China Insight
Chinese Social Media Reactions to Israel-Hamas War: Pro-Palestinian Sentiments and Anti-Semitic Discourse
Chinese perspectives on the Israel-Palestine conflict are influenced by China’s historical context and perceptions of its role in the world today.
Published
2 years agoon

PREMIUM CONTENT
The Israel-Hamas war has been dominating discussions on Weibo recently. Amid the different Chinese responses to what’s happening in Israel and Gaza, recurring trends and narratives highlight how social media reactions and their pro-Palestine stance are connected to China’s own historical context and perceived global role, as well as Chinese anti-Jewish prejudices.
After the Hamas attacks began on October 7, the Israel-Hamas war has been a major topic of discussion on Chinese social media.
Over the past two weeks, a series of critical events have unfolded since Palestinian militant group Hamas fired more than 5,000 rockets from the Gaza Strip into Israel and infiltrated Isreal. The attacks killed a large number of Israeli civilians, including the 260 deaths at the Supernova music festival massacre. As deadly fights continued, the Israeli government formally declared war and retaliated against Hamas.
Israel has since dropped some 6,000 bombs on the Gaza Strip, killing hundreds of Palestians. More than a million people have fled their homes in the Gaza Strip.
On October 17 and 18, various media reported that at least 500 people were killed in a devastating blast hitting the Al-Ahli Arab hospital in Gaza City, a day before US President Biden arrived in Israel for a wartime diplomatic trip, marking a public show of support for Israel.
While Palestinian officials blamed Israel for the hospital blast, Israel asserts it was a rocket launched by an Islamist militant group that caused the explosion. This claim was later backed by American officials, who cited intelligence suggesting that the explosion was indeed caused by an armed Palestinian group.
On Chinese social media sites, various discussions related to the Israel-Hamas war and all the latest developments have attracted a lot of attention. From October 7 to October 19, the Weibo hashtag “Palestian-Israeli Conflict” (#巴以冲突#) received over 2 billion views. One hashtag related to the Gaza hospital explosion received over 320 million views in a day (#加沙地带一医院遭袭数百人死亡#).
Amid all of the hashtags, posts, videos, images, and discussions on Chinese social media, we have identified three prominent trends concerning the Israel-Hamas conflict: growing pro-Palestinian sentiments, a surge in anti-Jewish racism, and an increased focus on China’s role on the world stage and how its calls for peaceful resolutions contrast with U.S. policies.
1. Pro-Palestine Sentiments
There is a clear trend on Weibo, as well as on other Chinese social platforms like Douyin and even Xiaohongshu, that netizens are demonstrating greater support for the Palestinian side than for Israel.
Some posts (here, here) argue that if the recent attacks on civilians by Hamas militants are labeled as “extreme terrorism,” Israel’s actions against Palestinians over the years should be seen as a form of “mild terrorism.”
This view is repeated by many bloggers and regular netizens all over Chinese social media, where numerous videos depict bombings in Gaza, emphasizing heartbreaking scenes of severely injured children and their grieving parents and siblings.
In Weibo’s ‘hot’ section, which features currently popular posts, it’s evident that there’s a stronger emphasis on images and videos portraying the suffering in Palestine compared to those depicting hardships on the Israeli side.
These distressing videos evoke significant sympathy on Chinese social media, where some commenters suggest that the Hamas movement is becoming more prominent because of the suffering Palestians are enduring (“If my child were killed like that, I would immediately turn into a terrorist as well.”) Others argue that Hamas should be seen as guerrilla fighters rather than terrorists.
The pro-Palestinian sentiments go beyond netizens’ views alone, and are strengthened by Chinese media reports and official positions. The Chinese Foreign Ministry’s initial response to the conflict focused on expressing concerns about the escalating tensions and voicing China’s stance that civilians should be protected and that further deterioration should be prevented.
They reiterated that the fundamental solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the path to peace, according to China, lies in the implementation of the “two-state solution” (两国方案) and the establishment of an independent Palestinian state.
Days later, on October 13, Chinese Foreign Ministry’s Wang Yi stated that the “historical injustice suffered by the Palestinian people” lies at the root of the conflict between Israel and Palestinians, emphasizing the “two-state solution” and the importance of realizing the dream of an independent State of Palestine.
Wang also stated on October 15 that Israel’s bombing campaign had gone “beyond the scope of self-defence” and that it “should stop collective punishment of the people of Gaza.”
One Weibo newsblogger called Creamy Banana (@Creamy蕉, 140k fans) writes:
“What many people do not understand is that when we support Palestine in the Israel-Palestine [conflict], is that we do not support a specific regional political group, that we do not support or oppose a specific racial group, and that we certainly do not support a particular religion. None of that. In this issue, supporting Palestine means supporting justice, supporting the weak, supporting the eggs resisting the high wall, it’s as simple as that.
For instance, during World War II, when Jews were massacred by the Nazis, we sympathized and supported the Jews because they were the weak ones and the victims at that time. Now, Israel is involved in genocide against Palestine, killing civilians, attacking hospitals, and it is the Palestinians who are the weak and the victims. Former victims—the Jews—have now become the perpetrators.
Good people and bad people, justice and evil, they are all relative and ever-changing. This may be the complexity of human nature. There is no absolute goodness, no absolute evil. You can be a victim and a villain hurting others at the same time.”
While the blogger argues that the pro-Palestine sentiment on Chinese social media is unrelated to politics or race, this isn’t exactly accurate. Many Chinese netizens’ support for the Palestinians is closely connected to current geopolitics, America’s pro-Israel stance, existing prejudice towards Jews, and China’s own historical context.
As suggested by Yiyi Chen in “The Basis of China’s Pro-Palestine Stance and the Current Status of Its Implementation” (2013), China leans towards supporting the Arab side because, in the Chinese perspective on the Israel-Palestine conflict, Israel was established by aligning with the Imperial powers of its era. In this context, the Palestians are seen as sufferers of imperialism (p. 216).
This deeply resonates with many Chinese, who, both explicitly and implicitly, associate the current Palestinian issue with China’s historical scars of the “hundred years of national humiliation,” during which China also suffered from imperialism by Western powers and Japan from 1839 to the 1940s.
“The Gaza children shaken and trembling from Israeli bombardments experience scenes similar to what China went through during the War of Resitance against Japan,” one Weibo user wrote: “So don’t say that it has nothing to do with you.”
“We’re helping Palestine, but we’re helping ourselves from 70 years ago,” (“帮的是巴勒斯坦,也是七十几年前的自己”) one commenter (@
姜橙橙_捏唐冽大脸) wrote, receiving over 5500 likes. Others reiterated similar views, writing: “It’s because we endured hardship that we now hold the umbrella for others who are suffering.”
Another reason for the pro-Palestine stance, as detailed by Chen, is rooted in reciprocity. The Chinese tend to support the Palestinians as a way of reciprocating the solidarity shown by Arab countries during the 1960s and 1970s when China was isolated due to Western animosity (p. 216).
Furthermore, and this is particularly evident in the numerous posts and blogs within China’s online media landscape, support for Palestine also stems from opposition to the United States and a lack of trust in Israel due to the close alliance between the U.S. and Israel.
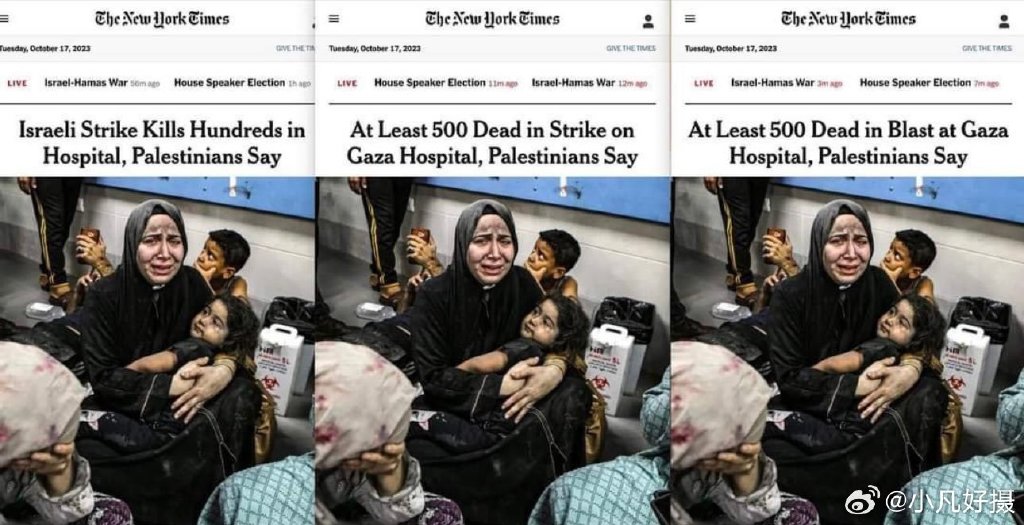
New York Times changing its headline, image posted and reposted on Weibo.
This distrust also extends to American media, which is seen as biased and untrustworthy on Chinese social media platforms. For instance, when the New York Times modified its headlines about the Gaza hospital blast to reflect new information indicating that Israel might not be responsible, many Chinese netizens viewed it as another instance of American media deliberately distorting facts and concealing the truth.
“They did it because of political correctness,” some suggested: “They were afraid to trigger the anger of the Jewish people.”
2. Anti-Semitic Sentiments
Apart from the general pro-Palestinian views on Weibo, there are also voices on Chinese social media denouncing Hamas and the people who support them. For instance, when a video captured students from New York University (NYU) tearing down posters depicting Israeli children held hostage by Hamas, many commenters condemned their actions and questioned why they didn’t go to Gaza themselves. Others comment general phrases such as, “The Hamas evil must be eradicated” (“消灭哈马斯恶魔”).
But despite some condemnation of Hamas, it is hard to find many strong pro-Israel voices on Weibo these days.1 Notably, the Israeli Embassy in Beijing, which is one of the most popular foreign embassy Weibo accounts with 2.4 million followers, is currently not only shadowbanned on the platform (it does not immediately show up in search results), it has also disabled comments on many of its posts or is showing only a limited number of replies.
The posts that do allow comments do not only show strong anti-Israeli sentiments, denouncing Israel as a state engaged in acts of terror and genocide in Gaza, but they also display instances of anti-Semitic racism.
For instance, when the Israeli Embassy posted about the Kutz family, murdered by Hamas terrorists in their home, some netizens commented: “Auschwitz misses you.”
References to the Holocaust, Hitler, Goebbels, and related topics are also evident in many other posts on Weibo. Some bloggers (@扫天下媒体, over 70,000 fans) write things such as “(..) the Germans have since long seen through the true nature and character of the Jewish people.”
Alongside openly anti-Semitic comments, there are anti-Semitic conspiracy theories circulating on Chinese social media. Some of these theories mention Hollywood actors or American political figures of Jewish descent, hinting that Jews control different parts of America’s political, entertainment, and business sectors.
The ubiquity of anti-Semitic comments in China’s online media sphere may be surprising, especially considering how bilateral relations between China and Israel have blossomed since the 2000s.
Not only did a 2019 Pew Research Center study discover that the Israeli public held a “very favorable” opinion of China, but a 2016 China Radio International feature also sought the views of Chinese people on Jews and Israelis. The responses were generally positive, with many respondents describing Jews and Israelis as “very smart” (Yellinek 2022, 185-192).
There are also those who generally express pity for Jews, considering them “stateless” or “oppressed,” and empathizing with their historical struggles. This is one of the reasons why the Holocaust, and Holocaust studies, have received relatively more attention in China than in other Asian countries (Haime 2020; Timmermans 2016).
In 2010, the animated film A Jewish Girl in Shanghai (犹太女孩在上海) was proudly described as “China’s first homegrown Jewish film” – it was part of a renewed remembrance of shared Jewish-Chinese history (read more). The Shanghai Jewish Refugees Museum was opened in 2007 to commemorate the Jewish refugees who lived in Shanghai during World War II, and the first musical themed around the Jews in Shanghai saw the light at the Shanghai International Arts Festival in 2015, the same year when a renewed Chinese translation of The Diary of Anne Frank was published.
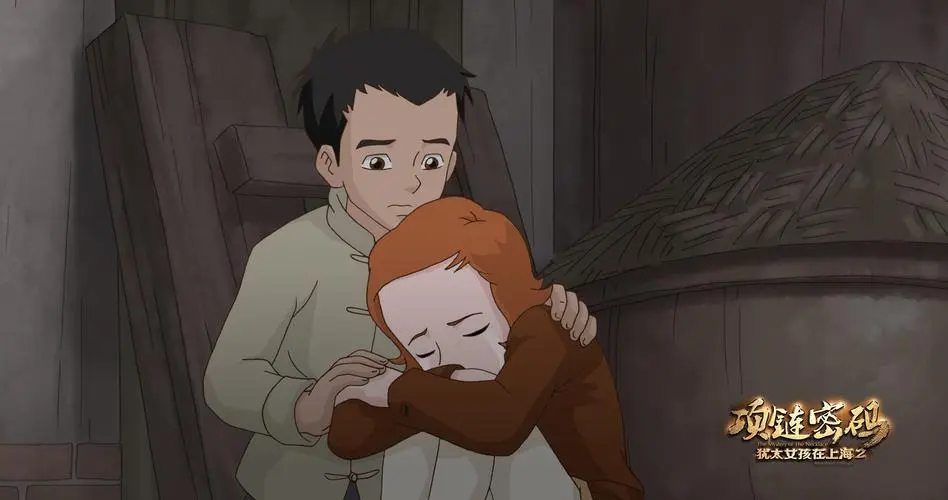

Still from Jewish Girl in Shanghai, China’s first domestic Jewish film.
However, the perception of ‘Jews’ or ‘Jewishness’ in China is multifaceted and often conflicting, as shown by various studies. According to Zhou Xun (2016), Chinese attitudes towards Jews and Jewishness are often a mixture of curiosity and envy, yet Jews are primarily seen as a racialized ‘Other’ who differ significantly from social groups in China. Xun suggests that anti-Semitic language in China is frequently borrowed from Western sources, but that the racialized discourse itself is inherently rooted in Chinese society.
The many popular books that exist about Jews in China, ranging from What’s Behind Jewish Success to 16 Reasons for Jews Getting Wealthy, demonstrate that the authors’ perceptions of Jewishness are often riddled with misunderstandings and stereotypes. These books frequently highlight the perceived success of Jews in business and education to promote values highly cherished by the Chinese (Ross 2016, 25-30).
While many prevailing opinions and stereotypes about Jews in China today revolve around their perceived success, intelligence, and warmheartedness, there are also those who portray them as devious, dominating, and cruel.
The recent surge of anti-Semitism on Chinese social media underscores that ‘Othering’ and stereotyping of Jewish people can focus on their perceived admirable traits in times of flourishing Israel-China relations, but that this praise, exaggerated and rooted in prejudice, can just as swiftly turn into hatred in times of Israel-Palestine conflict escalation.
3. Sending Help: China as Responsible World Leader
Another key trend within Chinese online discussions about the Israel-Hamas conflict is the focus on China’s role as a geopolitical influencer: many see China as a promoter of global peace that is “mending the world.”
Within this context, the topic of China providing humanitarian assistance to Palestinians gained traction on Weibo recently (#中国政府向巴勒斯坦提供紧急人道主义援助#, #中方向巴方提供紧急人道主义援助#), referring to China’s efforts to provide emergency humanitarian assistance to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).
“We bring emergency relief, others bring bullets,” some commenters wrote.
This ubiquitous narrative of China as a responsible, fair, and peaceful global power, supported by Chinese state media reports, underscores a distinction between American and Chinese influence on the world stage. It implies that the U.S. frequently interferes and provokes conflicts, while China discreetly offers aid and works to reduce tensions.
In this context, reports of Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi telling his U.S. counterpart, Anthony Blinken, that the United States should genuinely play a constructive role in the Israel-Hamas war and push for a political solution sparked hundreds of online comments praising China for being a responsible and peaceful leader (#中方呼吁召开巴以冲突国际和会#) .
On October 18, the United States vetoed a UN resolution calling for a humanitarian pause in the Israel-Hamas war, citing Israel’s right to self-defence. China was one of the countries voting in favor of the ‘humanitarian pauses’ resolution.
In response to the American decision to vote against the resolution, China’s permanent representative to the United Nations, Zhang Jun, said: “We cannot help but doubt that some countries do not genuinely wish to resolve the issue” (#联合国巴以问题决议草案遭美一票否决#).
Among the comments are statements like: “This clearly indicates a lack of desire for peace.” “They’re the tumor of the world.” “The U.S. is lacking moral values.”
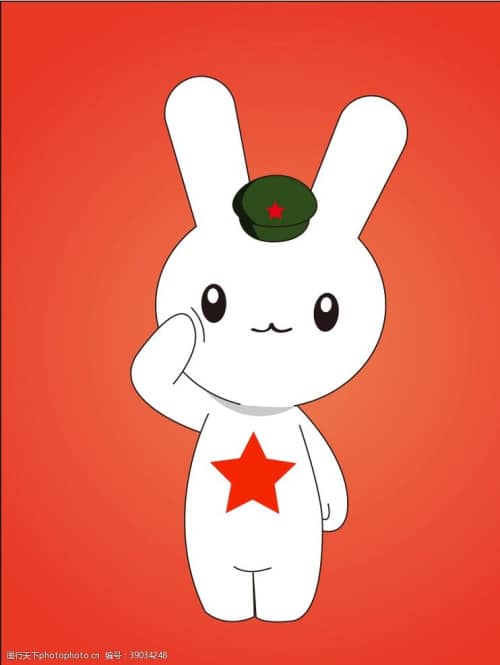

China as the rabbit in the Chinese webcomic series Year Hare Affair (那年那兔那些事儿).
One popular Weibo reply suggested that “the rabbit is quietly patching up [mending] the world” (“兔子总在默默为世界缝缝补补”). In this context, the ‘rabbit’ is ‘China’, referring the Chinese webcomic Year Hare Affair (那年那兔那些事儿) in which different animals represented different countries.
These phrases about China “mending the world” have been posted numerous times on Chinese social media (also: “世界破破烂烂,兔子缝缝补补”). Some of these posts also include a political cartoon showing Western media solely focusing on a crying baby in Israel while turning their backs to the bodies in Gaza.
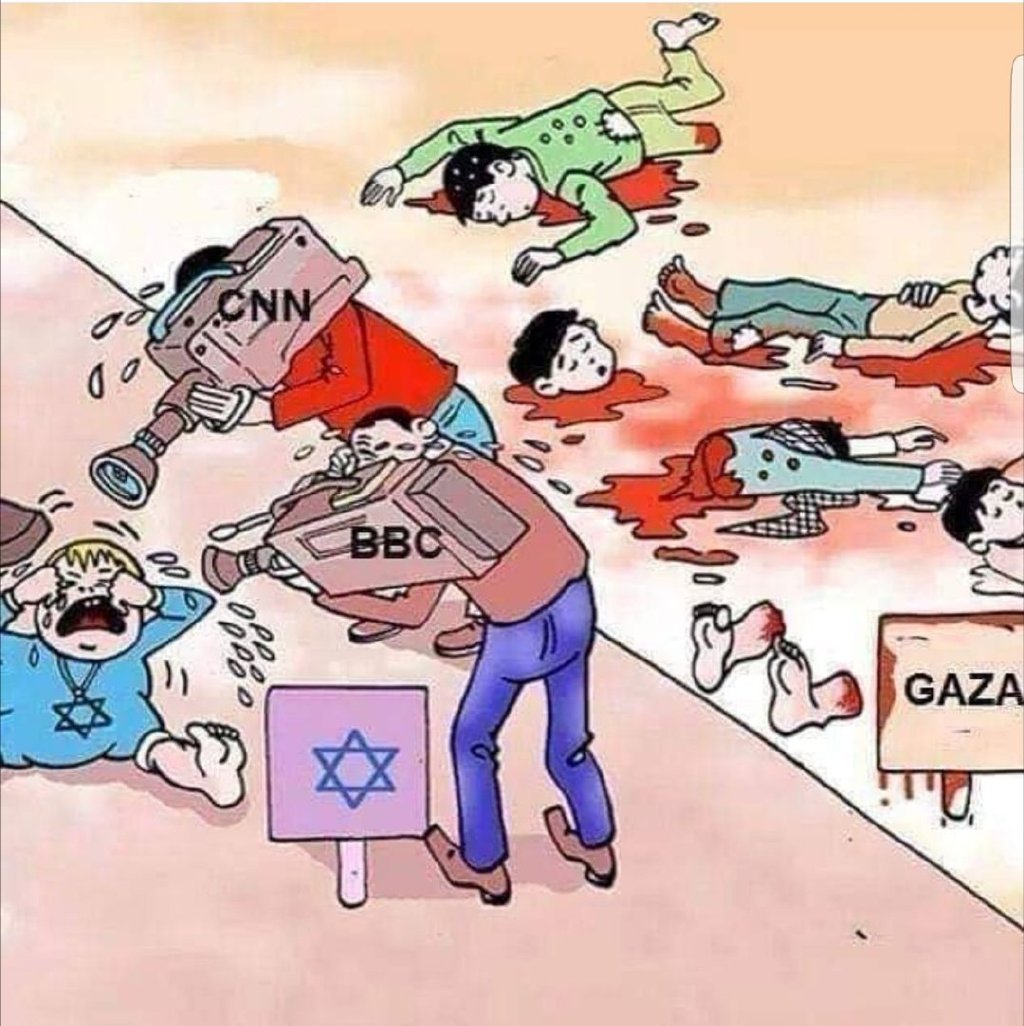

Posted on Weibo (@粤港澳小小胖).
Meanwhile, there are also many commenters who simply express their hopes for a swift end to the war. “I hope for peace between Palestine and Israel. War is merciless.”
Some netizens also just share their appreciation for living in China. “We are not living in peaceful times, but at least we’re living in peaceful China.”
By Manya Koetse
1 Given the scope of this article and its time sensitivity, this comment exclusively focuses on online discussions on Weibo on October 16-19, and it does not reflect the period prior to the current Israel-Hamas conflict
References
Chen, Yiyi. 2013. “The Basis of China’s Pro-Palestine Stance and the Current Status of Its Implementation.” Digest of Middle East Studies 22 (2): 215-228.
Haime, Jordyn. 2020. “Chinese Philo-Semitism: Why China Admires the Jewish People.” Student Research Projects. 26. https://scholars.unh.edu/student_research/26
Ross, James R. 2016. “Images of Jews in Contemporary Books, Blogs, and Films”. The Image of Jews in Contemporary China, edited by James R. Ross and Song Lihong, Boston, USA: Academic Studies Press, pp. 24-36.
Timmermans, Glenn. 2016. “Holocaust Studies and Holocaust Education in China”. The Image of Jews in Contemporary China, edited by James R. Ross and Song Lihong, Boston, USA: Academic Studies Press, pp. 185-205.
Xun, Zhou. “Perceiving Jews in Modern China”. The Image of Jews in Contemporary China, edited by James R. Ross and Song Lihong, Boston, USA: Academic Studies Press, pp. 5-23.
Yellinek, Roie. 2022. “China’s Media Strategy Towards Israel.” Israel Affairs 28: 184-198.
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

You may like
China Insight
“Jiangyou Bullying Incident”: From Online Outrage to Offline Protest
“You think we’re scared of you? It’s not like we haven’t been to jail before.”
Published
2 months agoon
August 6, 2025
These days have been filled with tension and anger in the city of Jiangyou (江油市), Sichuan, after a rare, large-scale protest broke out following public outrage over a severe bullying incident and how it was handled.
The bullying incident at the center of this story happened outside school premises in Mianyang on the afternoon of July 22. Footage of the assault, recorded by bystanders at the scene, began circulating widely online on August 2, sparking widespread outrage among concerned netizens, many of them worried parents.
The violent altercation involved three girls between the ages of 13 and 15 who ganged up on another minor, a 14-year-old girl named Lai (赖).
After Lai and a 15-year-old girl named Liu (刘) reportedly had a dispute, Liu gathered two of her friends—the 13-year-old also named Liu (刘) and a 14-year-old named Peng (彭)—to gang up on Lai.
The three underage girls lured Lai to an abandoned building, where they subjected her to hours of verbal and physical violence. The footage showed how they took turns in kicking, slapping, and pushing her.
At one point, after Lai said she would call the police, one of the bullies yelled: “You think we’re scared of you? It’s not like we haven’t been to jail before. I’ve been in more than ten times—it doesn’t even take 20 minutes to get out” (“你以为我们会怕你吗?又不是没进去过,我都进去十多次了,没二十分钟就出来了”).
That same night, the incident was reported to police. It took authorities until August 2 to bring in all involved parties for questioning, and a police report was issued on the morning of Monday, August 4.

Police report by Jiangyou Public Security Bureau, confirming the details of the incident and the (legal) consequences for the attackers.
Two of the girls (the 15- and 14-year-old) were given administrative penalties and will be sent to a specialized correctional school. The younger Liu and other bystanders were formally reprimanded.
“Parents Speak Out for the Bullied Girl”
The way the incident was handled—not just the relatively late official report, but mostly the perceived lenient punishment—triggered anger online.
Many people who had seen the video responded emotionally and felt that the underage girls should be stripped of their rights to take their exams, and that the bullying incident should forever haunt them in the same way it will undoubtedly haunt their victim.
Especially the phrase “It’s not like I haven’t been taken in [to jail] before” struck a chord, as it showed just how calculated the bullies were—and how, by counting on the leniency of the Chinese judicial system for minors, they made the system complicit in their determination to turn those hours into a living hell for Lai.
China has been dealing with an epidemic of school violence for years. In 2016, Chinese netizens were already urging authorities to address the problem of extreme bullying in schools, partly because minors under the age of 16 rarely face criminal punishment for their actions.
Since 2021, children between the ages of 12 and 14 can be held criminally responsible for extreme and cruel cases resulting in death or disability—but their legal prosecution must first be approved by the Supreme People’s Procuratorate (SPP).
It has not done much to stop the violence.
Discussions around extreme bullying like this have repeatedly flared up over the years, such as in 2020, when a 15-year-old schoolboy named Yuan (袁) in Shaanxi was fatally beaten and buried by a group of minors.
Last year, a young boy named Wang Ziyao (王子耀) was killed by three classmates after suffering years of bullying. His body was found in a greenhouse just 100 meters from the home of one of the suspects, and the case shocked and enraged local residents.
But the problem is widespread among girls, too.
In 2016, we already reported on how so-called ‘campus violence videos’ (校园暴力视频) had become a concerning trend. In these kinds of videos—often showing multiple bullies beating up a single victim on camera—it’s not uncommon to see girls as the aggressors.
Girls often form cliques to gang up on a victim to show that they are in control or to gain popularity. They also tend to be more inclined than boys to make cruel jokes or stage pranks meant to embarrass or humiliate their target. This may partly explain why there seem to be more campus violence videos on Chinese social media showing girls bullying girls than boys bullying boys.
In the case of Lai, she appears to have been particularly vulnerable. One of her relatives posted online that her mother is deaf and mute, and her father allegedly is disabled. This fact may have contributed to why Lai was repeatedly targeted and bullied by the same group of girls, who reportedly took away her phone and socially isolated her at school.
In response to the incident, netizens started posting the hashtag “Parents Speak Up for the Bullied Girl” (“#家长们为被霸凌女孩发声#), not only to support Lai and her family, but to demand harsher punishments for school bullies and for stricter crackdown on this nationwide problem.
From Online Anger to Offline Protest
While many people spoke out for Lai online, hundreds also wanted to show up for her in person.
On August 4, dozens of people gathered in front of the Jiangyou Municipal Government building (江油市人民政府) to demand justice and support Lai’s parents, who had come to express their grievances to the authorities—at one point even bowing to the ground in a plea for justice to be served for their daughter.

Footage and images circulating on social media showing the parents of Lai, the victim, bowing on the ground to demand justice from authorities.
As the crowd grew larger, tensions escalated, eventually leading to clashes between protesters and police.
The arrests at the scene did little to ease the situation. As night fell, the mood grew increasingly grim, and some protesters began throwing objects at the police.
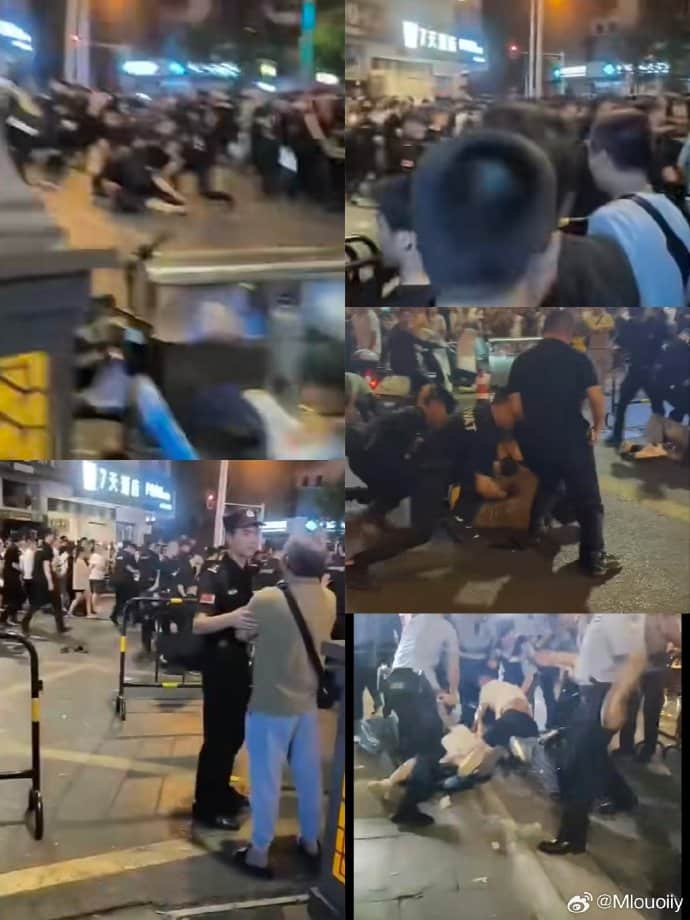

Images of the protest, posted on Weibo.
Near the east section of Shixian Road (诗仙路东段), more people gathered. Hundreds of individuals filming and livestreaming captured footage of the police crackdown—officers beating protesters, dragging them away, and deploying pepper spray.

Netizens’ digital artwork about the bullying incident, the parents’ grievances, and the public protest and its crackdown in Jiangyou. Shared by 程Clarence.
Although the protests briefly gained traction on social media and became a trending topic on Weibo, the search term was soon removed from the platform’s trending list.
Lasting Mental Scars
On Tuesday, August 5, several topics related to the Jiangyou bullying incident began trending again on Chinese social media.
On the short video app Kuaishou, a collective demand for justice surged to the number one spot, under the tag “A large number of Jiangyou parents demand justice for the victim” (江油大批家长为受害学生讨公道).
As of now, none of the perpetrators’ families have come forward to apologize.
As for Lai—according to the latest reports, she did not suffer serious physical injuries from the bullying incident, but according to her own parents, the mental scars will last. She will need continued mental health support and counseling going forward.
Although many posts about the incident and the ensuing protests have been taken offline, ‘Jiangyou’s Bullying Incident’ has already become one more case in the growing list of brutal school bullying incidents that have surfaced on Chinese social media in recent years. The heat of local anger may fade over time, but the rising number of such cases continues to fuel public frustration nationwide—especially if local authorities fail to do more to address and prevent school bullying.
“Not being able to protect our children, that’s a disgrace to our schools and the police,” one commenter wrote: “I want to thank all those mothers who have raised their voices for the bullied child. Each of us must say no to bullies, and we must do all we can to stop them. I hope the lawmakers agree.”
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Insight
The Secret Life of Monks: Shi Yongxin’s Shaolin Scandal Casts a Shadow on Monastic Integrity
“To put it bluntly, temples have been places of deception, corruption, opportunism, and exploitation since ancient times.”
Published
2 months agoon
July 28, 2025
This week, news about a well-known Chinese monk going off the Buddhist path has triggered many discussions on Chinese social media.
The story revolves around Shi Yongxin (释永信), the head monk at China’s famous Shaolin Temple (少林寺) in Dengfeng, Henan. Shi is suspected of embezzlement of temple funds and illicit relationships, and is currently under investigation.
In recent days, wild rumors have been circulating online claiming that Shi fled to the United States after being exposed. On July 26, a supposed “police bulletin” began circulating, alleging that Shi Yongxin had attempted to leave the country with seven lovers, 21 children, and six temple staff. It also claimed he was stopped by authorities before exiting China, that he had secretly obtained U.S. citizenship a decade ago, and that he had misused donations and assumed fake identities.
Although that specific report has since been refuted by Chinese official media, it quickly became clear that there was real fire behind all that smoke.

The report that circulated online and was later confirmed to be fake
Because despite all the sensationalized gossip (some posts even claimed Shi had 174 illegitimate children!), what’s certain is that Shi Yongxin seriously crossed the line. On July 27, 2025, the Shaolin Temple Management Office (少林寺管理处) issued an official statement through its verified channels, including its WeChat account. The statement read:

The report that circulated online and was later confirmed to be fake.
Shi Yongxin, the Abbot of Shaolin Temple, is suspected of criminal offenses, including misappropriating and taking project funds and temple assets. He seriously violated Buddhist discipline, maintained improper relationships with multiple women over a long period and fathered illegitimate children. He is currently under joint investigation by multiple departments. Relevant information will be made public in due course.
Shaolin Temple Management Office
July 27, 2025
China’s Buddhist Association (中国佛教协会) also released a statement on July 28, in which it stated that, in coordination with the Henan Provincial Buddhist Association (河南省佛教协会), Shi Yongxin has been officially stripped of his monastic status.
Various Chinese media sources report that Shi Yongxin was taken away by police on Friday, July 25. Chinese media outlet Caixin suggests that it must not have come as a complete surprise, since Shi had allegedly already been restricted from leaving the country since around the Spring Festival period (late January 2025) (#释永信春节前后已被限制出境#).
About Shi Yongxin
Shi Yongxin is not just any abbot. He’s the abbot of the Shaolin Monastery (少林寺), which is one of the most famous Buddhist temples in the world and is known as the birthplace of Shaolin Kung Fu. The temple was founded in 495 CE. Besides being a Buddhist monastery, it also operates as a popular tourist attraction, a kung fu school, and a cultural brand.
Shi has been running the monastery for 38 years, a fact that also went trending on Weibo these days (#释永信已全面主持少林寺38年#, 140 million views by Monday).
Shi Yongxin is the monastic name of Liu Yingcheng (刘应成), born in Yinshang county in Fuyang, Anhui, in 1965. He came to Shaolin Temple in 1981 and became a disciple of abbot Shi Xingzheng (释行正), who passed away in 1987. Shi Yongxin then followed in his footsteps and managed the temple affairs. He formally became head monk in 1999.
Moreover, Shi Yongxin reportedly served as President of the Henan Provincial Buddhist Association since 1998 and as Vice President of the Buddhist Association of China since 2002.

Shi Yongxin, photos via Weibo.
Shi Yongxin was thus an incredibly powerful figure—not only because of the decades he spent overseeing temple affairs, but also due to his influence within public, institutional, and religious spheres.
Holding such a visible role, Shi Yongxin (释永信) also had (or has—though it’s unlikely he’ll ever post again) a Weibo account with over 882,000 followers (@释永信师父). His last post, made on July 24, was a Buddhist text about the ‘Pure Land’ (净土)—a realm said to make the path toward enlightenment easier.
That post has since attracted hundreds of replies. While some devoted followers express disbelief over the scandal, many others respond with cynicism, questioning whether anything about Buddhism remains truly ‘pure.’
One widely shared post shows an artist sitting in front of a painting of Shi Yongxin, writing, “Worked on this painting for six months, just finished late last night—feels like the sky’s collapsed.” The second picture, posted by someone else, says, “Just change it a bit.”

