China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Show-Inspired Journeys: Chinese Netizens Explore Next Travel Destination Through Favorite TV Series
The rising influence of Chinese TV dramas on tourism highlights the synergy between entertainment & social media in China, serving as a powerful tool for travel promotion.
Published
7 months agoon
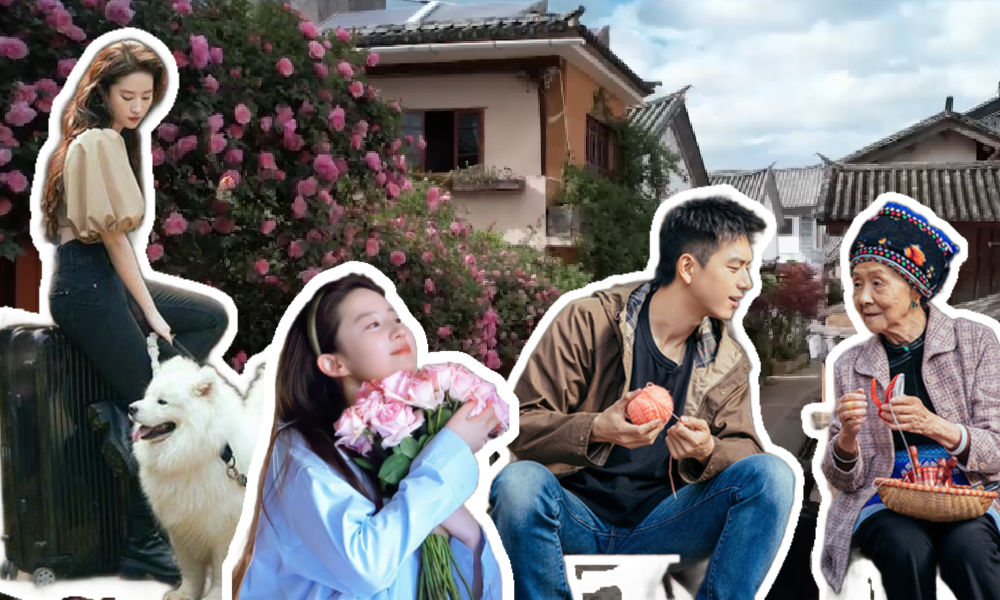

The Chinese TV series Meet Yourself has significantly boosted the popularity of Dali in Yunnan. The series’ success, coupled with the official funding behind it, not only underscores the impactful role of Chinese dramas in tourism but also illustrates how Chinese travel destination promotional strategies are being reshaped in a competitive post-Covid era.
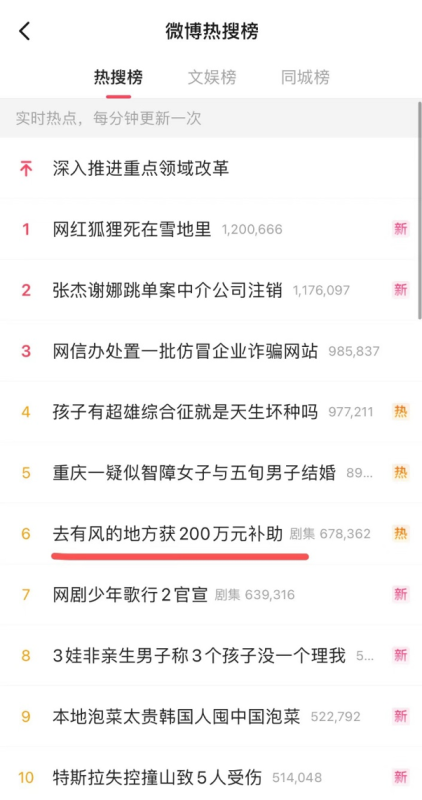
On December 25th, the Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture’s Culture and Tourism Bureau in Yunnan Province, Southwest China, announced a proposed subsidy of 2 million yuan ($282k) for the Chinese TV series Meet Yourself (去有风的地方).
The news soon went trending on Weibo (#去有风的地方获200万元补助#). Many found it noteworthy, especially since the announcement clarified that this funding is part of the prefecture’s special fund for cultural and tourism industry development, and the TV series was the only project under consideration.
There are several reasons why Dali might consider this strategy.
Firstly, Dali plays a pivotal role in Meet Yourself. Launched in January 2023, the TV series quickly became an online sensation, achieving an impressive rating of 8.7 out of 10 on Douban—a platform in China similar to IMDb. Spanning 40 episodes, the series features actress Liu Yifei (刘亦菲), renowned for her role in Disney’s live-action Mulan, and Chinese actor Li Xian (李现).
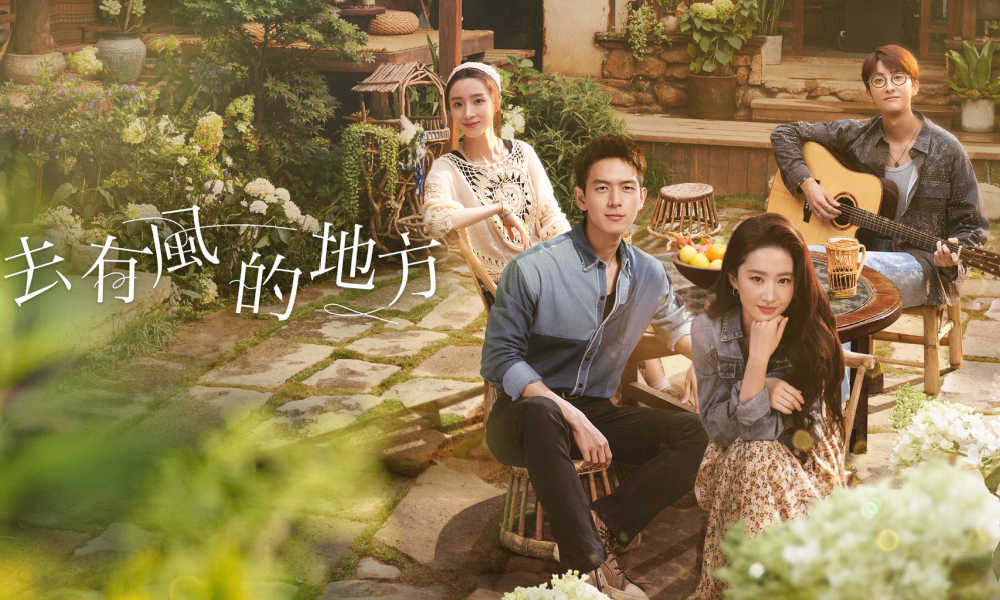

Promotional image for Meet Yourself (去有风的地方).
The narrative follows a white-collar worker in her mid-30s who, following her best friend’s unexpected cancer diagnosis and subsequent passing, embarks on a quest to understand the true meaning and purpose of life.
The TV series not only captivated audiences because of its soothing narrative about life and interpersonal relationships, but the show was also a hit because most of its scenes were filmed in Dali and showed picturesque rural landscapes and portrayed a slow-paced, idyllic lifestyle.
The show accumulated more than 3 billion views on the streaming platform Mango TV by the time its final episode aired on February 2, 2023. It also sparked numerous trending topics on Weibo during that time. For instance, one snapshot from the drama, “Liu Yifei Holding Flowers” (刘亦菲捧花), also went viral, with many netizens even changing their profile pictures to this image. Captivated by Liu’s beauty and charm, they believed that the image possessed some sort of magical power, like the symbolic significance of koi fish in Chinese culture and how they’re believed to bring good luck.
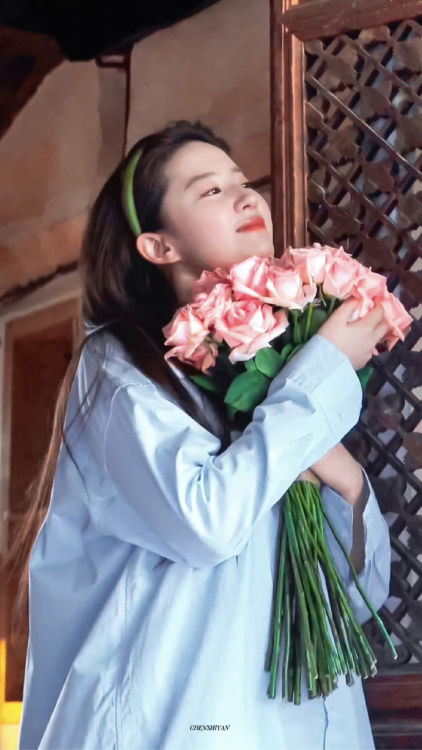

The ‘lucky’ Liu Yifei holding flowers image.
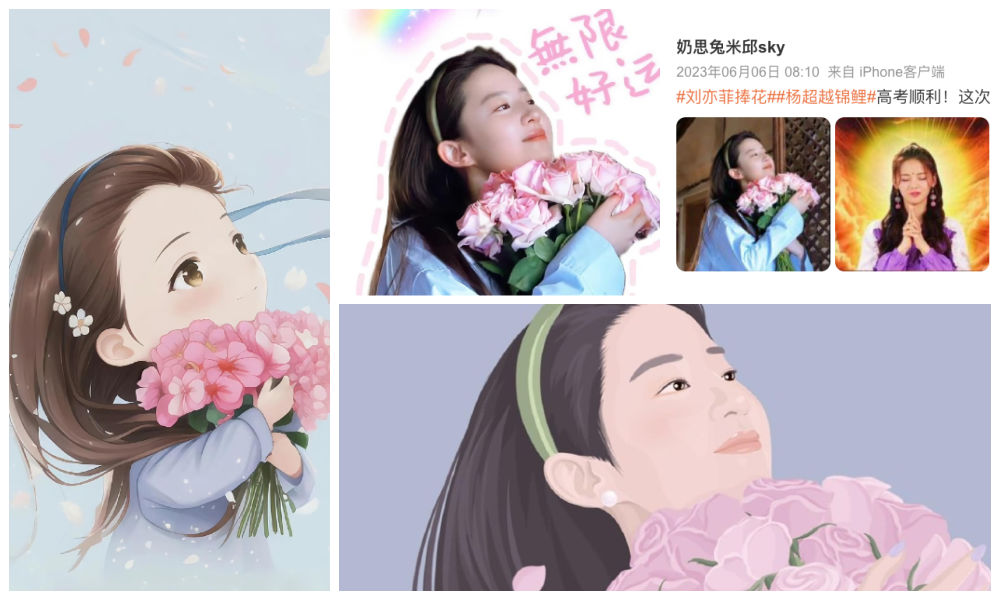

The lucky Liu Yifei holding flowers meme spread across social media in various ways.
Benefiting directly from the popularity generated by the TV series, Yunnan experienced a surge in visitors during the 2023 Spring Festival holiday. This influx significantly boosted its tourism revenue to an impressive 38.4 billion yuan (approximately US$5.4 billion), surpassing all other provinces and regions in the country.
The primary filming location of the drama, the Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture, welcomed over 4.2 million visitors, marking a significant year-on-year increase. Within the first six days of the holiday, Dali boasted the highest room occupancy rate nationwide, and became the fifth most visited tourist destination across the country.
TV Series Inspiring Real-Life Travel to Featured Destination
Dali is not the only city or travel destination that has become popular because of Chinese dramas or TV shows. The recent Chinese TV series There Will Be Ample Time (故乡,别来无恙), in which Chengdu plays a major role, has also come to be seen as a promotion for the Sichuan Province capital city.
The series revolves around four women who grew up together, chose different paths in life, and then reconnect in Chengdu. The series showcases the city’s laid-back lifestyle, especially in contrast to the fast-paced metropolises like Beijing and Shanghai where the featured women return from.

Scene from There Will be Ample Time (故乡,别来无恙).
Back in 2003, the TV series Lost Time (似水年华), which was filmed in the historic scenic town of Wuzhen, also became popular. Lost Time was written, directed, and starred by the renowned Chinese actor and director Huang Lei (黄磊). The series narrates a poignant love story of a couple in their thirties who meet in Wuzhen, only to be separated by the vast distance between Wuzhen and Taipei.
The TV series successfully showcased the timeless beauty of the Wuzhen water town to a broader Chinese audience and, indirectly, promoted the town’s unique artistic and cultural atmosphere. This later led to the establishment of the Wuzhen Theatre Festival, a celebration of performing arts and a center for cultural exchange. The festival has since become one of the premier events in China and Asia. Each year, as the festival unfolds, there is a significant increase in business, with tourists flocking to the area.
On social media today, Lost Time is still seen as one of the major reasons why Wuzhen became so popular among Chinese travelers.

Wuzhen featured in Lost Time (似水年华).
But it’s not only the television series that portray a slower-paced and romantic lifestyle that motivate viewers to visit the showcased destinations. In 2020, the filming locations of the popular Chinese crime and suspense drama The Bad Kids (隐秘的角落) not only entertained its audience but also boosted tourism in the actual places where it was shot.
Much of the filming for the TV thriller took place in Chikan, an old township located in Zhanjiang in Guangdong. As a result, Zhanjiang’s popularity as a tourist destination skyrocketed by 261 percent in a single week.
Earlier in 2023, Jiangmen in Guangdong Province also gained popularity after it was featured in the popular crime TV drama The Knockout (狂飙). As a result, it became a sought-after destination during the May Day holiday, drawing numerous TV enthusiasts to the city. Jiangmen reportedly received over 765,200 visitors in the first two days of the May Day holiday alone, generating a revenue of approximately 439 million yuan (US$62.2 million).
Jiangmen’s popularity went beyond the May Day holiday. The Knockout caused a steady influx of visitors to the Guangdong city. From January to October of 2023, the city saw a total of 20,278,200 tourists, a reported year-on-year increase of 85.36%. This resulted in a tourism revenue of 19.649 billion yuan, representing an impressive increase of 133.77%.
Beyond the TV Screen: Social Media Creating Travel Hits
Over the past few years, we’ve seen how there are always unpredictable factors that help Chinese destinations suddenly become a hit among travelers. For instance, in late 2021, a song titled “Mohe Ballroom” (漠河舞厅) gained popularity across various social media platforms in China. This song narrates the story of a man who, for thirty years, danced alone in the Mohe Ballroom following the death of his beloved wife.
Prior to the song’s release, many Chinese netizens were familiar with Mohe as it is the northernmost point of China, and it is extremely cold. As the song gained traction on social media, the local government seized the opportunity to promote the city’s ice and snow tourism. Now, Mohe has emerged as a new destination for tourists seeking a unique, chilly experience.
Another example is Zibo, an ancient industrial city, which treated students well during their Covid quarantine period. So, when China lifted all Covid restrictions in the spring of 2023, these students returned to express their gratitude and celebrate the city. Their contagious enthusiasm, coupled with their social media posts about the city, sparked nationwide interest and people soon flocked to Zibo to enjoy the vibe and the local BBQ (read more here).
During the summer of 2023, the city of Tianjin became online hit due to a group of energetic seniors who transformed a local bridge into a stage for their remarkable water acrobatics. Tianjin’s so-called “diving grandpas” attracted attention for their daring dives into the river from the Stone Lion Forest Bridge (狮子林桥). Videos of their dives quickly went viral on China’s social media, drawing tourists, including many foreign residents in China, to witness the spectacle firsthand. Some people even joined to dive, including He Chong (何冲), the 2008 Olympic Champion in the 3m springboard.
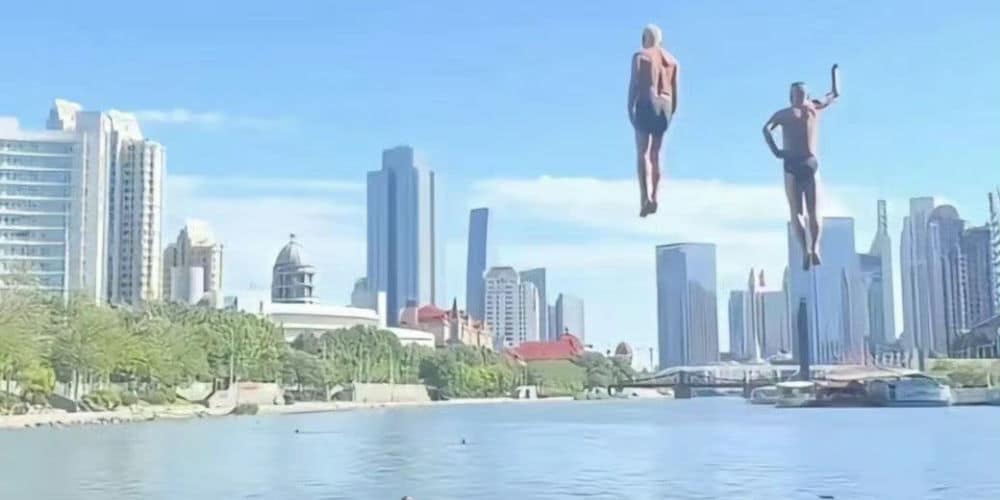

Tianjin’s diving grandpas had to stop their diving activities after rising to internet fame, causing too many people to dive into the river.
In a playful twist, some visitors created their own scorecards, acting as judges and rating the divers’ performances. However, this spontaneous event eventually had to be toned down due to safety concerns. Despite this, the event kept Tianjin in the spotlight for quite a while as a tourist destination.
Social media has become a vital tool for cities and tourist destinations aiming to attract potential visitors. While some destinations organically become online sensations due to a combination of factors, other efforts are more deliberate and strategic. For instance, in spring of 2023, Chinese local government officials went all out to promote their hometowns via online channels, going viral on Weibo, Douyin, and beyond for dressing up in traditional outfits and creating original videos about their hometowns with low to zero budget.
However, when an article by Xinhua News criticized this approach, suggesting that local officials should prioritize improving service quality in their hometowns rather than striving for internet fame, the online trend appeared to wane.
Over the last year, different regions and industries in China made significant efforts to boost their local economies through tourism to recover from the impact of the pandemic. The China Tourism Academy recently published a report that forecasts that the number of China’s domestic tourists in 2023 has hit 5.407 billion, and domestic tourism revenue will amount to 5.2 trillion yuan. This figure allegedly represents a recovery to 90% compared to pre-Covid year 2019.
The upcoming Chinese New Year’s holiday is expected to kick off a promising start for the Chinese tourism industry in 2024. According to Trip.com data, bookings for the 2024 New Year’s holiday have surged by over threefold compared to the corresponding period last year. Furthermore, Tongcheng Travel highlights skiing, hot springs, Northern Lights viewing, music events, outdoor activities, island retreats, cruises, staycations, and firework displays as the top domestic travel preferences during this holiday season.
As China has significantly relaxed several travel and visa policies for both Chinese and international travelers, the number of outbound travel bookings for the New Year’s holiday on Trip.com has also seen a nearly fivefold increase compared to the same period last year while inbound tourism is on the rise.
Meanwhile, the way in which the TV drama Meet Yourself (去有风的地方) has boosted the tourism industry of Dali, which already was a popular tourist destination, is generating ongoing discussions on Chinese social media as it is a good example of how the integration of destination themes can captivate viewers’ attention, inspiring them to visit and discover the real-life locations.
In this way, TV shows serve as powerful platforms for local tourism authorities across China. First, utilizing television series provides them with a higher level of control compared to other methods of online promotion, including more fleeting trends. The show’s narratives, vibe, and filming locations can precisely showcase a destination’s unique features, attractions, and local culture.
Second, featuring destinations in TV series effectively accomplishes two goals at once, as Chinese TV dramas and online communities have become strongly intertwined. This amplifies the influence and reach of such productions, as fans engage, share, discuss, and promote the series and associated destinations across various social media platforms. And so, a featured scene or image, such as the one with Liu Yifei, can transcend the series itself and become an entire trend of its own on Chinese social media channels.
For travelers, visiting a destination featured in a beloved TV drama is not just about exploring a new location—it’s about experiencing a feeling and and immersing oneself in a fantasy. This trend won’t end with Meet Yourself, as new dramas inspire viewers to visit new locations again. As fans are binge watching the TV series Love Me, Love My Voice (很想很想你), Guangxi’s Guilin is the next hotspot attracting attention online for its portrayal in the show. “I finished watching the show,” one viewer wrote, “Now I want to start traveling.”
By Wendy Huang
Follow @whatsonweibo
Edited for clarity by Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. Please note that your comment below will need to be manually approved if you’re a first-time poster here.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
Wendy Huang is a China-based Beijing Language and Culture University graduate who currently works for a Public Relations & Media software company. She believes that, despite the many obstacles, Chinese social media sites such as Weibo can help Chinese internet users to become more informed and open-minded regarding various social issues in present-day China.

Also Read
China Books & Literature
Why Chinese Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Shopping Festival
Bookworms love to get a good deal on books, but when the deals are too good, it can actually harm the publishing industry.
Published
2 months agoon
June 8, 2024By
Ruixin Zhang
JD.com’s 618 shopping festival is driving down book prices to such an extent that it has prompted a boycott by Chinese publishers, who are concerned about the financial sustainability of their industry.
When June begins, promotional campaigns for China’s 618 Online Shopping Festival suddenly appear everywhere—it’s hard to ignore.
The 618 Festival is a product of China’s booming e-commerce culture. Taking place annually on June 18th, it is China’s largest mid-year shopping carnival. While Alibaba’s “Singles’ Day” shopping festival has been taking place on November 11th since 2009, the 618 Festival was launched by another Chinese e-commerce giant, JD.com (京东), to celebrate the company’s anniversary, boost its sales, and increase its brand value.
By now, other e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and Pinduoduo have joined the 618 Festival, and it has turned into another major nationwide shopping spree event.
For many book lovers in China, 618 has become the perfect opportunity to stock up on books. In previous years, e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Dangdang (当当) would roll out tempting offers during the festival, such as “300 RMB ($41) off for every 500 RMB ($69) spent” or “50 RMB ($7) off for every 100 RMB ($13.8) spent.”
Starting in May, about a month before 618, the largest bookworm community group on the Douban platform, nicknamed “Buying Like Landsliding, Reading Like Silk Spinning” (买书如山倒,看书如抽丝), would start buzzing with activity, discussing book sales, comparing shopping lists, or sharing views about different issues.

