui County.

One restaurant that made Tianshui’s malatang particularly famous is Haiying Malatang (海英麻辣烫) in the city’s Qinzhou District. On February 13, the tiny restaurant, which has been around for three decades, welcomed an online influencer (@一杯梁白开) who posted about her visit.
The vlogger was so enthusiastic about her taste of “Gansu-style malatang,” that she urged her followers to try it out. It was the start of something much bigger than she could have imagined.
Replicating Zibo
Tianshui isn’t the first city to capture the spotlight on Chinese social media. Cities such as Zibo and Harbin have previously surged in popularity, becoming overnight sensations on platforms like Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin.
This phenomenon of Chinese cities transforming into hot travel destinations due to social media frenzy became particularly noteworthy in early 2023.
During the Covid years, various factors sparked a friendly competition among Chinese cities, each competing to attract the most visitors and to promote their city in the best way possible.
The Covid pandemic had diverse impacts on the Chinese domestic tourism industry. On one hand, domestic tourism flourished due to the pandemic, as Chinese travelers opted for destinations closer to home amid travel restrictions. On the other hand, the zero-Covid policy, with its lockdowns and the absence of foreign visitors, posed significant challenges to the tourism sector.
Following the abolition of the zero-Covid policy, tourism and marketing departments across China swung into action to revitalize their local economy. China’s social media platforms became battlegrounds to capture the attention of Chinese netizens. Local government officials dressed up in traditional outfits and created original videos to convince tourists to visit their hometowns.
Zibo was the first city to become an absolute social media sensation in the post-Covid era. The old industrial and mining city was not exactly known as a trendy tourist destination, but saw its hotel bookings going up 800% in 2023 compared to pre-Covid year 2019. Among others factors contributing to its success, the city’s online marketing campaign and how it turned its local BBQ culture into a unique selling point were both critical.

Zibo crowds, image via 163.com.
Since 2023, multiple cities have tried to replicate the success of Zibo. Although not all have achieved similar results, Harbin has done very well by becoming a meme-worthy tourist attraction earlier in 2024, emphasizing its snow spectacle and friendly local culture.
By promoting its distinctive take on malatang, Tianshui has emerged as the next city to captivate online audiences, leading to a surge in visitor numbers.
Like with Zibo and Harbin, one particular important strategy used by these tourist offices is to swiftly respond to content created by travel bloggers or food vloggers about their cities, boosting the online attention and immediately seizing the opportunity to turn online success into offline visits.
A Timeline
What does it take to become a Chinese ‘celebrity city’? Since late February and early March of this year, various Douyin accounts started posting about Tianshui and its malatang.
They initially were the main reason driving tourists to the city to try out malatang, but they were not the only reason – city marketing and state media coverage also played a role in how the success of Tianshui played out.
Here’s a timeline of how its (online) frenzy unfolded:
- July 25, 2023: First video on Douyin about Tianshui’s malatang, after which 45 more videos by various accounts followed in the following six months.
- Feb 5, 2024: Douyin account ‘Chuanshuo Zhong de Bozi’ (传说中的波仔) posts a video about malatang streetfood in Gansu
- Feb 13, 2024: Douyin account ‘Yibei Liangbaikai’ (一杯梁白开) posts a video suggesting the “nationwide popularization of Gansu-style malatang.” This video is an important breakthrough moment in the success of Tianshui as a malatang city.
- Feb – March ~, 2024: The Tianshui Culture & Tourism Bureau is visiting sites, conducting research, and organizing meetings with different departments to establish the “Tianshui city + malatang” brand (文旅+天水麻辣烫”品牌) as the city’s new “business card.”
- March 11, 2024: Tianshui city launches a dedicated ‘spicy and hot’ bus line to cater to visitors who want to quickly reach the city’s renowned malatang spots.
- March 13-14, 2024: China’s Baidu search engine witnesses exponential growth in online searches for Tianshui malatang.
- March 14-15, 2024: The boss of Tianshui’s popular Haiying restaurant goes viral after videos show him overwhelmed and worried he can’t keep up. His facial expression becomes a meme, with netizens dubbing it the “can’t keep up-expression” (“烫不完表情”).

The worried and stressed expression of this malatang diner boss went viral overnight.
- March 17, 2024: Chinese media report about free ‘Tianshui malatang’ wifi being offered to visitors as a special service while they’re standing in line at malatang restaurants.
- March 18, 2024: Tianshui opens its first ‘Malatang Street’ where about 40 stalls sell malatang.
- March 18, 2024: Chinese local media report that one Tianshui hair salon (Tony) has changed its shop into a malatang shop overnight, showing just how big the hype has become.
- March 21, 2024: A dedicated ‘Tianshui malatang’ train started riding from Lanzhou West Station to Tianshui (#天水麻辣烫专列开行#).
- March 21, 2024: Chinese actor Jia Nailiang (贾乃亮) makes a video about having Tianshui malatang, further adding to its online success.
- March 30, 2024: A rare occurrence: as the main attraction near Tianshui, the Maiji Mountain Scenic Area announces that they’ve reached the maximum number of visitors and don’t have the capacity to welcome any more visitors, suspending all ticket sales for the day.
- April 1, 2024: Chinese presenter Zhang Dada was spotted making malatang in a local Tianshui restaurant, drawing in even more crowds.
A New Moment to Shine
Fame attracts criticism, and that also holds true for China’s ‘celebrity cities.’
Some argue that Tianshui’s malatang is overrated, considering the richness of Gansu cuisine, which offers much more than just malatang alone.
When Zibo reached hype status, it also faced scrutiny, with some commenters suggesting that the popularity of Zibo BBQ was a symptom of a society that’s all about consumerism and “empty social spectacle.”
There is a lot to say about the downsides of suddenly becoming a ‘celebrity city’ and the superficiality and fleetingness that comes with these kinds of trends. But for many locals, it is seen as an important moment as they see their businesses and cities thrive.
Even after the hype fades, local businesses can maintain their success by branding themselves as previously viral restaurants. When I visited Zibo a few months after its initial buzz, many once-popular spots marketed themselves as ‘wanghong’ (网红) or viral celebrity restaurants.
For the city itself, being in the spotlight holds its own value in the long run. Even after the hype has peaked and subsided, the gained national recognition ensures that these “trendy” places will continue to attract visitors in the future.
According to data from Ctrip, Tianshui experienced a 40% increase in tourism spending since March (specifically from March 1st to March 16th). State media reports claim that the city saw 2.3 million visitors in the first three weeks of March, with total tourism revenue reaching nearly 1.4 billion yuan ($193.7 million).
There are more ripple effects of Tianshui’s success: Maiji Shan Grottoes are witnessing a surge in visitors, and local e-commerce companies are experiencing a spike in orders from outside the city. Even when they’re not in Tianshui, people still want a piece of Tianshui.
By now, it’s clear that tourism marketing in China will never be the same again. Zibo, Harbin, and Tianshui exemplify a new era of destination hype, requiring a unique selling point, social media success, strong city marketing, and a friendly and fair business culture at the grassroots level.
While Zibo’s success was largely organic, Harbin’s was more orchestrated, and Tianshui learned from both. Now, other potential ‘celebrity’ cities are preparing to go viral, learning from the successes and failures of their predecessors to shine when their time comes.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Where to Eat and Drink in Beijing: Yellen’s Picks

Weibo Watch: Burning BMWs

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

A Snowball Effect: How Cold Harbin Became the Hottest Place in China

Jia Ling Returns to the Limelight with New “YOLO” Movie and 110-Pound Weight Loss Announcement

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Weibo Watch: Frogs in Wells

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight1 month ago
China Insight1 month agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoA Snowball Effect: How Cold Harbin Became the Hottest Place in China
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 months agoJia Ling Returns to the Limelight with New “YOLO” Movie and 110-Pound Weight Loss Announcement
-

 China Arts & Entertainment2 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment2 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday