China Military
Mao-Era Military Marriage Regulations Under Fire on Weibo
“The crime of destruction of the military marriage” (破坏军婚罪) apparently is not a crime if you’re cheating from within the army.
Published
5 years agoon
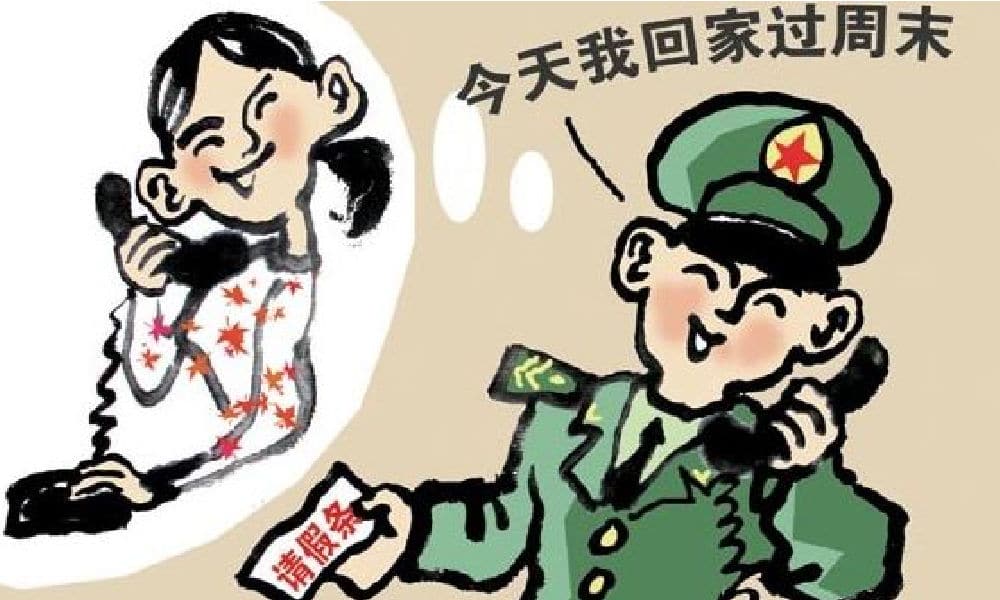

If you have an affair with a military spouse, it is a criminal offense. But if you’re cheating from within the military, it is not considered a crime against military marriage. On Weibo, the story of one military wife has sparked anger among netizens about the Mao-era military marriage regulations.
An online discussion regarding marriage regulations for military personnel in China has been censored following anger over supposed unequal treatment of “the crime of destruction of the military marriage” (破坏军婚罪).
The discussion was triggered by an online post of a military wife who claimed her husband cheated on her with another female army member. It concerns a Chinese serviceman by the name of Gu Yan (顾炎) and a female officer named Shen Jingwen (沈静雯). The hashtag “Gu Yan, Shen Jingwen” (#顾炎沈静雯#) soon went viral on Weibo.
The lengthy story was originally published on Weibo by Gu Yan’s wife, a medical doctor.
According to the online account, Gu Yan and his wife met each other during their junior high school days, and then each went on to study in different fields. Gu Yan trained to join the army; his wife specialized in the medical field and became an anesthesiologist. The couple got married in 2016, had a child in 2017, and their future looked bright until the husband and wife were separated for eight months during the COVID19 epidemic.
According to Gu’s wife, it was during their long time apart that Gu started seeing Shen Jingwen, an army staff member whose father also serves as a commander in the army. The affair soon became serious, and Gu supposedly became more invested in this new relationship than in his marriage, even to the point of blocking his wife, who then contacted his unit to report the affair.
Gu’s wife alleges that Shen Jingwen threatened and bullied her and that she suffered abuse by her husband. Screenshots and phone conversation recordings to prove this behavior towards Gu’s wife were also leaked online.
In her online post, Gu’s wife indicates that the situation between her, her husband and Shen had become untenable but that she had nowhere to turn to since the existing laws mostly protect those who are serving in the army. Even if she wanted a divorce, she could not get one if he would not want to file for divorce.
The ‘destruction of military marriage’ (破坏军婚罪) is a criminal offense in China, but in this case, the law did not apply because it concerned a military officer starting an extramarital relationship with another member of military staff. The law mainly focuses on non-marital acts that occur between non-military personnel and military spouses.
The law is a controversial one. As previously explained by Sixth Tone, it is a Mao-era law to prevent military spouses from straying. In 2016, one man from Beijing was prosecuted under the law for living with a soldier’s wife for two months.
In 2019, one man was sentenced to two years’ imprisonment for living together with a military spouse and also fathering her child with prior knowledge that her husband was a serviceman, as reported by China Military.
Although the regulations on the protection of marriage of soldiers date back much longer, breaking up a military marriage was also listed as a criminal offense under “The Offenses Against Marriage and the Family (Arts. 179-184)” in the Criminal Law that was enacted in 1979.1
Weibo netizens are sharing screenshots of the Baidu Encyclopedia page explaining the law, with one segment clearly stating that “if it concerns an illicit love affair between two members of the army, and their partners are not members of the army, then this does not constitute as a crime of destructing a military marriage [破坏军婚罪].”
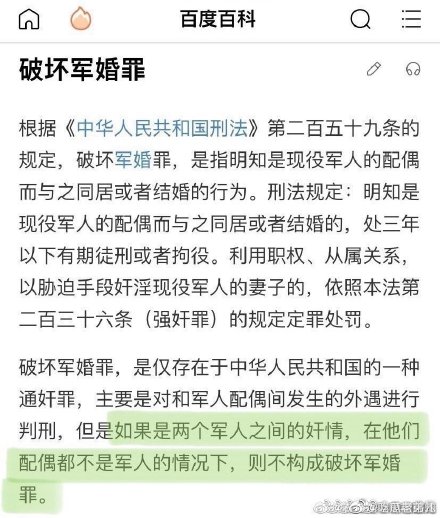
Censorship showed the sensitivity of the topic; not only was it removed from Weibo, but also from other sites such as Q&A site Zhihu.com. The sentence from the Baidu page that was highlighted and shared online also no longer shows up on the Encyclopedia page.

A 404 page comes up when clicking on a page dedicated to this topic on Zhihu.
“The moment this hit the Weibo hot search lists, it was gone within minutes,” one person on a Baidu message board wrote.
The sensitive nature of the topic partly lies in the fact that this is about members of the military, who are usually praised as heroes for their sacrifices for the country.
“To me, the word ‘serviceman’ always sounded like a divine word,” one commenter writes on Weibo: “I’d never expected that it could also bring up loathing in me.”
Meanwhile, many alternative hashtags popped up on social media to replace the censored ones. Besides the “Gu Wen Shen Jingwen” hashtag (#顾炎沈静雯#), there are also many others including “Military Cheating Is Not Considered a Crime against Military Marriage” (#军人出轨不算破坏军婚罪#), “Gu Wen and Shen Jingwen Are Shameless” (#顾炎沈静雯不要脸#) and the creative hashtag “Female Jun People Break Jun Marriage” (#女jun人破坏jun婚#), with ‘jun’ being pinyin for the Chinese character ‘军’ (army).
A mainstream sentiment expressed online is that existing laws regarding military marriages are clearly unfair: anyone who cohabitates with a spouse of an active member of the military could be sentenced, while someone within the military could cheat on their wife without any consequences for them nor for their extramarital sex partner.
Many netizens defend Gu’s wife and condemn Gu and his military girlfriend for abusing their power and taking advantage of their position to bully the weakest party, especially while there is a child involved.
“If a military wife needs to rely on netizens to assert their legitimate marital rights and interests, it really is a disgrace to the Chinese PLA [People’s Liberation Army]”, one blogger wrote.
On the evening of March 19, the Weibo account ‘People’s Frontline’ (@人民前线), an official channel of the People’s Liberation Army, responded to the situation. Their official statement confirms that their department previously received a complaint from Gu’s wife about the living situation of her husband within the army, and that both Gu and Shen were given discipline sanctions. Gu and his wife are currently getting a divorce.
The statement also says that the PLA does not condone the actions of individual members of the army who violate social morals and family virtues. The statement was shared over 18,000 times on Saturday.
Some netizens praised the official statement, saying it showed that the army was becoming more “open and transparent.”
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
1 Leng, Shao-Chuan. 1982. “Crime and Punishment in Post-Mao China.” China Law Reporter 2, no. 1: 5-35.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2021 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

Chapter Dive
Evil Unbound (731): How a Chinese Anti-Japanese War Film Backfired
731 was China’s most anticipated war movie of the year — how could it fail so miserably to live up to public expectations?
Published
4 months agoon
September 24, 2025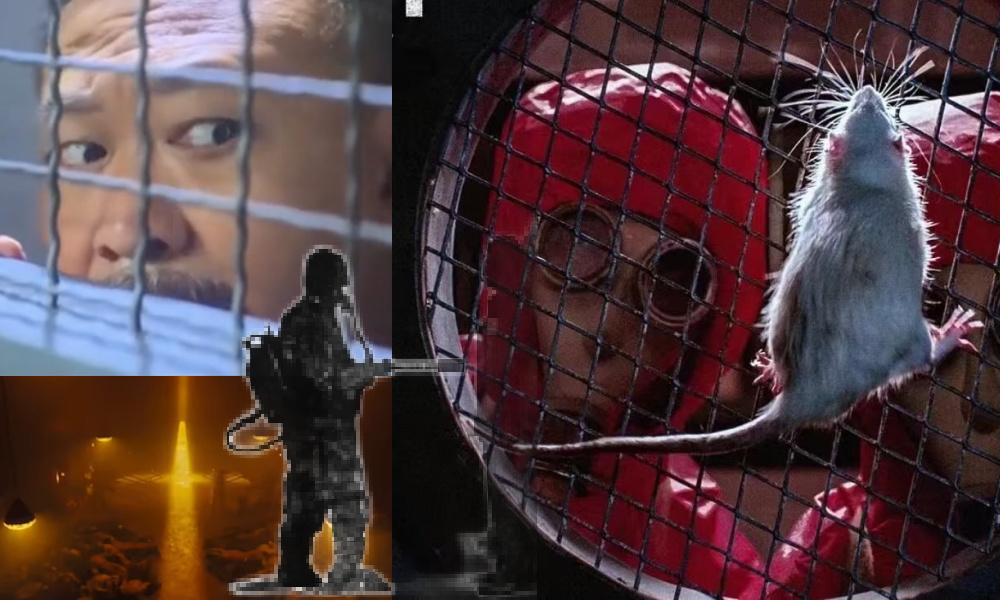
🔥 This is premium content and also appeared in the Weibo Watch newsletter. Subscribe to stay in the loop.
How did Evil Unbound (731), one of the most anticipated Chinese war movies of 2025, go from patriotic hype to online backlash? A deep dive into the official narrative, the audience reception, and everything that’s particular about this movie.
731 and 918, those were the numbers dominating Chinese social media over the past week. Both numbers carry heavy historical weight, but the recent discussions surrounding them reveal two parallel worlds of the official narrative vs the audience experience of a controversial new World War II film.
It was “9.18” on Thursday, when China commemorated the 94th anniversary of the September 18th Incident (九一八事变). On that day in 1931, a small explosion on a Japanese-owned railway near Shenyang (Mukden) was used as a pretext to invade Manchuria.
While many older Chinese were taught in school that the war began in 1937, recent state-led campaigns increasingly emphasize 1931 as the true beginning of China’s “14-year-long war” (1931–1945). Over the past decade, the 918 commemorations have become more prominent online, shaping public memory through nationalistic messaging.
This year, the commemoration had an extra dimension, as it wove the release of Evil Unbound (English title), also known as 731, into the patriotic media narratives around 918.

Patriotic film poster putting 918 and 731 together.
The much-anticipated war movie 731 depicts the atrocities of Japan’s Unit 731 (731部队), notorious for conducting horrific biological warfare experiments in Harbin during World War II under Major General Shiro Ishii (石井四郎), a former army surgeon and biologist with a particular interest in historical plagues. Under his command, Japan’s biological warfare and human experimentation in China were carried out on a larger scale than anywhere else between the 1930s and 1940s.
After the war, because the US felt his knowledge on bioweapons was of great value, Ishii was granted political immunity deal and was never brought to trial.
Together with the Nanjing Massacre, Unit 731 has come to symbolize the peak horrors of Japan’s wartime atrocities. Public attention for this history has grown in recent years, especially since the 2015 opening of the Harbin-based Museum of Evidence of War Crimes by Unit 731.
It was around that same time, about a decade ago, when Chinese director Zhao Linshan (赵林山) started working on the movie Evil Unbound (731), produced by Changchun Film Group in collaboration with the Propaganda Departments of Shandong, Jilin, Heilongjiang, and Harbin.
It finally premiered nationwide on Thursday, ‘9.18’ at exactly 9:18 and shattered 10 box office records on its opening day. Screened 258,000 times in a single day, it rapidly surpassed 200 million yuan (US$28 million) in ticket sales. After three days, the box office exceeded 1 billion yuan (US$140 million).
The film focuses on Unit 731 in the final days before Japan’s defeat in 1945, portraying how local salesman Wang Yongzhang (王永章, played by Jiang Wu 姜武) is imprisoned together with other civilians. They are promised freedom in exchange for “health checks and epidemic prevention cooperation,” and are subjected to frostbite experiments, poison gas, and vivisections.

Official film posters for Evil Unbound/731.
“What we made is not a movie — it is historical evidence,” director Zhao said about the film.
A state-orchestrated hashtag ecosystem is currently amplifying the film’s ‘success.’ Similar to previous viral war film hits such as The Battle at Lake Changjin (长津湖) and Nanjing Photo Studio (Dead to Rights 南京照相馆), the media campaigns highlight the film’s commercial performance, its educational and historical value, the ‘authenticity’ of its production process, and its emotional reception and overseas recognition.
Recent trending hashtags, from Kuaishou to Weibo and beyond, include:
- 电影731票房再创新高 – “Film 731 sets another box office record”
- 没有人能在看731时不流泪 – “No one can watch 731 without crying”
- 观众掩面哭泣 / 哭到没法接受采访 – “Audiences cover faces in tears” or “Audiences too moved to be interviewed”
- 观众自发起立唱国歌 – “Audience spontaneously stand up to sing national anthem”
- 海外观众看731不停抹泪 – “Overseas audiences weeping when seeing 731”
- 9岁小孩看完731后泪奔 – “9-year-old child burst into tears after watching 731”
- 日本观众看完电影731后情绪崩溃 – “Japanese audiences having emotional breakdown after watching 731”
- 让731这段历史不再沉默 – “The history of 731 can no longer be silenced”
There are hundreds of other hashtags contributing to this official narrative, that portrays Evil Unbound as an absolute patriotic and commercial triumph.
From Anticipation to Backlash: 731 Between Shawshank and Squid Game
Outside of this official narrative, however, audiences are telling a very different story. Despite months of anticipation, the film has been met with overwhelmingly negative reviews.
On Weibo, the hashtag “731 Film Review” (#731影评#) was pulled offline. On Douban, the movie’s ratings meter was switched off entirely (“暂无评分”). On IMDb, the film is currently rated 3.1.
Usually, criticism of patriotic films is a slippery slope. People have been censored, blocked, or even detained for criticizing war films. But criticism of this film is so widespread, and so ubiquitous across social media platforms, that it is barely containable.
Many viewers called the movie “trash,” while others said they felt “defrauded”.[1] One commenter suggested the director tried to make The Shawshank Redemption but ended up with Squid Game.[2] Others called it “bizarre”[3], or concluded: “The short review section doesn’t even allow enough characters to describe how unbearable this movie is.”[4]
Viewing the film, I must admit I also felt confused – the movie is nothing like you would expect after the state-led promotion of the film.
The opening minutes quickly set a messy historical context, leaping from the 1925 Geneva Protocol to China’s 1943 counteroffensives, to Iwo Jima, and to Japan’s “Operation PX” plan (Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night), a scheme to attack the United States with biological weapons—before landing in Harbin and Unit 731 in the year 1945.
About ten minutes in, the movie seems to switch tracks and take inspiration from Squid Game, the 2021 South Korean survival drama.
Some details appear almost one-to-one from the Netflix show: the cold speaker voice, characters labeled by numbers, stylized lighting (including the Japanese flag’s red dot turned into menacing red spotlight), and eerily sterile sets that create a cold, clinical atmosphere stripped of humanity.

Scenes from 731.
Narrative elements also echo Squid Game’s deadly competitions, including an actual life-or-death rope pulling game. In 731, “winners” are promised freedom (but actually sent for experiments) and “losers” surviving slightly longer, until even these rules seemingly disappear, leaving viewers just as lost as the characters.
Beyond these echoes of Squid Game and The Shawshank Redemption (with their themes of prison break, brotherhood, and hope), where horror meets drama and occasionally even comedy, I also thought I saw traces of The Green Mile (there’s even a befriended mouse), The Shining, One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest, and even Kill Bill.
If this all sounds like a fever dream, that’s about right.
While the film undoubtedly has artistic value in its visual references and symbolism, at times it seems more intent on presenting itself as an arthouse production than on telling a coherent historical war story.

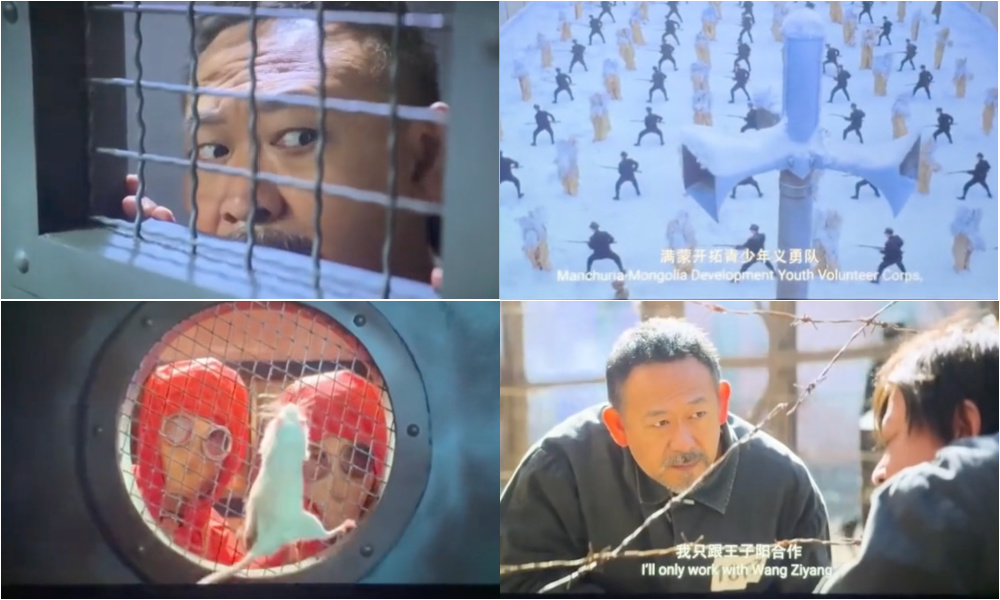
731 scene showing Japanese flags with red lasers/spotlights one the left. Some of the movie’s camera angle points, color use, narrative elements and settings show some similarities with Squid Game (image on right).

731 (left), Squid Game (right)

Scene from 731, which I thought sometimes had some echoes from The Shining.

Another reference to Stanley Kubrick? 731 on the left, Clockwork Orange on the right.
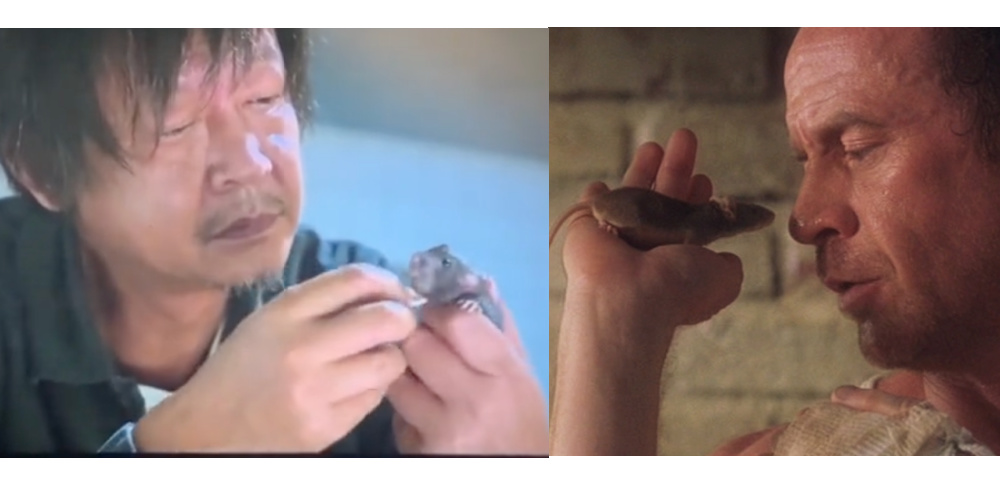

Prison mouse friend. 731 (left) and The Green Mile (right).
And that is also what most of the online critique is about – people feel that while the movie is supposed to be about creating awareness of a particularly horrific part of Chinese war history, the actual factual history seems to have ended up in the background.
One commenter from Harbin wrote:[5]
💬 “For Harbin, 731 is the most painful chapter of history. This movie uses a mass of absurd visuals and music to tell a story that has almost nothing to do with real history. All the information that truly should have been shown is brushed over in passing words, and in the end it just tells audiences ‘never forget history’? This tramples on the history of 731. Stupid and vulgar.”
Others are also upset over historical inaccuracies in the film — from the makeup to the sets, the props, and the biological experiments. Even the toilet paper used by the prisoners isn’t very realistic, with some commenters saying these kinds of details ‘drove them crazy’:
💬 “I’m born after 1990, and even I grew up with worse toilet paper than what the aggressors in those years apparently gave to their prisoners. Theirs was so high-quality you could fold it into bows and baby shoes. Must have been strong, durable, and waterproof.”[6]
One other reviewer on Douban wrote:
💬 “As a prison break film it’s not exciting, as a historical film it’s too careless, and as a drama it’s too fragmented.”[7]
Douban reviewer Qingyun (青云) noted that it jumps from relatively calm scenes to intense emotional outbursts or extreme cruelty without any buildup — instead of moving viewers to tears, it alienates them from the story and its characters.
He adds:
💬 “The film wants to exploit history’s seriousness to entertain the public, but also fears the theme is too depressing and will affect the box office, so it stuffs in commercial gimmicks (jokes, fantasy, spectacle). This opportunism sacrifices the solemnity that is rewired for the historical topic, while also failing to provide as qualified entertainment. The result: it offends history and disappoints audiences.”[8]
Most of these disappointed reviewers argued that the chance to tell the story of Unit 731 was wasted by a director and script that offered little context to the subject, with some even suggesting that another, 37-year-old film (Men Behind the Sun, 黑太阳731, 1988) did a better job of conveying the history of Japan’s biological warfare in China.
A ‘Masterful Cult Film,’ But a ‘Total Failure’ as a War Movie
Despite the wave of strongly negative feedback, there are also those who did find the film moving, giving it five-star reviews — some from those who stress the film’s value as a reminder to “never forget national humiliation,” while others genuinely appreciate its creative vision.
Douban commenter ‘Bat Lord’ (蝙蝠君) called it a “masterful cult film” with the film’s aesthetics being “built on a foundation of Western stereotypical Orientalism of Japan and layered with Christian martyrdom.”[9]
As an example, Bat Lord describes a recurring scene in which prisoners are taken from their cells toward “freedom,” only to be taken to lethal human experiments. They are escorted by Japanese guards in traditional kimonos with samurai swords, led by a geisha carrying a bright red umbrella and wearing impossibly high okobo clogs, followed by Edo-period guards with topknots and white kimono. Bat Lord calls it “Orientalist punk seen through a Western gaze” (“有一种西方视角的东方主义朋克的味道”).
The reviewer also interprets the main characters, the Chinese prisoners, as representations of Christian martyrdom. Cross symbols are indeed everywhere in the film, with prisoner No. 017 constantly drawing crosses on the wall, and an ingenious escape plan hidden in a dictionary as a series of crosses.
At the climax, after battling guards in kimonos with wooden swords, the prisoners flee toward a crematorium resembling a cathedral of light, where crosses formed from pure white beams symbolize freedom. But behind the cross loom the Japanese executioners. After a bloody massacre, the survivors are captured and executed — tied to crosses arranged around a pit, with fleas dropped on them from above as Japanese officers watch from a grandstand.
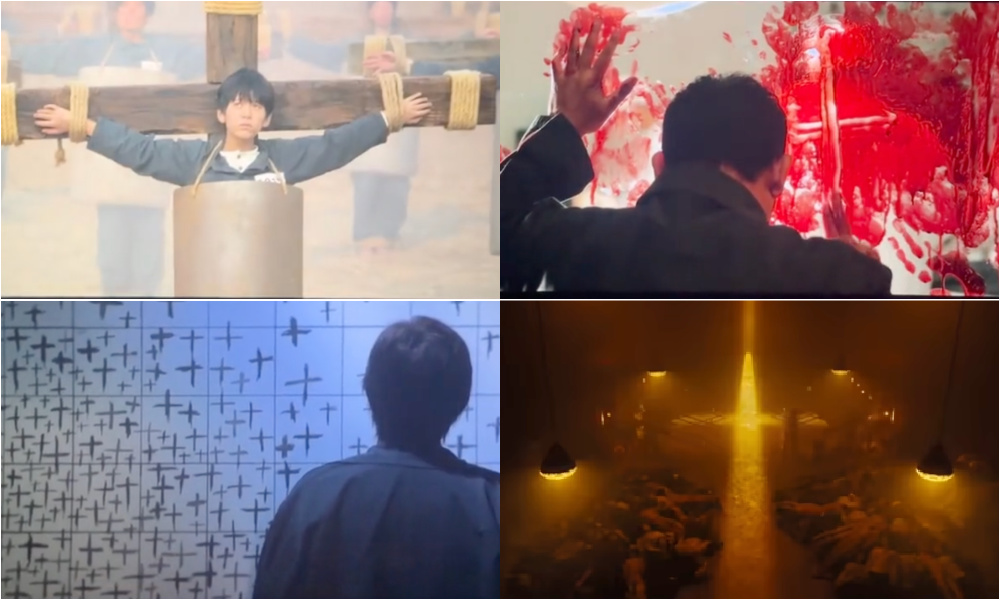

Cross symbols appear throughout the film.
💬 “It’s clearly a direct homage to Christian martyrs who were sacrificed in the Colosseum during the ancient Roman Empire. In the end, all the protagonists die martyrs’ deaths,” Bat Lord writes.[10]
He concludes that the film is “4/5 as an art house film, but zero points as a war movie”:
💬 “As a mainstream patriotic commercial blockbuster, it is a complete and utter failure (..) But as a niche cult prank film, it actually has some positive points (…) – built on exaggerated Orientalist visions of Japan, it feels strangely authentic. This kind of deconstruction of Japanese culture isn’t something the Japanese themselves could do — only the West or China, as seen in works like The Last Samurai, Ghost of Tsushima, and Shogun.” [11]
He adds:
💬 “The biggest problem is the subject matter. Using 731 — such a solemn, tragic history — only to hollow out its pain, exploit national emotions, and repackage it as a cult prank film disguised as a patriotic blockbuster, inevitably backfires. If it had been framed as a semi-fictional low-budget black comedy, the backlash wouldn’t be so severe.”[12]
“No Japanese in Heaven”: Over-‘Othering’ the Enemy
How could 731 have failed so miserably to live up to public expectations?
In recent years, Chinese museums, books, and popular culture have made many attempts to revitalize the history of war and make it more relevant to younger generations. In many cases, this has been successful, from popular war dramas to blockbuster films.
But Unit 731 is perhaps an especially difficult subject to adapt into a commercially successful film for a broad audience, especially since it chose to leave out the kind of contextualization that Oppenheimer provided in exploring the history, process, and character development that led to the atomic bomb.
Like the gas chambers of Auschwitz or Mengele’s brutal experiments, its history is so gruesome that there is little to focus on beyond the suffering of the victims and the cruelty of the perpetrators. (The film had already been postponed once, as it allegedly failed to pass official screenings due to its graphic scenes.)
War films in China are expected to reflect — or help shape — national identity. In 731, this means boosting national unity by focusing on Japan as the ultimate “Other,” the ‘constructed outsider’ against which the own national identity is defined.
The entire nation is cast as an enemy, depicted through exaggerated cultural symbols — geishas, kimonos, samurai, and cherry blossoms — regardless of whether they belonged in the actual prison setting. Japan’s national colors and imagery are fused with scenes of bloody and barbaric slaughter, turning Japanese cultural identity itself into a target.
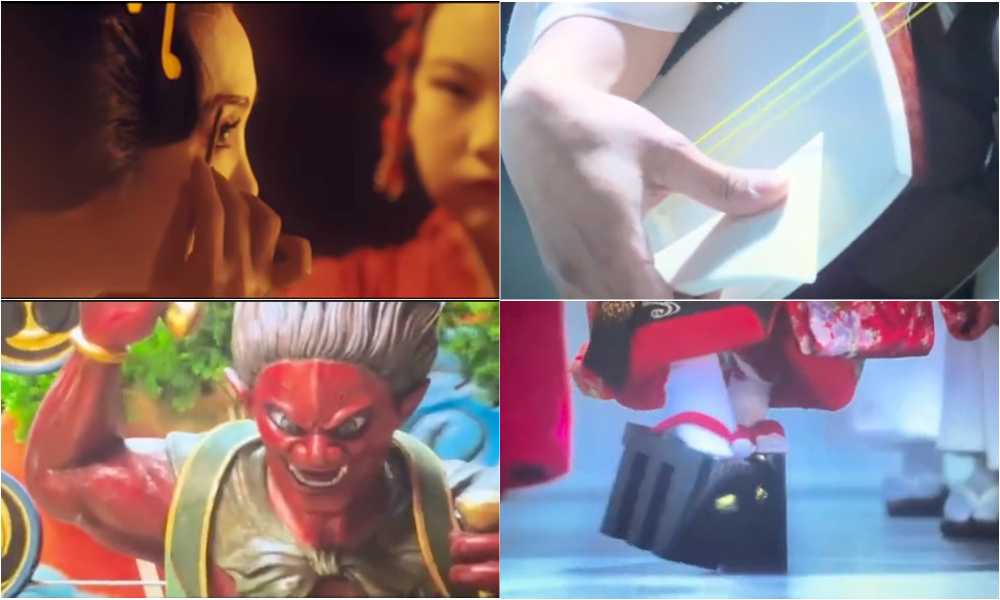

References to Japanese cultural symbols in the film.
In doing so, the film not only holds Japan as a whole responsible for its wartime aggression, but also strengthens Chinese identity by defining it in opposition to Japan, visually contrasting “good” versus “evil” through opposing characters, colors, and symbols.
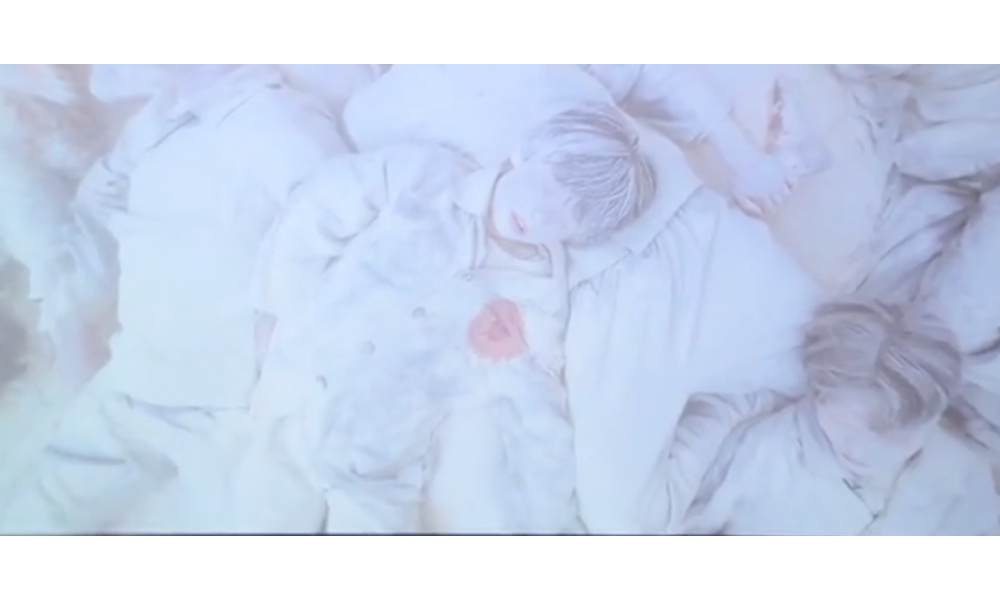

Clear visual symbols: dead Chinese bodies covered in white dust. With the red circle of blood, the scene resembles a Japanese flag.
This contrast is also made explicit in dialogue: at the beginning of the film, for instance, a young boy enters the stark white prison halls and asks, “Master, are we in heaven?” to which the older Chinese man replies, “Nonsense, how could there be Japanese in heaven?”
In promoting the film, director Zhao Linshan (赵林山) reinforced the image of Japan as the eternal “Other” by explaining that he had insisted none of the Japanese roles could have possibly played by Chinese actors, suggesting they would not be able to convey their evilness. Despite the difficulty of bringing over more than 80 Japanese actors during China’s ‘zero Covid’ era, when 731 was largely filmed, Zhao maintained that “only the Japanese can play this dual nature.”
While Chinese social media is often filled with anti-Japanese sentiment, many viewers criticized the depiction of “Japan” and the Unit 731 staff — not because of the anti-Japanese angle, but because they felt it trivialized history. They argued that Unit 731 was already so horrific that it needed no added gimmicks, tropes, or exaggerated villains to make it look bad.
As Douban reviewer Qingyun wrote:
💬 “Portraying devils as clowns diminishes their true guilt. The real criminals were rational, organized, and intelligent, embodying the will of Japanese militarism as a systematic project. Making them idiots (..) greatly underestimates the danger and organization of militarism, and is a severe simplification of history.”[13]
This critique goes further, suggesting the film both weakens its warning value (“the true terror is that advanced civilization and barbarism can coexist”) and cheapens the victims’ suffering (“if the enemy is so stupid, the tragedy seems less grave”).
On Weibo, one commenter criticized this one-sided approach:
💬 “I saw an auntie in Hangzhou who, after watching the movie 731, said she hated the Japanese devils so much — that she would hate them for her entire life. But this elderly woman, brainwashed by hatred education for a lifetime, doesn’t stop to think that (..) so many other brutal slaughters happened throughout Chinese history. If you only speak of hate, can your hate keep up with all of them? Shouldn’t we instead explore and reflect more deeply on the underlying causes of these events? Better to talk less of hate and more of love — because only the most genuine love from the depths of the human heart can ultimately prevent such tragedies from happening again.”[14]
Some viewers who appreciated the film, however, disagreed. One Weibo user wrote: “I watched the film with my husband and on our way home we scolded the Japanese, wishing we could throw two more atomic bombs on them. It was a good film.”
Between the history and the hate, the official narrative, the polarized audience reactions, and disagreements over the film’s message, 731 has brought more controversy than clarity.
But beyond the debate and confusion, one message remains clear. As one viewer wrote:
“The film wasn’t what I expected, but I’m not sure what I even expected? A good story? More like a documentary? There’s one thing I can say for sure: this movie is just a shell — the history itself is the soul.”[15]
By Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
References
- “看完有种被诈骗的感觉” (source: Douban).
- “一句话评价《731》,导演按照《肖申克的救赎》拍出了《鱿鱼游戏》” (source: Xiaohongshu).
- “令人非常迷惑” (source: Douban).
- “短评骂的字数不够了实在是忍不了了” (source: Douban).
- “作为一个哈尔滨人,去过至少三次纪念馆,731对于哈尔滨就是最沉痛的一段历史,这个电影用大量极其荒诞的镜头和音乐,讲述一个基本跟真实历史毫无关系的故事,所有真正需要拍出来的信息全部是文字一笔带过,最后却告诉观众勿忘历史?这是对731这段历史的践踏。弱智且下流” (Source: comment section Sina).
- “作为一个90后,我出生的那个年代卫生纸质量都达不到侵略者给实验体使用的,纸的质量太好了,又是编蝴蝶结,又是编鞋子的,我猜应该是坚韧又耐用,透水都不断的那种吧” (Source: Douban long reviews).
- “或许是删减太多或许是各种局限,当做越狱不精彩,当做历史片太随意,当做剧情片太碎片”(Source: Douban).
- “影片既想利用沉重历史的严肃性作为宣传噱头,又担心题材过于压抑影响票房,于是强行注入商业娱乐元素(搞笑、幻想、刺激场面)。这种“既要…又要…”的投机心态导致影片既失去了历史题材必需的敬畏感,又未能提供合格的娱乐体验。最终,它既冒犯了历史,也辜负了观众”(Source Douban, review by Qingyun (青云).
- “西方刻板印象东方主义日本与基督殉难的碰撞,cult片的杰出之作”(Source: Douban, review by ‘Bat Lord’ (蝙蝠君).
- “很明显也在致敬古罗马帝国时期殉道在斗兽场的圣徒们。最终主角团全员殉道,无一幸免。”
- “这个片作为主流主旋律商业大片是完全的,彻头彻尾的失败,彷佛那纯纯的依托!甚至从预告片开始这电影就没有任何一丝一毫的符合历史,我从一开始就完全没有抱任何期望的去看,结果发现这片作为小众邪典整蛊片却颇有可取之处(。。)当你不认为这片是正常电影之后,这片表达出的那股子真的是超正宗的外国视角下的刻板印象东方主义日本美学、东方朋克味,这种对日本文化的魔怔向的解构其实我个人还真感觉挺不错的。这种解构日本人是搞不出来的,目前只有欧美和中国能搞出来,代表作就是《最后的武士》、《对马岛》、《幕府将军》之类的作品,里面的日本文化,日本武士道精神一个赛一个魔怔,欧美是往骑士幻想的那个路子去走的,我们是往黑暗邪典的路子去走的“
- “所以这片的最大问题还是选择了731这个严肃题材,完全在消解历史的悲痛,消费民族的情感,拍了个小众邪典整蛊片后,还按照主流商业片来包装和宣发,如果他拍成半架空的超小成本黑色喜剧我觉得反噬恐怕不会有这么大”(Source: Douban).
- “它美化了真正的邪恶:将恶魔塑造成小丑,实际上减轻了他们的罪责。真实的731部队不是一群疯癫的傻瓜,而是清醒的、有组织的、高智商的罪犯。他们的行为是日本军国主义国家意志的体现,是一个系统性的工程。把他们拍得弱智,仿佛这场悲剧只是一群笨蛋造成的意外,这极大地低估了军国主义的危害性和组织性,是对历史的严重简化”(source: Douban).
- “看到一位杭州阿姨看完电影731后讲太恨日本鬼子了,要一辈子一辈子的恨。这个被仇恨教育洗脑一辈子的老太太,您也不思考一下,嘉定三屠,江东六十四屯,南京大屠杀等等一系列的野蛮屠杀事件在中国历史上发生的太多了,光讲恨您恨的过来吗?不应该是更多的探究和反省发生这些事的深层原因嘛!还是少谈恨多讲爱吧,只有发自心底人类最真实的爱才能最后解决这些惨案在人类世界的发生吧”(Source: Weibo).
- Weibo user “红屋顶上的猫”: “我不知道该怎么评。首先在这个忙乱的日子里安排自己去看这个电影,我也说不清楚我是想铭记那段历史,还是想比较小时候看过的《荒原城堡731》,还有那部《黑太阳》。其次我也不知道电影从越狱视角切入,写实和魔幻风格交替,是好还是不好?但它和我想象的不一样,可我也不知道自己想看到的到底是什么样?甚至我也说不清我对这场电影的期待是什么?讲好故事?还是拍成纪录片?我只能确定,电影只是个壳子,那段历史才是灵魂。”
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Military
China’s “Post Parade Afterglow”: 6 Social Media Trends
From Putin’s ‘happiness in China’ to sunburn “medals”: this is China’s post-parade social buzz.
Published
4 months agoon
September 14, 2025
🔥 Quick Take: Trending in China
This is a brief update from our curated roundup of what’s trending in China this week. A version of this story also appears in the Weibo Watch newsletter. Subscribe to stay in the loop.
In the last newsletter, I promised to follow up with more ‘post-parade’ responses. On Weibo and other social media platforms in China, hundreds of hashtags have emerged around the theme of the “afterglow after the parade” (阅兵后劲). In addition to the featured ‘AFP versus Xinhua’ discussion, here are some other noteworthy social media trends following the September 3 event, which turned out to be one of China’s largest military parades:
1 🇨🇳 “I’m So Happy in China”: Putin and Kim Jong-un’s Daughter in the Picture
Besides everything happening on Tiananmen Square during the parade, many netizens were just as interested—if not more—in what was going on at the sidelines. The presence of Putin and Kim Jong-un drew a lot of attention, and since political discussions are highly controlled on Chinese social media—especially during such high-profile events—online conversations mostly focused on smaller, more personal details.
One viral clip posted by Ta Kung Wen Wei Media (大公文匯網, a pro-Beijing Hong Kong media outlet) showed Putin during his various visits to China, where he always seems to enjoy local delicacies. The video’s caption read: “You have no idea how happy I am in China!” (“我在中国的快乐谁懂啊?!”).
As for Kim Jong-un, his daughter Kim Ju Ae, who accompanied him on this trip to China, became the social media star of the day. Many netizens still remembered her from a few years ago, when she joined her father at a Pyongyang military banquet and a widely publicized military parade. At the time, she was believed to be around ten years old, and Chinese bloggers nicknamed the round-cheeked girl “Golden Chubby” (金胖子) and “Golden Fourth Fatty” (金四胖).

In 2023 versus 2025
Now, however, the little girl has grown into a young lady. Many praised her style and grace, calling her a “little princess” (小公主). The hashtag “Kim Jong-un brought his daughter” (#金正恩把女儿金主爱带来了#) garnered over 190 million views on Weibo.
2 🎥 An Unexpected Face at Military Parade: US Pawnshop Owner Evan Kail
The American Evan Kail, a former pawnshop owner from Minnesota, was among the more unexpected faces at the parade. He appeared to be a semi-official guest, not watching the parade from Tiananmen Square but instead joining hundreds of locals to view it via livestream at the Temple of Heaven, where he was surrounded by cameras and media—making his attendance part of the broader media circus surrounding the military parade (#埃文凯尔天坛观看阅兵直播#).
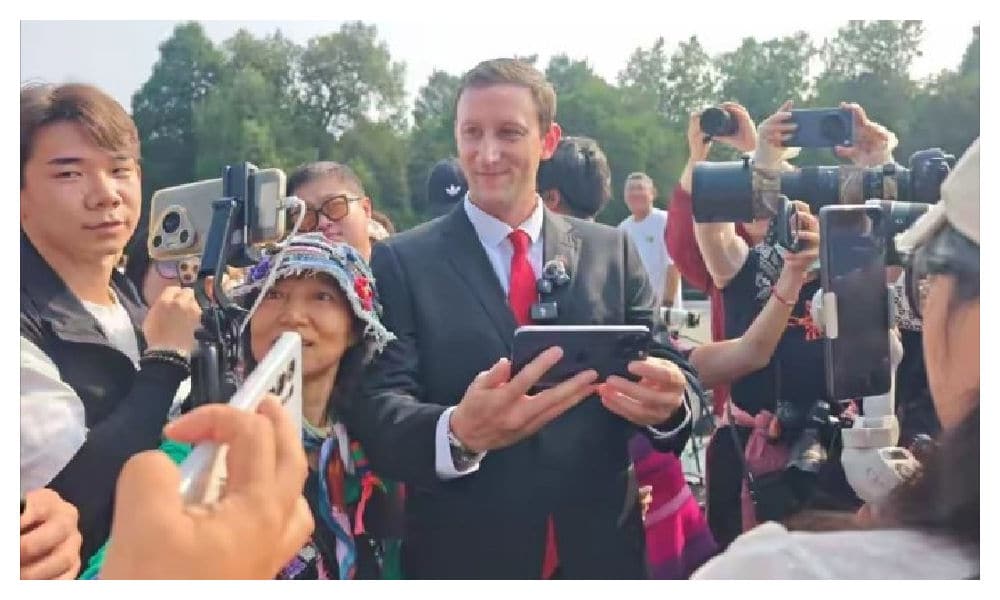

Kail first went trending in 2022, when he posted a video asking for help after coming across an old war photo album he believed contained rare and previously unseen images of the Nanjing Massacre. He eventually donated the album to China. Although the book reportedly turned out not to contain photos of Nanjing but rather of Shanghai (with some images likely being mass-produced souvenir photos—and the authenticity of the album not really being the focus here), Kail is still well respected in China for bringing international attention to the atrocities of Nanjing. He recently published a book in China, and his story has been widely promoted by Chinese state media outlets.
3🏅 Parade Soldiers’ Sunburn Tan Lines Praised as “Special Medals”
Some of the post-parade “afterglow” discussions on social media focused on videos showing soldiers returning from the September 3 parade. They were easily recognizable at train stations and airports by the stark sun lines on their faces—caused by long hours of outdoor training and marching while wearing helmets with chin straps (see videos).

The “special medal” sun lines
Netizens called the marks a “special medal” (特殊的勋章), and the clips of soldiers returning home with their sunburnt faces also added a more vulnerable and human touch to those perfect military formations.
4 🤐 Man Detained Over “Parade-Insulting Comments”
It wasn’t all roses online during the military parade—although most netizens probably wouldn’t have noticed due to strict censorship. Some people were punished for expressing online criticism. One 47-year-old man surnamed Meng (孟) from Hubei was turned into a warning for others and was detained after posting “insulting” comments about the September 3 military parade on a livestream on WeChat. Another man from Tianjin saw his Weibo page blocked after he suggested that watching the parade is a shallow or fake form of patriotism—and it’s highly likely he was not the only one.
5 🚀 Military Model Toys Boom 175% in Sales Following Parade
Another post-parade effect: China has seen a surge in consumer interest in military-themed toys, from fighter jets to missiles and tanks. Starting on September 3, the military model category on Chinese e-commerce platform JD.com reported a 175% increase in sales.

6 🪖 The Next Military Parade
Thought this was it? Not quite. Chinese media are already stirring anticipation for future military parades with the hashtag “Looking Forward to the Next Military Parade” (#期待下次阅兵了#). While nothing has been confirmed, the next likely milestone years for large-scale parades are 2027 (the People’s Liberation Army’s 100th anniversary) and 2029 (the 80th anniversary of the founding of the People’s Republic of China). To be continued…
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe
Eye on Digital China is a reader-supported publication by
Manya Koetse (@manyapan) and powered by What’s on Weibo.
It offers independent analysis of China’s online culture, media, and social trends.
To receive the newsletter and support this work, consider
becoming a paid subscriber.

Get in touch
Have a tip, story lead, or book recommendation? Interested in contributing? For ideas, suggestions, or just a quick hello, reach out here.

Trump, Taiwan & The Three-Body Problem: How Chinese Social Media Frames the US Strike on Venezuela

China’s 2025 Year in Review in 12 Phrases

China’s 10 Biggest Social Media Stories of 2025

Why Were 100,000 Pregnant Women’s Blood Samples Smuggled Out of China?

When an Entertainment Scandal Gets Political: How Wong Kar-wai Survived a Nationalist Storm

From Nobel Farewell to ‘VIP Toilets’: What’s Trending in China

China Trend Watch: Japan Tensions, Nexperia Fallout, Yunnan’s ‘Wild Child,’ & “Modern Opium”

Eye on Digital China: How Chinese Social Media Evolved from the Blog Era to the AI-driven Age

From Tents to ‘Tangping Travel”: New Travel Trends among Young Chinese

Signals: Hasan Piker’s China Trip & the Unexpected Journey of a Chinese School Uniform to Angola
Popular Reads
-

 China Arts & Entertainment6 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment6 months agoHidden Cameras and Taboo Topics: The Many Layers of the “Nanjing Sister Hong” Scandal
-

 China Insight8 months ago
China Insight8 months agoUnderstanding the Dr. Xiao Medical Scandal
-

 China Digital12 months ago
China Digital12 months ago“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained
-

 China Insight5 months ago
China Insight5 months ago“Jiangyou Bullying Incident”: From Online Outrage to Offline Protest