Social media users share lists of which books to buy during the 618 shopping festivities.
This year, however, the mood within the group was different. Many members posted that before the 618 season began, books from various publishers were suddenly taken down from e-commerce platforms, disappearing from their online shopping carts. This unusual occurrence sparked discussions among book lovers, with speculations arising about a potential conflict between Chinese publishers and e-commerce platforms.
A joint statement posted in May provided clarity. According to Chinese media outlet The Paper (@澎湃新闻), eight publishers in Beijing and the Shanghai Publishing and Distribution Association, which represent 46 publishing units in Shanghai, issued a statement indicating they refuse to participate in this year’s 618 promotional campaign as proposed by JD.com.
The collective industry boycott has a clear motivation: during JD’s 618 promotional campaign, which offers all books at steep discounts (e.g., 60-70% off) for eight days, publishers lose money on each book sold. Meanwhile, JD.com continues to profit by forcing publishers to sell books at significantly reduced prices (e.g., 80% off). For many publishers, it is simply not sustainable to sell books at 20% of the original price.
One person who has openly spoken out against JD.com’s practices is Shen Haobo (沈浩波), founder and CEO of Chinese book publisher Motie Group (磨铁集团). Shen shared a post on WeChat Moments on May 31st, stating that Motie has completely stopped shipping to JD.com as it opposes the company’s low-price promotions. Shen said it felt like JD.com is “repeatedly rubbing our faces into the ground.”
Nevertheless, many netizens expressed confusion over the situation. Under the hashtag topic “Multiple Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Book Promotions” (#多家出版社抵制618图书大促#), people complained about the relatively high cost of physical books.
With a single legitimate copy often costing 50-60 RMB ($7-$8.3), and children’s books often costing much more, many Chinese readers can only afford to buy books during big sales. They question the justification for these rising prices, as books used to be much more affordable.
Book blogger TaoLangGe (@陶朗歌) argues that for ordinary readers in China, the removal of discounted books is not good news. As consumers, most people are not concerned with the “life and death of the publishing industry” and naturally prefer cheaper books.
However, industry insiders argue that a “price war” on books may not truly benefit buyers in the end, as it is actually driving up the prices as a forced response to the frequent discount promotions by e-commerce platforms.
China News (@中国新闻网) interviewed publisher San Shi (三石), who noted that people’s expectations of book prices can be easily influenced by promotional activities, leading to a subconscious belief that purchasing books at such low prices is normal. Publishers, therefore, feel compelled to reduce costs and adopt price competition to attract buyers. However, the space for cost reduction in paper and printing is limited.
Eventually, this pressure could affect the quality and layout of books, including their binding, design, and editing. In the long run, if a vicious cycle develops, it would be detrimental to the production and publication of high-quality books, ultimately disappointing book lovers who will struggle to find the books they want, in the format they prefer.
This debate temporarily resolved with JD.com’s compromise. According to The Paper, JD.com has started to abandon its previous strategy of offering extreme discounts across all book categories. Publishers now have a certain degree of autonomy, able to decide the types of books and discount rates for platform promotions.
While most previously delisted books have returned for sale, JD.com’s silence on their official social media channels leaves people worried about the future of China’s publishing industry in an era dominated by e-commerce platforms, especially at a time when online shops and livestreamers keep competing over who has the best book deals, hyping up promotional campaigns like ‘9.9 RMB ($1.4) per book with free shipping’ to ‘1 RMB ($0.15) books.’
This year’s developments surrounding the publishing industry and 618 has led to some discussions that have created more awareness among Chinese consumers about the true price of books. “I was planning to bulk buy books this year,” one commenter wrote: “But then I looked at my bookshelf and saw that some of last year’s books haven’t even been unwrapped yet.”
Another commenter wrote: “Although I’m just an ordinary reader, I still feel very sad about this situation. It’s reasonable to say that lower prices are good for readers, but what I see is an unfavorable outlook for publishers and the book market. If this continues, no one will want to work in this industry, and for readers who do not like e-books and only prefer physical books, this is definitely not a good thing at all!”
By Ruixin Zhang, edited with further input by Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Chinese Sun Protection Fashion: Move over Facekini, Here’s the Peek-a-Boo Polo
From facekini to no-face hoodie: China’s anti-tan fashion continues to evolve.
Published
2 months agoon
June 6, 2024
It has been ten years since the Chinese “facekini”—a head garment worn by Chinese ‘aunties’ at the beach or swimming pool to prevent sunburn—went international.
Although the facekini’s debut in French fashion magazines did not lead to an international craze, it did turn the term “facekini” (脸基尼), coined in 2012, into an internationally recognized word.

The facekini went viral in 2014.
In recent years, China has seen a rise in anti-tan, sun-protection garments. More than just preventing sunburn, these garments aim to prevent any tanning at all, helping Chinese women—and some men—maintain as pale a complexion as possible, as fair skin is deemed aesthetically ideal.
As temperatures are soaring across China, online fashion stores on Taobao and other platforms are offering all kinds of fashion solutions to prevent the skin, mainly the face, from being exposed to the sun.

One of these solutions is the reversed no-face sun protection hoodie, or the ‘peek-a-boo polo,’ a dress shirt with a reverse hoodie featuring eye holes and a zipper for the mouth area.

This sun-protective garment is available in various sizes and models, with some inspired by or made by the Japanese NOTHOMME brand. These garments can be worn in two ways—hoodie front or hoodie back. Prices range from 100 to 280 yuan ($13-$38) per shirt/jacket.

The no-face hoodie sun protection shirt is sold in various colors and variations on Chinese e-commerce sites.
Some shops on Taobao joke about the extreme sun-protective fashion, writing: “During the day, you don’t know which one is your wife. At night they’ll return to normal and you’ll see it’s your wife.”

On Xiaohongshu, fashion commenters note how Chinese sun protective clothing has become more extreme over the past few years, with “sunburn protection warriors” (防晒战士) thinking of all kinds of solutions to avoid a tan.
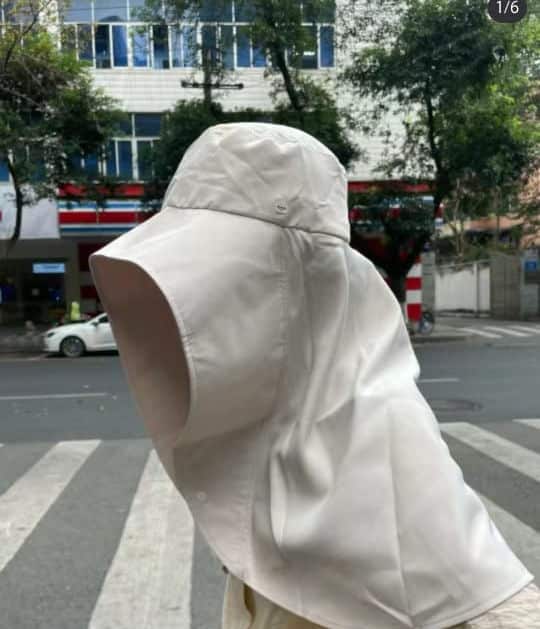




Although there are many jokes surrounding China’s “sun protection warriors,” some people believe they are taking it too far, even comparing them to Muslim women dressed in burqas.
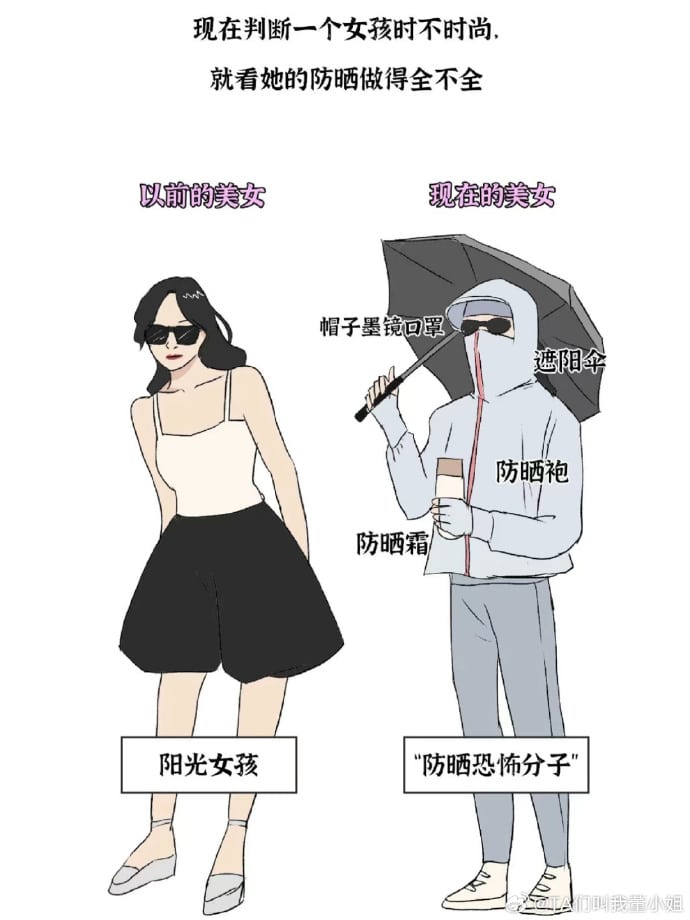
Image shared on Weibo by @TA们叫我董小姐, comparing pretty girls before (left) and nowadays (right), also labeled “sunscreen terrorists.”
Some Xiaohongshu influencers argue that instead of wrapping themselves up like mummies, people should pay more attention to the UV index, suggesting that applying sunscreen and using a parasol or hat usually offers enough protection.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?




