China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Top 10 Most Popular Smartphones in China 2017 (According to Weibo)
Just before the biggest online shopping events of the year, these are the most popular smartphone brands in China 2017 – a top 10 list compiled by What’s on Weibo.
Published
6 years agoon
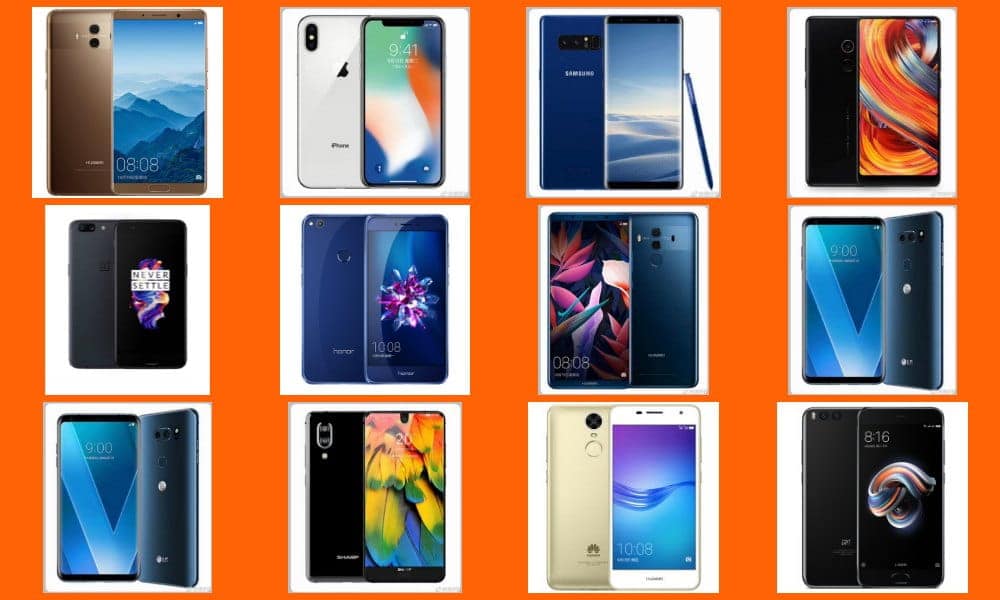
The sales of smartphones are going through the roof during China’s annual e-commerce shopping festival Single’s Day (11/11). What smartphone brands and models are the most popular on Chinese social media this year?
UPDATE! Now read our Top 10 of Most Popular Chinese Smartphones in 2018 and check out our Top 10 China’s Most Popular Smartphone Brands & Models (May/June 2019)
The countdown to Single’s Day, China’s annual largest online shopping event on November 11, is about to start. Smartphones are always amongst the top-selling items during the yearly big sale, and the various newly-launched models are hitting the social media top trending topic lists on a daily basis weeks before. Time to take a look into what phones are currently most popular amongst Chinese netizens.
Sina News recently reported that an increasing number of young Chinese consumers are willing to spend their entire monthly income or even more on a new mobile phone. Since more than 95% of Internet users in China use mobile devices rather than desktop computers to go online, chosing the right mobile is all the more important for Chinese consumers.
And for this season, the ‘right mobile’ (1) has a futuristic ‘bezel-less’ screen without edges: the bigger, the brighter, the better. With the growing importance of selfies in this social media era, the perfect phone of the moment (2) also has a high-performing front facing camera. It is also noteworthy that (3) many of the hottest phones of this moment come in various sizes and especially in various trendy colors to offer buyers more choice, tailored to their personal taste.
To create more insight into the most popular smartphone brands in China, we have compiled a list of ten Weibo smartphone brands with the most followers here.* Note that we did not include the iPhone, because despite the various channels related to iPhone on Weibo, there is no official iPhone channel.
To give you an indication, however, the Sina Weibo iPhone User Channel (@微博iPhone客户端) has a staggering 53.3 million followers – which would still make it one of China’s most popular mobile phones on social media, despite its declining popularity due to competition from domestic brands. The launch of the iPhone X on Friday is also a much-anticipated one in China.
The following smartphones currently have the largest following on Sina Weibo. With Single’s Day coming up, all brands are promoting their latest models, giving a hint to consumers on what to buy for the big November 11 online sales:
1. OPPO @OPPO企业官方微博
27.222.000+ followers

The number one smartphone brand in China – according to Weibo – is Oppo, a Guangdong-based brand officially launched in 2004. Oppo is mainly known for targeting China’s young consumers with its trendy designs and smart marketing. In 2016, the brand was ranked as the number 4 smartphone brand globally.
Right before Single’s Day, Oppo is now pushing forward its newest Oppo R11s model phone on social media. The phone will be released on November 2, and together with the much-anticipated R11s Plus model, could become one of the top-sellers on November 11.

Oppo is launching the Oppo R11s as a smartphone that is not just beautiful (with an all-screen ‘bezel-less’ display), but also smart. The phone can be unlocked within 0.08 seconds through the latest facial recognition technology.
Oppo’s smartphones are known as excellent selfie-making-tools, and its latest model is also promoted for having a 20-megapixel front and back camera. Oppo uses the Weibo hashtag ‘Oppo’s All-New 20MP Front&Back R11s’ (#OPPO全新前后2000万R11s#) to discuss the new model. On Tuesday, two days before the official launch, the hashtag was already viewed over 640 million times. There’s no pricing announced yet (will update). Update: prices start at CNY 2999 (±450$).
2. Vivo @Vivo智能手机
23.337.000+ followers
Vivo is another Chinese domestic brand that has gained worldwide success, first entering the market in 2009. Its headquarters are based in Dongguan, Guangdong.
On September 30, Vivo launched its Vivo X20 Plus and VivoX20, the successor of best-seller Vivo X9. With a price of CNY 2,998 (±$450) on JD.com, it is a popular phone that offers some advanced features, 6.01 inch (18:9) full view display, and dual camera setup, for a very reasonable price.

The popularity of the Vivo X20 is evident on Weibo. Hashtag (#vivo全面屏手机X20#) has been viewed over a billion times.
(NB: there is something noteworthy about the Weibo account of Vivo, which had 23+ million followers on October 26, and a staggering 29+ million followers only five days later. Although most reputable brands do not want to associate their brand with fake accounts, it is possible that some fans were bought – or perhaps the brand has just hugely gained popularity over the past week. In that case, it is actually Vivo that is the number one on this list. For now, we’ll stick to the follower numbers as counted between October 24-27.)
3. Xiaomi @小米
16.872.000+ followers
Since the launch of its first smartphone in 2011, Beijing-brand Xiaomi has become one of the world’s largest smartphone makers.
The Xiaomi (Mi) brand was initially often called an ‘iPhone copycat,’ but it is now a trendsetting brand in the smartphone business. With its 2016 Mi Mix model, the brand was among the first to ditch thick bezels and go beyond the 16:9 aspect ratio to introduce the ‘all screen’ or ‘bezel-less’ screens, which are all the buzz now. The Mi Mix became one of the year’s hottest smartphones.
The Mi Mix 2, Xiaomi 6, and Xiaomi Note 3 are the devices currently being promoted through the Xiaomi official Weibo channel.
With a Phillipe Starck design and premium IPS LCD screen, the Mi Mix 2 has already been getting ravenous reviews on tech sites. Some reviews, however, do note its ‘underperforming camera.’
The ‘Xiaomi Note 3’ topic #小米Note3# is also very popular on Weibo, where it has received 560 million views thus far.
It is sold for CNY 2199 (±330$) on JD.com; much cheaper than the Mix 2 which is sold for approximately CNY 3299 (±496$). With a price of CNY 2999 (±450$), the Xiaomi 6 is in between.
4. Honor (荣耀) @荣耀手机
16.638.000+ followers

Honor, established in 2013, is the budget-friendly sister of the Huawei brand. The company’s sub-brand has been doing very well over the past year. Rather than focusing on hyping up its brand name through celebrity campaigns, Honor focuses on great value for money.
On the brand’s Weibo account, it promotes its Honor V9 and Honor V9 Play as the to-buy models for November 11. The latter is currently sold for as low as CNY 999 (±150$). The Honor V9 starts at CNY 2599 (±390$).
Both the Honor V9 (#荣耀V9#) and Honor V9 Play (#荣耀V9play#) have received a lot of attention on social media this year, with millions of views and comments.

The Honor V9 has a 5.7-inch curved glass screen. It has dual SIM and an internal storage of either 64GB or 128GN expandable to 256GB by microSD.
The latest Honor models are available in multiple trendy colors. But above all of this, it is the affordability that makes this phone popular.
5. Huawei @华为
14.631.000+ followers.

Huawei remains to be one of China’s top smartphone brands. Its new model Huawei Mate 10, the follow-up to last year’s Mate 9, became a trending topic on Weibo earlier this week, with the hashtag #华为Mate10# receiving over 480 million views in some days time.

In China, the Mate 10 (128GB) is available at approximately CNY 4499.00 (±675$). With its thin bezels, 5.9-inch display, fingerprint sensor, fast-charging battery, and trendy colors (Midnight Blue, Titanium Gray, Mocha Brown, Pink Gold), this model forms a serious competition to the iPhone X.
6. Meizu @魅族科技
13.509.000+ followers.

Meizu is another Chinese homegrown brand, established by high school dropout Jack Wong (Huáng Zhāng 黄章) in 2003. Since then, it has grown out to be the 11th best-selling smartphone maker in the world.

Its newest model is the Pro 7, starting from CNY 2499 (±375$), follows all the latest trends: it has thin bezels, a strong battery and dual camera, and a slick design. The model is also available in various colors, which is one of the major trends of the season – of course, a pink edition is crucial nowadays.
7. Samsung @三星
8.690.000+ followers.

Samsung has three official accounts on Weibo; Samsung Electronics, Samsung China, and Samsung Galaxy. The latter, by far, has the most followers of the three. This account, with well over 8,5 million followers, is fully dedicated to Samsung’s high-end mobile phones.
The brand is now especially highlighting its Samsung Galaxy Note 8 model. Starting from CNY 6980 (±1050$) this is amongst the most expensive popular smartphones around.
Despite the fact that it is high-tech, the phone has not seen a very warm welcome in China. There could be various reasons for this; political tensions between Korea and China over THAAD, Samsung’s harmed reputation over its battery catastrophe, or simply the fact that Chinese consumers are value-oriented.
The Note 8 is barely any bigger than the cheaper Galaxy S8+. Although Samsung’s Note series became all the rage when they set the ‘phablet’ trend, the newest flagship models of other brands all have comparably large, bezel-less screens. With phones such as the Huawei Mate 10, the Xiaomi Mix 2, Oppo R11s, iPhone X, and Vivo X20, Samsung Note 8 is facing some serious competition within its range.
8. Sony Xperia 索尼Xperia
4.471.900+ followers.

Sony Xperia is the only Japanese brand amongst China’s most popular smartphone brands.
The brand is currently promoting its Xperia XZ Premium, which was first spotted in red back in May when it appeared on Weibo.

The Xperia XZ Premium has a 5.2-inch LCD display and specific rectangular design. With 1,3 million views for the ‘Xperia XZ Premium Launch’ (#索尼xperia xz1发布#) topic on Weibo, the phone is currently not amongst the top hottest models in China.
The brand is promoting its smartphone’s “3D Creator” on Weibo. This feature allows users to scan their face, food, or other objects and makes a 3D avatar of it that can be shared on social media or 3D print. “Can I take a picture of an Xperia XZ Premium and then make a 3D print of an Xperia XZ Premium?”, some netizens jokingly comment.
The model was officially launched in China on October 27, its price (64GB/red) is approximately CNY 6399 (±962$) – a lot more expensive than the budget-friendly red Honor V9.
9. Gionee @金立
3.134.000+ followers.

Gionee is a Chinese smartphone manufacturer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong. Founded in 2002, it is one of China’s largest mobile phone manufacturers.
Gionee is now actively promoting the successor of last year’s M6: the M7 model, which was launched in September 2017.
Its campaign for this phone actively focuses on China’s 30-something generation who are worried about their career and (young) children. Perhaps because Gionee is one of the older brands amongst its new smartphone competitors, it tells the 30-somethings “we’re growing (and advancing) together.”

The M7 has a 6.01-inch full HD display, fingerprint sensor, DUAL-sim, and goes with the trend with its full view 18:9 display. It is priced around CNY 2799 (±420$).
10. Nubia @努比亚
2.518.000+ followers.

As with Meizu and Gionee, Nubia is a Chinese brand that is generally less well-known in Europe or America than other Chinese brands such as Xiaomi or Huawei. Nevertheless, Nubia, owned by parent company ZTE, has been doing very well in China’s top-scoring smartphone lists since it was officially launched in 2015.
Before Single’s Day, the brand is now promoting its newly-launched Z17S and Z17 Mini S model. The first is priced around CNY 2999 (±450$) and the latter is more budget-friendly with CNY 1999 (±300$).
The Z17S (#努比亚Z17S#) competes with all the more expensive flagship models in offering users a 5.73 inch full HD+ screen of 18:9 ratio, and two cameras on the front. It comes in colors black and blue.
An addition to the list
With 2.2+ million followers on Sina Weibo, OnePlus (@一加手机) should also be mentioned here.

Founded in 2013, OnePlus (一加科技) is a relatively new Chinese smartphone brand. Its headquarters are based in Guangdong. The brand’s One Plus 5 model is currently also popular on Sina Weibo, despite being the most expensive phone (CNY 4288/645$) the brand has ever made.
Recent top-selling lists
A recent top 30 list (in Chinese, September 27) of best-sold smartphones on e-commerce platform Tmall shows the following top 10:
1. Honor8 32 GB (¥1099/±165$)
2. iPhone7 Plus 32GB (¥5198/±785$)
3. Vivo X9 64GB (¥2598/±392$)
4. Huawei Mate9 32 GB (¥2899/±437$)
5. Oppo RII 64GB (¥2999/±452$)
6. Samsung Galaxy S8 64GB (¥5688/±858$)
7. Honor V9 64GB (¥2699/±407$)
8. Oppo R9S Plus 64 GB (¥3199/±482$)
9. Gionee M2017 128 GB (¥6999/)
10. Moto Z 65 GB (¥3699/±558$)
According to this week’s (last week of October) best-selling smartphones (热卖排行), Suning and JD.com – some of China’s top mobile phone retailers – both show a different top 3:
Suning:
1. Apple iPhone 8 64GB
2. Apple iPhone 8 Plus
3. Xiaomi Redmi 4x 64GB
JD.com:
1. Xiaomi Mix2 64GB
2. Xiaomi 6 128 GB
3. Vivo X20 64 GB
The many different top smartphone lists on Chinese tech and e-commerce sites show that smartphone trends are changing fast, and also suggests that best-phone-lists on Chinese media sites often differ from each other for various reasons.
According to some predictions by experts on Weibo, the hottest phones of this year’s online e-commerce festival on November 11 will be the iPhone X, Xiaomi MIX2, Meizu Pro 7, Oppo R11, Vivo X20 and the OnePlus 5.
By Manya Koetse
Follow @whatsonweibo
* This list does not take the possible use of manipulated followers into account here.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us.
©2017 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron
Who’s gonna buy this Zara dress in China? “I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”
Published
3 days agoon
April 19, 2024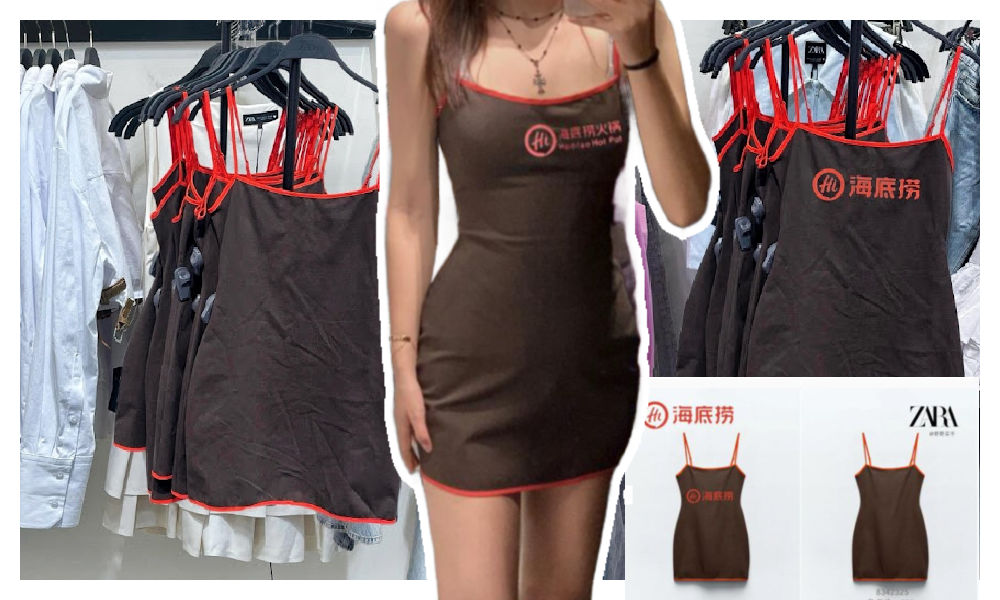
A short dress sold by Zara has gone viral in China for looking like the aprons used by the popular Chinese hotpot chain Haidilao.
“I really thought it was a Zara x Haidialo collab,” some customers commented. Others also agree that the first thing they thought about when seeing the Zara dress was the Haidilao apron.

The “original” vs the Zara dress.
The dress has become a popular topic on Xiaohongshu and other social media, where some images show the dress with the Haidilao logo photoshopped on it to emphasize the similarity.

One post on Xiaohongshu discussing the dress, with the caption “Curious about the inspiration behind Zara’s design,” garnered over 28,000 replies.
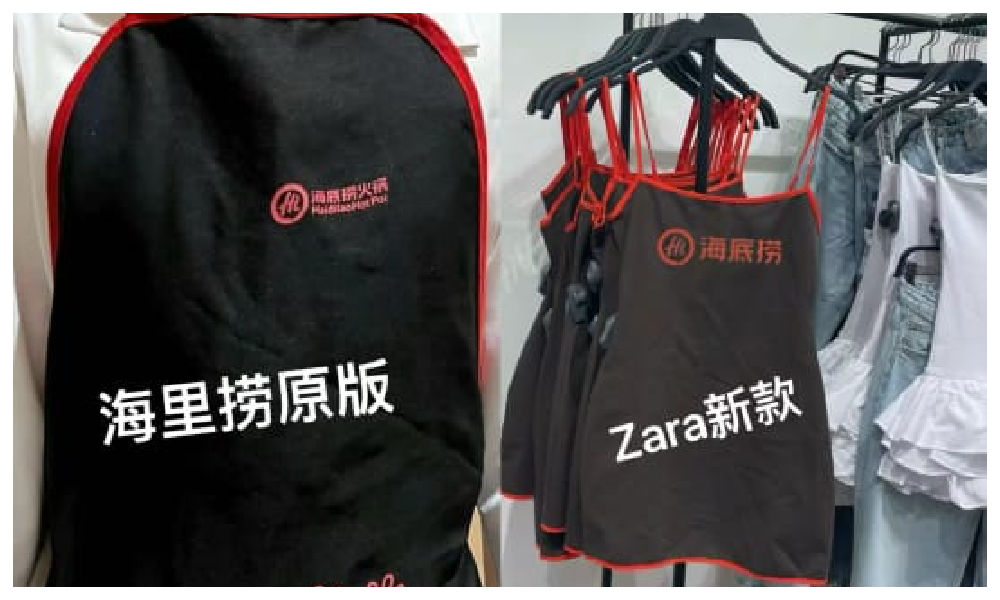
Haidilao, with its numerous restaurants across China, is renowned for its hospitality and exceptional customer service. Anyone who has ever dined at their restaurants is familiar with the Haidilao apron provided to diners for protecting their clothes from food or oil stains while enjoying hotpot.
These aprons are meant for use during the meal and should be returned to the staff afterward, rather than taken home.
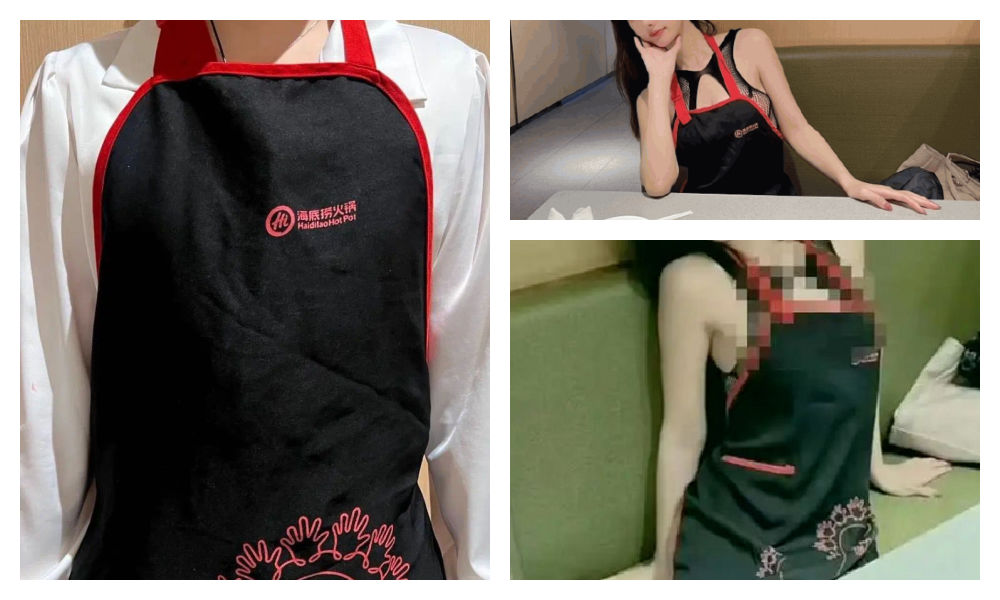

The Haidilao apron.
However, many people who have dined at Haidilao may have encountered the following scenario: after indulging in drinks and hotpot, they realize they are still wearing a Haidilao apron upon leaving the restaurant. Consequently, many hotpot enthusiasts may have an ‘accidental’ Haidilao apron tucked away at home somewhere.
This only adds to the humor of the latest Zara dress looking like the apron. The similarity between the Zara dress and the Haidilao apron is actually so striking, that some people are afraid to be accused of being a thief if they would wear it.
One Weibo commenter wrote: “The most confusing item of this season from Zara has come out. It’s like a Zara x Haidilao collaboration apron… This… I can’t wear it: I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”

Funnily enough, the Haidilao apron similarity seems to have set off a trend of girls trying on the Zara dress and posting photos of themselves wearing it.

It’s doubtful that they’re actually purchasing the dress. Although some commenters say the dress is not bad, most people associate it too closely with the Haidilao brand: it just makes them hungry for hotpot.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Zibo had its BBQ moment. Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine with its special take on malatang. Tourism marketing in China will never be the same again.
Published
3 weeks agoon
April 1, 2024
Since the early post-pandemic days, Chinese cities have stepped up their game to attract more tourists. The dynamics of Chinese social media make it possible for smaller, lesser-known destinations to gain overnight fame as a ‘celebrity city.’ Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine.
During this Qingming Festival holiday, there is one Chinese city that will definitely welcome more visitors than usual. Tianshui, the second largest city in Gansu Province, has emerged as the latest travel hotspot among domestic tourists following its recent surge in popularity online.
Situated approximately halfway along the Lanzhou-Xi’an rail line, this ancient city wasn’t previously a top destination for tourists. Most travelers would typically pass through the industrial city to see the Maiji Shan Grottoes, the fourth largest Buddhist cave complex in China, renowned for its famous rock carvings along the Silk Road.
But now, there is another reason to visit Tianshui: malatang.
Gansu-Style Malatang
Málàtàng (麻辣烫), which literally means ‘numb spicy hot,’ is a popular Chinese street food dish featuring a diverse array of ingredients cooked in a soup base infused with Sichuan pepper and dried chili pepper. There are multiple ways to enjoy malatang.
When dining at smaller street stalls, it’s common to find a selection of skewered foods—ranging from meats to quail eggs and vegetables—simmering in a large vat of flavorful spicy broth. This communal dining experience is affordable and convenient for solo diners or smaller groups seeking a hotpot-style meal.
In malatang restaurants, patrons can usually choose from a selection of self-serve skewered ingredients. You have them weighed, pay, and then have it prepared and served in a bowl with a preferred soup base, often with the option to choose the level of spiciness, from super hot to mild.
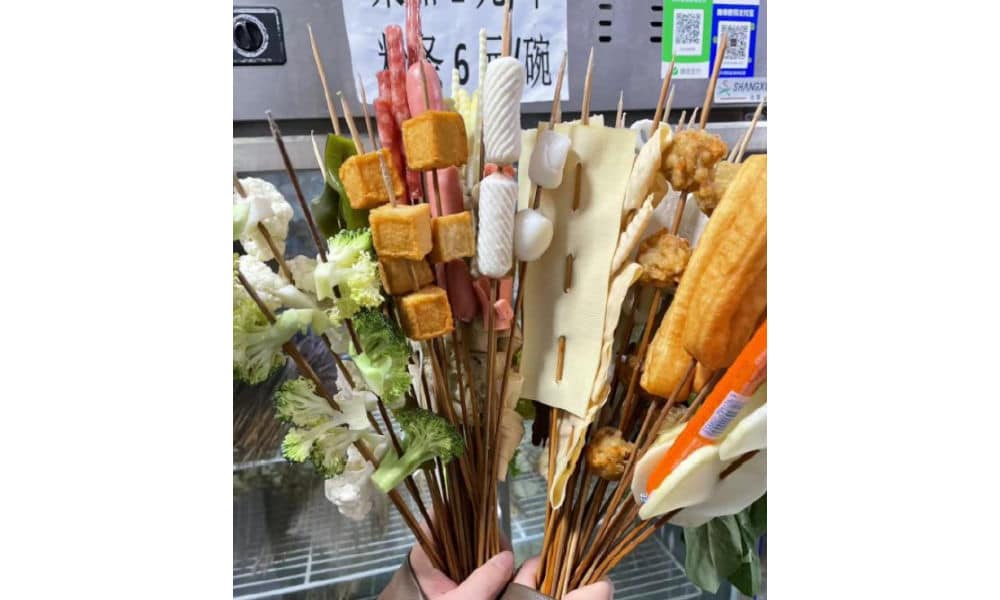

Although malatang originated in Sichuan, it is now common all over China. What makes Tianshui malatang stand out is its “Gansu-style” take, with a special focus on hand-pulled noodles, potato, and spicy oil.
An important ingredient for the soup base is the somewhat sweet and fragrant Gangu chili, produced in Tianshui’s Gangu County, known as “the hometown of peppers.”
Another ingredient is Maiji peppercorns (used in the sauce), and there are more locally produced ingredients, such as the black fungi from Qingshui County.
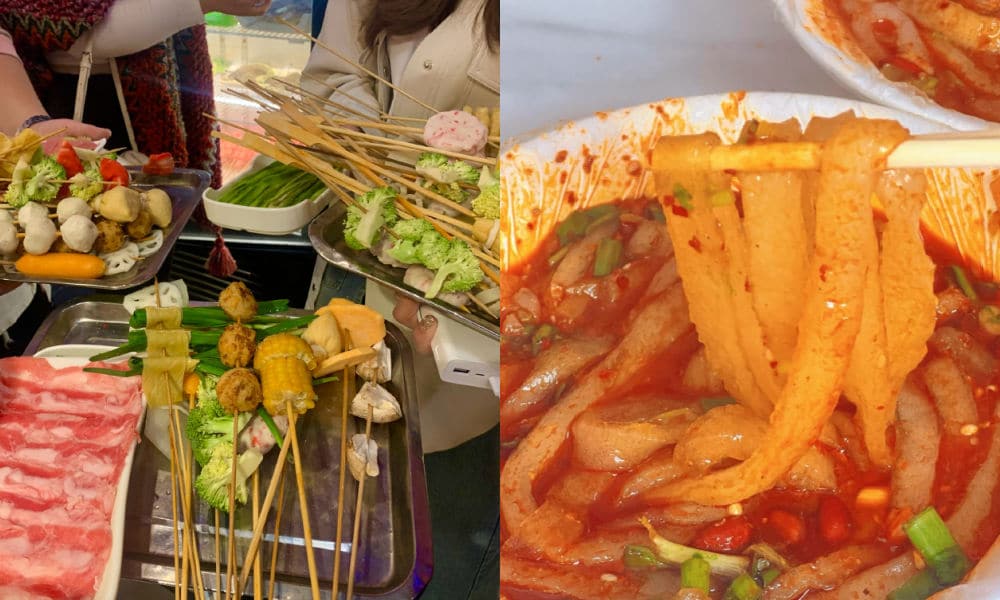

One restaurant that made Tianshui’s malatang particularly famous is Haiying Malatang (海英麻辣烫) in the city’s Qinzhou District. On February 13, the tiny restaurant, which has been around for three decades, welcomed an online influencer (@一杯梁白开) who posted about her visit.
The vlogger was so enthusiastic about her taste of “Gansu-style malatang,” that she urged her followers to try it out. It was the start of something much bigger than she could have imagined.
Replicating Zibo
Tianshui isn’t the first city to capture the spotlight on Chinese social media. Cities such as Zibo and Harbin have previously surged in popularity, becoming overnight sensations on platforms like Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin.
This phenomenon of Chinese cities transforming into hot travel destinations due to social media frenzy became particularly noteworthy in early 2023.
During the Covid years, various factors sparked a friendly competition among Chinese cities, each competing to attract the most visitors and to promote their city in the best way possible.
The Covid pandemic had diverse impacts on the Chinese domestic tourism industry. On one hand, domestic tourism flourished due to the pandemic, as Chinese travelers opted for destinations closer to home amid travel restrictions. On the other hand, the zero-Covid policy, with its lockdowns and the absence of foreign visitors, posed significant challenges to the tourism sector.
Following the abolition of the zero-Covid policy, tourism and marketing departments across China swung into action to revitalize their local economy. China’s social media platforms became battlegrounds to capture the attention of Chinese netizens. Local government officials dressed up in traditional outfits and created original videos to convince tourists to visit their hometowns.
Zibo was the first city to become an absolute social media sensation in the post-Covid era. The old industrial and mining city was not exactly known as a trendy tourist destination, but saw its hotel bookings going up 800% in 2023 compared to pre-Covid year 2019. Among others factors contributing to its success, the city’s online marketing campaign and how it turned its local BBQ culture into a unique selling point were both critical.

Zibo crowds, image via 163.com.
Since 2023, multiple cities have tried to replicate the success of Zibo. Although not all have achieved similar results, Harbin has done very well by becoming a meme-worthy tourist attraction earlier in 2024, emphasizing its snow spectacle and friendly local culture.
By promoting its distinctive take on malatang, Tianshui has emerged as the next city to captivate online audiences, leading to a surge in visitor numbers.
Like with Zibo and Harbin, one particular important strategy used by these tourist offices is to swiftly respond to content created by travel bloggers or food vloggers about their cities, boosting the online attention and immediately seizing the opportunity to turn online success into offline visits.
A Timeline
What does it take to become a Chinese ‘celebrity city’? Since late February and early March of this year, various Douyin accounts started posting about Tianshui and its malatang.
They initially were the main reason driving tourists to the city to try out malatang, but they were not the only reason – city marketing and state media coverage also played a role in how the success of Tianshui played out.
Here’s a timeline of how its (online) frenzy unfolded:
- July 25, 2023: First video on Douyin about Tianshui’s malatang, after which 45 more videos by various accounts followed in the following six months.
- Feb 5, 2024: Douyin account ‘Chuanshuo Zhong de Bozi’ (传说中的波仔) posts a video about malatang streetfood in Gansu
- Feb 13, 2024: Douyin account ‘Yibei Liangbaikai’ (一杯梁白开) posts a video suggesting the “nationwide popularization of Gansu-style malatang.” This video is an important breakthrough moment in the success of Tianshui as a malatang city.
- Feb – March ~, 2024: The Tianshui Culture & Tourism Bureau is visiting sites, conducting research, and organizing meetings with different departments to establish the “Tianshui city + malatang” brand (文旅+天水麻辣烫”品牌) as the city’s new “business card.”
- March 11, 2024: Tianshui city launches a dedicated ‘spicy and hot’ bus line to cater to visitors who want to quickly reach the city’s renowned malatang spots.
- March 13-14, 2024: China’s Baidu search engine witnesses exponential growth in online searches for Tianshui malatang.
- March 14-15, 2024: The boss of Tianshui’s popular Haiying restaurant goes viral after videos show him overwhelmed and worried he can’t keep up. His facial expression becomes a meme, with netizens dubbing it the “can’t keep up-expression” (“烫不完表情”).

The worried and stressed expression of this malatang diner boss went viral overnight.
- March 17, 2024: Chinese media report about free ‘Tianshui malatang’ wifi being offered to visitors as a special service while they’re standing in line at malatang restaurants.
- March 18, 2024: Tianshui opens its first ‘Malatang Street’ where about 40 stalls sell malatang.
- March 18, 2024: Chinese local media report that one Tianshui hair salon (Tony) has changed its shop into a malatang shop overnight, showing just how big the hype has become.
- March 21, 2024: A dedicated ‘Tianshui malatang’ train started riding from Lanzhou West Station to Tianshui (#天水麻辣烫专列开行#).
- March 21, 2024: Chinese actor Jia Nailiang (贾乃亮) makes a video about having Tianshui malatang, further adding to its online success.
- March 30, 2024: A rare occurrence: as the main attraction near Tianshui, the Maiji Mountain Scenic Area announces that they’ve reached the maximum number of visitors and don’t have the capacity to welcome any more visitors, suspending all ticket sales for the day.
- April 1, 2024: Chinese presenter Zhang Dada was spotted making malatang in a local Tianshui restaurant, drawing in even more crowds.
A New Moment to Shine
Fame attracts criticism, and that also holds true for China’s ‘celebrity cities.’
Some argue that Tianshui’s malatang is overrated, considering the richness of Gansu cuisine, which offers much more than just malatang alone.
When Zibo reached hype status, it also faced scrutiny, with some commenters suggesting that the popularity of Zibo BBQ was a symptom of a society that’s all about consumerism and “empty social spectacle.”
There is a lot to say about the downsides of suddenly becoming a ‘celebrity city’ and the superficiality and fleetingness that comes with these kinds of trends. But for many locals, it is seen as an important moment as they see their businesses and cities thrive.
Even after the hype fades, local businesses can maintain their success by branding themselves as previously viral restaurants. When I visited Zibo a few months after its initial buzz, many once-popular spots marketed themselves as ‘wanghong’ (网红) or viral celebrity restaurants.
For the city itself, being in the spotlight holds its own value in the long run. Even after the hype has peaked and subsided, the gained national recognition ensures that these “trendy” places will continue to attract visitors in the future.
According to data from Ctrip, Tianshui experienced a 40% increase in tourism spending since March (specifically from March 1st to March 16th). State media reports claim that the city saw 2.3 million visitors in the first three weeks of March, with total tourism revenue reaching nearly 1.4 billion yuan ($193.7 million).
There are more ripple effects of Tianshui’s success: Maiji Shan Grottoes are witnessing a surge in visitors, and local e-commerce companies are experiencing a spike in orders from outside the city. Even when they’re not in Tianshui, people still want a piece of Tianshui.
By now, it’s clear that tourism marketing in China will never be the same again. Zibo, Harbin, and Tianshui exemplify a new era of destination hype, requiring a unique selling point, social media success, strong city marketing, and a friendly and fair business culture at the grassroots level.
While Zibo’s success was largely organic, Harbin’s was more orchestrated, and Tianshui learned from both. Now, other potential ‘celebrity’ cities are preparing to go viral, learning from the successes and failures of their predecessors to shine when their time comes.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Where to Eat and Drink in Beijing: Yellen’s Picks

Weibo Watch: Burning BMWs

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Weibo Watch: Frogs in Wells

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

In Hot Water: The Nongfu Spring Controversy Explained

The Benz Guy from Baoding and the Granny Xu Line-Cutting Controversy
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight2 months ago
China Insight2 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Arts & Entertainment2 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment2 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday
-

 China Media1 month ago
China Media1 month agoParty Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”
-

 China World2 months ago
China World2 months agoFrom Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)





Ed Sander
November 6, 2017 at 3:25 am
OnePlus is basically owned by Oppo.
I personally wouldn’t look at Weibo followers or online sales to determine the popularity of smartphones. As you mentioned, zombie-followers can be bought and ‘old followers’ do not necessarily have to use that phone anymore.
Online sales on specific platforms are influenced by promotions and do not take into account the offline sales, which are pretty important for brands like Oppo, Vivo and Huawei.
I would advise to look at figures by the IDC instead. Earlier this year, based on market share, the top 5 was: Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, iPhone and Xiaomi.
Another source, Gfk, showed the same ranking in May, while market research firm Counterpoint had Apple and Xiaomi switching places.
Ed
admin
November 6, 2017 at 3:37 am
It is true that popularity on Weibo does not necessarily represent sales figures. This is just a list we wanted to provide of the brands with most following on Weibo, of which the hashtags of new model announcements are topping the trending topics lists daily. If readers are looking for a different type of list they should certainly follow the lists you advice.
Compare phones side by side
January 9, 2018 at 2:32 pm
This is really one of the best post and great information about smartphones, I liked it and enjoyed reading it. Keep sharing such an important posts
mobile makr
January 30, 2018 at 11:48 am
oppo and vivo are no.1 stupid phones xxxxxxxxx 🙁
Srinivas
February 8, 2018 at 6:50 pm
Well, the article very much useful about top china mobiles. Also read about top 5 Indian Smart phones (Non-China) with price and specification
CLICK ON LINK
http://gstrendsnow.blogspot.in/2018/02/top-5-indian-brand-smart-phones-non.html