China Health & Science
The Essential Balm: How to Use Tiger Balm & Qing Liang You
The best ways to use Tiger Balm according to Chinese social media users.
Published
6 years agoon
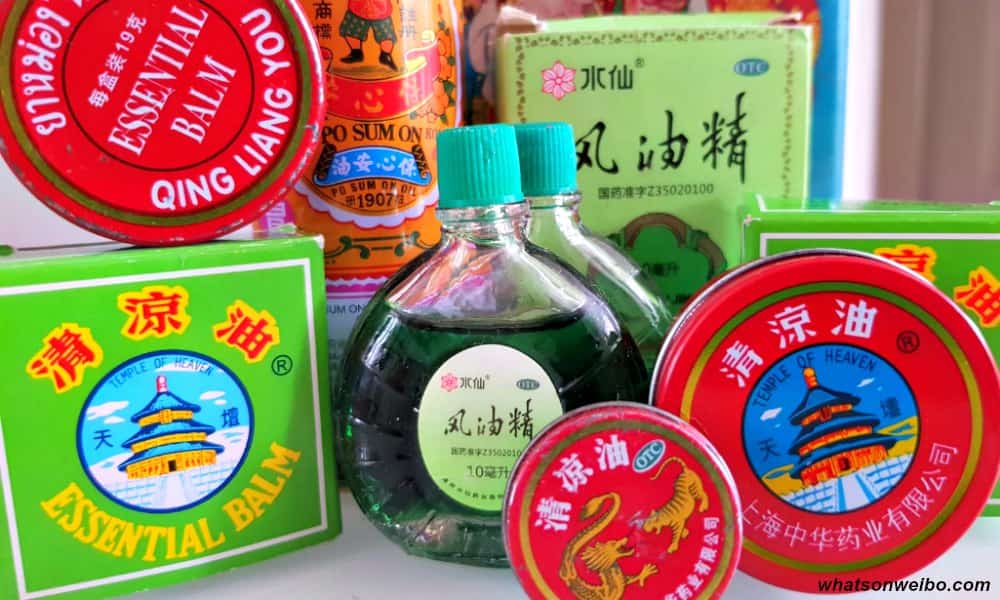

Some Chinese social media users claim Tiger Balm (or ‘Essential Balm’) is a “cure-all” product (包治百病) – why this century-old product is still popular today: the how-to-use tips from Weibo users.
What is simply known as ‘Tiger Balm’ in most Western countries, is also known as Fēng yóu jīng (风油精, lit. ‘wind oil’) or Qīng liáng yóu (清凉油, lit. ‘cool oil’) in China, usually translated as ‘Essential Balm.’
The translation ‘essential’ is quite literal in the sense that the balm is in fact essential to many Chinese households; virtually all pharmacies, supermarkets, airports shops and convenience stores in the PRC will sell it.
The over-the-counter balm (or oil) is a product that often pops up on Chinese social media. A recent video on streaming platform Billibilli calls it a “cure-all” product (包治百病), while netizens on Weibo share tips on how they use the balm on a daily basis.

Qingliangyou and fengyoujing; the essential oils/balms, via Billibilli.
The Tiger Balm brand name in Chinese is Hǔbiao Wànjīnyóu (虎標萬金油), which literally means ‘tiger-marked jack of all trades.’
All of these balms or oils are practically the same kind of ‘heat rubs,’ topical preparations for application to the skin, mainly made from menthol, camphor, clove oil, mint oil, and cajuput/eucalyptus oil.

The Chinese fengyoujing is an oily liquid that comes in a small bottle (10ml), while both the Tiger Balm brand and so-called ‘Essential Balm’ (various brands) come as balsam in a small tin. Because the first-mentioned is more easily applied as liquid, its effects are somewhat stronger than the balm.
A Tiger Balm History
The original Tiger Balm was developed in Birma in the 1870s, by the Fujian-born herbalist Aw Chu Kin (Hu Ziqin 胡子钦). Different to what the name suggests, Tiger Balm does not contain any ingredients related to the tiger, but was named after Aw’s son, whose name literally meant ‘Gentle Tiger’ (Aw Boonhaw or Hu Wenhu 胡文虎).
He was the son who later inherited the recipe of the balm, and turned Tiger Balm into a household name together with his brother (Hu Wenbao 胡文豹).
Aw Chu Kin was born in a small village. His father was also a herbalist, but the family was very poor. In search for a better live, the young Aw later moved to Birma (Myanmar), where he set up his own apothecary in Yangon in 1870 under the name of ‘Eng Aun Tong’ (永安堂药行).
Aw had three sons and a daughter. When he passed away in 1908, he left his company to the two sons who had helped him with his business. They later moved to Singapore, where they continued their father’s business and officially launched Tiger Balm as a brand in 1925, based on their father’s recipes.

The brothers used a remarkable promotion method for their balm; from 1926 on, they drove a vehicle that had a big tiger head on its front (see image). The horn of the car sounded like a tiger roar – a good way to attract the attention of people and to give them some free samples of their balm.
How to Use Tiger Balm: General Uses
The century-old product is still wildly popular today, with various companies now producing (nearly) identical products.
Note: not recommended to use for pregnant women, children under the age of 3, avoid contact with eyes, keep out of reach of children, and do not apply to injured skin or burns. If you’re in doubt about tiger balm usages and/or allergies, consult a doctor before using.
Among the main purposes of Tiger Balm and Qing Liang You is that it can be used as an anti-itching remedy for mosquito bites and insect stings.
For those with rheumatic pains, tiger balm can be also used as a painkiller by applying it in the lower back area, legs, and directly on sore muscles and bones.
Tiger Balm is also said to be helpful against a cold and have a stuffed nose, by putting some balm right underneath and around the nostrils to let the nose clear up.
To prevent dizziness and carsickness, the balm can be used to slightly moisten the lips or temples to prevent nausea.
Social Media Tips
On Weibo, dozens of people share their use of Tiger Balm and the likes on their accounts every day – especially during the hot summer.
* Some Chinese students simply recommend keeping a small tin of balm nearby for those late study hours; they claim sniffing the balm awakens the mind.
* “I apply some balm before I take a shower,” one commenter says: “Now my whole body feels cool as a breeze.” By applying some balm to parts of the body, the skin gets cooled – a comfortable feeling in times of hot weather or fever.
* Social media user Xixi (@西西咕噜咕噜) uses Tiger Balm in hot summer days. Opening up the lid of the balm a few times a day in front of the van spreads its cooling breeze throughout the room: “I’m crazy about this fragrance.” (Tip! Mosquitos and other insects dislike this smell; this method is also effective as a repellent.)

* “I’ve been suffering from a head-ache for days,” a Weibo user named ‘I’ve been studying for hours today’ (@今儿学了几个小时) says: “Rubbing some qingliangyou on my temples really helps.” Tiger balm is often promoted as a remedy against headache, by rubbing some tiger balm on the forehead or temples (mind your eyes).
* “After cutting red peppers, you can smear some Tiger Balm on your fingers,” another Weibo user (@萍了早煤) writes: “also use some plain vinegar to wash it off. It helps.”

* “You can use Tiger Balm / Qing Liang You to improve blood circulation and decrease swellings,” one Guangdong micro-blogger writes. It is indeed said that one of the active ingredients, camphor, dilates the blood vessels and brings blood closer to the skin’s surface; increasing circulation and warmth.
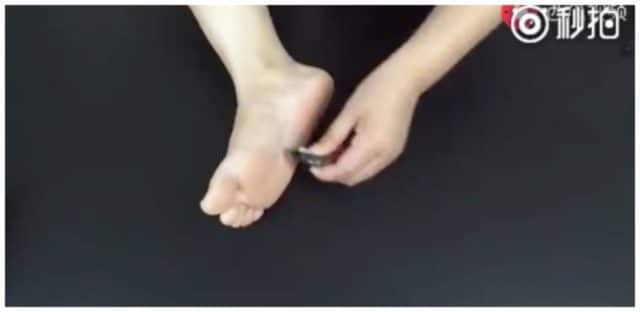
* Another popular Weibo account (@好运逗比) recommends rubbing some drops of the fengyoujing (the liquid rub) to the soles of the feet before wearing shoes to prevent smelly feet at the end of the day.
* There are also Weibo accounts recommending Tiger Balm / Qing Liang You as the must-bring item on travels to prevent mosquito bites, car or sea sickness, and for treatment of headaches.
* There are also some people who say they use Tiger Balm on their face as a way to treat acne/pimples, but we’d highly recommend consulting with a doctor before doing so, as the balm is not recommended to be used on irritable skin.
Still not had enough tips? You can check out one of What’s on Weibo’s earliest articles, titled ‘20 Ways to Use Tiger Balm,’ for more tips on how to use this ‘jack for all trades’ balm.
By Manya Koetse
Follow @whatsonweibo
Where to Buy
Tiger Balm is practically available everywhere. Check your local pharmacy or convenience store. The brand also has an online shop where their products can be purchased. For small cases of essential balm to carry with you at all times check here.
The Temple of Heaven balm can be purchased at Beijing airport and many other places, but online it is purchasable here.
The classic oil, which is somewhat stronger, is available here.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us.
©2018 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

Also Read
China Food & Drinks
Chinese Woman with Heartbreak Passes Away after Drinking Bottle of Baijiu
Three friends are held partially responsible for not intervening when the woman consumed 500ml of baijiu.
Published
4 months agoon
December 15, 2023
An incident that happened on the night of May 21, 2023, has become a trending topic on Chinese social media today after a local court examined the case.
A woman named ‘Xiao Qiu’ (alias), a resident of Jiangxi’s Nanchang, apparently attempted to drink her sorrows away after a heartbreaking breakup.
She spent the night at a friend’s house, where she drank about 50cl of baijiu (白酒), a popular Chinese spirit distilled from fermented sorghum that contains between 35% and 60% alcohol. One entire bottle of baijiu, such as Moutai, is usually 50cl.
She was together with three female friends. One of them also consumed baijiu, although not as much, and the two other friends did not drink at all.
As reported by Jiupai News, the intoxicated Xiao Qu ended up sleeping in her car, while one of her sober friends stayed with her. However, at about 5 AM, her friend discovered that Xiao Qiu was no longer breathing. Just about an hour later, she was declared dead at the local Emergency Center. The cause of death was ruled as cardiac and respiratory failure due to alcohol poisoning.
The court found that Xiao Qu’s friends were partly responsible for her death, citing their failure to prevent her excessive drinking and inadequate assistance following her baijiu binge drink session. Each friend was directed to contribute to the compensation for medical expenses and pain and suffering incurred by Qiu’s family.
The friend who also consumed baijiu was assigned a 6% compensation responsibility, while the other two were assigned 3% each.
On Weibo, many commenters do not agree with the court’s decision, asserting that adult individuals should not be held accountable when a friend goes on a drinking spree. Some commenters wrote: “You can tell someone not to drink, but what if they don’t listen?” “Should we record ourselves telling friends not to drink too much from now on?”
This is not the first time for friends to be held liable for an alcohol-related death in China. In 2018, multiple stories went viral involving people who died after excessive drinking at social gatherings.
One case involved a 30-year-old Chinese man who was found dead in his hotel room bathtub in Yangzhou after a formal dinner with friends where he allegedly drank heavily. The man reportedly died of a heart attack. His friends reached a 1 million yuan (±US$157,000) settlement with his family, with the cost shared among the friends who were present during the night.

Surveillance cameras in Jinhua captured how the man was unable to stand or walk after drinking with his friends.
Another case involved a man who died when he was left by his friends at a hotel in Jinhua, Zhejiang province, after heavily drinking at a banquet. Surveillance cameras captured how the man was unable to stand or walk after drinking with his friends. Those friends also paid a compensation together of 610,000 yuan (US$96,000) to the man’s family.
Organisers of an alcohol drinking contest in Henan province were also ordered to pay a compensation of over US$70,000 after one participant died due to excessive alcohol intake in July of 2017.
These cases also triggered online discussions about how Chinese traditional drinking culture often encourages people at the table to drink as much as they can or to exceed their limits; the goal sometimes is to literally “take someone to the ground by drinking.” When someone proposes a toast, everyone at the table is required to finish their glasses, sometimes at a very high pace.
In light of the latest news, some commenters write on Weibo: “No matter what kind of drinking gathering it is, for someone who is already drunk, others should intervene to prevent them from continuing to drink. Even if they invite, provoke, or insist on drinking themselves, they should not be allowed to continue. Otherwise, it not only harms them, you might end up facing legal responsibility yourself.”
Others remind people that overindulging in alcohol when you’re in a state of distress is never a good idea, and that no heartbreak is worth getting drunk over: “There are plenty of other fish in the sea.”
By Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Health & Science
‘Sister Blood Points’ Controversy: Shanghai Woman’s Tibet Blood Donations Ignite Privilege Debate
Dozens of local public officials in Tibet donated blood to rescue a Shanghainese woman. Netizens believe it’s a matter of privilege.
Published
4 months agoon
December 9, 2023
The medical rescue of a critically injured Shanghai woman in Tibet has recently triggered major controversy on Chinese social media after netizens suspected that the woman’s treatment may have been facilitated through the abuse of power.
What was supposed to be a romantic honeymoon getaway turned into a nightmare for newlyweds Yu Yanyan (27, 余言言) and her husband Tao Li (29, 陶立).
On October 14, just two weeks after their wedding, the couple from Shanghai was driving on China’s National Highway 219. Their destination was Ngari Prefecture in Tibet’s far west, where the average elevation is 4500 meters.
As they drove by the famous mountain pass Jieshan Daban (界山達阪), situated at an altitude of 5347 meters, they suddenly realized that the altitude was affecting them. Soon, Tao Li, who was driving the car, lost consciousness and crashed the car. Yu Yanyan, on the passenger side, was badly injured in the crash.
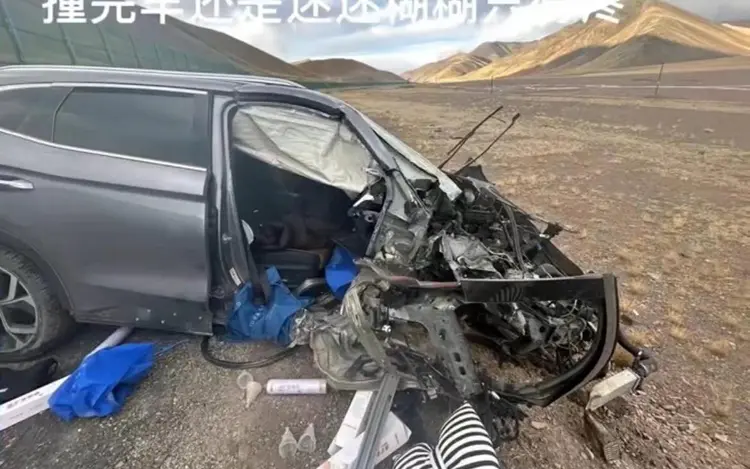

The crashed car, image via Beijing News/Xinjinbao (source).
What followed was a complicated, time-sensitive, and costly rescue operation. At the Ngari People’s Hospital (阿里地区人民医院), Yu was diagnosed with a ruptured liver, abdominal bleeding, hemorrhagic shock, and thoracic trauma. She was losing a lot of blood in a short time and required surgery, but there was not enough blood available for a blood transfusion at the time in the sparsely populated region, as reported by Beijing News.
Tibetan Civil Servants to the Rescue
While the hospital made efforts to secure donations, specifically requiring an adequate supply of A+ type blood, Yu’s husband was reportedly advised to reach out to the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (上海卫健委) to inquire about potential assistance. One of his aunts, or his ‘auntie’, allegedly helped him to contact them.
These efforts appeared to be fruitful. Between October 16-17, just days following the crash, numerous members of the public and dozens of local civil servants in Tibet, including firefighters, policemen, and military personnel, stepped forward to donate blood, contributing to over 7000 mL of A-type Rh-positive blood that ultimately saved Yu’s life.
Allegedly thanks to the Tibet office of the Shanghai Municipal People’s Government, a medical specialist from Shanghai was even sent to assist in the medical treatment of Yu at the Ngari hospital.
As Yu later required more advanced medical care and surgeries, she was advised to go to a bigger hospital. She was then transferred via a specially arranged chartered plane. The total costs of this medical chartered plane flight from Ngari to Sichuan’s Huaxi hospital (四川华西医院), arranged by Yu’s father, allegedly cost 1,2 million yuan (US$169.230).

After receiving surgery at the Huaxi Hospital, Yu was in stable condition and was transferred to Shanghai.
An Abuse of Power?
Yu’s story began drawing notice, eventually garnering nationwide media coverage, after Yu herself posted a video on her social media account (Douyin) in which she recounted her experiences. Yu, who only had a relatively small group of followers, told about her rescue operation and her recovery. But instead of garnering sympathy, it led to many questions from netizens and went viral. The video was later deleted.

Screenshots from the since deleted Douyin video.
Who was the ‘auntie’ who reached out to the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission? How were Tibet public officials made to donate blood for this Shanghai patient? What power dynamics were in play that facilitated the mobilization of people in this manner by the family?
People became upset, as they suspected Yu’s life had only been saved because of an abuse of power, and that ordinary Chinese patients would never have never received a similar treatment.
They started referring to Yu as ‘Sister Blood Points.’ The Chinese term is xuè cáo jiě 血槽姐, with xuè cáo 血槽 (lit. blood groove) often being used in the world of gaming to refer to the health bar, an image in video games that shows the player how much energy or blood or strength they have left before it’s game over.
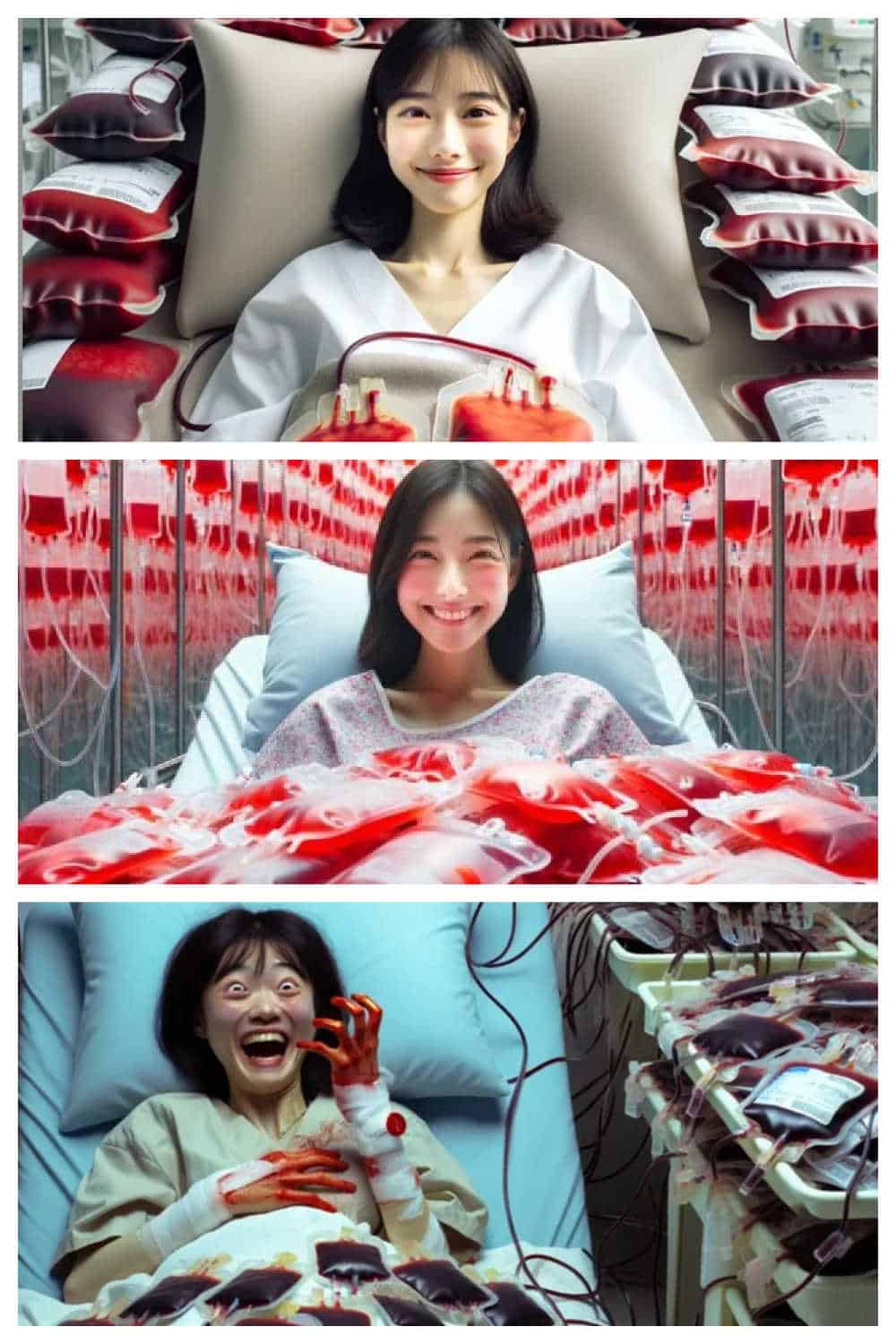

Various online AI-generated images featuring a portrayal of “Sister Blood Points.”
There were also various digital (AI-generated) images showing Yu surrounded by bags of donated blood, portraying her as a privileged, blood-sucking Shanghai ‘princess’ in Tibet.
Following the online commotion, the Ngari Propaganda Department issued a statement on November 29 promising to look into the issue. Additionally, in the first week of December, various Chinese media outlets also started to investigate the case.
An Ordinary Patient in Extraordinary Circumstances
On December 6, online newspaper The Paper (澎湃新闻) published an article together with Shangguan News (上观新闻) which answered some of the most pressing questions surrounding the case.
The Paper reported that they found no officially organized mobilization of public officials or members of the public to donate blood. Instead, local workers and individuals donated blood after learning about the woman’s situation through various channels, including from the hospital staff. Yu Yanyan’s husband Tao called the successful blood donation campaign a result of “multi-party mobilization” (“这是我们多方动员的结果,确实不是有组织的。”)
The Shanghai Municipal Health Commission also denied that they had contacted health authorities in Tibet to ask civil servants to donate blood. They claimed their members of staff did not personally know the patient nor any members of her or her husband’s family.
Furthermore, the article says that the woman known as ‘auntie’ is a 60-year-old retired woman who previously worked at a crafts factory. Upon learning about Yu’s predicament, she forwarded the information to her daughter-in-law, who works at a bank and also did all she could to spread the news and ask for help. This eventually led to the Tibet office of the Shanghai Municipal People’s Government being updated on the situation.
The Tibet office has refuted any suggestion that personal relationships influenced the procedures that resulted in the dispatch of a Shanghai medical expert to assist at Ngari People’s Hospital. A Shanghai medical team stationed in Tibet received a request for urgent support at the hospital and, following their ethical work guidelines, dispatched an expert to provide assistance.
The Paper further stated that nor Yu, nor her husband or their family were officials. In order to pay for the medical flight, Yu’s parents used family savings and borrowed money from others.
All of the information that was coming out about the entire ordeal seemed to indicate that Yu was just an ordinary patient in extraordinary circumstances.
A Sign of Distrust
While certain commenters believe that the latest information has put an end to weeks of speculation, others continue to harbor suspicions that there might be more to the story – they are not satisfied with the answers provided on December 6.
As some netizens dug up screenshots of online calls for help from Tao, Yu’s husband, some commenters responded: “This only makes it clearer that there’s no special status (特殊身份) here. Real influential officials wouldn’t go so low as to seek help online. A simple phone call would have quickly resolved their issue.”
In the end, the entire ordeal, now labeled “The Civil Servant Blood Donation Incident” (公务员献血事件) on Chinese social media, reveals more about public distrust in the transparency of China’s healthcare system than it does about Yu, her family, or the situation in Tibet.
While frustrations regarding privilege and power abuse within China’s healthcare system have existed for years, this issue has gained significant public attention this year in light of the launch of a top-down anti-corruption campaign targeting the healthcare industry.
This issue is especially important due to China’s longstanding struggle with public mistrust in the medical care sector. Some studies even suggest that China’s healthcare system has suffered from a “trust crisis among the public” since the 1990s (Chen & Cheng 2022, 2).
Multiple factors contribute to the relatively low trust in the Chinese healthcare system, but access and costs both play major roles. The sentence “Getting medical attention is difficult, getting medical attention is expensive” (Kànbìng nán, kànbìng guì 看病难,看病贵) has become a well-known expression among Chinese patients dissatisfied with the challenges they encounter in both accessibility and affordability when seeking medical treatments.
Most medical providers in China have become increasingly commercialized and profit-driven since the 1980s, leading to problems with crime and corruption within the medical system as medical professionals are expected to balance both a focus on patient well-being and financial gain. With doctors contending with low pay and incentive-based labor, bribery has emerged as a well-known problem, often considered somewhat of an “open secret” (Fun & Yao 2017, 30-31).
The prevalence of such issues has fueled public frustration, making individual cases like Yu Yanyan’s a source of intense controversy. In an environment where “getting medical attention is difficult, getting medical attention is expensive,” and where corruption is a notorious problem, many people simply do not think it is possible for one young woman to receive so much medical assistance from doctors and civil servants without the involvement of connections, power abuse, and bribery in the process.
Now that more details about the ‘blood point sister’ story have come to light, most netizens have started to question the truth behind this story and realize that Yu might just be an ordinary citizen, while some bloggers are still demanding more answers. In the end, most agree that it is not really about Miss Yu at all, but about whether or not they could expect similar medical treatment if they would end up in such a terrible situation.
“Is there currently an emergency response system in place that allows ordinary people to seek help in equally urgent crises?” (“当前是否存在一个紧急响应机制,可以让普通人在遇到同样紧急的危机时,能寻求帮助?”) one Sina blogger wonders.
“It is actually not important to know if they had special privileges or not,” one Weibo commenter writes: “I just hope that if patients need donated blood in the future, they will get the same treatment.”
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
References:
Chen, Lu, and Miaoting Cheng. 2022. “Exploring Chinese Elderly’s Trust in the Healthcare System: Empirical Evidence from a Population-Based Survey in China.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19 (24): 16461-.
Fun, Yujing & Zelin Yao. 2017. “A State of Contradiction: Medical Corruption and Strain in Beijing Public Hospitals. In: Børge Bakken (Ed.), Crime and the Chinese Dream, Hong Kong University Press: 20–39.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Where to Eat and Drink in Beijing: Yellen’s Picks

Weibo Watch: Burning BMWs

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

The Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

A Snowball Effect: How Cold Harbin Became the Hottest Place in China

Jia Ling Returns to the Limelight with New “YOLO” Movie and 110-Pound Weight Loss Announcement

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Weibo Watch: Frogs in Wells

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight1 month ago
China Insight1 month agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoA Snowball Effect: How Cold Harbin Became the Hottest Place in China
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 months agoJia Ling Returns to the Limelight with New “YOLO” Movie and 110-Pound Weight Loss Announcement
-

 China Arts & Entertainment2 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment2 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday




