China Celebs
Chinese Social Media Users Stand up Against Body Shaming
Published
5 years agoon

Recent photos of famous actress Gong Li that showed her curvier figure have gone viral on Sina Weibo, receiving over 850 million clicks. With Gong Li’s weight gain becoming all the talk on Weibo, the public’s focus on her appearance has sparked an online wave of body positivity posts, with web users rejecting the all-too-common phenomenon of body shaming on Chinese social media.
First, there was the ‘A4 Waist‘ hype, then there was the ‘iPhone6 Legs‘ trend, the ‘belly button backhand,’ and the online challenge of putting coins in your collarbone to show off how thin you are (锁骨放硬币). Over the past five years, China has seen multiple social media trends that propagated a thin figure as the ruling beauty standard.
But now a different kind of trend is hitting Weibo’s hotlists: one that rejects body shaming and promotes the acceptance of a greater diversity in body sizes and shapes in China.
On August 26, Weibo user @_HYIII_ from Shanghai posted several pictures, writing:
“Reject body shaming! Why should we all have the same figure? Tall or short, thin or fat, all have their own characteristics. Embrace yourself, and show off your own unique beauty!”
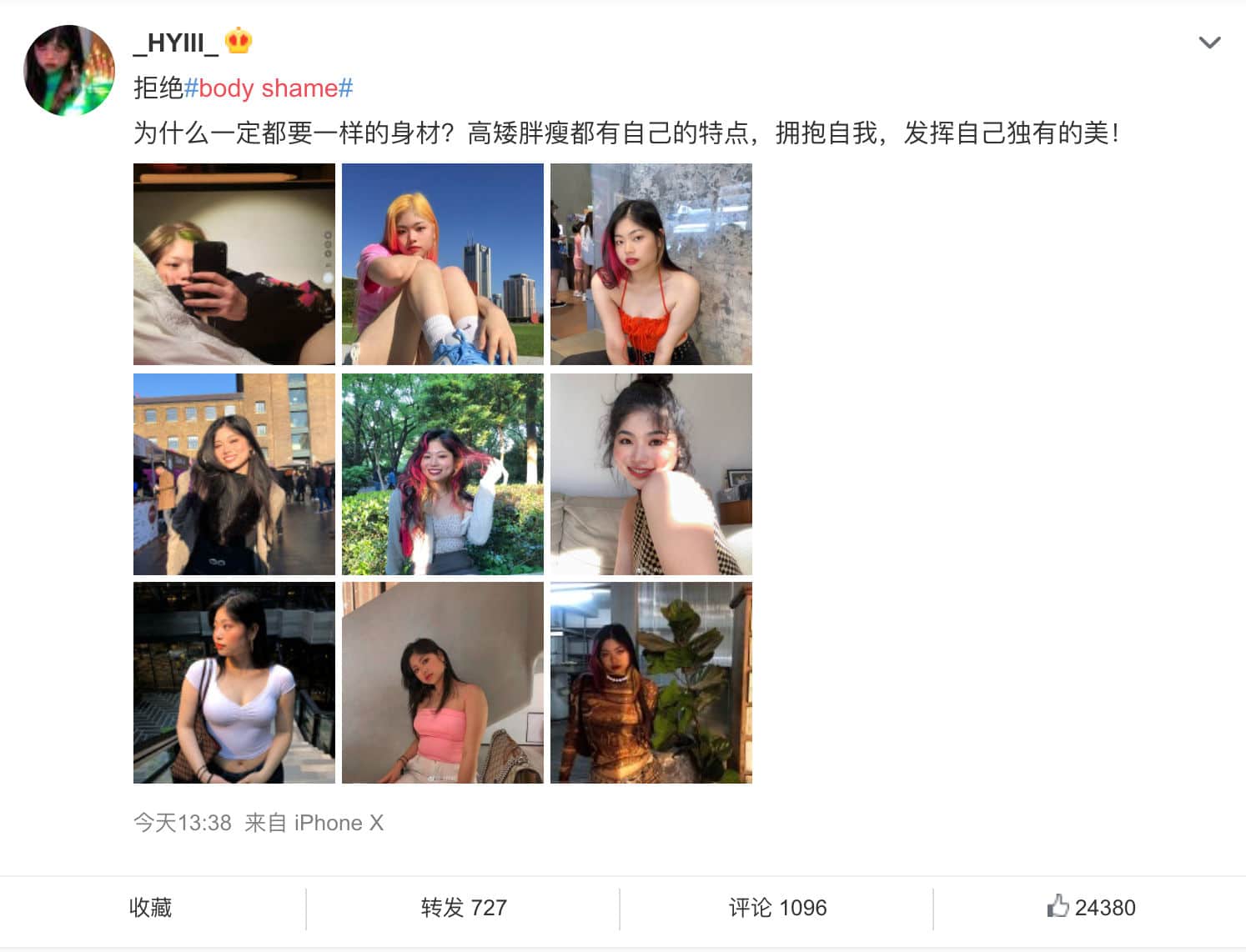
The post was soon shared over 900 times, receiving more than 32,000 likes, with the “body shame” phrase soon reaching the top keyword trending list of Sina Weibo.
Gong Li Weight Gain
The body positivity post by ‘_HYIII_’ is going viral on the same day that the apparent weight gain of Chinese actress Gong Li (巩俐) is attracting major attention on Chinese social media platforms such as Weibo and Douyin.
The 54-year-old actress, who is known for starring in famous movies such as Farewell My Concubine, To Live, and Memoirs of a Geisha, was spotted taking a walk with her husband in France on August 24. The photos went viral, with media outlets such as Sina Entertainment noting how Gong Li had become “much rounder” and had put on some “happy fat” (幸福肥).
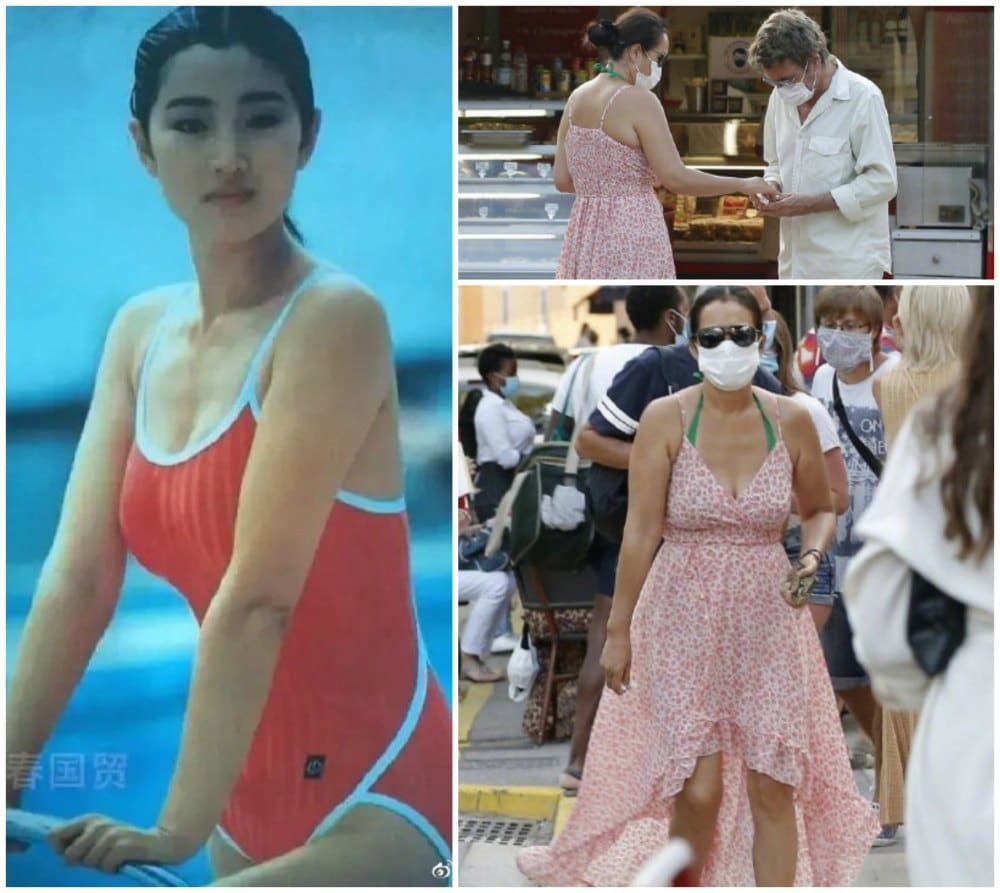

By now, the hashtag page “Gong Li’s Figure” (#巩俐身材#) has received more than 850 million (!) views on Weibo, with thousands of people commenting on the appearance of the actress. In the comment sections, there were many who lashed out against the focus on Gong Li’s weight gain.
“She just has a regular female body shape. Stop using ‘white / skinny / young’ as the main beauty standard to assess other people,” one commenter said, with another person writing: “Why do you all keep focusing on her figure, did she steal your rice and eat it?!”
“Why do you all keep focusing on her figure, did she steal your rice and eat it?”
Some people suggested that the COVID19 pandemic might have to do with Gong Li’s weight gain, with others writing: “If she is healthy is what matters, skinny or fat is not the way to assess her beauty.”
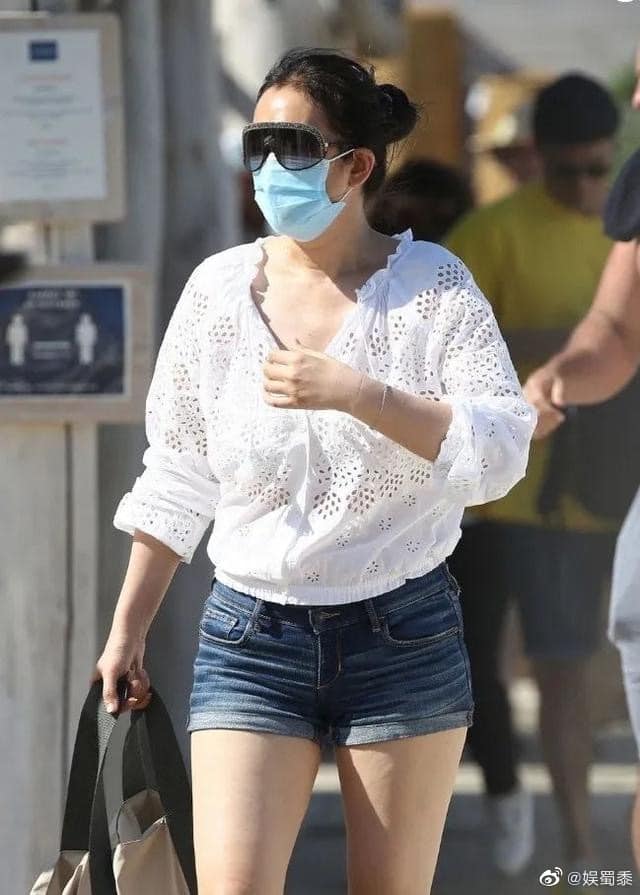

What stands out from the discussions flooding social media at this time, is that a majority of web users seem to be fed up with the fact that a skinny body is the common standard of women’s beauty in China today – and that accomplished and talented women such as Gong Li are still judged by the size of their waist.
Say No to Body Shaming
In light of the controversy surrounding Gong Li’s recent photos and the following discussions, posts on ‘body shaming’ (身材羞辱) are now flooding Weibo, with many Weibo users calling on people to “reject body shaming” (拒绝#body shame#) and to stop imposing strict beauty standards upon Chinese women.
The pressure to be thin, whether it comes from the media or from others within one’s social circle, is very real and can seriously affect one’s self-esteem. Various studies have found an association between body dissatisfaction and social pressure to be thin and body shaming in Chinese adolescents and young adults (Yan et al 2018).
The main message in this recent Weibo grassroots campaign against body shaming, is that there are many ways in which women can be beautiful and that their beauty should not be merely defined by limited views on the ideal weight, height, or skin color.
Over the past decades, women’s beauty ideals have undergone drastic changes in China, where there has been a traditional preference for “round faces” and “plump bodies.” In today’s society, thin bodies, sharp faces, and a pointy chin are usually regarded as the standard of female ideal beauty (Jung 2018, 68). China’s most popular photo apps, such as Meitu or Pitu, often also include features to make one’s face pointier or one’s legs more skinny.
This is not the first time Weibo sees a growing trend of women opposing strict beauty standards. Although the word ‘body shaming’ has not often been included in previous trends, there have been major trends of women opposing popular skinny challenges and even one social media campaign in which young women showed their hairy armpits to trigger discussions on China’s female aesthetics.
Especially in times of a pandemic, many netizens now stress the importance of health: “Skinny or fat, it really doesn’t matter how much you weigh, as long as you’re healthy – that’s what counts.”
Also read:
- Anorexia in China – Same, But Different
- Binging and Purging as Online Trend: From China’s “Big Stomach Stars” to “Vomit Bars”
- Move Over ‘A4 Waist’, Here Comes the ‘iPhone6 Legs’ Hype – Growing Concerns Over China’s Online Skinny Trends
By Manya Koetse
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
References
Jung, Jaehee. 2018. “Young Women’s Perceptions of Traditional and Contemporary Female Beauty Ideals in China.” Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal 47 (1): 56-72.
Yan, Hanyi ; Wu, Yingru ; Oniffrey, Theresa ; Brinkley, Jason ; Zhang, Rui ; Zhang, Xinge ; Wang, Yueqiao ; Chen, Guoxun ; Li, Rui ; Moore, Justin. 2018. “Body Weight Misperception and Its Association with Unhealthy Eating Behaviors among Adolescents in China.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15 (5): 936.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2020 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China Celebs
China Trend Watch: Quiet Nationalism, Loud Statements, and Nanjing Memorial Day
From war memory to viral eggs, salty cakes, an unfortunate dinner party and farewell to an iconic actress.
Published
1 month agoon
December 14, 2025
🔥 China Trend Watch — Week 50 (2025)
Part of Eye on Digital China. This edition was sent to paid subscribers — subscribe to receive the next issue in your inbox.
Welcome to the Eye on Digital China newsletter. This is the China Trend Watch edition — a quick catch-up on real-time conversations.
I’ve rounded up my latest China trip that brought me from Chongqing to Nanjing, Wuhan, Zaozhuang and Beijing, for some of my research on Chinese remembrances of war. Along the way, I have met many friendly people and had interesting converations, from hanging out with a group of Wuhan teenagers to lively conversations with retired seniors in Shandong.
A small and short personal observation, if I may, regarding the current tensions between China and Japan.
I vividly remember the atmosphere on the streets during earlier moments when tensions ran sky-high—most notably in 2012, after a major diplomatic crisis erupted over Japan’s nationalization of several disputed Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands. That episode triggered large-scale anti-Japanese protests across China and spilled unmistakably into everyday life. In Beijing’s Sanlitun area, for instance, there was a street food vendor who put up a large sign proclaiming, “The Diaoyu Islands belong to China.” In the hutong neighborhoods, it seemed as though virtually every household had hung a Chinese flag by its door. Books about Japan that I purchased locally later turned out to have entire pages ripped out. My favorite sushi restaurant suddenly displayed a sign explaining that its brand was, in fact, very Chinese and had nothing to do with Japan. Nearby, in the clothing markets around the Beijing Zoo, T-shirts bearing nationalistic slogans related to the islands dispute were on sale at multiple stalls.
By contrast, during my most recent stay in Nanjing and beyond—despite the increasingly militant tone of state media and social media campaigns surrounding Japan, and despite the undeniable persistence of anti-Japanese sentiment—I noticed far fewer visible expressions of it in daily life. There were no slogan T-shirts, no banners, no overt street-level signaling. While news came out that a string of Japanese performances in China were canceled, I noticed hotel waitress fully dressed in a Japanese kimono at an in-house Japanese restaurant. Local bookstores are filled with works by Japanese authors, and Japanese popular culture appear to be thriving and coexisting comfortably with China’s own flourishing ACG (anime, comics, and games) industry.
Is there simply less anti-Japanese sentiment than over a decade ago? Or is it, perhaps, that in today’s highly digitalized Xi Jinping era, nationalist narratives are more tightly managed and increasingly channeled online—making people more cautious, more restrained, or simply less inclined to express political sentiments openly in public space?
A cab driver in Chongqing told me he believed there was “something wrong” with Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi and the influence she has had on bilateral relations since her rise to power. While supporting his government’s tough stance and expressing sadness over the scars left by war, he also mentioned that he had enjoyed a pleasant conversation earlier that same morning with a young Japanese man he had driven to the train station.
“We didn’t talk about the latest clash,” he said. “If find that too sensitive to mention. He spoke Chinese, he studied Chinese, like you. I don’t hate today’s Japanese people at all. In the end, we’re all just people. What’s happening now is something between the leadership.”
He spoke at length while driving me to the station, signaling that the topic clearly weighed on him. It left me with the sense that the absence of banners or T-shirts does not mean the issue has faded from everyday life, only that it is not expressed as a mass spectacle like it was in earlier years. It has become quieter, more online, and more filtered through official narratives, but it is still very much alive.
There is a lot more to say, but it is Sunday after all, and there is plenty more to read here, so let’s dive in.
- 🍓 Chinese consumers were pretty salty this week when discovering their pricey strawberry cake from Alibaba supermarket chain Hema (盒马) tasted all wrong. Hema acknowledged a production issue (they didn’t say it outright, but salt was allegedly used instead of sugar) and the incident triggered discussions about food safety & quality control in automated food production, especially when such a major mistake happens at high-profile companies.
- 🌡️ China’s announced ban on mercury thermometers (as of Jan 1st 2026) has sparked a buying frenzy, as many consumers, reluctant to switch to electronic alternatives, still prefer mercury models for their perceived accuracy and convenience. Despite nearly half of annual mercury poisoning cases being linked to broken thermometers, prices have now surged from around 4 yuan ($0.6) to over 30 yuan ($4.25), and stores have reported complete sellouts.
- ❄️ Beijing welcomed its first snowfall of winter 2025 this week, leading to lovely social media pics and the Beijing Palace Museum tickets selling out instantly. Experiencing and capturing that first snowfall at the Forbidden City has become somewhat of a holy grail on social media.
- 🕵️♂️ A local construction site in Shanghai unexpectedly became the scene of a modern-day treasure hunt after dozens of residents armed with shovels and metal detectors rushed to the area following online rumors that silver coins (including valuable older ones) had been found. Authorities had to intervene and, while not confirming the rumors, emphasized that any buried cultural relics belong to the state.
- 🇷🇺 Since this month, Chinese citizens can enter Russia visa-free for up to 30 days, a policy that led Chinese state media to claim that “Russia is replacing Japan as a new favorite among Chinese tourists.” On social media, however, the vibe is different, with travelers complaining about high prices, poor internet, lack of online payments, unreliable ATMs, and the need for thorough trip preparation — all reasons why Russia is unlikely to become the go-to destination for the Chinese New Year.
- 🫏 An investigation by Beijing Evening News revealed that many of the capital’s popular donkey meat sandwich shops are actually serving horse meat without informing customers. China’s donkey shortage — driven by declining domestic supply, rising demand for the traditional Chinese medicine Ejiao (which uses donkey hides), and an African export ban — has been a hot topic this year. Now that it’s directly affecting a beloved delicacy, the issue is drawing even more public attention.
1. Why This Year’s Nanjing Memorial Day Felt Different

Posters published by various Chinese state media outlets to commemorate the Nanjing Massacre.
December 13 marked the 88th anniversary of the fall of Nanjing, and this year’s Nanjing Memorial Day (南京大屠杀难者国家公祭日), although described as a low-key commemoration by foreign media, was trending all over Chinese social media.
During the Second Sino-Japanese War, on December 12, 1937, the Japanese army attacked Nanjing from various directions, and defending Chinese forces suffered heavy casualties. A day later, the city was captured. It marked the beginning of a six-week-long massacre filled with looting, arson, and rape, during which, according to China’s official data, at least 300,000 residents, including children, elderly, and women, were brutally murdered.
This year, the Nanjing Massacre Memorial Day, which was first officially held as a state-level event in 2014, carried extra weight. This dark chapter of history has continuously been a sensitive topic in Sino-Japanese relations, but with recent diplomatic tensions between the two countries reaching new heights, the Memorial Day was especially tied to current-day relations between China and Japan and to Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi, who has been described by Chinese media as an “ultranationalist” with tendencies to downplay Japan’s wartime aggression. Takaichi’s November 2025 parliamentary statement that a Chinese military action against Taiwan could be considered a “survival-threatening situation” for Japan, allowing for the deployment of its Self-Defense Forces, continues to fuel Chinese anger.
The link between history and current-day bilateral relations was visible not only on social media, but also during the commemoration itself, where Shi Taifeng (石泰峰), head of the ruling Communist Party’s Organization Department, said that any attempt to revive militarism and challenge the postwar international order is “doomed to fail.”
Besides the many online posters disseminated by Chinese official accounts on social media focusing on mourning, quiet commemoration, and honoring the lives of the 300,000 Chinese compatriots killed in Nanjing, one official online visual stood out for displaying a louder and more aggressive message—namely that posted by the official Weibo account of the Eastern Theater Command of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (@东部战区).

The visual posted by the PLA Eastern Theater Command, titled: Rite of the Great Saber (大刀祭).
The visual showed a strong hand holding a giant blood-stained blade that is beheading a skeleton wearing a helmet marked “militarism,” with images related to the Nanjing Massacre visible on the blade and, behind it, a map of East Asia. The number “300000” appears in red, dripping like blood. At the top, the characters read “Rite of the Great Saber” or “The Great Saber Sacrifice” (大刀祭).
The official account explained the visual, writing: “(…) 88 years have passed and the blood of the heroic dead has not yet dried, [yet] the ghost of militarism is making a comeback. Each year, on National Memorial Day, a deafening alarm is sounded, reminding us that we must—at all times hold high the great saber offered in blood sacrifice, resolutely cut off filthy heads, never allow militarism to return, and never allow historical tragedy to be repeated.”
The text’s “cut off filthy heads” phrasing is similar to part of a now-deleted tweet sent out last month by the Chinese Consul General in Osaka, Xue Jian (薛剑), who responded to Takaichi’s controversial Taiwan remarks by writing (in Japanese): “If you come charging in on your own like that, there’s nothing to do but cut that filthy neck down without a moment’s hesitation. Are you prepared?” (“勝手に突っ込んできたその汚い首は一瞬の躊躇もなく斬ってやるしかない。覚悟が出来ているのか。”)
The recent visuals, social media approach, and shifts in texts reflect a clear change in tone in Chinese official discourse regarding Japan and the memory of war, moving the narrative from victimhood toward a more confrontational and militant tone.
2. He Qing, China’s “No. 1 Classical Beauty”, Passes Away at 61

He Qing. Images on the sides: the four famous roles in China’s most iconic tv dramas.
China’s “No. 1 Classical Beauty” (古典第一美女), He Qing (何晴), who starred in all four of China’s most beloved and canonical television dramas, passed away on Saturday at the age of 61. On December 14, news of the famous actress’s passing was trending across virtually all Chinese social media apps.
Born in 1964 into an artistic family in Jiangshan, Zhejiang Province, He Qing received traditional Chinese opera (Kunqu) training at the Zhejiang Kunqu Opera Troupe. Her debut in the entertainment industry may have come by chance, as she reportedly once met Chinese director Yang Jie (杨洁) on a train, which led to her joining the production of Journey to the West (西游记), where she played Lingji Bodhisattva (灵吉菩萨).
In China, He Qing is remembered as a veteran actress in much the same way that some famous Hong Kong actresses became renowned for their beauty, iconic roles, and for essentially becoming household names. More than just glitter and glamour, He Qing was especially a symbol of classical Chinese beauty and literary culture. She was the only actress to star in screen adaptations of all four of China’s “Four Great Classical Novels” (演遍四大名著): besides Journey to the West (西游记, 1986), she also appeared in Dream of the Red Chamber (红楼梦, 1987), Romance of the Three Kingdoms (三国演义, 1994), and Water Margin (水浒传, 1998).
She was married to fellow actor Xu Yajun (许亚军), with whom she had a son, Xu He (许何). Although the two later divorced, she remained close to her ex-husband and even befriended his new (and fourth) wife, Zhang Shu (张澍).
In 2015, He Qing was diagnosed with a brain tumor. After her diagnosis, she withdrew from the entertainment industry to focus on her recovery and lived a low-key life in her later years.
Her passing has prompted an outpouring of tributes from Chinese netizens and colleagues in the entertainment industry. Mourning her loss comes with a sense of nostalgia for the past, and many have praised He Qing for her timeless beauty and authenticity, which will be remembered long after her passing.
3. And Then There Were None: Dinner Party of Ten Leaves One Man with the Bill

Ten dine together, nine slip away..one left for the bill, who he refused to pay…
Do you know that nursery rhyme where ten little soldiers disappear one by one until none remain at the end? That is more or less what happened earlier this month in Chongqing, when ten people dined together at a restaurant, but—once it came time to pay—nine people left one by one.
One had to answer a phone call, another had to use the restroom, and in the end, just before midnight, only Mr. Zhang was left, facing a bill of 1,262 yuan ($180), which he refused to pay. He argued that he could not afford it and that the dinner party hadn’t been initiated by him at all; as merely a participant, the bill shouldn’t have been his responsibility.
After the restaurant called the police, the organizer of the dinner was contacted. But he, too, said he couldn’t pay. Through police mediation, Mr. Zhang then wrote a written commitment promising to pay the bill the following day and left his ID as collateral, but he still failed to make the payment.
By now, the restaurant is planning to sue and has also contacted the Chinese media. According to Zhang, who apparently has been unable to contact his “friends” to collect the money: “I did make the promise, but if I pay the money, wouldn’t that make me a sucker?” (“我的确承诺了,但你说我把钱付了,我是不是冤大头啊”)
As the story went completely viral (by now, even Hu Xijin has weighed in) comment sections filled with broader social reflections on alcohol-fueled group gatherings and unclear payment rules, where one person sometimes ends up paying for everything despite feeling it wasn’t their role to do so. In this era of digital payments, many argue it should be easy enough to go Dutch and settle the bill immediately via a group payment app.
Although Zhang is seen by some as a victim, others argue that he is still a “sucker” for not paying after having promised to do so. As one commenter put it: “Out of the ten of them, not a single one is a good person.”
Real Person Vibes [活人感 (huóréngǎn)

Every December, the ten most popular buzzwords, key terms, or expressions of the year are listed by the Chinese linguistics magazine Yǎowén Jiáozì (咬文嚼字), selecting words that reflect present-day society and changing times. Each year, the list goes trending and is widely disseminated by Chinese media.
This week, the 2025 list was released, including terms such as Digital Nomads 数字游民 (shù zì yóu mín), Sū Chāo (苏超), referring to the hugely popular amateur Jiangsu Super League football competition, and “Pre-made ××” (预制, yù zhì), following a year filled with discussions about pre-fab and pre-made food (see article).
My favorite word on the list is “Real-Person Vibes” (活人感 huó rén gǎn). The term literally consists of three characters meaning “living – human – feeling,” and it describes people, stories, or things that feel unpolished, spontaneous, and unfiltered—something that has become increasingly relevant in a year dominated by AI-generated content and visuals.
Amid over-curated feeds and AI-produced text, we crave huóréngǎn: authenticity, small imperfections, and liveliness as an antidote to a digital, artificial world.
The 9:12 Boiled Egg That Took Over Douyin
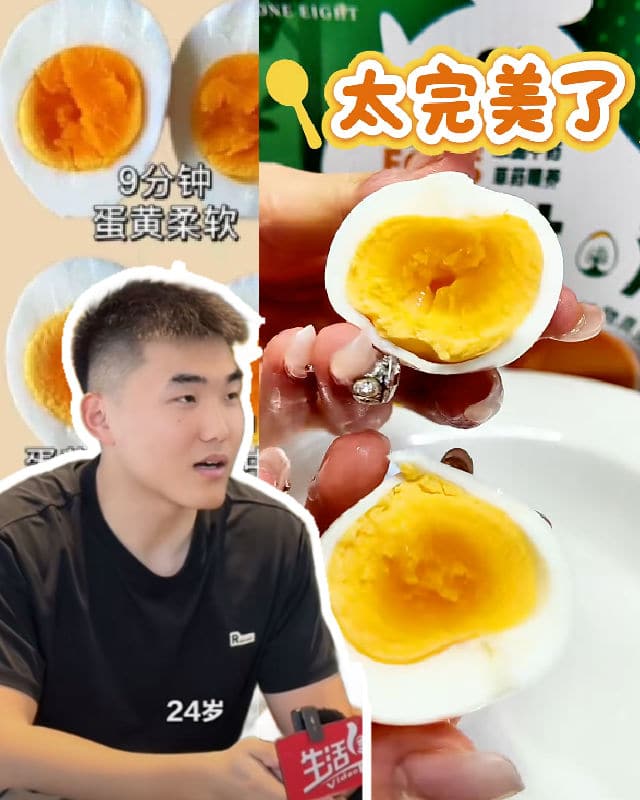

How do you get a perfect boiled egg? A Douyin user known as “Loves Eating Eggs” (爱吃蛋) has become all the rage after leaving a precise comment on how to boil eggs. His advice: First boil the water, then add the eggs, boil for exactly 9 minutes and 12 seconds, remove, and immediately run under cold water.
That simple tip catapulted his follower count from around 200 to over 3.5 million in a single week (I just checked—he’s up to 4.2 million now).
The new viral hit is a 24-year-old self-proclaimed egg expert (of course, his English nickname should be the Eggxpert). He claims to have eaten 40 eggs a day for the past five years and knows exactly how every second of boiling, frying, or stirring affects an egg. He regularly posts videos showing eggs cooked for different lengths of time.
It has earned him the nicknames “Egg God” (蛋神) and “Boiled Egg Immortal” (煮蛋仙人), and has sent boiled eggs (9 minutes and 12 seconds exactly) all over social media feeds.
Thanks for reading this Eye on Digital China China Trend Watch. For slower-moving trends and deeper structural analysis, keep an eye on the upcoming newsletters.
And if you happen to be reading this without a subscription and appreciate my work, consider joining to receive future issues straight in your inbox.
Housekeeping reminder: if you’re receiving duplicate newsletters, it’s likely because you signed up on both the main What’s on Weibo website and the Eye on Digital China Substack. If you’re a paying member on one of the two, you may receive the premium newsletter twice. Please keep the one you’re paying for, and feel free to unsubscribe from the other.
Many thanks to Miranda Barnes for helping curate some of the topics in this edition.
— Manya
Spotted an error or want to add something? Comment below or
email me. First-time commenters require manual approval.
©2025 Eye on Digital China / What’s on Weibo. Do not reproduce without permission —
contact info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Celebs
He Qing, China’s “No. 1 Classical Beauty”, Passes Away at 61
He Qing is remembered as a veteran actress, a symbol of classical Chinese beauty and literary culture.
Published
1 month agoon
December 14, 2025
🔥China Trend Watch — Week 50 (2025) This text is part of the Eye on Digital China newsletter which was sent to paid subscribers — subscribe to receive the next issue in your inbox.
China’s “No. 1 Classical Beauty” (古典第一美女), He Qing (何晴), who starred in all four of China’s most beloved and canonical television dramas, passed away on Saturday at the age of 61. On December 14, news of the famous actress’s passing was trending across virtually all Chinese social media apps.
Born in 1964 into an artistic family in Jiangshan, Zhejiang Province, He Qing received traditional Chinese opera (Kunqu) training at the Zhejiang Kunqu Opera Troupe. Her debut in the entertainment industry may have come by chance, as she reportedly once met Chinese director Yang Jie (杨洁) on a train, which led to her joining the production of Journey to the West (西游记), where she played Lingji Bodhisattva (灵吉菩萨).
In China, He Qing is remembered as a veteran actress in much the same way that some famous Hong Kong actresses became renowned for their beauty, iconic roles, and for essentially becoming household names. More than just glitter and glamour, He Qing was especially a symbol of classical Chinese beauty and literary culture. She was the only actress to star in screen adaptations of all four of China’s “Four Great Classical Novels” (演遍四大名著): besides Journey to the West (西游记, 1986), she also appeared in Dream of the Red Chamber (红楼梦, 1987), Romance of the Three Kingdoms (三国演义, 1994), and Water Margin (水浒传, 1998).
She was married to fellow actor Xu Yajun (许亚军), with whom she had a son, Xu He (许何). Although the two later divorced, she remained close to her ex-husband and even befriended his new (and fourth) wife, Zhang Shu (张澍).
In 2015, He Qing was diagnosed with a brain tumor. After her diagnosis, she withdrew from the entertainment industry to focus on her recovery and lived a low-key life in her later years.
Her passing has prompted an outpouring of tributes from Chinese netizens and colleagues in the entertainment industry. Mourning her loss comes with a sense of nostalgia for the past, and many have praised He Qing for her timeless beauty and authenticity, which will be remembered long after her passing.
Read the entire newsletter here.
Spotted an error or want to add something? Comment below or email me. First-time commenters require manual approval.
©2025 Eye on Digital China / What’s on Weibo. Do not reproduce without permission — contact info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe
Eye on Digital China is a reader-supported publication by
Manya Koetse (@manyapan) and powered by What’s on Weibo.
It offers independent analysis of China’s online culture, media, and social trends.
To receive the newsletter and support this work, consider
becoming a paid subscriber.

Get in touch
Have a tip, story lead, or book recommendation? Interested in contributing? For ideas, suggestions, or just a quick hello, reach out here.

China Trend Watch: From a Hospital in Crisis to Chaotic Pig Feasts

The “Are You Dead Yet?” Phenomenon: How a Dark Satire Became China’s #1 Paid App

Trump, Taiwan & The Three-Body Problem: How Chinese Social Media Frames the US Strike on Venezuela

China’s 2025 Year in Review in 12 Phrases

China’s 10 Biggest Social Media Stories of 2025

China Trend Watch: Japan Tensions, Nexperia Fallout, Yunnan’s ‘Wild Child,’ & “Modern Opium”

Eye on Digital China: How Chinese Social Media Evolved from the Blog Era to the AI-driven Age

Signals: Hasan Piker’s China Trip & the Unexpected Journey of a Chinese School Uniform to Angola

Trump and Takaichi: The Unexpected Love Affair

China Trend Watch: Hong Kong Fire Updates, Nantong’s Viral Moment & Japanese Concert Cancellations
Popular Reads
-

 China Arts & Entertainment6 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment6 months agoHidden Cameras and Taboo Topics: The Many Layers of the “Nanjing Sister Hong” Scandal
-

 China Insight9 months ago
China Insight9 months agoUnderstanding the Dr. Xiao Medical Scandal
-

 China Insight6 months ago
China Insight6 months ago“Jiangyou Bullying Incident”: From Online Outrage to Offline Protest
-

 China Insight9 months ago
China Insight9 months agoChina Is Not Censoring Its Social Media to Please the West



