China Insight
China’s Celebrity Diplomats: The Online Fan Culture Surrounding Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Wang Wenbin
The fan culture surrounding Wang Wenbin comes at a time when China’s ‘diplomat dream team’ already has a steady fanbase on social media.
Published
2 years agoon

PREMIUM CONTENT | ARCHIVE
From TikTok fan videos to Weibo super topics – there’s a lively fan culture surrounding China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Wang Wenbin. He is not the only ‘celebrity spokesperson’ on Chinese social media. Fans see China’s diplomats as national heroes and online idols.
In December of 2022, Wang Wenbin, top diplomat and the 32nd spokesperson for China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, was spotted out and about at Huangshan Mountain by Chinese netizens.
Soon, videos of Wang spread on Weibo and Douyin, where many people expressed excitement about seeing the top diplomat at the popular tourist spot and outside of the usual formal setting.
Wang Wenbing (汪文斌, b. 1971) is the Deputy Director of the Foreign Ministry Information Department of China. He studied at China’s Foreign Affairs University, majoring in French and economics, and has been working for China’s Foreign Ministry since 1993. Wang previously also took up the post as ambassador in Tunisia from 2018 to 2020.
Wang was in Huangshan, Anhui, to attend a visit of various international VIP guests from the IMF, World Bank, OECD, etc. on the occasion of the Seventh “1 6” Roundtable, which convened in the province of Anhui. Wang Wenbin originally is from Xindu village in Tongcheng, Anhui.
The fact that Wang was spotted in Anhui at that time was noteworthy. It was the first time since Covid that various Chinese officials welcomed and entertained international guests, marking an end to China’s zero-Covid era; and it was all taking place in Wang’s home province, where he is also known as “Anhui’s pride.”
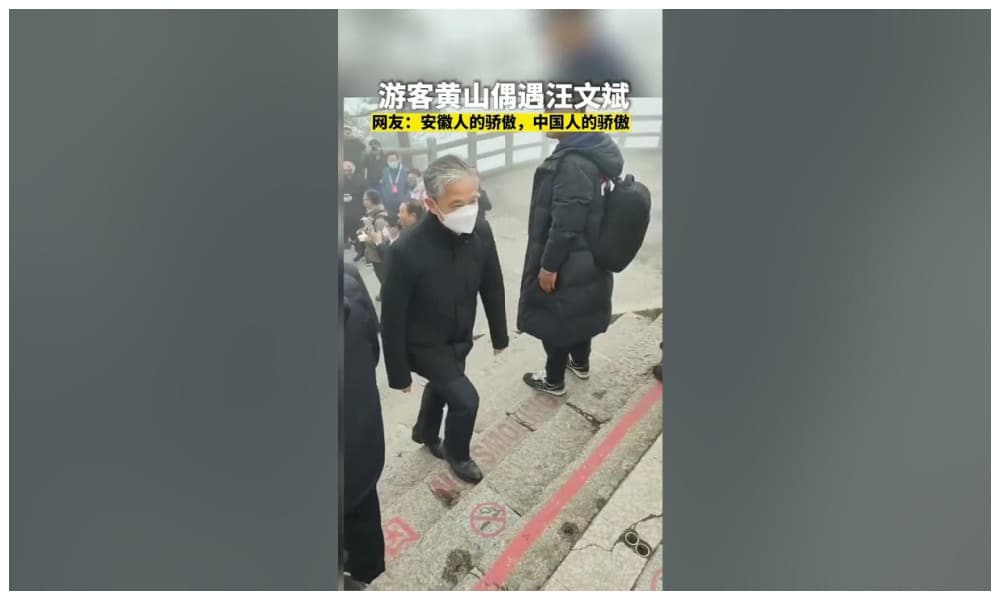

Wang Wenbin, top diplomat and spokesperson for China's MFA, was out and about in Anhui, and many people were happy to see him IRL and posted their videos of him on social media,calling him “the pride of Anhui, the pride of China.”
The 2022 excitement on Chinese social media surrounding the new Wang Wenbin videos went far beyond ‘Anhui’s pride’ alone; it showed the wider popularity of the top official on Chinese social media and signaled a broader trend of Chinese diplomats becoming online celebrities.
From fan videos on Douyin (TikTok) and Bilibili to discussion threads on Zhihu, Chinese diplomats have become idolized on social media over the past few years. Besides all the fan accounts on various Chinese social media platforms, Wang Wenbin also has dedicated ‘super topic’ communities on Weibo, which are forums focused on particular topics or celebrities.
There is the “Wang Wenbin Super Topic” page and also the “Wang Wenbing Exchange” (汪文斌交流) and the Wang Wenbin’s Bin’s Sweets” forum (汪文斌的斌糖). These public online forums contain thousands of posts dedicated to Wang.
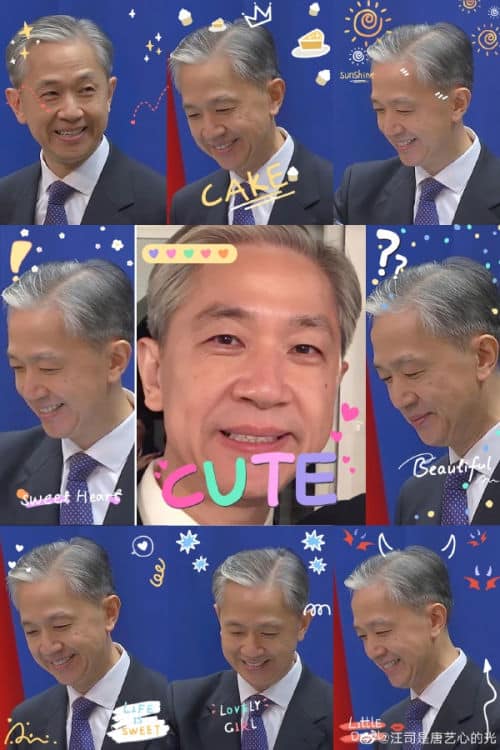
One of the supertopic forums on Weibo dedicated to Wang Wenbin.
The Wang Wenbin supertopic pages are all about content featuring Wang in his role as the spokesperson of the Foreign Ministry, replying to various questions during regular press conferences. Netizens are creative in editing images of Wang, adding quotes or drawings, and they make special fan videos.
Some of these videos have added texts or special effects, showing Wang Wenbin surrounded by sparkles and floating hearts as a sign of affection. Commenters praise Wang for being “so simple, so assertive,” while others complement the diplomat on being so “hard-working,” “concise and comprehensive.”

Wang Wenbin ‘fan art’ on one of the supertopic pages.
There are also those who praise Wang’s looks and expressions, saying his facial features are “handsome,” “cute,” “adorable,” and saying that ‘Uncle Wang’ is just too “cool.”
At a time of growing U.S.-China tensions and recurring international hot issues including China’s stance on the war in Ukraine and the Taiwan question, Wang Wenbin and his immediate colleagues Mao Ning (毛宁) and Hua Chunying (华春莹) are featured more prominently on social media by official media accounts that highlight answers given during the regular Foreign Ministry press conferences, which are held five times per week.
As Wang Wenbin is given greater visibility on Chinese social media by state media accounts, the online fan communities dedicated to Wang grow more lively as they have more material to express their enthusiasm about the Foreign Ministry spokesperson.
DIPLOMAT DREAM TEAM
Chinese Diplomats Becoming Celebrities
Wang is not the first Chinese top official or diplomat to become an online celebrity. Former Foreign Ministry spokesperson Zhao Lijian (赵立坚) previously also became very popular among Chinese netizens.
Zhao rose to popularity in 2020, the year he started his job as the spokesperson for the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA), and many netizens loved him for his “disarming smile” and because of his demeanor, as many joked Zhao often looked like he could not wait to get off work.
An online meme culture developed around Zhao, who often repeated certain phrases or expressions during press conferences. Among them was the expression “shìmù yǐdài” (拭目以待), to eagerly wait for something to happen, literally meaning “to wipe one’s eyes and wait” (e.g. he used it in 2022 in the context of China waiting to see if Pelosi would actually dare to visit Taiwan or not). Phrases such as these became widely known and were used in affectionate online jokes about Zhao.

Shìmù yǐdài 拭目以待, to eagerly wait for something to happen, literally “to wipe one’s eyes and wait,” is one of Zhao Lijian’s famous phrases.
Even though Zhao was moved from his position as spokesperson and transferred to the Boundary and Ocean Affairs department earlier in 2023, there are still online communities dedicated to him where new posts with Zhao-related images, gifs, and videos keep flooding in.
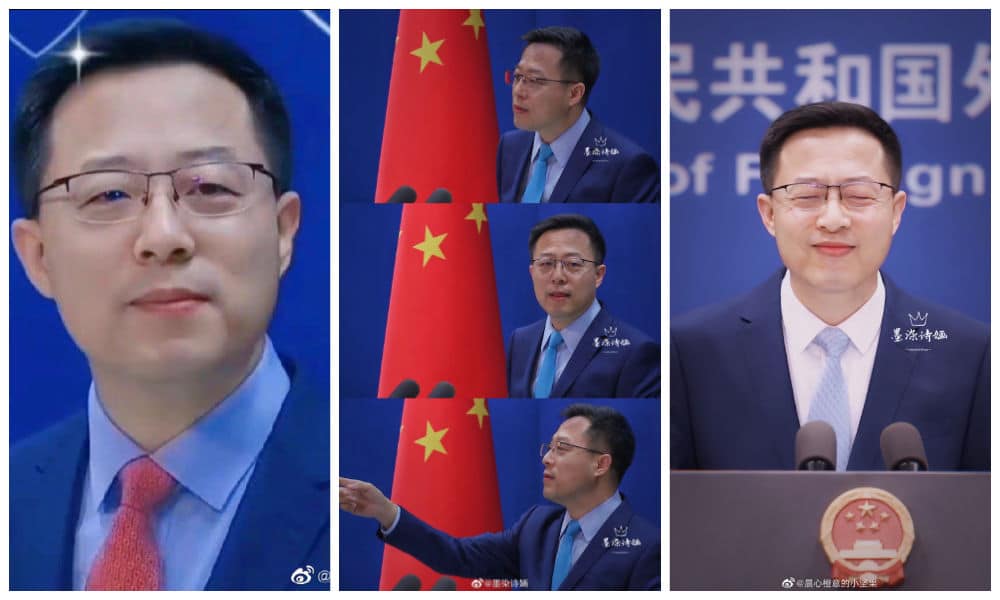

Even though Zhao has left his post as spokesperson, the online communities dedicated to him are still lively.
Before Zhao’s rise to fame, China’s MFA spokespeople and other diplomats had already gained an online fanbase. Around 2017, the concept of China’s “diplomat dream team” (外交天团) started to be used more frequently by Chinese media and social media users.
This was around the same time when Hong Lei (洪磊), Geng Shuang (耿爽), Lu Kang (陆慷), and Hua Chunying (华春莹) served as spokespeople for the Foreign Ministry and when their remarks on diplomatic events carried a more assertive and confrontational tone of voice facing heightening tensions with the U.S. over trade, the South China Sea, and human rights.
For example, China Daily ran an article about the “wonderful responses” from China’s diplomat dream team in 2017 (link) and they ran another similar one in 2018 (link).

An early example of China’s “Diplomat Dream Team.” Left: China’s top diplomat Wang Yi, former spokesperson Hong Lei, spokesperson Hua Chunying, diplomat Lu Kang, and Minister of Foreign Affairs Qin Gang.
But it was not until 2020 when China’s top diplomats and the “spokesperson top team” (发言人天团) really garnered online attention as they were often featured in headlines and created a stir.
Not only was 2020 the year that ‘celebrity diplomat’ Zhao Lijian joined the spokesperson team, it was also a year of complex international developments including the Covid outbreak and worsening diplomatic relations between the U.S. and China driven by ‘eye for an eye’ strategies; one day after the Chinese consulate in Houston was forced to close, China also ordered the American consulate in Chengdu to shut its doors.
In July of 2020, Wang Wenbin joined the ‘top team’ of Chinese diplomats, which was praised online as China’s “strongest diplomatic mission.”

China’s “diplomat top team,” image via Zhihu blogger.
In 2021, the top-level US-China talks in Alaska further contributed to the social media frenzy surrounding China’s diplomatic corps. Foreign Minister Wang Yi, also nicknamed the ‘captain’ of the diplomatic team, traveled to Anchorage with Chinese top diplomat Yang Jiechi (杨洁篪) for the tough meeting. Before entering a session of the high-level talks, the diplomats were filmed walking together when Wang asked Yang if he had lunch, with Yang then answering: “Yes, I had instant noodles.”

‘Noodle gate’ blew up on Chinese socials, where many saw the incident as a sign of American inhospitality and rude treatment of the Chinese top diplomats. The incident also added to the popularity of Yang Jiechi and Wang Yi.
There are various reasons why Chinese diplomats and MFA representatives have become particularly popular over the past few years.
Some of the main causes related to the celebrity culture surrounding Chinese modern-day diplomats lies in (1) their new role in China’s (online) media environment, (2) the way they have become an example to ordinary people, and (3) the shift in Chinese diplomacy that has turned them into ‘wolf warrior’ heroes.
1. CHINESE DIPLOMATS & SOCIAL MEDIA
Chinese Diplomacy in the Age of Social Media
The growing fame of Chinese diplomats and spokespeople is very much an online phenomenon, and so their surge in popularity goes hand in hand with the rise of (China’s) social media.
The role of social media is crucial in three ways. First, Chinese official accounts and state media use social media as an important channel to spread official propaganda and narratives. Although China’s MFA spokespersons are meant to be the face of China to the world, their role is just important – and perhaps even more weighty – for the audiences at home as symbols of China’s foreign policies.
Second, social media is also increasingly used by Chinese diplomats individually as a platform to voice the stances they represent. In an article titled “China’s Internet Celebrity Diplomats” (2020), Christian Shepherd described how Zhao Lijian used social media to build “a personal brand that is rare for a Foreign Ministry spokesperson” as China’s most high-profile official on Twitter.
In our 2020 article about this topic, What’s on Weibo found that there was a significant surge in Chinese official accounts arriving on Twitter in 2019 and in early 2020. The first surge of Chinese diplomatic accounts happened in 2019 at the time of the Hong Kong Protests; a second peak in Chinese official accounts joining Twitter took place in the period of January to March 2020 during the international Covid-19 crisis.
At the time of writing, Zhao has over two million followers on Twitter (@zlj517). Zhao Lijian is also active on Weibo (@赵立坚个人微博), where he has over 8 million fans. Foreign Ministry spokesperson Hua Chunying is not active on Weibo, but she has two million followers on Twitter (@Hua Chunying 华春莹).
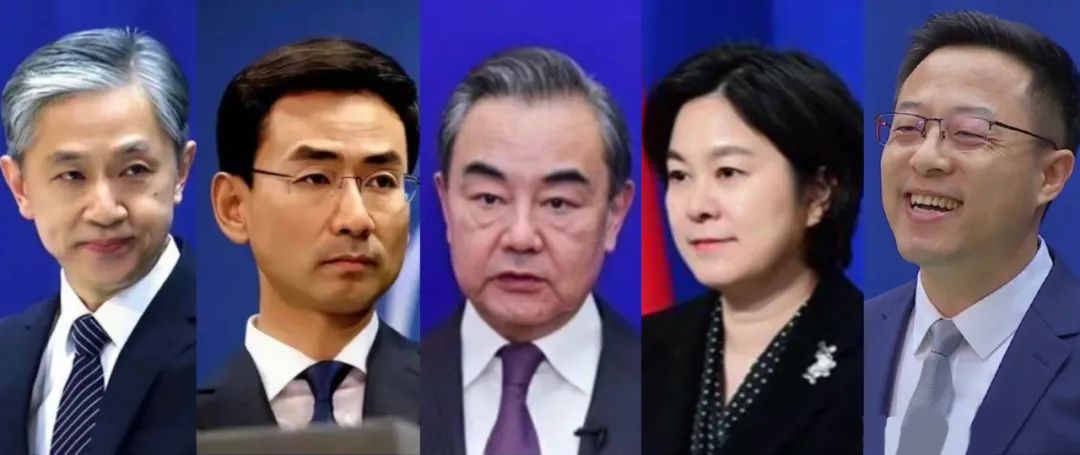

Wang Wenbin, Geng Shuang, Wang Yi, Hua Cunying, Zhao Lijian.
Third, social media platforms allow for communities to form around Chinese diplomats in a way that would be unthinkable in the pre-social media era.
There has been a lot of attention for celebrities taking on diplomatic roles, but less so for diplomats taking on celebrity roles. Studies about diplomats or politicians becoming internet celebrities often focus on those who are also active on social media themselves, making them more accessible and relatable.
But diplomats such as Wang Wenbin are an exception: Wang Wenbin does not have an official Twitter account, nor is he active on Weibo or any other popular social media platforms. Nevertheless, there are thriving online communities surrounding him that help bridge the divide between the top level diplomat and ordinary people, creating connections between diplomats and Chinese people in novel ways.
In the Chinese social media environment, the fan culture surrounding China’s top diplomats is fuelled by the dynamics of the official propaganda apparatus and state media campaigns disseminating hashtags and videos that underline the main messages of China’s Foreign Ministry. Although it often builds on official media content, the online fan culture itself is non-official and functions in similar ways as other idol fan communities do.
2. CHINESE DIPLOMATS & THE PEOPLE
The Person Behind the Diplomat
There is another dimension to the online interaction between netizens and the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokespersons and diplomats. They are not just being idolized, they are also being humanized.
Besides the more serious patriotic and nationalist videos, it is often the small flaws and funny interactions that go trending on social media and make China’s diplomats more likeable to the audience.
Fans of Wang Wenbin or Zhao Lijian like to create images or videos that highlight the moments in which the diplomats share a quick smile, make a little mistake, or are caught in a situation that is different from their usual role as spokesperson.
It might be as small as a strand of hair sticking out during a speech, a misunderstanding with a journalist, or how Wang Wenbin is fiddling with his translation headset during an international conference. These kind of moments are not highlighted to ridicule the diplomat; on the contrary, netizens treasure these moments in which diplomats become more likable and relatable.

Another way in which netizens like to catch a glimpse of the private person behind the public diplomat is by sharing old photos and getting to know more about them in their younger years.



Wang Wenbin in his younger years.
On Weibo, Bilibili, and Douyin, there are dozens of videos comparing photos of Chinese diplomats, including Wang, in their younger years versus now (e.g. 外交天团年轻的样子).
For many fans, Chinese diplomats also serve as an inspiration. “I love them, they’re my role models,” one Weibo blogger writes, posting photos of diplomats such as Wang Yi, Hua Chunying, Zhao Lijian, Hong Lei, Geng Shuang, and Lu Kang.
For many, Wang Wenbin especially is a role model because of his language skills. Wang speaks several foreign languages including English and French. He previously also attracted attention for sending out new year’s wishes in 11 different languages.
“I really like him because he encourages me to do well in my studies,” one fan account (@是汪叔和赵叔啊) writes.
3. CHINESE DIPLOMATS & THE WORLD
Wolf Warrior Heroes
The widespread admiration for Chinese diplomats and MFA spokespersons has various social, cultural, and historical reasons, and nationalism also plays a big role in this, as their growing online popularity is accompanied by the rise of so-called “wolf-warrior diplomacy” and the soaring cyber nationalism that comes with it.
The term “wolf warrior diplomacy” (战狼外交) became a buzzword for China’s diplomacy since around 2020 (Dai & Luqiu 2022). It is a reference to the highly successful Chinese blockbusters Wolf Warrior (战狼, 2015) and Wolf Warrior II (战狼2, 2017), and basically means a style of diplomacy that uses a much harsher and more confrontational rhetoric – which poses a contrast to a more restrained and softer tactic in foreign diplomacy.
Hua Chunying and Zhao Lijian were among the most visible wolf warrior diplomats as they were the main MFA spokespersons in early 2020 and were both active on Twitter, where they also actively confronted external criticism of China.
Zhao Lijian also became known for tweeting out a photoshopped image of an Australian soldier murdering a child, alluding to a report on unlawful killings of Afghan civilians and prisoners by Australian troops. His controversial post led to Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison demanding an apology from China (read more about this kind of political visuals in our article here).
In a 2022 article titled “Why Have Chinese Diplomats Become So Aggressive?,” author Nien-chung Chang-Liao argues that China’s more aggressive style of diplomacy is not just meant to persuade foreign audiences to accept Chinese narratives in international relations, but could also be viewed as a way to appeal to nationalist attitudes at home, while also demonstrating loyalty to the Party and Xi Jinping – who emphasizes the need for confidence in China’s new era.
The approach seems fruitful: over 70% of respondents to a survey by Global Times allegedly indicated that they thought a ‘wolf-warrior’ style diplomacy improves China’s global image. Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Hua Chunying also indicated that she had no issue with the ‘wolf warrior’ label and even embraces it (Chang-liao 2022, 179-181).
While Zhao Lijian was known as the real ‘wolf warrior diplomat,’ Wang Wenbin’s style is perceived as being more “calm,” “scholarly,” and “refined,” even though he he still seen as critical and assertive.
Recently, it was Wang Wenbin who slammed U.S. claims that China might arm Russian troops in the war in Ukraine, saying “it is the United States and not China that is endlessly shipping weapons to the battlefield.” Wang also called the shootdown of the alleged Chinese spy balloon “100 percent hysteria,” and he recently urged the United States to give up its “hegemonic” approaches to international affairs.
For many Wang Wenbin fans, this style of assertive yet ‘refined’ foreign policy strikes a chord, as they support how Wang shapes China’s image abroad: “It’s the perfect interpretation of being a great and elegant great power.”

“Today’s problems are complex and manifold, but Uncle [Wang] is organized and clear and answers with a smile. From beginning to end, I always admire him,” one comment says.
One Weibo blogger writes to Wang: “You’re so busy, you must be tired. I hope you can also take some time to rest. I just wish you all the best.”
Another fan writes: “Uncle, you work so hard, you are not afraid of facing the ‘hail of bullets’ fired at you by foreign media in the blue room, you defend our country, you are our hero!”
By Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
References
Chang-Liao, Nien-chung. 2022. “Why Have Chinese Diplomats Become So
Aggressive?” Survival, 64:1: 179-190.
Dai, Yaoyao, and Luwei Rose Luqiu. 2022. “Wolf Warriors and Diplomacy in the New Era.” China Review 22 (2): 253-283.
Shepherd, Christian. 2020. “China’s Internet Celebrity Diplomats.” Australian Financial Review, Dec. 10, page 27.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China Insight
Understanding the Dr. Xiao Medical Scandal
Behind the scandal at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital: the doctor, the trainee, and the letter that took over the Chinese internet.
Published
2 months agoon
May 5, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Dear Reader,
A controversy that has been brewing recently has completely taken over the Chinese internet over the past week, becoming the biggest public scandal on Chinese social media in 2025 so far.
At the center of it all is Dr. Xiao Fei, a well-known thoracic surgeon at the prestigious China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing who has come under fire in the medical world following revelations that he cheated on his wife with a head nurse, a trainee, and others.
This may sound like a Chinese version of an episode of Grey’s Anatomy, but it goes far beyond messy relationships alone and reveals serious social concerns and exposes deeper systemic problems involving academic and medical institutions.
To understand how this unfolded, I’ll walk you through the main people involved, the events that led up to it, and the key issues that turned this medical controversy into a nationwide talking point.
Main People Involved
👨⚕️ Xiao Fei (肖飞): associate chief thoracic surgeon at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital (中日友好医院) in Beijing, with a PhD in surgery from Peking University’s medicine department. He had worked at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital since 2012, rising from resident doctor to associate chief surgeon, and was selected for the hospital’s “Elite Program” (菁英计划). He also served as a graduate advisor at Peking Union Medical College (北京协和医学院). A former Communist Party member, he was awarded the title of “Outstanding Communist Party Member” (优秀共产党员) at the hospital in 2020. Xiao is the central figure in the scandal involving multiple affairs and professional misconduct. Born in 1986 and a native of Shaanxi.
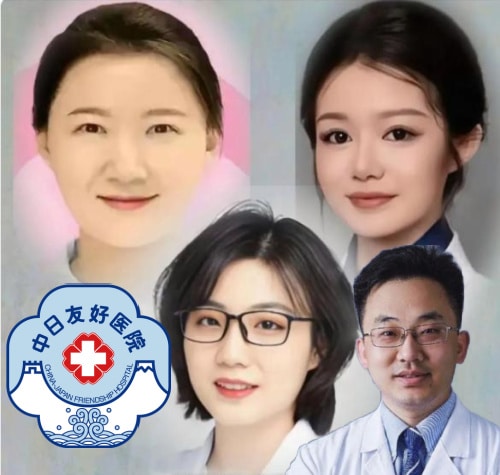

The main people involved: Gu Xiaoya (lower left) and Xiao Fei, and Shi Yuhui (top left) and Dong Xiying.
👩⚕️ Gu Xiaoya (谷潇雅): associate chief ophthalmologist at Beijing Hospital. Legal wife of Xiao Fei and mother to their daughter. She also holds a PhD in clinical medicine from Peking University. She is the “whistleblower” who exposed the scandal through a detailed letter and supporting material backing up her claims. Native Beijinger.
👩⚕️ Shi Yuhui (石玉慧): head nurse of the thoracic surgery department at China-Japan Friendship Hospital. She began an affair with Xiao Fei in early 2019—both were married at the time. During their relationship, she became pregnant twice and miscarried both times. Despite interventions of her own husband and Xiao’s wife, she maintained contact with Xiao and allegedly harassed Gu Xiaoya through 2024. Born in 1981.
👩⚕️ Dong Xiying (董袭莹): former urology resident at China-Japan Friendship Hospital. Studied economics at Barnard College in New York (graduated in 2019), then earned her medical doctorate through the “4+4” clinical medicine program at Peking Union Medical College (北京协和医学院). Currently serves as a resident physician at the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. She comes from a privileged background: her father is an executive at a state-owned enterprise; her mother is a vice president at the University of Science and Technology Beijing (北京科技大学). She began a relationship with Xiao in 2024 and is reportedly pregnant with his child, due in June.
From One Letter to Nationwide Concern
This story first started to gain traction within various circles on Chinese social media since around April 21, when a long letter written by Gu Xiaoya (谷潇雅), the legal wife of the renowned surgeon Xiao Fei, was widely circulated, from WeChat to Weibo and Zhihu and beyond.
Soon, Chinese media outlets picked up the story, causing it to snowball and going trending on social media. The first time it trended on Weibo was on Sunday, April 27.
✉️ The letter that started it all
Gu’s letter, dated April 18, 2025, was addressed to the Disciplinary Committee at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing. In the letter and attached materials, Gu Xiaoya details how her husband had been cheating on her since 2016 — including exact dates, locations, and chat records to support her claims.

First part of Gu’s letter
She writes that she wanted to report her husband’s extramarital affairs, as well as his apparent intent to have a child out of wedlock, because she believed his behavior “seriously violated social morality and professional ethics, and had a profoundly negative impact on both the hospital and the education of medical students.”
Gu explains that she first discovered Xiao Fei’s infidelity when she checked his phone in October 2019 and uncovered his secret affair with Shi Yuhui (石玉慧), a head nurse in his department, with whom he had been involved since at least February of that year. The two would also stay in hotel rooms together during trips, some work-related. According to Gu — and backed by hospital records — Shi became pregnant twice in 2019, both pregnancies ending in miscarriages.
Gu says that efforts to stop the affair were fruitless, even when Shi’s own husband was involved in trying to end the affair, and that Shi Yuhui continued to harass Gu for years afterward.
However, in June 2024, while on duty in the operating room, Xiao began another new affair — this time with Dong Xiying, a urology resident physician. Their relationship developed quickly. According to her medical training schedule, Dong was supposed to move on to another department in July 2024, but Xiao allegedly intervened to ensure she remained in thoracic surgery.
During this period, Gu claims that during a surgery on July 5, 2024, Xiao Fei had a dispute in the operating room involving his affair partner, Dong Xiying, and a nurse. As a result, Xiao left the operating room with Dong (allegedly to comfort her), even though a patient had already been anesthetized and was lying on the operating table. They were gone for 40 minutes, during which the anesthetist and nurse were left to manage the patient alone.
Gu mentions that medical staff involved in or aware of the operation later raised concerns in internal group chats or reported the incident directly to the hospital’s education or supervisory offices.

In a screenshot of the Surgical Anesthesia Department Nurses Group, one nurse said:
💬 “First thing in the morning, Xiao Fei was chaotic – he completely lost his temper on a phone call, tore off his surgical gown, and left the operating room. He called Zhang Ying (张颖) angrily saying if the circulating nurse wasn’t replaced, he would cancel the surgery. He then unfastened the scrubs of the trainee doctor Dong, and left with her. The surgery was left undone! They had just connected the electrosurgical unit when Xiao left with the trainee doctor, leaving the anesthetized patient lying in the OR. There is no doctor present during surgical time!”
In October 2024, Xiao filed for divorce. Gu later discovered that he was already living with Dong Xiying, who had become pregnant the previous month.
Gu also learned that Xiao had been involved in other affairs dating back to 2016, when Gu was pregnant with their daughter, and that he would stay at different hotels with various female members of staff and nurses.
She claims she initially hoped to avoid legal action, but Xiao’s threats to seek full custody of their daughter pushed her to expose his affairs and seek justice.
💥 Far-reaching consequences
On April 27 – the day this topic dropped in Weibo’s top trending lists – the China-Japan Friendship Hospital issued an official statement to respond to the controversy. The hospital confirmed that the allegations involving their staff member Dr. Xiao were basically true (#中日友好医院通报肖某问题属实#). They suspended Xiao while investigating the matter.
Soon, one statement after another, news reports and hashtags followed. Dr. Xiao was expelled from the Communist Party, his profile was removed from the hospital’s website, and his employment was terminated.
Around April 30, public attention began shifting toward Dong Xiying (董袭莹) and her academic credentials. The young physician, who graduated from Barnard College in New York with a degree in economics, entered the “4+4” MD/PhD medical training program at Peking Union Medical College (PUMC) in 2019. Within a few years, she was praised as a model student within the 4+4 track (non-medical undergraduate + 4 years medical training).
Netizens soon discovered that PUMC had been quietly removing articles from its website related to Dong. Her PhD thesis disappeared from public databases, and her name was edited out of the President’s Commencement Address. As more details about her privileged background surfaced, growing doubts emerged about her qualifications and how she gained admission to the program.
It is rumored that Dong has now left China for the US.
The hospital has not yet released details on how – and if – Shi Yuhui will be dealt with.
On May 1st, China’s National Health Commission announced an official investigation into the matter, looking into the allegations against Xiao and also reviewing the academic and work history of Dong Xiying.
The scandal has caused something of an earthquake — not just within medical circles, but also in academic ones, and across the internet at large, where netizens are particularly concerned about the broader social issues this story touches on.

Some netizens made mindmaps of the scandal to explain who the main persons nvolved are and what the key issues are. Shared by Qiao Kaiwan on Weibo.
There are many layers to this story, and perhaps more yet to be uncovered. One popular Weibo blogger (Qiao Kaiwan @乔凯文) commented about the scandal, and the role played by Dong Xiying:
💬 “(..) it’s rare for a central figure in a single case to touch on five major socially sensitive issues all at once: educational fairness (教育公平), doctor-patient trust (医患信任), marital fidelity (婚姻忠诚), class solidification [lack of upward mobility] (阶层固化), and academic corruption (学术腐败)…”
At its core, public concern centers around various major themes that are all tied to deeply rooted cultural values or long-standing social issues. Since there is some overlap within these topics, I’ll focus on three main values vs concerns here.
1. Fairness in Education & Corruption in Academia
Fairness and corruption within China’s education system are recurring hot social topics. Education is widely regarded as the main path to upward mobility, which makes the system fiercely competitive—starting as early as kindergarten. The pressure to succeed in the gaokao college entrance exams begins years before the tests are actually taken.
Most Chinese parents are willing to invest heavily in their children’s education, driven by the fear that their kids will fall behind. This intense competition is reflected in the popularity of the term nèijuǎn (内卷), “involution,” which describes a situation where students (or professionals) must overwork and go above and beyond just to keep up with peers. Everyone ends up standing on their toes to keep pushing the bar—yet no one moves forward (read more about this here).
Especially in such a competitive system, where entire families invest so much time, energy, and resources into helping younger generations succeed, academic corruption is a sensitive issue that affects trust in the entire system and exacerbates common people’s disillusionment with meritocracy. Yet academic corruption—ranging from plagiarism and data manipulation to power abuse and favoritism—has been a widespread and increasingly discussed problem in mainland China since the 1990s.
Central to the current controversy surrounding Xiao Fei and Dong Xiying is the “4+4 program,” an experimental and relatively new medical education model inspired by the American system. Unlike China’s traditional path (five years of undergraduate study in medicine followed by three years of graduate training), this program allows students to complete four years of non-medical undergraduate education, followed by four years of medical training. It’s a fast track in which students can begin practicing medicine after just one year of residency instead of three. It was originally intended to create opportunities for talented individuals who decide to pursue medicine later on in their academic careers.
It sounds good in theory, but many feel that the program—with its high undergraduate standards and required letters of recommendation—essentially serves as a “backdoor” into medicine for the elite. Only a small number of applicants are admitted: the quota for both the 2025 and 2026 cohorts at PUCM is just 45 students.
Online, many are questioning whether Dong really met the proper standards for admission. How could someone with an economics degree from a liberal arts college become a so-called “medical talent” in just a few years? In contrast, people have pointed to Chen Ruyue (陈如月), a finance graduate from the prestigious Peking University who was also passionate about medicine and applied for the same program, but was rejected. Netizens wonder, “Where is the fairness in medical education?”
Many suspect Dong benefited from privileged access via family connections—her mother Mi Zhenli (米振莉) is a vice president at the University of Science and Technology Beijing (USTB), and her father Dong Xiaohui (董晓辉) is a senior executive at a state-owned enterprise.
Suspicions deepened when people discovered that Dong’s PhD supervisor, the orthopedic academician Qiu Guixing (邱贵兴), had no connection to her research field. Her clinical trajectory involves many different areas, from gynecological imaging and internal medicine to thoracic surgery and urology, a seemingly patchy path that raised further questions because this “magical and legendary swift crossovers between medical fields”of Dong could supposedly only mean that she is either an “unprecedented genius” or that her stardom medical rise was faciliated by “countless invisible hands” (comments by popular Weibo blogger @庚白星君).
There’s more that’s raised eyebrows.
Dong’s academic publishing history shows that she authored eleven research papers over a period of three years across various disciplines, from orthopedics to gynecology and urology. There are doubts over the exact role played by Dong in some of these studies. Dong was still a resident at the lowest level with relatively little experience, yet was able to publish bladder cancer diagnosis and treatment guidelines—she was listed as the first author on three English-language papers about bladder cancer clinical guidelines. Some allege that her contributions, like translating Chinese guidelines to English, do not merit a first-author mention.
There are also concerns about plagiarism. Claims have emerged that Dong’s 2023 doctoral thesis shows significant similarities to an invention patent submitted in 2022 by several professors and Zhao Jihuai (赵基淮), a hearing-impaired graduate student from the University of Science and Technology Beijing (USTB), who is mentored by Professor Ban Xiaojuan (班晓娟), Dong’s aunt.
It also does not help that PUMC, once promoting Dong as a success story, has now deleted related articles from its site and edited her name out of the President’s Commencement Address that mentioned her.
Concerns about Dong’s academic background and the apparent bending of rules inevitably also cast a shadow over the medical institutions where she trained. According to Gu’s letter, Dong was expected to rotate through various departments as part of her residency. However, instead of moving on to spinal surgery after completing her thoracic surgery rotation, she was allowed to remain—allegedly due to personal connections and pressure from Dr. Xiao—even though the hospital’s education team had initially objected.
If true, this could not only point to routine abuses of power within the medical training systems, but also creates unease over how qualified doctors such a Dong actually are, which also affects the trust patients place in hospitals.
2. Trust Between Patients and Doctors & Medical Negligence
The main incident in this scandal that has sparked widespread controversy is the moment when Dr. Xiao reportedly left the operating room together with Dong for an entire 40 minutes during a surgery, leaving the anesthetized patient on the table.
The idea that even a chief doctor such as Xiao can violate medical ethics by leaving a surgery mid-procedure for 40 minutes deepens fears about medical professionalism.
Trust between patients and doctors and worries over medical negligence are recurring topics on Chinese social media. There have been dozens of incidents that previously went viral showing how some doctors abuse or scam patients, or put commercial interests above the health of their patients. Some stories that gained nationwide attention in previous years include an anesthesiologist from Shandong who live-streamed while a patient was undergoing gynecological surgery, or a young patient who was asked to pay more money while already undergoing a surgery.
Such distrust in doctor-patient relations flared up again in light of this incident, in which a sedated patient was, against all protocol, left on the operating table mid-surgery—allegedly due only to a quarrel between another nurse and Xiao’s mistress that made him angry.
Xiao has given two media interviews in response to the allegations. Regarding the claim that he stormed out of the operating room with Dong, leaving a patient behind, he reportedly stated that he was not gone for 40 minutes, but for a maximum of 20 minutes to calm down after a dispute.
Although Xiao has admitted to inappropriate relationships with a head nurse and a training resident physician (refuting allegations of affairs with other nurses or members of staff), he firmly denied more serious allegations involving medical safety.
In an interview with Jiupai News, he said:
💬 “I have clear supporting evidence that around 9 AM, I left the operating table after an argument. I left to coordinate, not to ‘demand.’ I coordinated with a senior staff member in the operating room about whether it would be possible to replace the circulating nurse under these circumstances. Then I went upstairs to measure my blood pressure, drink some water, and take some blood-pressure medication. After calming down a bit, I immediately returned to the OR. I believe this was entirely reasonable. In fact, I was precisely concerned about the patient’s safety. Before I left, I gave specific instructions to the nurse at the table. Our anesthesiologist was present as well, and their professional competence is fully sufficient to ensure the safety of a patient who had not yet undergone any surgical procedure.”
Regardless of the circumstances, the fact that Xiao Fei left an anesthetized patient during surgery is not only one of the reasons that cost him his job—it’s also one of the reasons why he has temporarily become the most hated doctor in China among the public.
The fact that he tried to defend his actions only seemed to aggravate public opinion against him: “So he thinks 20 minutes is a short time to leave a surgery?” some say; “completely outrageous,” “a serious threat to patient safety.”
“Xiao is morally bankrupt,” another commenter wrote: “He is still trying to make excuses for leaving the OR mid-surgery. As chief surgeon he seriously violated his professional values. Not only doesn’t he reflect, he doesn’t even have remorse.”
3. Moral Integrity & Marital Infidelity
In the end, this entire scandal started because Xiao was caught cheating with multiple women at his workplace. That alone is seen as a lack of moral integrity and a violation of professional ethics, which are also tied to corruption and power abuse.
In China’s corruption cases, extramarital affairs often serve as red flags — not every official with a mistress is corrupt, but most corrupt officials do have one.
One of the most high-profile public cases involving an extramarital affair was in 2023, when Chinese official Hu Jiyong (胡继勇), who held a high-ranking position at PetroChina, was caught walking hand in hand with his mistress by a TikTok photographer during a work trip to Chengdu.
Chinese state media wrote that “being a Communist Party of China member, Hu has moral obligations, which he transgressed by having an alleged extramarital affair.”
Hu Jiyong was dismissed from his positions as executive director, general manager, and Party Committee secretary. His mistress, coincidentally also a Miss Dong, also lost her job at the company. For Xiao Fei and Dong Xiying, the exposure of their illicit affair might have even more serious repercussions.
In the end, Gu’s letter had a major impact on everyone involved. Xiao’s actions not only carried serious consequences for Gu and their young daughter, but also ended his career, affected both Dong Xiying and Shi Yuhui and their families, and damaged the reputations of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and PUMC.
The entire scandal is not really about Xiao or Dong anymore. It is about the entire system around them that facilitated their affair and made it possible to bend the rules and engage in unethical and unprofessional behavior.
On May 5, Chinese political commentator and columnist Sima Pingbang (@司马平邦), who has 7 million followers on Weibo, wrote: “What I think of the Xiao Fei and Dong Xiying incident: The academic authorities behind them must be brought down!”
Meanwhile, despite the serious concerns behind the scandal, plenty of people are also just enjoying the online spectacle. Some performers are even incorporating the story of Xiao and Dong into their comedy shows. It’s not Grey’s Anatomy — it’s actually much more dramatic, and hasn’t even reached its final episode yet…
Thanks to Miranda Barnes and Ruixin Zhang for their input and contributions to this newsletter.
Also, welcome to the new premium members of What’s on Weibo! Please know that I’m always open to suggestions—if you spot any noteworthy trends you’d like to learn more about, don’t hesitate to reach out. I always enjoy receiving your emails. It’s great to see the subscriber community growing.
That said, What’s on Weibo still needs to expand its member base to cover all costs and keep subscription prices as they are. If you enjoy one of our articles, this newsletter, or the site in general, please spread the word (or consider gifting a subscription to someone who might love it too)!
Best,
Manya
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Thanks to Miranda Barnes and Ruixin Zhang for their input and contributions to this newsletter.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Insight
China Is Not Censoring Its Social Media to Please the West
Russian recruitment ads, China’s censorship, and how Western media sometimes guess Beijing’s stance by reading between the wrong lines.
Published
3 months agoon
April 27, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Dear Reader,
Recently, news broke that two Chinese nationals were captured by Ukrainian forces while fighting on the Russian side in eastern Ukraine. Their capture quickly made international headlines, not just because of their nationality but also because of how they allegedly got there.
As I worked on an article about this case, I kept running into something noteworthy: the recurring assumption that if something is visible on Chinese social media, it must have the government’s tacit approval.
Here, I’ll briefly get into more about the story and why that assumption misses the mark.
Russian Army Ads on Chinese Social Media
Earlier this month, Ukrainian President Zelensky announced that two Chinese nationals fighting for Russia on Ukrainian soil were captured by Ukrainian troops. On Monday, April 14, the two Chinese men – handcuffed and guarded – spoke during a press conference in Kyiv. They were identified as the 33-year old Wang Guangjun (王广军) from Henan and the 26-year old Zhang Renbo (张仁波) from Jiangxi.

Zhang and Wang during the press conference, image via Weibo user @边沁-Bentham.
Zelensky has claimed that at least “several hundred” more Chinese citizens are fighting on Russia’s side in Ukraine. On April 9, he stated that Ukraine had obtained the surnames and passport details of 155 Chinese mercenaries recruited by Russia through social media platforms.
The Kyiv Independent reported that both Wang and Zhang stated that they were not sent to the war by the Chinese government, and joined of their own free will.
While Wang claims he joined the Russian army after seeing an advertisement on Chinese social media, Zhang said he came to Russia in December for construction work and was recruited for military service there. Both men joined for monetary gain. Wang said he was promised to make $2,000-$3,000 per month, but that his phone and bank card were later taken from him.
The news that Chinese nationals were captured while fighting on the Russian side made international headlines — particularly the claim that Russia is recruiting Chinese mercenaries through social media, which has become a focal point in various media reports, such as this one by The Guardian, this article by ABC News, and this video report by RFE.
Some reports, including the latter, suggest a link between online recruitment ads circulating on Chinese social media, Beijing’s stance toward Russia, and the fact that these ads have not been censored. Zelensky himself stated that Russia has been recruiting Chinese citizens via social media, and that “official Beijing knows about this.”
RFE writes:
📰✍️ “Zelenskyy himself has stopped short of saying the Chinese government authorized the mercenaries’ involvement in Ukraine, but he has accused Beijing of turning a blind eye to Russia’s recruitment of its citizens.
And there’s some indication Chinese authorities haven’t made a concerted effort to stop them.
The Chinese Internet is heavily censored, and social media is closely monitored and controlled, yet many of these recruitment posts — some of which are months old — are still online and being shared.”
Kafkaesque Territory
Over recent years, I have noticed a recurring assumption in English-language media coverage when it comes to interpreting China’s stance on certain issues — from international conflicts to social issues: if something is not censored, it is assumed to be officially condoned.
A 2023 report by Human Rights Watch (HRW), for example, argued that China needs to take more robust measures to combat anti-Black racism on social media platforms. The report suggested that Chinese authorities systematically fail to properly address this issue, and that platforms like Bilibili, Kuaishou, Weibo, and Xiaohongshu should intensify efforts to remove problematic content that perpetuates racial stereotypes, belittles interracial relationships, impersonates Black people, etc.
One radio editor who later called me to talk about this report also suggested that surely, if it was not being censored, the authorities must approve of it?
Similar discussions came up when there was a significant rise in anti-Jewish sentiments and anti-Semitic posts on Chinese social media after the beginning of the Israel-Hamas War. An opinion piece in the Washington Post by Josh Rogin titled “Fueling online antisemitism is China’s new tool against the West” argued that, because antisemitism was ubiquitous on Chinese social media, it thus must be promoted by Chinese authorities — suggesting that this is how it works “on China’s internet, where no opinion is allowed to flourish without government approval.”
Rogin wrote:
📰✍️ “This unprecedented surge in antisemitism online in China could be possible only with the blessing of the Chinese government, which appears to be using anti-Jewish hate as a tool of its anti-U.S. and anti-Western diplomacy.”
“Of course, not all criticism of Israel is antisemitic, and antisemitism existed in China before Oct. 7. But via its internet censorship regime and state-controlled media, Chinese authorities have been fueling the flames of anti-Jewish hate online.”
The piece also quoted Aaron Keyak, the US Deputy Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism, in saying:
📰✍️ “What we saw after October 7 was a drastic change in the social media within China. The antisemitism became more unplugged, more free-flowing,” (…) “And because we know that the Chinese internet is not free, that’s a conscious decision by the Chinese government to allow that kind of rhetoric to be greatly increased.”
The pervasiveness of both anti-Black racism and anti-Semitic content on Chinese social media raises significant concerns. Belonging to a different category of concern, it’s understandable that certain Russian army recruitment ads circulating on various Chinese platforms trigger some alarm bells.
However, this line of arguing that lumps together the censoring policies of various Chinese social media platforms and Beijing’s official stance is not only flawed — it is also heading into somewhat Kafkaesque territory, where Western media outlets, generally rooted in free speech ideals, end up criticizing China not for censoring too much, but for not censoring enough.
Getting China’s Censorship Dynamics Wrong
There are several misunderstandings in the line of thinking that if something circulates on Chinese social media, it must ipso facto be tolerated by the authorities.
🔍 1. Mistaking China’s Censorship Model for the Western One
First, it conflates how censorship operates on Chinese platforms with how moderation works on Western platforms.
Those who are not used to surfing around Weibo, Douyin, Kuaishou, and others might be surprised to find just how much questionable content remains uncensored on Chinese social media. From graphic violence to deadly accidents, bloody war videos, raunchy images, doxxing, discrimination, or dangerous stunts — scrolling these apps can sometimes seriously be bad for your blood pressure.
At the same time, doomscrolling Chinese social media also makes you realize how tightly platforms like Facebook, TikTok, YouTube, or Instagram are moderated (TikTok’s parent company is Chinese, but its community guidelines are tuned to align with EU/US standards). Even the slightest hint at shocking or sexual content or violence could get you flagged on Western social media.
(For example, one video I made years ago about a Chinese woman intentionally tripping a 4-year-old in a restaurant got flagged by YouTube for “graphic violence,” another post I made about a deadly flash flood in the mountains of Pengzhou was removed by TikTok for “promoting dangerous activities”).
The emergence of online videos showing military violence, assaults against women, bullying among schoolchildren, or irresponsible pet ownership does not suggest that Beijing tacitly endorses violence, misogyny, campus aggression, or animal cruelty. Rather, it reflects the realities of a vast and multifaceted online ecosystem where millions of videos, images, and posts get uploaded every single day, and where, with over a billion users, not every corner of social media is going to be wholesome or tightly controlled.
It also means that some issues, even though they could be considered sensitive, are not prioritized by social media moderating systems (whether automated or human) or by Chinese regulators.
🔄 2. China’s Censorship is Selective and Shifts Over Time
Censorship in China is not static. It constantly changes in response to evolving and changing social, economic, and (geo)political contexts.
There are many laws & regulations regarding online content, involving the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) and other regulatory bodies, which set rules for internet content — from Weibo posts to online advertisements, from livestreaming to online series and web novels. Social media platforms moderate their own content in various ways, adhering to state regulators and self-censoring through AI algorithms and human reviewers.
Outside the regulatory framework, there is a lot of grey area. For state regulators, social media censorship is just one way to protect national security, Party power, economic stability, and cultural cohesion. For Chinese platform businesses, it is a necessary evil — they must navigate complicated dynamics between keeping social media flourishing while keeping (cyberspace) authorities content. If they don’t, they risk punishment, which affects business. They are busy enough moderating priority content and generally won’t touch content that poses no immediate threat to their operations, even if it could be considered sensitive.
This doesn’t mean censorship cannot fluctuate with the times — on the contrary, it changes all the time. Something that once seemed unharmful might later be perceived as disruptive and still get censored.
In some ways, there is overlap with how companies like Meta (Facebook, Instagram) moderate their content; they also use a combination of AI tools and human moderators to identify and remove content. However, the regulatory frameworks from which they operate are closely tied to their respective legal, historical, and social contexts, resulting in very different censorship practices.
One thing that is prevalent in the guidelines of companies like Meta or Google is the need to keep content far away from explicit material or violent and shocking content, in order to remain “advertiser-friendly” within their socio-cultural and legal contexts. This is very different from the Chinese online environment, where one of the main priorities for social media companies is to avoid politically controversial or subversive content to keep things as “Party-friendly” as possible.
🌏 3. Imposing Western Ethical Standards on China
An (overlapping) misunderstanding behind the suggestion that any sensitive or questionable content that emerges on Chinese social media must be tolerated by the authorities is that Western media outlets are projecting Western ethical standards onto China’s internet governance.
Assuming that all sensitive content must be immediately censored or flagged — because that’s what would happen under Western frameworks — ignores China’s different historical, political, and social contexts.
China’s censorship is not intended to please the West; it serves domestic political, cultural, economic and social goals under the Party’s leadership. Besides the censorship, there’s a major propaganda apparatus that goes beyond deleting posts and focuses on guiding public opinion and controlling the official narrative.
Criticizing China for censoring too little on issues that are of concern in the West misses the point. China’s censorship serves Chinese interests, not the moral priorities of the international community.
Furthermore, telling the country known for having the world’s most sophisticated censorship apparatus that it is “not censoring the right things” is not only somewhat Orwellian – it also reinforces existing frustrations in China that the West often acts as a morally superior enforcer on the global stage, pointing fingers at China despite ongoing instances of violence, racism, and injustice within their own societies.
Two Soldiers, One “Hype”?
Back to the article I’ve been working on and the case of Chinese mercenaries Wang, Zhang, and the Russian recruitment ads circulating on Chinese social media. These army recruitment ads definitely circulated (example, example, example, example), although not ubiquitously — they mostly appeared within specific circles on platforms like Douyin or Zhihu, and mainly if you were looking for them. Often, they seemed to be shared more for their novelty or news value rather than for direct recruitment purposes. (Similarly, some Ukrainian recruitment ads were also shared online.)
Before Zelensky’s big reveal, there had already been speculation about whether Chinese nationals might be serving in Russian military units. In March 2025, some influential X accounts claimed that footage from Donetsk showed Chinese individuals wearing Russian military uniforms. At the time, as you can read here, this suggestion caused some banter and disbelief on Chinese social media. Some users suggested that the men seen in the footage could be cosplayers or Chinese vloggers who had traveled to Russia to play-act as soldiers — since military cosplay and related tourism are popular in certain online niches — the same niches where those Russian recruitment ads were being shared.

Stills from the video that made its rounds online in early March 2025.
Recent reports and various online accounts, however, indicate that Chinese nationals fighting in the Russian army is more than just cosplay — it is a reality, although it remains unclear how many people are actually involved. At the same time, the “cosplay” and “military enthusiast” (军迷COS) theory is not far-fetched and seems to hold water in some cases. In fact, these two realities may very well coexist.
In response to Zelensky’s statements about Chinese nationals fighting in Ukraine and Beijing’s alleged role, one sentiment raised online is that the issue is being purposely “hyped” by foreign media and by Zelensky himself.
This idea was echoed in some popular internet posts. In one post that circulated on social media (Zhihu, Weibo), author Liu Renzhi (刘任之) on the WeChat account of Russian Big World (俄语大世界) wrote: “Why does Zelensky continue to hype up the incident of Chinese nationals captured by the Ukrainian army? There are three reasons” (“泽连斯基为何要持续炒作中国公民在乌军被俘事件?有三方面原因”).
In this piece, Liu suggests that Zelensky intentionally amplified the story about Chinese nationals in the Russian army — among other things, by posting at least two videos about them on social media (link, link) — even though, as Liu notes, “it is nothing new that foreign nationals fight on both sides, and China’s position has been clearly stated.”
China’s Foreign Ministry has previously responded to questions about Chinese nationals in the Russian army, stating that:
🇨🇳📢 “We’ve issued multiple security alerts to ask Chinese nationals to stay away from areas of armed conflict, avoid any form of involvement in armed conflict, and in particular avoid participation in any party’s military operations.”
“China’s position on the issue of the Ukraine crisis is consistent and clear. We have all along been committed to promoting talks for peace and ending the conflict. We urge relevant parties to have a correct and clear understanding of China’s objective and just position and refrain from political manipulation and hype. ”
According to the blogger Liu, Zelensky supposedly “hyped” the situation for these reasons:
➡️ To attract global attention & rally support for Ukraine’s cause at a time when international attention to Ukraine has waned due to Trump and his own efforts to push for a Russia–Ukraine reconciliation. By playing up the “Chinese nationals in the war” narrative, Zelensky is catering to Western media interest and refocusing global attention on Ukraine.
➡️ To specifically seek Western support. Liu writes that Zelensky purposely promotes the news of the Chinese soldiers to hint at Chinese involvement in times of US trade war with China and efforts to ally with Russia against China, as a way to signal that Ukraine is also on the side of the ‘West’ in helping the US in its confrontation with China.
➡️ To put pressure on China. Liu suggests that Kyiv believes China has not remained fully neutral in the war. By exposing Chinese captives, Zelensky therefore aims to apply international pressure on China, pushing it to distance itself from Russia.
It would be interesting to know more about the Chinese online responses to this theory, but Liu’s article has been taken offline from all the sites where it initially appeared.
There is plenty more to say about pro-Russian sentiments on Chinese social media, and about the stories behind the Chinese mercenaries in Russia. But the problem with the latter now is that since this issue became an international political talking point and drew attention on Chinese social media, research has become significantly harder: Chinese platforms collectively started taking down related content shortly after the Wang and Zhang news broke.
Not only has Liu’s post been removed, but so have most posts about the two soldiers — along with the accounts of some young Chinese men who were seemingly vlogging from the Russo-Ukrainian battlefield, such as the Douyin account Li Jianwei (李建伟, nicknamed @狼血龙魂).
Some reporters I spoke with also told me their struggles, pointing at Douyin, Weibo, and Zhihu becoming more active in taking down content related to Chinese nationals fighting on the Russian side.
In other words: when nobody was paying attention, the content was there — hidden in the margins, not a priority for censors. But now that everyone is noticing, it’s getting wiped.
Does that mean Beijing changed its stance? No – it simply became a more sensitive topic, and now falls under stricter censorship.
“It’s making it a lot harder to research the topic like this,” one European journalist complained to me.
The very fact that so much content is now being censored just because Western media are paying attention is yet another reminder that China is definitely not censoring to please the West — and certainly not to accommodate Western media.
Best,
Manya
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
PS If you’re interested to know more about what motivates those Chinese joining the Russian army, see Chai Jing’s interview with a Chinese mercenary, translation via China Digital Times Part 1 and Part 2.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe
What’s on Weibo is a reader-supported publication, run by Manya Koetse (@manyapan), offering independent analysis of social trends in China for over a decade. To receive new posts and support our work, consider becoming a paid subscriber.


A Very Short Guide to China’s Most Popular Designer Toys

The Next Labubu: What the Rise of Wakuku Tells Us About China’s Collectible Toy Wave

Jiehun Huazhai (结婚化债): Getting Married to Pay Off Debts

Yearnings, Dreamcore, and the Rise of AI Nostalgia in China

Beauty Influencer Du Meizhu Accused of Scamming Fan Out of $27K

China Is Not Censoring Its Social Media to Please the West

Inside the Labubu Craze and the Globalization of Chinese Designer Toys

China Reacts: 3 Trending Hashtags Shaping the Tariff War Narrative

China Trending Week 15/16: Gu Ming Viral Collab, Maozi & Meigui Fallout, Datong Post-Engagement Rape Case

Chinese New Nickname for Trump Mixes Fairy Tales with Tariff War

No Quiet Qingming: From High-Tech Tomb-Sweeping to IShowSpeed & the Seven China Streams

Understanding the Dr. Xiao Medical Scandal

Behind the Mysterious Death of Chinese Internet Celebrity Cat Wukong

Do You Know Who Li Gang Is? Anti-Corruption Official Arrested for Corruption

China’s Major Food Delivery Showdown: What to Know about the JD.com vs. Meituan Clash
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Society10 months ago
China Society10 months agoDeath of Chinese Female Motorcycle Influencer ‘Shigao ProMax’ Sparks Debate on Risky Rides for Online Attention
-

 China World11 months ago
China World11 months agoChina at Paris 2024 Olympics Trend File: Medals and Moments on Chinese Social Media
-

 China Memes & Viral11 months ago
China Memes & Viral11 months agoTeam China’s 10 Most Meme-Worthy Moments at the 2024 Paris Olympics
-

 China Memes & Viral12 months ago
China Memes & Viral12 months agoAbout Wang Chuqin’s Broken Paddle at Paris 2024