One aspect of the scandal fueling online discussions is the fact that Shi Yongxin had led the monastery for so long. Rumors about his “chaotic private life” and unethical behavior surfaced years ago, going back to at least 2015 (#释永信10年前就曾被举报私生活混乱#; #释永信曾被举报向弟子索要供养钱#). One of the questions now echoing across social media is: why wasn’t he held accountable sooner? “Who was protecting him?”
“The Tip of the Iceberg”
The Shi Yongxin scandal does not just hurt the reputation and cultural brand of the Shaolin Monastery; it also damages a certain image of Buddhist monks as a collective of people with true faith and integrity.
According to well-known knowledge blogger Pingyuan Gongzi Zhao Sheng (@平原公子赵胜), many people’s understanding of abbots or Buddhist masters (“方丈大师们”) is flawed, since it’s generally believed they attained their high positions within the monasteries due to their moral virtue or deep understanding of Buddhism. In reality, Zhao Sheng argues, these individuals often rise to power because they are skilled at earning money and gaining influence.
“To put it bluntly,” Zhao Sheng writes, “temples have been places of deception, corruption, opportunism, and exploitation since ancient times.”
The blogger argues that much of the influence and power of Buddhist masters was stripped away under Mao Zedong, but that some new famous monks rose in the 1980s, using their skills and connections to rebuild temples and turn them into thriving enterprises.
“If you want to find a few people in temples who truly have faith, who truly have personal integrity, and who are truly dedicated to saving all living things, it’s not that they don’t exist—but it’s rather difficult, like finding a needle in a haystack,” Zhao Sheng wrote.
Some commenters suggest that Shi Yongxin is just the tip of the iceberg (“冰山一角”). They believe that if someone as influential as him can be involved in such misconduct—despite whistleblowers having tried to expose him for over a decade—there must be many more cases of power abuse and corruption within China’s monasteries.
“I previously donated money to the temple,” one commenter on Xiaohongshu wrote: “Although it wasn’t much, it does make me a bit uncomfortable now.”
Another person posted that the Shi Yongxin scandal gave them a sense of despair.
Some older posts about the extravagant lifestyles of head monks — including their luxury cars — have also resurfaced online and are once again making the rounds, suggesting that netizens are actively revisiting other potential instances of misconduct within the monastic world.

Abbot Guangquan Fashi (光泉法师) with a Ferrari California T, Kaihao Fashi (开豪法师) with a Porsche Panamera, Shi Yongxin (释永信) linked to an Audi Q7, and Huiqing (慧庆) and a BMW 7 Series.
One image that resurfaced online shows Shi Yongxin—allegedly driving an Audi Q7—alongside other abbots, such as Guangquan Fashi (光泉法师), the head monk of Lingyin Temple (灵隐寺), who is associated with a Ferrari.
More images like these are now circulating, as people delve into the ‘secret lives of monks’ beyond the spiritual, shifting focus to their material lives instead.

Monks from major temples, including Qin Shangshi (钦尚师) of Famen Temple, E’erdeni (鄂尔德尼) of Jokhang Temple in Lhasa, Yin Le (印乐) of Baima Temple, and Huiqing (慧庆) of Baishou Temple, are rumored to be associated with high-end cars like BMWs, a Porsche Cayenne, and a Range Rover.
While the results of the investigation into Shi Yongxin are still pending, many netizens are already looking beyond him. One person writes: “Are you realizing now? It’s not just Shaolin Temple that has money, other temples aren’t exactly short on money either.”
Another person wonders: “Are the monks in today’s temples actually still truly devoted to spiritual practice at all?”
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe
What’s on Weibo is a reader-supported publication, run by Manya Koetse (@manyapan), offering independent analysis of social trends in China for over a decade. To receive new posts and support our work, consider becoming a paid subscriber.

Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!

China Faces Unprecedented Donkey Shortage Crisis

Nanchang Crowd Confuses Fan for Knife — Man Kicked Down and Taken Away

The Wong Kar-wai Scandal Explained: The Dark Side of ‘Blossoms Shanghai’

China’s National Day Holiday Hit: Jingdezhen’s “Chicken Chop Bro”

Evil Unbound (731): How a Chinese Anti-Japanese War Film Backfired

Hidden Cameras and Taboo Topics: The Many Layers of the “Nanjing Sister Hong” Scandal

“Jiangyou Bullying Incident”: From Online Outrage to Offline Protest

The Rising Online Movement for Smoke-Free Public Spaces in China

China Trend Watch: Pagoda Fruit Backlash, Tiananmen Parade Drill & Alipay Outage (Aug 11–12)

From Schadenfreude to Sympathy: Chinese Online Reactions to Charlie Kirk Shooting
Popular Reads
-

 China Memes & Viral3 months ago
China Memes & Viral3 months agoHidden Cameras and Taboo Topics: The Many Layers of the “Nanjing Sister Hong” Scandal
-

 China Books & Literature11 months ago
China Books & Literature11 months agoThe Price of Writing Smut: Inside China’s Crackdown on Erotic Fiction
-

 China Insight5 months ago
China Insight5 months agoUnderstanding the Dr. Xiao Medical Scandal
-

 China Memes & Viral9 months ago
China Memes & Viral9 months agoOur Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained



