China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Show-Inspired Journeys: Chinese Netizens Explore Next Travel Destination Through Favorite TV Series
The rising influence of Chinese TV dramas on tourism highlights the synergy between entertainment & social media in China, serving as a powerful tool for travel promotion.
Published
2 years agoon
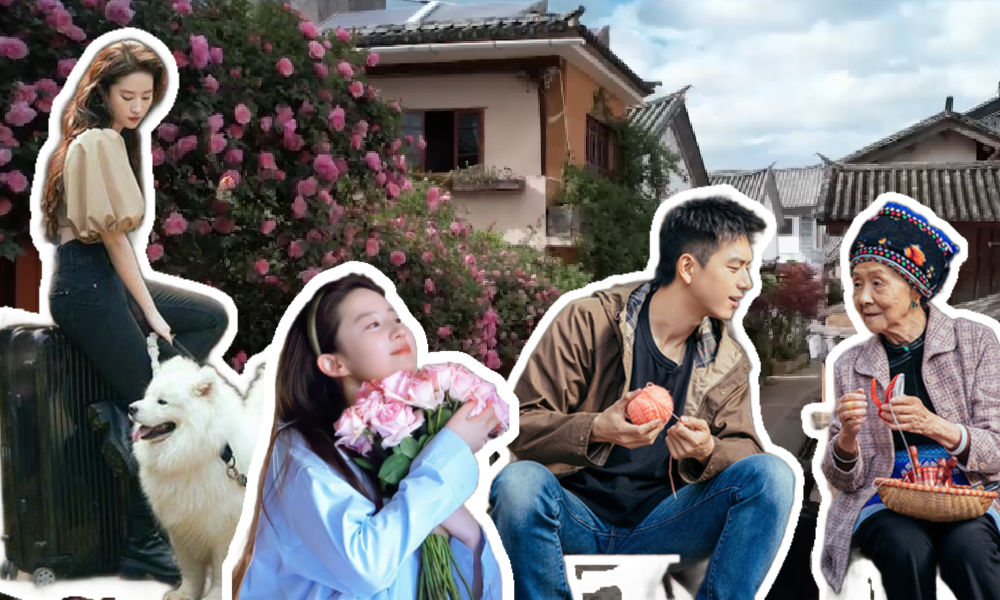

The Chinese TV series Meet Yourself has significantly boosted the popularity of Dali in Yunnan. The series’ success, coupled with the official funding behind it, not only underscores the impactful role of Chinese dramas in tourism but also illustrates how Chinese travel destination promotional strategies are being reshaped in a competitive post-Covid era.
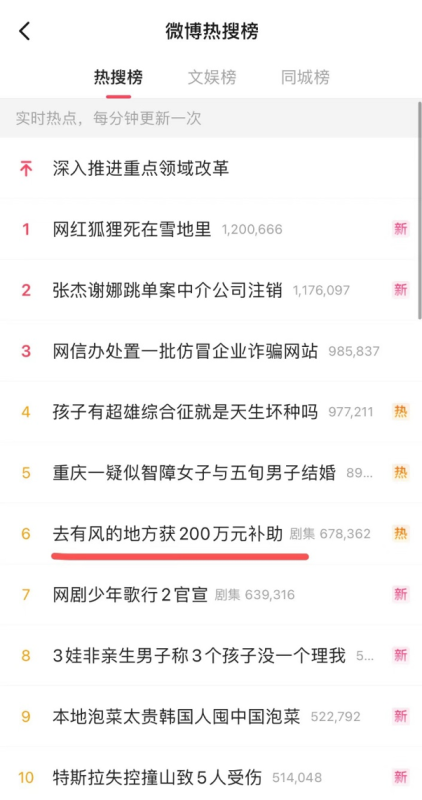
On December 25th, the Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture’s Culture and Tourism Bureau in Yunnan Province, Southwest China, announced a proposed subsidy of 2 million yuan ($282k) for the Chinese TV series Meet Yourself (去有风的地方).
The news soon went trending on Weibo (#去有风的地方获200万元补助#). Many found it noteworthy, especially since the announcement clarified that this funding is part of the prefecture’s special fund for cultural and tourism industry development, and the TV series was the only project under consideration.
There are several reasons why Dali might consider this strategy.
Firstly, Dali plays a pivotal role in Meet Yourself. Launched in January 2023, the TV series quickly became an online sensation, achieving an impressive rating of 8.7 out of 10 on Douban—a platform in China similar to IMDb. Spanning 40 episodes, the series features actress Liu Yifei (刘亦菲), renowned for her role in Disney’s live-action Mulan, and Chinese actor Li Xian (李现).
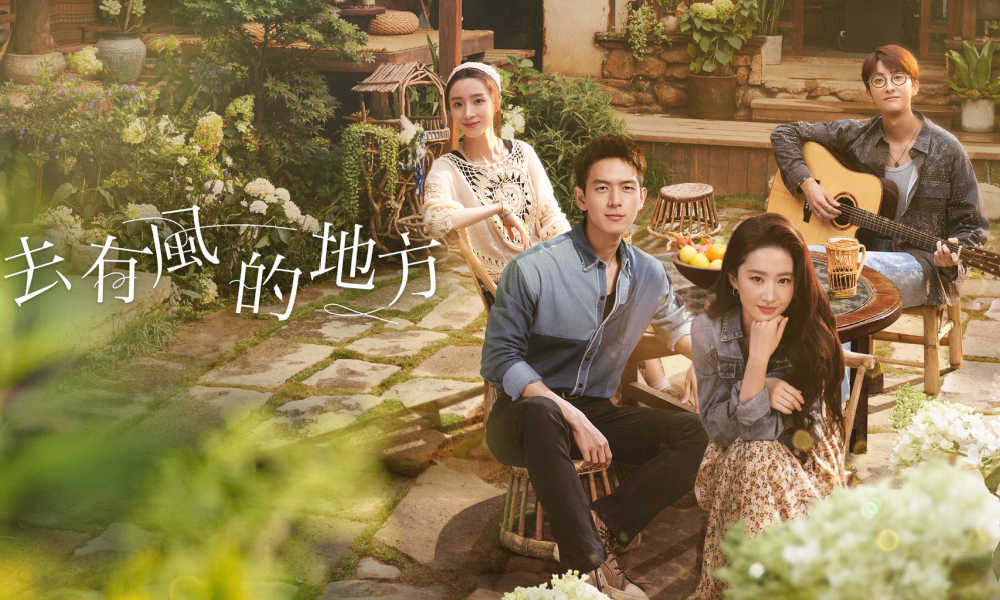

Promotional image for Meet Yourself (去有风的地方).
The narrative follows a white-collar worker in her mid-30s who, following her best friend’s unexpected cancer diagnosis and subsequent passing, embarks on a quest to understand the true meaning and purpose of life.
The TV series not only captivated audiences because of its soothing narrative about life and interpersonal relationships, but the show was also a hit because most of its scenes were filmed in Dali and showed picturesque rural landscapes and portrayed a slow-paced, idyllic lifestyle.
The show accumulated more than 3 billion views on the streaming platform Mango TV by the time its final episode aired on February 2, 2023. It also sparked numerous trending topics on Weibo during that time. For instance, one snapshot from the drama, “Liu Yifei Holding Flowers” (刘亦菲捧花), also went viral, with many netizens even changing their profile pictures to this image. Captivated by Liu’s beauty and charm, they believed that the image possessed some sort of magical power, like the symbolic significance of koi fish in Chinese culture and how they’re believed to bring good luck.
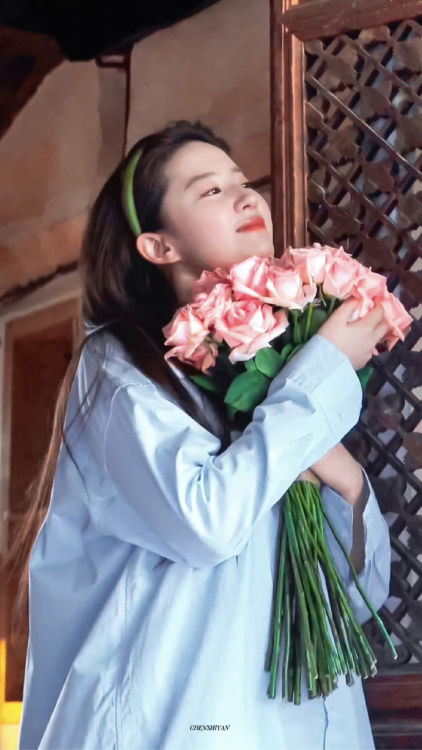

The ‘lucky’ Liu Yifei holding flowers image.

The lucky Liu Yifei holding flowers meme spread across social media in various ways.
Benefiting directly from the popularity generated by the TV series, Yunnan experienced a surge in visitors during the 2023 Spring Festival holiday. This influx significantly boosted its tourism revenue to an impressive 38.4 billion yuan (approximately US$5.4 billion), surpassing all other provinces and regions in the country.
The primary filming location of the drama, the Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture, welcomed over 4.2 million visitors, marking a significant year-on-year increase. Within the first six days of the holiday, Dali boasted the highest room occupancy rate nationwide, and became the fifth most visited tourist destination across the country.
TV Series Inspiring Real-Life Travel to Featured Destination
Dali is not the only city or travel destination that has become popular because of Chinese dramas or TV shows. The recent Chinese TV series There Will Be Ample Time (故乡,别来无恙), in which Chengdu plays a major role, has also come to be seen as a promotion for the Sichuan Province capital city.
The series revolves around four women who grew up together, chose different paths in life, and then reconnect in Chengdu. The series showcases the city’s laid-back lifestyle, especially in contrast to the fast-paced metropolises like Beijing and Shanghai where the featured women return from.
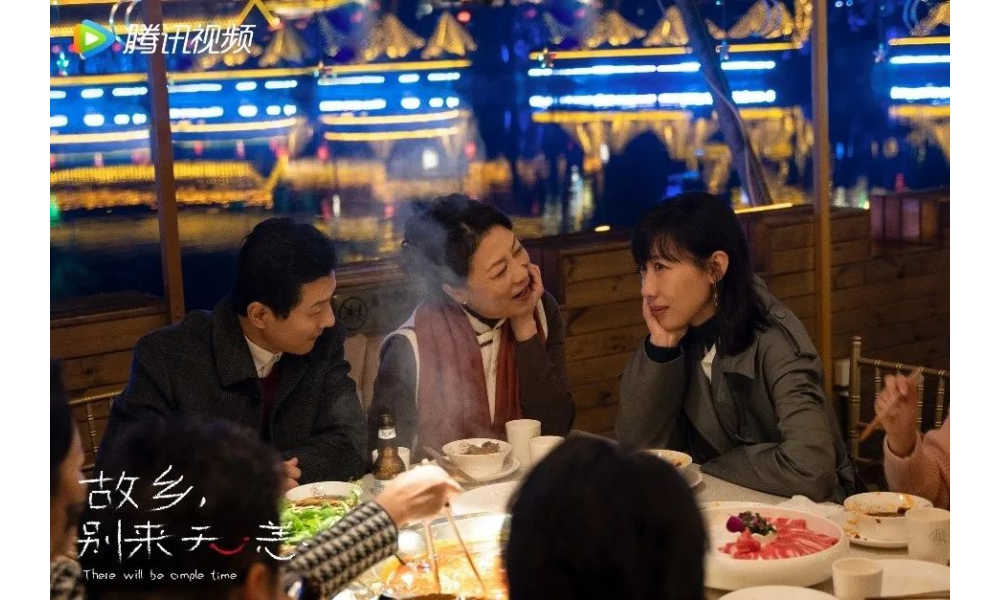

Scene from There Will be Ample Time (故乡,别来无恙).
Back in 2003, the TV series Lost Time (似水年华), which was filmed in the historic scenic town of Wuzhen, also became popular. Lost Time was written, directed, and starred by the renowned Chinese actor and director Huang Lei (黄磊). The series narrates a poignant love story of a couple in their thirties who meet in Wuzhen, only to be separated by the vast distance between Wuzhen and Taipei.
The TV series successfully showcased the timeless beauty of the Wuzhen water town to a broader Chinese audience and, indirectly, promoted the town’s unique artistic and cultural atmosphere. This later led to the establishment of the Wuzhen Theatre Festival, a celebration of performing arts and a center for cultural exchange. The festival has since become one of the premier events in China and Asia. Each year, as the festival unfolds, there is a significant increase in business, with tourists flocking to the area.
On social media today, Lost Time is still seen as one of the major reasons why Wuzhen became so popular among Chinese travelers.

Wuzhen featured in Lost Time (似水年华).
But it’s not only the television series that portray a slower-paced and romantic lifestyle that motivate viewers to visit the showcased destinations. In 2020, the filming locations of the popular Chinese crime and suspense drama The Bad Kids (隐秘的角落) not only entertained its audience but also boosted tourism in the actual places where it was shot.
Much of the filming for the TV thriller took place in Chikan, an old township located in Zhanjiang in Guangdong. As a result, Zhanjiang’s popularity as a tourist destination skyrocketed by 261 percent in a single week.
Earlier in 2023, Jiangmen in Guangdong Province also gained popularity after it was featured in the popular crime TV drama The Knockout (狂飙). As a result, it became a sought-after destination during the May Day holiday, drawing numerous TV enthusiasts to the city. Jiangmen reportedly received over 765,200 visitors in the first two days of the May Day holiday alone, generating a revenue of approximately 439 million yuan (US$62.2 million).
Jiangmen’s popularity went beyond the May Day holiday. The Knockout caused a steady influx of visitors to the Guangdong city. From January to October of 2023, the city saw a total of 20,278,200 tourists, a reported year-on-year increase of 85.36%. This resulted in a tourism revenue of 19.649 billion yuan, representing an impressive increase of 133.77%.
Beyond the TV Screen: Social Media Creating Travel Hits
Over the past few years, we’ve seen how there are always unpredictable factors that help Chinese destinations suddenly become a hit among travelers. For instance, in late 2021, a song titled “Mohe Ballroom” (漠河舞厅) gained popularity across various social media platforms in China. This song narrates the story of a man who, for thirty years, danced alone in the Mohe Ballroom following the death of his beloved wife.
Prior to the song’s release, many Chinese netizens were familiar with Mohe as it is the northernmost point of China, and it is extremely cold. As the song gained traction on social media, the local government seized the opportunity to promote the city’s ice and snow tourism. Now, Mohe has emerged as a new destination for tourists seeking a unique, chilly experience.
Another example is Zibo, an ancient industrial city, which treated students well during their Covid quarantine period. So, when China lifted all Covid restrictions in the spring of 2023, these students returned to express their gratitude and celebrate the city. Their contagious enthusiasm, coupled with their social media posts about the city, sparked nationwide interest and people soon flocked to Zibo to enjoy the vibe and the local BBQ (read more here).
During the summer of 2023, the city of Tianjin became online hit due to a group of energetic seniors who transformed a local bridge into a stage for their remarkable water acrobatics. Tianjin’s so-called “diving grandpas” attracted attention for their daring dives into the river from the Stone Lion Forest Bridge (狮子林桥). Videos of their dives quickly went viral on China’s social media, drawing tourists, including many foreign residents in China, to witness the spectacle firsthand. Some people even joined to dive, including He Chong (何冲), the 2008 Olympic Champion in the 3m springboard.
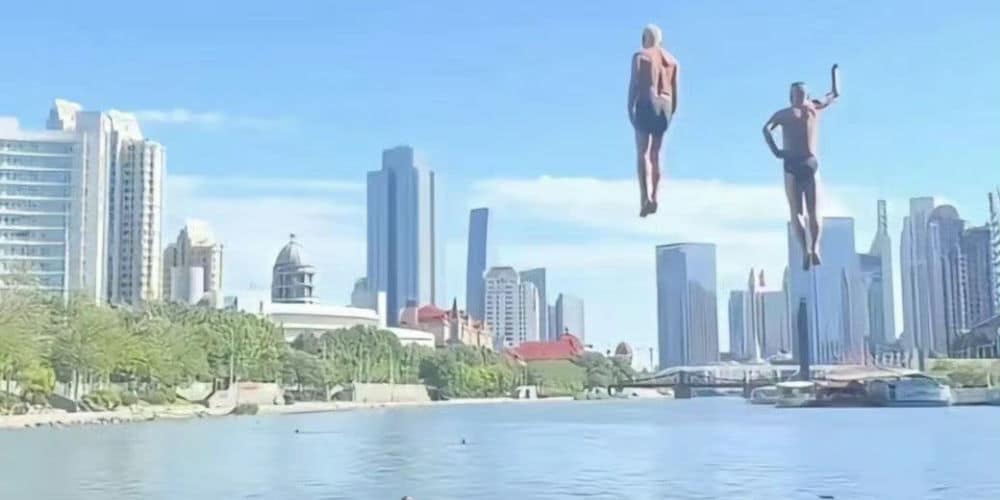

Tianjin’s diving grandpas had to stop their diving activities after rising to internet fame, causing too many people to dive into the river.
In a playful twist, some visitors created their own scorecards, acting as judges and rating the divers’ performances. However, this spontaneous event eventually had to be toned down due to safety concerns. Despite this, the event kept Tianjin in the spotlight for quite a while as a tourist destination.
Social media has become a vital tool for cities and tourist destinations aiming to attract potential visitors. While some destinations organically become online sensations due to a combination of factors, other efforts are more deliberate and strategic. For instance, in spring of 2023, Chinese local government officials went all out to promote their hometowns via online channels, going viral on Weibo, Douyin, and beyond for dressing up in traditional outfits and creating original videos about their hometowns with low to zero budget.
However, when an article by Xinhua News criticized this approach, suggesting that local officials should prioritize improving service quality in their hometowns rather than striving for internet fame, the online trend appeared to wane.
Over the last year, different regions and industries in China made significant efforts to boost their local economies through tourism to recover from the impact of the pandemic. The China Tourism Academy recently published a report that forecasts that the number of China’s domestic tourists in 2023 has hit 5.407 billion, and domestic tourism revenue will amount to 5.2 trillion yuan. This figure allegedly represents a recovery to 90% compared to pre-Covid year 2019.
The upcoming Chinese New Year’s holiday is expected to kick off a promising start for the Chinese tourism industry in 2024. According to Trip.com data, bookings for the 2024 New Year’s holiday have surged by over threefold compared to the corresponding period last year. Furthermore, Tongcheng Travel highlights skiing, hot springs, Northern Lights viewing, music events, outdoor activities, island retreats, cruises, staycations, and firework displays as the top domestic travel preferences during this holiday season.
As China has significantly relaxed several travel and visa policies for both Chinese and international travelers, the number of outbound travel bookings for the New Year’s holiday on Trip.com has also seen a nearly fivefold increase compared to the same period last year while inbound tourism is on the rise.
Meanwhile, the way in which the TV drama Meet Yourself (去有风的地方) has boosted the tourism industry of Dali, which already was a popular tourist destination, is generating ongoing discussions on Chinese social media as it is a good example of how the integration of destination themes can captivate viewers’ attention, inspiring them to visit and discover the real-life locations.
In this way, TV shows serve as powerful platforms for local tourism authorities across China. First, utilizing television series provides them with a higher level of control compared to other methods of online promotion, including more fleeting trends. The show’s narratives, vibe, and filming locations can precisely showcase a destination’s unique features, attractions, and local culture.
Second, featuring destinations in TV series effectively accomplishes two goals at once, as Chinese TV dramas and online communities have become strongly intertwined. This amplifies the influence and reach of such productions, as fans engage, share, discuss, and promote the series and associated destinations across various social media platforms. And so, a featured scene or image, such as the one with Liu Yifei, can transcend the series itself and become an entire trend of its own on Chinese social media channels.
For travelers, visiting a destination featured in a beloved TV drama is not just about exploring a new location—it’s about experiencing a feeling and and immersing oneself in a fantasy. This trend won’t end with Meet Yourself, as new dramas inspire viewers to visit new locations again. As fans are binge watching the TV series Love Me, Love My Voice (很想很想你), Guangxi’s Guilin is the next hotspot attracting attention online for its portrayal in the show. “I finished watching the show,” one viewer wrote, “Now I want to start traveling.”
By Wendy Huang
Follow @whatsonweibo
Edited for clarity by Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. Please note that your comment below will need to be manually approved if you’re a first-time poster here.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
Wendy Huang is a China-based Beijing Language and Culture University graduate who currently works for a Public Relations & Media software company. She believes that, despite the many obstacles, Chinese social media sites such as Weibo can help Chinese internet users to become more informed and open-minded regarding various social issues in present-day China.

China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Signals: Hasan Piker’s China Trip & the Unexpected Journey of a Chinese School Uniform to Angola
Hasan Piker’s controversial China tour, a Chinese school uniform resurfaces in Africa, a new winter hotspot, why Chinese elites ‘run’ to Tokyo, and more.
Published
2 months agoon
November 21, 2025
🌊 Signals — Week 47 (2025)
Part of Eye on Digital China, Signals highlights slower trends and online currents behind the daily scroll. This edition was sent to paid subscribers — subscribe to receive the next issue in your inbox.
Welcome to another edition of Eye on Digital China. Different from the China Trend Watch (check the latest one here if you missed it), this edition, part of the new Signals series, is about the slower side of China’s social media: the recurring themes and underlying shifts that signal broader trends beyond the quick daily headlines. Together with the deeper dives, the three combined aim to give you clear updates and a fuller overview of what’s happening in China’s online conversations & digital spaces.
For the coming two weeks, I’ll be traveling from Beijing to Chongqing and beyond (more on that soon) so please bear with me if my posting frequency dips a little. I’ll be sure to pick it up again soon and will do my best to keep you updated along the way. In the meantime, if you know of a must-try hotpot in Chongqing, please do let me know.
In this newsletter: Hasan Piker’s controversial China tour, a Chinese school uniform in Angola, a new winter hotspot, discussions on what happens to your Wechat after you die, why Chinese elites rùn to Tokyo, and more. Let’s dive in.
- 💰 The richest woman in China, according to the latest list by Hurun Research Institute, is the “queen of pharmaceuticals” Zhong Huijuan (钟慧娟) who has accumulated 141 billion yuan (over 19 billion USD). Women account for over 22% of Chinese billionaires (those with more than 5 billion RMB), underscoring China’s globally leading position in producing wealthy female entrepreneurs.
- 🧩 What happens to your WeChat after you die? A user who registered for NetEase Music with a newly reassigned phone number unexpectedly gained access to the late singer Coco Lee’s (李玟) account, as the number had originally belonged to her. The incident has reignited debate over how digital accounts should be handled after death, prompting platforms like NetEase and Tencent to reconsider policies on long-inactive accounts and take stronger measures to protect them.
- 📱 Although millions of viewers swoon over micro-dramas with fantasy storylines where rich, powerful men win over the “girl next door” through money and status, Chinese regulators are now stepping in to curb exaggerated plots featuring the so-called “dominant CEO” (霸道总裁) archetype, signaling stricter oversight for the booming short drama market.
- ☕ A popular Beijing coffee chain calling itself “People’s Cafe” (人民咖啡馆), with its style and logo evoking nationalist visual nostalgia, has changed its name after facing criticism for building its brand – including pricey coffee and merchandise – on Mao era and state-media political connotations. The cafe is now ‘Yachao People’s Cafe’ (要潮人民咖啡馆).
- 👀 Parents were recently shocked to see erotic ads appear on the Chinese nursery rhymes and children’s learning app BabyBus (宝宝巴士), which is meant for kids ages 0–8. BabyBus has since apologized, but the incident has sparked discussions about how to keep children safe from such content.
- 🧧The 2026 holiday schedule has continued to be a big topic of conversation as it includes a 9-day long Spring Festival break (from February 15 to February 23), making it the longest Lunar New Year holiday on record. The move not only gives people more time for family reunions, but also gives a huge boost to the domestic travel industry.
Hasan Piker’s Chinese Tour & The US–China Content Honeymoon
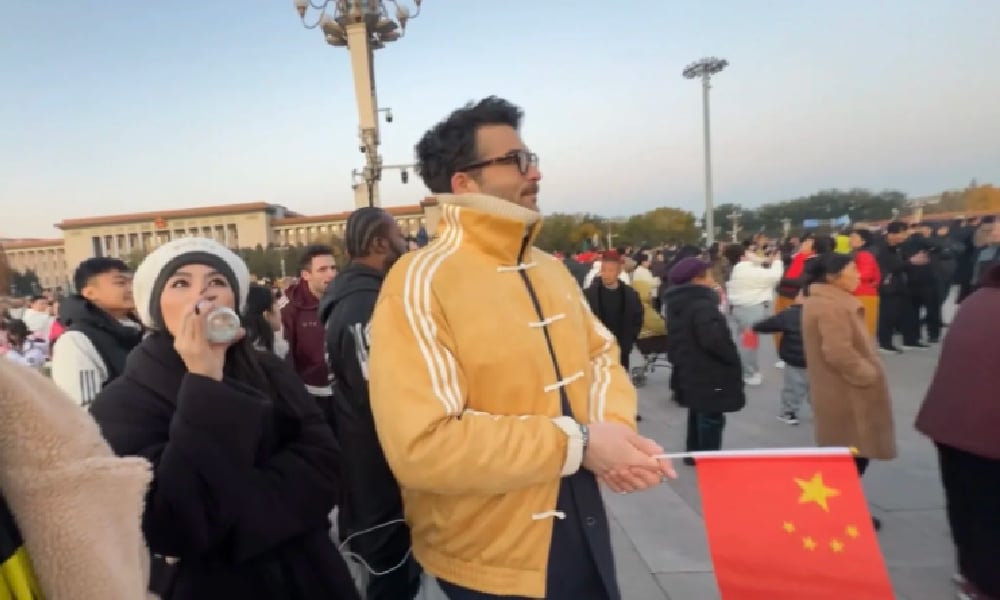

Livestreamer Hasan Piker during his visit to Tiananmen Square flag-rising ceremony.
It’s not time for the end-of-year overviews just yet – but I’ll already say that 2025 was the US–China ‘honeymoon’ year for content creation. It’s when China became “cool,” appealing, and eye-grabbing for young Western social media users, particularly Americans. The recent China trip of the prominent American online streamer Hasan Piker fits into that context.
This left-wing political commentator also known as ‘HasanAbi’ (3 million followers on Twitch, recently profiled by the New York Times) arrived in China for a two-week trip on November 11.

Piker screenshot from the interview with CGTN, published on CGTN.
His visit has been controversial on English-language social media, especially because Piker, known for his criticism of America (which he calls imperialist), has been overly praising China: calling himself “full Chinese,” waving the Chinese flag, joining state media outlet CGTN for an interview on China and the US, and gloating over a first-edition copy of Quotations from Chairman Mao (the Little Red Book). He portrays China as heavily misrepresented in the West and as a country the United States should learn from.
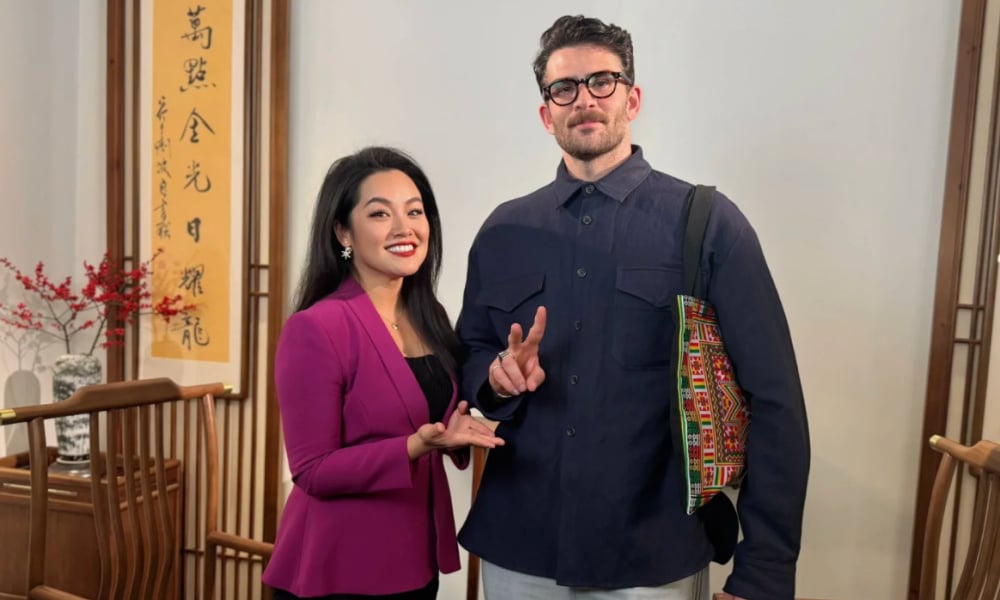

Hasan Piker did an interview with CGTN, posing with Li Jingjing 李菁菁.
During his livestreaming tour, Hasan, who is nicknamed “lemonbro” (柠檬哥) by Chinese netizens, also joined Chinese platforms Bilibili and Xiaohongshu.
But despite all the talk about Piker in the American online media sphere, online conversations, clicks, and views within China are underwhelming. As of now, he has around 24,000 followers on Bilibili, and he’s barely a topic of conversation on mainstream feeds.
Piker’s visit stands in stark contrast to that of American YouTuber IShowSpeed (Darren Watkins), who toured China in March. With lengthy livestreams from Beijing to Chongqing, his popularity exploded in China, where he came to be seen by many as a representative of cultural diplomacy.
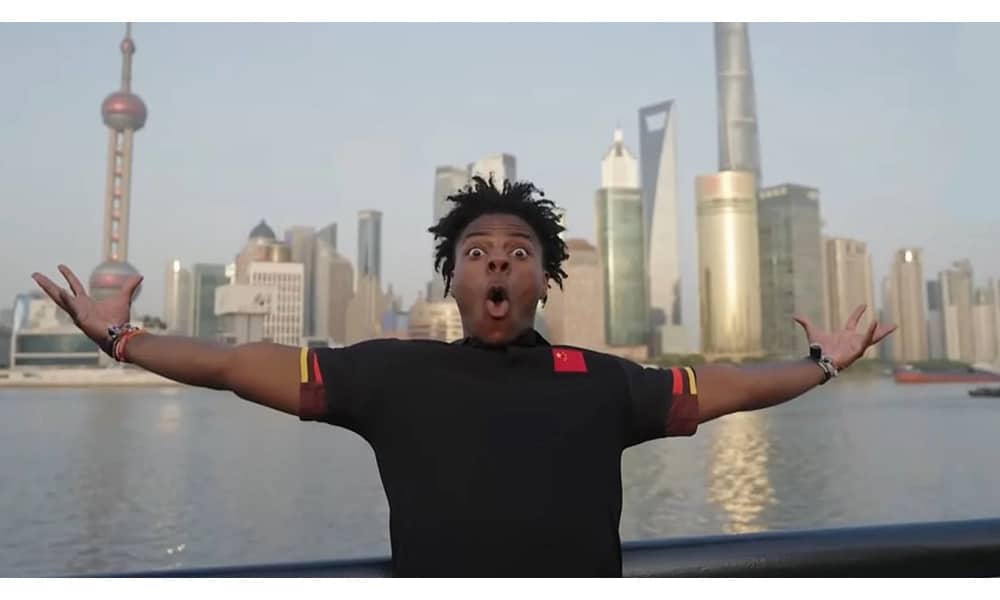

IShowspeed in China, March 2025.
IShowSpeed’s success followed another peak moment in online US–China cultural exchange. In January 2025, waves of foreign TikTok users and popular creators migrated to the Chinese lifestyle app Xiaohongshu amid the looming TikTok ban.
Initially, the mass migration of American users to Xiaohongshu was a symbolic protest against Trump and US policies. In a playful act of political defiance, they downloaded Xiaohongshu to show they weren’t scared of government warnings about Chinese data collection. (For clarity: while TikTok is a made-in-China app, it is not accessible inside mainland China, where Douyin is the domestic version run by the same parent company).
The influx of foreigners — who were quickly nicknamed “TikTok refugees” — soon turned into a moment of cultural celebration. As American creators introduced themselves, Chinese users welcomed them warmly, eager to practice English and teach newcomers how to navigate the app. Discussions about language, culture, and societal differences flourished. Before long, “TikTok refugees” and “Xiaohongshu natives” were collaborating on homework assignments, swapping recipes, and bonding through humor. It was a rare moment of social media doing what we hope it can do: connect people, build bridges, and replace prejudice with curiosity.
Some of that same enthusiasm was also visible during IShowSpeed’s China tour. Despite the tour inevitably getting entangled with political and commercial interests, much of it was simply about an American boy swept up in the high energy of China’s vibrant cities and everything they offer.
Different from IShowSpeed, who is known for his meme-worthy online presence, Piker is primarily known for his radical political views. His China enthusiasm feels driven less by cultural curiosity and more by his critique of America.
Because of his stances — such as describing the US as a police state — it’s easy for Western critics to accuse him of hypocrisy in praising China, especially after a brief run-in with security police while livestreaming at Tiananmen Square.
Seen in broader context, Piker’s China trip reflects a shift in how China is used in American online discourse.
Before, it was Chinese ‘public intellectuals’ (公知) who praised the US as a ‘lighthouse country’ (灯塔国), a beacon of democracy, to indirectly critique China and promote a Western modernization model. Later, Chinese online influencers showcased their lives abroad to emphasize how much ‘brighter the moon’ was outside China.
In the post-Covid years, the current reversed: Western content creators, from TikTok influencers to political commentators, increasingly use China to make arguments that are fundamentally about America.
Between these cycles, authentic cultural curiosity gets pushed to the sidelines. The TikTok-refugee moment in early January may have been the closest we’ve come in years: a brief window where Chinese and American users met each other with curiosity, camaraderie, and creativity.
Hasan’s tour, in contrast, reflects a newer phase, one where China is increasingly used as a stage for Western political identity rather than a complex and diverse country to understand on its own terms. I think the honeymoon phase is over.
“Liu Sihan, Your School Uniform Ended Up in Angola”: China’s Second-Hand Clothing in Africa
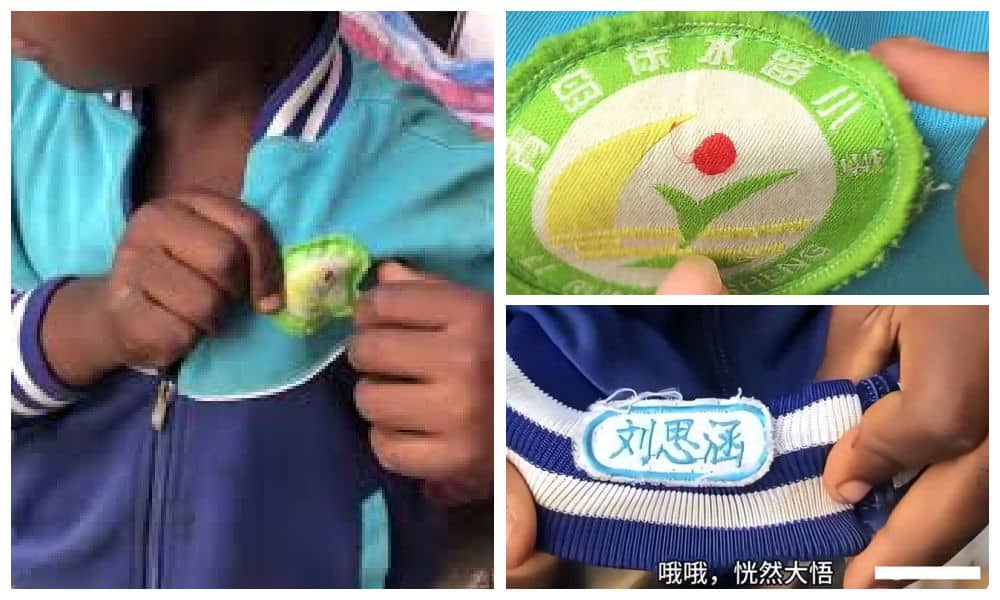

A Chinese school uniform went viral after a Chinese social media user spotted it in Angola.
“Liu Sihan, your schooluniform is hot in Africa” (刘思涵你的校服在非洲火了) is a sentence that unexpectedly trended after a Chinese blogger named Xiao Le (小乐) shared a video of a schoolkid in Angola wearing a Chinese second-hand uniform from Qingdao Xushuilu Primary School, that had the nametag Liu Sihan on it.
The topic sparked discussions about what actually happens to clothing after it’s donated, and many people were surprised to learn how widely Chinese discarded clothing circulates in parts of Africa.
Liu Sihan’s mother, whose daughter is now a 9th grader in Qingdao, had previously donated the uniform to a community clothing donation box (社区旧衣回收箱) after Liu outgrew it. She intended it to help someone in need, never imagining it to travel all the way to Africa.
In light of this story, one netizen shared a video showing a local African market selling all kinds of Chinese school items, including backpacks, and people wearing clothing once belonging to workers for Chinese delivery platforms. “In Africa, you can see school uniforms from all parts of China, and even Meituan and Eleme outfits,” one blogger wrote.
When it comes to second-hand clothing trade, we know much more about Europe–Africa and US–Africa flows than about Chinese exports, and it seems there haven’t been many studies on this specific topic yet. Still, alongside China’s rapid economic transformations, the rise of fast fashion, and the fact that China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of textiles, the country now has an enormous abundance of second-hand clothing.
According to a 2023 study by Wu et al. (link), China still has a long way to go in sustainable clothing disposal. Around 40% of Chinese consumers either keep unwanted clothes at home or throw them away.
But there may be a shift underway. Donation options are expanding quickly, from government bins to brand programs, and from second-hand stores to online platforms that offer at-home pickup.

Chinese social media users posting images of school/work uniforms from China worn by Africans.
As awareness grows around the benefits of donating clothing (reducing waste, supporting sustainability, and the emotional satisfaction of giving), donation rates may rise significantly. The story of Liu Sihan’s uniform, which many found amusing, might even encourage more people to donate. And if that happens, scenes of African children (and adults) wearing Chinese-donated clothes may become much more common than they now are.
Laojunshan: New Hotspot in Cold Winter
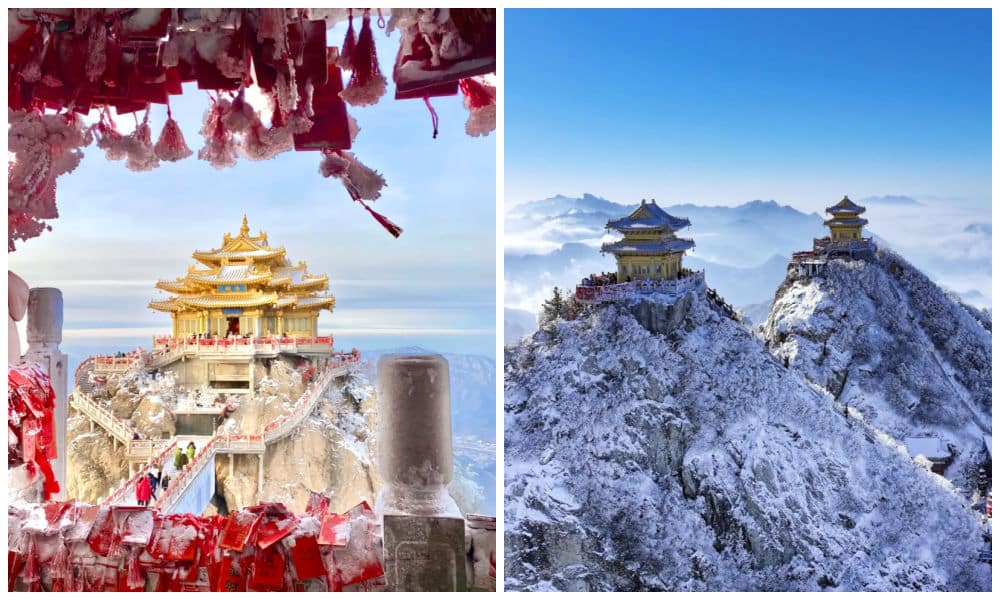

Images from Xiaohongshu, 背包里的星子, 旅行定制师小漾
Go to Zibo for BBQ, go to Tianshui for malatang, go to Harbin for the Ice Festival, cycle to Kaifeng for soup dumplings, or head to Dunhuang to ride a camel — over recent years, a number of Chinese domestic destinations have turned into viral hotspots, boosted by online marketing initiatives and Xiaohongshu influencers.
This year, Laojunshan is among the places climbing the trending lists as a must-visit spot for its spectacular snow-covered landscapes that remind many of classical Chinese paintings. Laojunshan (老君山), a scenic mountain in Henan Province, is attracting more domestic tourists for winter excursions.
Xiaohongshu is filled with travel tips: how to get there from Luoyang station (by bus), and the best times of day to catch the snow in perfect light (7–9 AM or around 6–6:30 PM).
With Laojunshan, we see a familiar pattern: local tourism bureaus, state media, and influencers collectively driving new waves of visitors to the area, bringing crucial revenue to local industries during what would otherwise be slower winter months.
WeChat New Features & Hong Kong Police on Douyin
🟦 WeChat has been gradually rolling out a new feature that allows users to recall a batch of messages all at once, which saves you the frantic effort of deleting each message individually after realizing you sent them to the wrong group (or just regret a late-night rant). Many users are welcoming the update, along with another feature that lets you delete a contact without wiping the entire chat history. This is useful for anyone who wants to preserve evidence of what happened before cutting ties.

🟦The Hong Kong Police Force recently celebrated its two-year anniversary on Douyin (the Chinese version of TikTok), having accumulated nearly 5 million followers during that time. To mark the occasion, they invited actor Simon Yam to record a commemorative video for their channel (@香港警察). The presence of the Hong Kong Police on the Chinese app — and the approachable, meme-friendly way they’ve chosen to engage with younger mainland audiences — is yet another signal of Hong Kong institutions’ strategic alignment with mainland China’s digital infrastructure, a shift that has been gradually taking place. The anniversary video proved popular on Douyin, attracting thousands of likes and comments.
Why Chinese Elite Rùn to Japan (by ChinaTalk)

Over the past week, Japan has been trending every single day on Chinese social media in light of escalating bilateral tensions after Japanese PM Takaichi made remarks about Taiwan that China views as a direct military threat. The diplomatic freeze is triggering all kinds of trends, from rising anti-Japanese sentiment online and a ban on Japanese seafood imports to Chinese authorities warning citizens not to travel to Japan.
You’d think Chinese people would want to be anywhere but Japan right now — but the reality is far more nuanced.
In a recent feature in ChinaTalk, Jordan Schneider interviewed Japanese journalist & researcher Takehiro Masutomo (舛友雄大) who has just published a book about Japan’s new Chinese diaspora, explaining what draws Chinese dissidents, intellectuals, billionaires, and middle-class families to Tokyo.
The book is titled Run Ri: 潤日 Following the Footsteps of Elite Chinese Escaping to Japan (only available in Japanese and Traditional Chinese for now). (The word Rùn 润/潤, by the way, is Chinese online slang and meme expresses the desire to escape the country.)
A very interesting read on how Chinese communities are settling in Japan, a place they see as freer than Hong Kong and safer than the U.S., and one they’re surprisingly optimistic about — even more so than the Japanese themselves.
Thanks for reading this Eye on Digital China Signals. For fast-moving trends and deeper dives, keep an eye on the upcoming newsletters.
And if you just so happen to be reading this without a subscription and appreciate my work, consider joining to receive future issues straight in your inbox.
A small housekeeping note:
This Eye on Digital China newsletter is co-published for subscribers on both Substack and the main site. If you’re registered on both platforms, you’ll receive duplicate emails — so if that bothers you, please pick your preferred platform and unsubscribe from the other.
Many thanks to Miranda Barnes for helping curate some of the topics in this edition.
— Manya
Spotted an error or want to add something? Comment below or email me.
First-time commenters require manual approval.
©2025 Eye on Digital China / What’s on Weibo. Do not reproduce without permission —
contact info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
House of Wahaha: Zong Fuli Resigns
In the year following her father’s death, Zong Fuli dealt with controversy after controversy as the head of Chinese food & beverage giant Wahaha.
Published
3 months agoon
October 14, 2025
It’s a bit like a Succession-style corporate drama 🍿.
Over the past few years, we’ve covered stories surrounding Chinese beverage giant Wahaha (娃哈哈) several times — and with good reason.
Since the passing of its much-beloved founder Zong Qinghou (宗庆后) in March 2024, the company has been caught in waves of internal turmoil.
Some context: Wahaha is regarded as a patriotic brand in China — not only because it’s the country’s equivalent of Coca-Cola or PepsiCo (they even launched their own cola in 1998 called “Future Cola” 非常可乐, with the slogan “The future will be better” 未来会更好), but also because its iconic drinks are tied to the childhood memories of millions.

Future Cola by Wahaha via Wikipedia.
There’s also the famous 2006 story when Zong Qinghou refused a buyout offer from Danone. Although the details of that deal are complex, the rejection was widely seen as Zong’s defense of a Chinese brand against foreign takeover, contributing to his status as a national business hero.
After the death of Zong, his daughter Zong Fuli, also known as Kelly Zong (宗馥莉), took over.
🔹 But Zong Fuli soon faced controversy after controversy, including revelations that Wahaha had outsourced production of some bottled water lines to cheaper contractors (link).
🔹 There was also a high-profile family inheritance dispute involving three illegitimate children of Zong Qinghou, now living in the US, who sued Zong Fuli in Hong Kong courts, claiming they were each entitled to multi-million-dollar trust funds and assets.
🔹 More legal trouble arrived when regulators and other shareholders objected to Zong Fuli using the “Wahaha” mark through subsidiaries and for new products outside officially approved channels (the company has 46% state ownership).
⚡️ The trending news of the moment is that Zong Fuli has officially resigned from all positions at Wahaha Group as chairman, legal representative, and director. She reportedly resigned on September 12, after which she started her own brand named “Wa Xiao Zong” (娃小宗). One related hashtag received over 320 million views on Weibo (#宗馥莉已经辞职#). Wahaha’s board confirmed the move on October 10, appointing Xu Simin (许思敏) as the new General Manager. Zong remains Wahaha’s second-largest shareholder.
🔹 To complicate matters further, Zong’s uncle, Zong Wei (宗伟), has now launched a rival brand — Hu Xiao Wa (沪小娃) — with product lines and distribution networks nearly identical to Wahaha’s.
As explained by Weibo blogger Tusiji (兔撕鸡大老爷), under Zong Qinghou, Wahaha relied on a family-run “feudal” system with various family-controlled factories. Zong Fuli allegedly tried to dismantle this system to centralize power, fracturing the Wahaha brand and angering both relatives and state investors.
Others also claim that Zong had already been engaged in a major “De-Wahaha-ization” (去娃哈哈化) campaign long before her resignation.
In August of this year, Zong gave an exclusive interview to Caijing (财经) magazine where she addressed leadership challenges and public controversies. In the interview, Zong spoke more about her views on running Wahaha, advocating long-term strategic growth over short-term results, and sharing her determination to not let controversy distract her from business operations. That plan seems to have failed.
While Chinese netizens are watching this family brand war unfold, many are rooting for Zong after everything she has gone through – they feel her father left her in a complicated mess after his death.
At the same time, others believe she tried to run Wahaha in a modern “Western” way and blame her for that.
For the brand image of Wahaha, the whole ordeal is a huge blow. Many people are now vowing not to buy the brand again.
As for Zong’s new brand, we’ll have to wait for the next episode in this family company drama to see how it unfolds.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe
Eye on Digital China is a reader-supported publication by
Manya Koetse (@manyapan) and powered by What’s on Weibo.
It offers independent analysis of China’s online culture, media, and social trends.
To receive the newsletter and support this work, consider
becoming a paid subscriber.

Get in touch
Have a tip, story lead, or book recommendation? Interested in contributing? For ideas, suggestions, or just a quick hello, reach out here.

The “Are You Dead Yet?” Phenomenon: How a Dark Satire Became China’s #1 Paid App

Trump, Taiwan & The Three-Body Problem: How Chinese Social Media Frames the US Strike on Venezuela

China’s 2025 Year in Review in 12 Phrases

China’s 10 Biggest Social Media Stories of 2025

Why Were 100,000 Pregnant Women’s Blood Samples Smuggled Out of China?

From Nobel Farewell to ‘VIP Toilets’: What’s Trending in China

China Trend Watch: Japan Tensions, Nexperia Fallout, Yunnan’s ‘Wild Child,’ & “Modern Opium”

Eye on Digital China: How Chinese Social Media Evolved from the Blog Era to the AI-driven Age

Signals: Hasan Piker’s China Trip & the Unexpected Journey of a Chinese School Uniform to Angola

Trump and Takaichi: The Unexpected Love Affair
Popular Reads
-

 China Arts & Entertainment6 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment6 months agoHidden Cameras and Taboo Topics: The Many Layers of the “Nanjing Sister Hong” Scandal
-

 China Insight8 months ago
China Insight8 months agoUnderstanding the Dr. Xiao Medical Scandal
-

 China Digital12 months ago
China Digital12 months ago“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained
-

 China Insight5 months ago
China Insight5 months ago“Jiangyou Bullying Incident”: From Online Outrage to Offline Protest




