Newsletter
Weibo Watch: Buddha’s Happiness and a Storm in a Latte Cup
Why was HeyTea’s Buddha brew discontinued? How to explain the major drama surrounding e-commerce influencer Dong Yuhui? Which other topics went viral on Weibo? We discuss al the ins & outs in this 20th edition of Weibo Watch.
Published
1 year agoon

PREMIUM NEWSLETTER | ISSUE #20
This week’s newsletter:
◼︎ 1. Editor’s Note – Blessed objects
◼︎ 2. What’s Featured – A closer look at the featured stories
◼︎ 3. What More to Know – Highlighting 8 hot topics
◼︎ 4. What Lies Behind – Behind the Dong Yuhui drama
◼︎ 5. What’s Noteworthy – Zhang Xuefeng and liberal arts
◼︎ 6. What’s Popular – MayDay alleged lipsync incident
◼︎ 7. What’s Memorable – More attention for Nanjing Massacre
◼︎ 8. Weibo Word of the Week – “Rat-like Handsome Guy”
Dear Reader,
What was supposed to be a “zen” cup of tea caused a stir in China earlier this month – a storm in a latte cup.
The well-known Chinese tea chain HeyTea (喜茶), comparable to a tea-centric Starbucks, collaborated with the Jingdezhen Ceramics Museum to release a special ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ (佛喜) latte tea series adorned with Buddha images on the cups, along with other merchandise such as stickers and magnets. The series featured three customized “Buddha’s Happiness” cups modeled on the “Speechless Bodhisattva” (无语菩萨).
The “Speechless Bodhisattva,” originally named the “Contemplative Arhat” (沉思罗汉), is a small statue from the Jingdezhen Ceramics Museum that already became the ‘museum viral hit’ of the October holiday this year due to its facial expression. Videos that went viral on Weibo showed crowds of people in front of the statue, trying to get a glimpse of its expression – not unlike the crowds in front of Mona Lisa.
In light of this popularity, it is not surprising that the special Buddha HeyTea x Jingdezhen collaboration soon gained popularity, especially among younger consumers. On the first day of the launch in late November, people lined up and the cups soon sold out in HeyTea stores across Chinese cities.

The HeyTea Buddha latte series, including merchandise, was pulled from shelves just three days after its launch.
However, the ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ success came to an abrupt halt when the Ethnic and Religious Affairs Bureau of Shenzhen (深圳市民族宗教事务局) intervened, citing regulations that prohibit commercial promotion of religion. HeyTea wasted no time challenging the objections made by the Bureau and promptly removed the tea series and all related merchandise from its stores, just three days after its initial launch.
The decision not only disappointed many but also sparked questions about the extent to which the HeyTea Buddha series genuinely conflicts with Chinese law.
As the issue became a topic of discussion, scrutiny arose regarding why other ‘made-in-China’ products, including Buddha keychains and Boddhisatva phone covers, are still allowed to be sold in the country. The popular WeChat blogging account Xinwenge also highlighted that, technically, the images weren’t even of Buddha but sculptures representing Arhats – Buddhist adepts or the highest ideal of a disciple of the Buddha. Moreover, the Jingdezhen Museum itself contributed significantly to the virality of the Speechless Boddhisatva; they even issued a special WeChat sticker series.

WeChat stickers (left), keychains of the Speechless Boddhisatva.
Some Chinese internet users, however, agreed that it was inappropriate for HeyTea to sell such ‘Buddha’ teas. Although they praised efforts to spread more love for Buddhism, especially among young people, they thought it was “extremely disrespectful” to have a Buddhist image on a tea cup that would end up in the trash.
For others, the discontinued milk tea cups became even more ‘sacred’ as they used them to make their own little office altars or lights.

From office altars to holy lights, the HeyTea cups are transformed to spiritual objects.
The HeyTea Buddha latte tea saga provides insights into various facets of present-day China. It shines a light on the success of domestic coffee and tea chains and the original collaborations they launch to attract more customers. A recent academic study into the success and appeal of Chinese (bubble) tea brands even calls the long queues in front of these shops a “ritualised leisure experience” (Yan et al. 2023).
As we’ve seen in the past, whether it’s a new shop opening or the launch of a fresh collaboration, these events can quickly escalate from garnering local attention to becoming nationwide phenomena, with social media playing a pivotal role. Displaying your HeyTea cup holds a certain status, acting as social currency across Chinese social media platforms (Hutchins 2023, Ch5).
The story also underscores just how careful brands need to be when launching the next original idea; it cannot be too tame or else it won’t speak to China’s young consumers, but it also cannot be too bold or else it might rub Chinese authorities the wrong way.
Furthermore, the HeyTea story shows the interaction between Buddhism, consumerism, and the Chinese state. Nowadays, commodification of Buddha is everywhere, also in Tibet – even though it goes against traditions. Although the use of Buddhist images to sell merchandise unrelated to Buddhism could be seen as a form of “cultural misappropriation” (Cantanese 2019, 2), the commercial success of such products show that most people do not only see nothing wrong with it, they actually appreciate when their cup of latte has another layer of meaning to it: just because it’s commercial doesn’t mean it is meaningless.
As reported by Jing Daily earlier this year, Chinese temple visits have seen a significant surge and about 50 percent of Chinese temple visitors are millennials or were from Gen Z. Aside from burning incense and praying, these younger visitors are particularly fond of the temple shops that sell “blessed objects.”
Especially in a time when younger consumers are turning away from meaningless spending and are feeling more connected to spirituality, finding a bit of Buddha in their latte brings joy. “It’s a pity they discontinued,” one Xiaohongshu user wrote, “At least I still have the Buddha magnet on my fridge.”
To explore other viral topics on Chinese social media, check out our latest stories below. This week’s newsletter includes contributions from Miranda Barnes. You’ll hear back from us in our next newsletter, which you will get right before the start of 2024.
In the meantime, wishing you a merry Christmas, with lots of love, and perhaps some ‘blessed objects’ below the Christmas tree.
Best,
Manya
References:
Cantanese, Alex John. 2019. Buddha in the Marketplace: The Commodification of Buddhist Objects in Tibet. University of Virginia Press.
Hutchins, Joanna. Chinafy: Why China is Leading the West in Innovation and How the Rest of the World Can Catch Up. Singapore: Marshall Cavendish Business.
Yan, Qi, Xiaolei Shen & Haobin Ben Ye. 2023. “The Cue Is in the Queue, Smart! Assessing the Ritualised Leisure Experiences of Long Queuing for a Bubble Tea Brand in China.” Leisure Studies.
What’s Trending

1: Blood Donations in Tibet Trigger Controversy | The medical rescue of a critically injured Shanghai woman in Tibet has recently triggered major controversy on Chinese social media after netizens suspected that the woman’s treatment may have been facilitated through the abuse of power. Dozens of local public officials in Tibet donated blood to rescue a Shanghainese woman. Many believe it’s a matter of privilege.

2: Death after Binge Drinking | A woman who spent a night binge drinking with friends ended up experiencing cardiac arrest due to alcohol poisoning. A Chinese court has determined that her friends share partial responsibility for failing to prevent her from excessive drinking.

3: Doubts over Lucky Winner | A Chinese hardcore lottery player defied all mathematical logic last week by winning over USD 30 million by purchasing a staggering 50,000 tickets with the same number. The fortunate resident of Nanchang in Jiangxi province invested a total of 100,000 RMB (approximately USD 14,000) to buy tickets for the Chinese ‘Happy 8’ (快乐8) lottery, visiting multiple sales outlets. Since all the tickets shared identical numbers, each ticket yielded a prize and instantly made the man a multimillionaire. However, on Chinese social media, where the story went trending, people are skeptical and suspect foul play.
What More to Know

◼︎ Kathy Chow Hoi-mei’s Death and Leaked Medical Records | The death of the 57-year-old renowned Hong Kong actress Kathy Chow Hoi-mei (Zhou Haimei, 周海媚), who became famous for her role in various TV series in the ‘80s and ‘90s, became a major topic on Weibo this week. The actress, who had been suffering from autoimmune disease lupus for many years, still posted a happy video days before she passed, thanking people for the birthday wishes she received earlier this month. On December 11, rumors of her death started circulating and on Tuesday evening, a medical record believed to be related to Chow’s emergency treatment prior to her death surfaced and detailed the related medical rescue information. Kathy Chow’s studio later released an official statement confirming the news of her passing. A hospital worker from Beijing was later detained for leaking private, medical information (Weibo hashtag Zhou Haimei Passes Away #周海媚去世#, 1.5 billion views).
◼︎ Gree’s Dirty Laundry | Dong Mingzhu (董明珠, 1954), the famous Chinese businesswoman who serves as president of Gree Electric, the major home appliance maker known for its air conditioners, became a trending topic this week for lashing out against Meng Yutong (孟羽童, 1998) during her talk at at a ceremony for new employees on December 13. The 25-year-old Meng Yutong was previously a secretary for Dong, but left the company in May of 2023, saying she was pursuing postgraduate studies. Before joining Gree, Meng was working on a career as an online influencer and participated in various (reality) TV shows. She joined Gree in 2021. In her public talk, Dong Mingzhu criticized Meng by suggesting she used her position at Gree to become an online celebrity and that she had created “a negative impact” within the company. Many netizens think that Dong’s criticism actually has more to do with generational differences, saying Dong expected Meng to follow a similar path as her – but times have changed (Weibo hashtag “Dong Mingzhu Lashes Out Against Meng Yutong” #董明珠怒斥孟羽童#, 450 million views).
◼︎ Beijing Subway Carriages Break Apart | On the night of December 14, a train accident occured on the Beijing Changping subway line (昌平线). Over thirty passengers sustained injuries after one of the carriages broke apart in the middle; there was an abrupt break in the articulated joint of carriages 0244 and 0245. Passengers reported a “sudden impact” at around 19:00 as the train was on its way from Xi’erqi (西二旗 ) to Life Science Park (生命科学园站). The incident caused passengers to be stuck for a large part of the evening before rescue and evacuation teams arrived at the scene. The incident caused significant disruption for commuters, as they could not get their train back while hundreds of people were waiting for a taxi. The cause of the incident is still under investigation. (Weibo Hashtag “Beijing Subway Changping Line Experiences Sudden Malfunction” #北京地铁昌平线突发故障#, 290 million views).
◼︎ 86 Years Since Nanjing Massacre | The “Nanjing Datusha,” literally: “Nanjing Massacre,” was commemorated in China this week, both online and offline. The commemoration took place on December 12, marking the Japanese invasion of the city of Nanjing in 1937, starting a six-week long massacre during which people were bombed out of their homes and shot in the streets. Japanese soldiers tortured, raped, and killed large numbers of common people; their corpses were piled up along the river. According to China’s official data, at least 300,000 people, including children, elderly and women, were killed during this winter. Over recent years, Chinese social media has played an increasingly important role in the commemoration of the Nanjing Massacre. Although Chinese official media play a pivotal role shaping the way this is remembered online, ordinary netizens also show a lot of interest for this part of war history that is engraved in China’s collective memory. (Weibo hashtag “These Numbers Are Scars in Hearts of Chinese That Can’t Be Healed” #这些数字是中国人心里无法愈合的伤疤#, 170 million views).
◼︎ Gao Yaojie Passes Away | The Chinese renowned gynecologist, academic, and AIDS activist Gao Yaojie (高耀潔) passed away at the age of 95 this week. Gao achieved international acclaim as a ‘whistleblower’ for exposing an AIDS epidemic that spread across rural China due to irregular and illegal blood donation processes during the 1990s. She was actively involved in the fight against HIV/AIDS, but was also silenced and put under house arrest by authorities. She eventually fled to the US, where she stayed until her death. Although Gao’s passing went trending on Chinese social media, the narratives surrounding her death are very different from those in foreign media; one of the most popular posts on Weibo asserted that Gao’s pessimism about the Party and China’s future was “completely wrong.” Another popular post claimed that her work had become used as an anti-Chinese tool for “hostile Western forces.” (Weibo hashtag “Dr. Gao Yaojie Passed Away” #高耀洁医生去世#, 180 million views).
◼︎ Beijing’s First Snow | The Forbidden City dressed in white, Beijing Zoo pandas playing in the snow, and a winter wonderland at Summer Palace; this week Chinese netizens and online media accounts posted numerous photos of the first snow falling the Chinese capital. Although many enjoyed the snowfall, it also caused disruptions from airports to train tracks and from schools to offices. As temperatures keep plummeting, more snowfall is expected along with potentially record low temperatures. (Weibo hashtag: Beijing’s Snow #北京的雪#, 99 million views).
◼︎ Xi in Vietnam | Xi Jinping’s first state visit to Vietnam in six years made headlines this week. This visit, aiming to strengthen ties between the communist-run nations, follows Hanoi’s recent efforts to enhance diplomatic relations with Washington after a recent visit by Biden. During a summit in Hanoi, Xi and Vietnamese leader Trong advocated for strengthening strategic ties and agreed to collaborate on various issues, including maritime patrols, trade, and crime prevention. China is Vietnam’s largest trading partner, with significant economic and investment ties between the two countries. (Weibo hashtag: Xi Jinping’s Vietnam Visit #习近平访问越南#, 38+ million views)
◼︎ Toddler’s Tragic Death | A very tragic story coming from the city of Dongguan, Guangdong, attracted the public’s attention this week: a 2-year-old child fell into a supermarket bread/flour mixing machine on Decemer 8 and did not survive. The parents are the owners of the supermarket bakery, who would take their child to work due to lack of childcare at home. The incident has generated online discussions on the importance of parents providing a safe environment for their children (Weibo Hashtag “Dongguan Child Dies after Falling into Supermarket Bread Blender” #东莞一儿童掉进超市面包搅拌机身亡#, 290 million views; “The Child Who Fell in the Breadmaking Machine is Son of Owner” #掉进搅拌机的是面包店老板家孩子#, 15.2 million views).
What Lies Behind

Behind the Influencer Drama at East Buy
In recent days, Dong Yuhui (董宇辉) has become a hot topic on Chinese social media after a live broadcast that captured widespread attention. Dong is a top livestreamer for the e-commerce platform East Buy (东方甄选), which is part of New Oriental (新东方). Formerly a celebrated teacher, Dong has garnered popularity among Chinese netizens for his enthusiasm, humble background, English proficiency, witty jokes, personal stories, honest talks, and singing talent (read more here).
The current buzz around Dong stems from ongoing drama at East Buy. Livestream viewers and Dong’s loyal fans were angered when the editorial team behind Dong claimed that many of his popular livestream talks and stories were not created by him alone but were the result of collaborative teamwork. This led people to believe that the company team was taking credit for Dong’s individual efforts.
This influencer drama, while not the first this year, stands out because fans are vehemently defending Dong. His followers even refer to him as the ‘National Son-in-Law.’ Many view the team’s comments as a form of betrayal and backstabbing.
The story has gained significant traction because people see themselves in Dong—a former farmer’s son who rose to China’s e-commerce stardom due to his talent and hard work. For many, he represents hope for ordinary people, a path they can dream of themselves. Now, facing workplace bullying, Dong’s fans are not just expressing support online; they are also redirecting their spending elsewhere, saying, “I only bought from them because I like Dong.”
Faced with an online boycott, a loss of millions of followers, and a drop in stock market prices, subsequent PR efforts to silence the issue went awry. In the end, the CEO of EasyBuy was removed, and New Oriental founder and chairman Yu Minhong (俞敏洪) stepped in to try to alleviate the marketing disaster by hosting a live stream jointly with Dong.
Online discussions continue, with some pointing out that this reveals a power struggle between big individual influencers and the traditional corporate structure under the influencer economy. The recent support for Dong indicates that e-commerce platforms need to carefully consider how they handle their most well-known employees. Although these influencers have grown through the platform, efforts to limit their influence might backfire and result in greater losses. The key lesson here is that companies should never turn against their most beloved underdogs, as it may come back to bite them in the ass.
What’s Noteworthy

Zhang Xuefeng and Liberal Arts
Oops, he did it again. Chinese educational internet influencer and exam prep coach Zhang Xuefeng (张雪峰) recently stirred up another trending discussion by seemingly belittling liberal arts during a livestream. He claimed that having a Liberal Arts Degree is equivalent to ending up in a lower status within the service industry.
Not too long ago, Zhang already caused some controversy by strongly discouraging Chinese youth from pursuing a degree in journalism.
This time again, many people are offended by Zhang’s remarks, suggesting it is wrong and extreme of him to lump all liberal arts majors together. However, there are also those who agree, saying that choosing an educational route in science and engineering is more fruitful. The numbers also indicate that science and engineering graduates are much more likely to be employed after getting their degree than liberal arts graduates.
Zhang Xuefeng later attempted to clarify his comments and offered a quasi-apology by wearing a T-shirt saying ‘sorry.’ He emphasized that he did not intend to criticize the service industry, expressing that there is nothing inherently wrong with being a part of it. Instead, he just wants people to be realistic about their expectations when choosing their educational paths.
Zhang’s comments are especially impactful due to a record number of Chinese college graduates entering the job market while facing bleak employment outlooks. In this light, picking the right educational path has become an extra important and weighty issue for both students and their parents.
What’s Popular

MayDay Alleged Lipsync Incident
The question of whether the members of the Taiwanese pop band Mayday lip-synced during their concert on the Chinese mainland has stirred up discussions on Chinese social media, amassing millions of views recently. The popular band performed in Shanghai on November 16, but speculations about lip-syncing arose when some concertgoers shared videos on social media, casting doubt on whether they had sung live.
This story became especially big when one music blogger, Shenglixue (@声理学) used specific software to analyze the videos, asserting that the singers were lip-syncing. The issue gained so much attention because lip-syncing during performances, or pretending to play musical instruments, goes against the guidelines issued by the government-backed China Association of Performing Arts and is considered a form of deception.
However, the band denied allegations of not singing live, labeling the rumors as “malicious slander.” Their concert in Paris was also livestreamed last week, allowing attentive listeners to occasionally hear off-key notes that were definitely not lip-synced. Earlier this week, a veteran music agent and associate professor from Taiwan’s Nantai University’s Department of Popular Music Industry also weighed in on the issue, refuting the lip-syncing allegations.
The music blogger who initially published the allegations has vowed not to post about Mayday anymore, as his personal details, including his mum’s name and photos, were leaked online by doxers.
What’s Memorable

Increasing International Attention for Nanjing Massacre
As Weibo commemorates the Nanjing Massacre this week, we revisit an article from last year about an American pawn shop owner discovering potentially unseen photos from this particularly gruesome chapter of the Second Sino-Japanese War.
When a TikTok video showcasing these images went viral, Chinese netizens were astonished by how little awareness Western social media users had about the events during the Japanese invasion of Nanjing in 1937. While it remained uncertain whether the photos found by the pawn shop owner were genuinely previously undiscovered images of Nanjing, the entire incident ultimately shifted towards fostering greater international awareness of this historical tragedy.
Weibo Word of the Week

“Rat-Type Handsome Guy” | Our Weibo Word of the Week is “Rat-Type Handsome Guy” (shǔ xì shuài gē 鼠系帅哥).
The term “Rat-Type Handsome Guy” (鼠系帅哥) has actually been around for some time, but attracted more attention on Chinese social media recently. The word is part of a group of other terms to describe popular aesthetics of famous men with features resembling animals.
In 2022, for example, the “Monkey-Type Handsomes” (猴系帅哥) were especially popular. The term was used to describe the kind of Chinese celebrities who were undeniably handsome and also showed some resemblance to monkeys due to their strong brow ridges, narrow and long face, thin upper lip, and prominent T-zone.
When categorizing handsome men in China’s entertainment industry into animal-types, from monkeys to snakes, from dogs to birds, it is not always only about facial features but also about a certain air or vibe (氛围感) that surrounds an idol. A loyal and cute dog-like vibe, a calm and strong ox-like feeling, or a sharp and sexy cat-like character.
Thi year, the ‘rat-like’ handsome men have been more in vogue. They have small eyes, a pointed jaw and a small mouth. Although not all actors who are rat-like are deemed handsome, those that are handsome are all the more rare – and popular.

Chinese actor Yang Di (杨迪) went trending for being a representative of the “Rat-Type Handsome Guy” (鼠系帅哥) recently. Although he himself proudly posted about it on Weibo, there are also many netizens who think that being ‘rat like’ is actually not really attractive and not worth boasting about.
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
Stories that are authored by the What's on Weibo Team are the stories that multiple authors contributed to. Please check the names at the end of the articles to see who the authors are.

Newsletter
IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well
Published
4 days agoon
March 30, 2025
“This man is doing God’s work. In just six hours, he eliminated all Western media propaganda about China,” Chinese influencer Li Sanjin (李三金) said in one of his videos this week. The man he referred to, allegedly doing ‘God’s work,’ is the American YouTuber and online streamer Darren Watkins, better known as IShowSpeed or Speed, who visited China this week and livestreamed from various locations.
With 37 million followers on his YouTube account, Watkins’ visit hasn’t exactly flown under the radar. His streams from China have already accumulated over 17.5 million views on YouTube alone, and he also became the talk of the week on Chinese social media.
In China, the 20-year-old IShowSpeed is known as Jiǎkànggē (甲亢哥), or “Hyper Bro,” since the immensely popular YouTube star is known for being highly energetic.
Although IShowSpeed is originally known for soccer and gaming-related content, he’s been streaming live from various countries over the past year, from Ecuador to Bolivia, from Australia to Indonesia, from Romania to Japan, and also from the Netherlands, where a mob of fans harassed the YouTuber to such an extent that the influencer fled and panicked, until the police intervened and asked him to shut down the livestream for safety reasons — which he did not comply with.
It was not the only time IShowSpeed’s visit got chaotic. He also got into trouble during livestreams from other countries. While streaming from Norway, he injured his ankle and was swarmed by a crowd while trying to get out. In Greece and Indonesia, he had to ask for police support as well. In Thailand, he crashed a tuk-tuk into a temple wall.
In China, IShowSpeed’s livestreams went far more smoothly, and netizens, state media, and other official channels raved about his visit and its favorable portrayal of the country and its culture.
🔹 Symbol of Cultural Exchange & Positive Diplomacy
“Jiǎkànggē” became one of the viral terms of the week, on Weibo, Kuaishou, Douyin, and Toutiao. During his China trip, the livestreamer hit several YouTube milestones — not only breaking the 37 million subscriber mark while on stream, but also surpassing the magic number of 10 million views in total.
Watkins, also known for being (sometimes aggressively) loud and chaotic, suddenly emerged as a symbol of cultural exchange and positive diplomacy. The past week saw hashtags such as:
#️⃣”IShowSpeed gives young foreigners a full-window view into China” (#甲亢哥给国外年轻人开了全景天窗#)
#️⃣”IShowSpeed’s Shanghai livestream breaks Western filter on China” (#甲亢哥上海直播打破西方对中国滤镜#)
#️⃣”American influencer IShowSpeed amazed by stable wifi on China’s high-speed train” (#美国网红甲亢哥被高铁稳定网络震惊#)
#️⃣”IShowSpeed praised deep tried tripe for being incredibly delicious” (#甲亢哥赞爆肚太好吃了#), or
#️⃣ “IShowSpeed bridges the cultural divide” (#甲亢哥弥合文化鸿沟#).
While in Chinese media, Watkins was lauded for shining a positive light on China, this message was also promoted on English-language social media, where he was praised by the Chinese embassy in the US (#驻美大使馆称赞甲亢哥中国行#), writing:
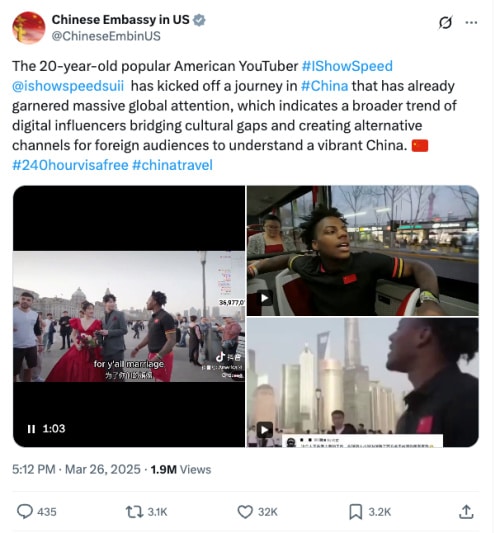
Post by Chinese Embassy in the US on X, March 26.
“This 20-year-old American internet star is bridging cultural gaps through digital means and creating new channels for foreign audiences to better understand China.”
So what exactly did IShowSpeed do while in China?
On March 24, Watkins livestreamed from Shanghai. He wandered around the city center, visited a KFC, danced with fellow streamers, stopped by a marriage market, ate noodles, played ping-pong, had hotpot, joined a dragon dance group and got acquainted with some traditional Chinese opera performance, and walked along the Bund.
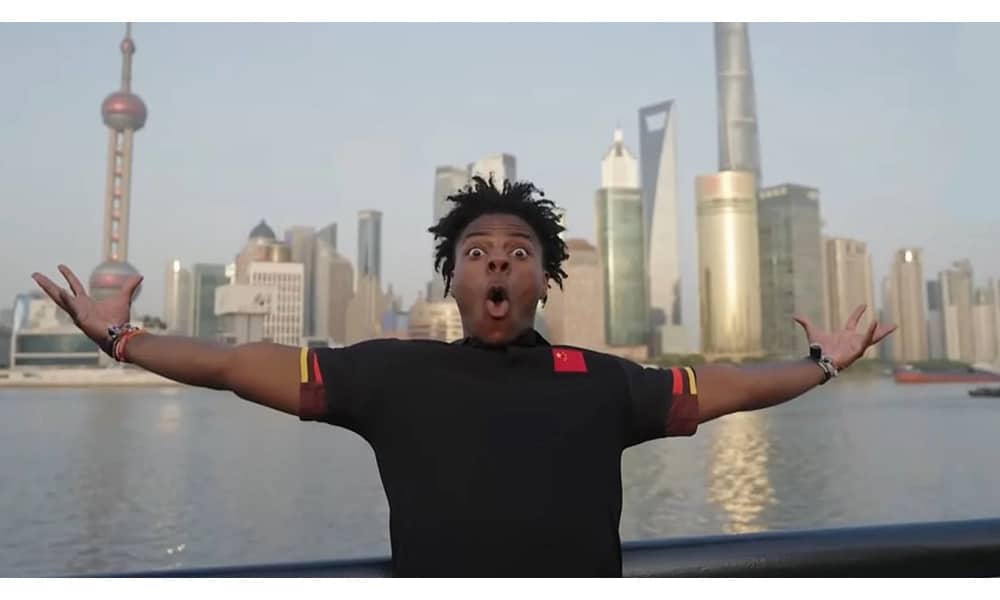

On March 26, he streamed from Beijing, starting in Donghuamen before briefly entering the Forbidden City—dressed in a Dongbei-style floral suit. He later took a stroll around Nanluoguxiang and the scenic Houhai lake, rode a train, and finally visited the Great Wall, where he did backflips.

In his stream on March 28, Watkins traveled to Henan to visit the famous Shaolin Temple in Dengfeng, hoping to find a master to teach him kung fu. He trained with Shaolin monks—footage that quickly went viral.
Lastly, on March 29, he opened his own Weibo account and published his first post. On Douyin, he shared a video of his visit to Fuxi Mountain in Zhengzhou, featuring the popular “Stairway to Heaven” tourist spot.
On social media, many viewers were captivated by the content. One major talking point was the remarkably strong internet connection that allowed him to livestream for six-hour stretches without losing signal in Shanghai. (Though his Beijing stream started off patchier, the drop was minor.) For many, it symbolized the quality of China’s 5G services.
Foreign viewers also praised how safe, friendly, and clean the country appeared, and how his streams highlighted various aspects of Chinese culture—from everyday people to traditional arts and local cuisine.
🔹 Telling & Spreading China’s Stories Well
It is no wonder the success of the Jiǎkànggē livestreams is celebrated by Chinese official media in an age where China’s foreign communication aims to increase China’s international discourse power, shaping how the world views China and making that image more credible, more respectable, and more lovable.
That’s not just an observation — it’s an official strategy. Introduced by Xi Jinping in 2013, “Telling China’s Story Well” (“讲好中国故事”) is a political slogan that has become a key propaganda strategy for China and continues to be a priority in finding different ways of promoting Chinese culture — new ways of telling China’s story in the social media age – while countering Western dominant narratives about China.
In increasingly digitalized times, it is not just about telling China’s story well, but also spreading China’s message effectively — preferably through genuine and engaging stories (Cai 2013; Qiushi 2021).
Especially young, non-official ‘storytellers’ can make China’s image more relatable and dynamic. One major example, highlighted in a 2022 case study by Zeng Dan (曾丹), is Chinese influencer Li Ziqi (李子柒). You’ve probably heard of her, or seen snippets of her videos: she creates soothing, cinematic content depicting China’s countryside lifestyle, focused on cooking, crafts, and gardening. With 26 million followers on YouTube, Li Ziqi became a viral sensation who successfully communicated an authentic and appealing ‘China story’ to a broad global audience.

Li Ziqi in one of her YouTube videos.
Although the calm and composed Li Ziqi and the loud, chaotic IShowSpeed couldn’t be more different, they have some things in common: both have large international fanbases, including their millions of YouTube subscribers; they offer perspectives that differ from Chinese state media or official channels; and they have the capacity not just to tell China’s story well, but to spread it effectively through videos and livestreams.
🔹 Spontaneous Stream or Scripted Propaganda?
IShowSpeed’s China streams have triggered a wave of responses from fans and viewers, sparking discussions across international social media and even making newspaper headlines.
In English-language online media spheres, there appear to be a range of perspectives on Watkins’ China trip:
📌 One prominent view—also echoed by various foreign influencers on YouTube and other platforms—is that IShowSpeed’s visit counters “Western media lies” about China and has successfully shown the “real China” through his livestreams. The Shanghai-based media outlet Radii claimed that “IShowSpeed’s China Tour is doing more for Chinese Soft Power than most diplomats ever could.”
📌 Others challenge this narrative, questioning which dominant Western portrayals of China IShowSpeed has actually disproven. Some argue that the idea of China being a “bleak place with nothing to do where people live in misery” is itself a false narrative, and that presenting IShowSpeed’s livestreams as a counter to that is its own form of propaganda (see: Chopsticks and Trains).
📌 There are also those who see Watkins’ trip as a form of scripted propaganda. To what extent were his livestreams planned or orchestrated? That question has become one of the central points of debate surrounding the hype around his visit.
These rumors have been addressed by cameraman Slipz (@shotbyslipz), who took to X on March 28, 2025. Slipz posted that the team is “(..) not making political content, not any documentary and no journalism,” and later added: “Fact: amount of money IShowSpeed has received from Chinese Government = $0.”
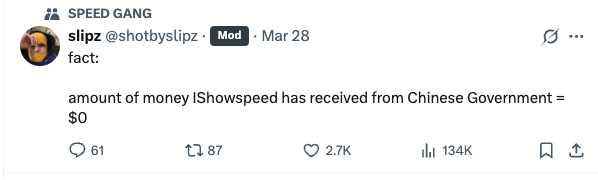
But does the fact that IShowSpeed did not receive money from the Chinese government mean that it wasn’t also a form of China promotion?
➡️ Organized — it definitely was. Any media trip in China has to be. IShowSpeed would have needed a visa, he had translators with him, and throughout the streams it’s evident that local guards and public security officers were present, walking alongside and helping to keep things under control, especially in crowded areas and at major tourist spots — from Nanjing Road in Shanghai to an entire group of guards seemingly accompanying the entourage in the Forbidden City.
One logistical “advantage” to his visit was the fact that YouTube is blocked in China. While some Chinese fans do bypass the Great Firewall to access the platform, IShowSpeed remains far less known in China than in many other countries — a factor that likely contributed to how smoothly the streams went and helped prevent chaos. The team also launched a Douyin account during the trip, where he now has over two million followers. (To stream directly to their 37 million followers on YouTube, Watkins’ team either needed a VPN to access WiFi or had arranged roaming SIM cards to stay connected.)
➡️ Was it staged? Many parts clearly weren’t: casual public conversations, spontaneous barber visits in both Shanghai and Beijing (with barbers looking unsure of how to handle the situation), and wholesome fan encounters. There was even a moment when Watkins walked into a public restroom and forgot to mute the sound.
But other parts of the trip were undeniably staged — or at least framed to appear spontaneous. When visiting a marriage market in Shanghai, for instance, two actors appeared, including one woman with a sign stating she was looking for someone “capable of doing backflips.”
When Watkins took a “random” ride in what was described as the fastest car in China — the Xiaomi SU7 Ultra — the vehicle appeared to be conveniently parked and ready.
Similarly, when the streamer “ran into” Chinese-American TikTok influencer Miles Moretti (李美越) in Beijing, it turned out to be the person who would give him the now-iconic bright Dongbei flower suit and accompany him on his journey.

The ping-pong, the kung fu, the Peking opera, the hotpot, the Forbidden City tour — it all plays into the kinds of experiences that official channels also like to highlight. While likely planned by Watkins’ team in coordination with local partners, it was all far more orderly and tourism-focused than, for example, Watkins’ chaotic visit to the Netherlands.
Watkins and his entourage were also well-informed about the local dos and don’ts. At one point, Watkins even mentions “following the rules,” and when Moretti tells him mid-stream that “somebody very important lives on our left,” Watkins asks “Who?” — but the camera zooms out and the question goes unanswered, suggesting they may have been reminded that certain names or topics were off-limits (judge the moment for yourself here).
The livestream didn’t always go exactly the way Watkins wanted, either. When he attempted to take more random walks around the city, the crew appeared to be informed that some areas were off-limits, and he was asked to return to the car to continue the trip (clips here and here).
🔹 The “Nàge” Song
One major talking point surrounding IShowSpeed’s China livestreams was “the N-word.” No, not that N-word — but the Chinese filler word “nàge” or “nèige” (那个). Like “uhm” in English or “eto” in Japanese, “nàge” is a hesitation marker commonly used in everyday Mandarin conversation. It also functions as a demonstrative pronoun meaning “that.”
The word has previously stirred controversy because of its phonetic resemblance to a racial slur in English. In 2020, an American professor at the University of Southern California’s Marshall School of Business was even temporarily suspended after using the word during an online communications class — some students misunderstood its context and took offense.
The word — and the song “Sunshine, Rainbow, White Pony” (阳光彩虹小白马) by Chinese singer Wowkie Zhang (大张伟), which repeatedly features the word nàge in its chorus — popped up multiple times during Watkins’ trip. The catchy tune essentially became the theme song of his visit.
The first nàge moment actually already appeared within the first five minutes of Watkins’ Shanghai stream, when a Chinese comedian approached him on the street, trying to recall a joke. “What?!” Watkins reacted, with laughter in the background. “That’s not a joke, you said n**! It’s my first five minutes in China!” he exclaimed, before patting the man’s back in a friendly gesture, clearly not offended.
🔄 It resurfaced again within the first hour when Watkins visited a marriage market and one of the performers sang the Wowkie Zhang song. Watkins initially acted shocked, then demanded they sing it again — only to burst out laughing and start singing along.
🔄 Later, he sang the song again with a street saxophonist and encouraged others to join in.
🔄 At other moments, he played up the drama again, feigning anger when a crowd broke into the chorus, and it became a recurring gag throughout the streams.
These incidents all seem staged. One of the main reasons Watkins is known to many netizens in China is because of an older video clip showing his exaggerated reaction to the nàge song — dating back to at least 2022. So while it may have looked spontaneous, Watkins was already familiar with the word and the viral song long before his China trip.The attention given to the nàge ‘controversy’ was likely amplified for views and engagement.
While Watkins was clearly in on this part of the show — as with others — he also seemed genuinely, and at times amusingly, unaware of many things in China. He repeatedly referred to RMB as “dollars,” mistook elderly women for retired YouTube streamers, and even assumed that a woman livestreaming near the Forbidden City was reading his chat and trying to collaborate with him — although she seemed totally uninterested and was just minding her own business.
🔹 A Win-Win Situation
In the end, IShowSpeed’s visit highlighted two sides effectively doing their job. Watkins and his team successfully arranged a YouTube trip that generated high ad revenue, attracted millions of new subscribers, and boosted his brand and global fame.
On the Chinese side, there was clearly coordination behind the scenes to ensure the trip went smoothly: avoiding controversy, ensuring safety, and showcasing positive aspects of Chinese culture. From traditional opera and kung fu to ping pong, IShowSpeed’s content gave center stage to the kinds of cultural highlights that align closely with China’s official narratives and tourism goals. Even if the government didn’t pay the YouTuber directly, as his team has emphasized (and there’s no reason to doubt them), the trip still fit seamlessly into China’s soft power strategy.
IShowSpeed’s China visit has created a unique media moment that resonates for several reasons: it’s the encounter of a young modern American with old traditional China; it is a streamer known for chaos visiting a nation known for control. And it brings different benefits to both sides: clicks and ad revenue for IShowSpeed, and free foreign-facing publicity for China.
No, IShowSpeed didn’t undo years of critical Western media coverage on China. But what his visit shows is that we’ve entered a phase where China is becoming more skilled at letting others help tell its story — in ways that resonate with a global, young, online audience. He didn’t do “God’s work.” He simply did what he always does: stream. And with China’s help, he streamed China very well.
There’s so much more I want to share with you this week — from Chinese reactions to the devastating Myanmar earthquake, to a recent podcast I joined with Dutch newspaper De Telegraaf (link in Dutch, for those interested). But it also happens to be my birthday today, and I’m really hoping to still grab some birthday hotpot — so I’ll wrap this up here. I’ll keep you informed on the other trends in the next newsletter.📨.
Best,
Manya
(@manyapan)
References:
Cai, Mingzhao 蔡名照. 2013. “Telling China’s Stories Well and Spreading China’s Voice: Thoroughly Studying and Implementing the Spirit of Comrade Xi Jinping’s Important Speech at the National Conference on Propaganda and Ideological Work [讲好中国故事,传播好中国声音——深入学习贯彻习近平同志在全国宣传思想工作会议上的重要讲话精神].” People’s Daily 人民日报, October 10. http://politics.people.com.cn/n/2013/1010/c1001-23144775.html. Accessed March 29.
Qiushi 求是网. 2021. “Xi Jinping: Telling China’s Story Well, Spread China’s Voice Well [习近平:讲好中国故事,传播好中国声音].” Qs Theory, June 6. http://www.qstheory.cn/zhuanqu/2021-06/02/c_1127522386.htm. Accessed March 29.
Zeng Dan 曾丹. 2022. “How to Tell China’s Story Well: Taking Li Ziqi as an Example [如何讲好中国故事——以李子柒为例].” Progress in Social Sciences 社会科学进展 4 (1): 10–19. https://doi.org/10.35534/pss.0401002.
What’s Featured

Quite terrifying and interesting, as this trending story touched upon so many different issues.
What started as a single snarky comment on Weibo spiraled into an online witch hunt, exposing not just some dark sides of online Kpop fandom but also, most importantly, the vulnerabilities in China’s digital privacy.
Read the story, the latest by Ruixin Zhang 👀
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
Newsletter
Weibo Watch: The Great Squat vs Sitting Toilet Debate in China🧻
This week, the Catch-22 of sitting versus squat toilets sparked heated discussion on Weibo after a Beijing News article exposed the messy reality of sitting toilets in Beijing malls.
Published
2 weeks agoon
March 23, 2025
PREMIUM NEWSLETTER | ISSUE #50
Dear Reader,
Shoe prints on top of the toilet seat are never a pretty sight. To prevent people from squatting over Western-style sitting toilets, there are some places that will place stickers above the toilet, reminding people that standing on the seat is strictly forbidden.

For years, this problem has sparked debate. Initially, these discussions would mostly take place outside of China, in places with a large number of Chinese tourists. In Switzerland, for example, the famous Rigi Railways caused controversy for introducing separate trains with special signs explaining to tourists, especially from China, how (not) to use the toilet.
Squat toilets are common across public areas in China, especially in rural regions, for a mix of historical, cultural, and practical reasons. There is also a long-held belief — backed by studies (like here or here) — that the squatting position is healthier for bowel movements (for more about the history of squat toilets in China, see Sixth Tone’s insightful article here).

Public squatting toilets in Beijing, images via Xiaohongshu.
Without access to the ground-level squat toilets they are used to — and feel more comfortable with — some people will climb on top of sitting toilets to use them in the way they’re accustomed to, seeing squatting as the more natural and hygienic method.

Not only does this make the toilet seat all messy and muddy, it is also quite a dangerous stunt to pull, can break the toilet, and lead to pee and poo going into all kinds of unintended directions. Quite shitty.
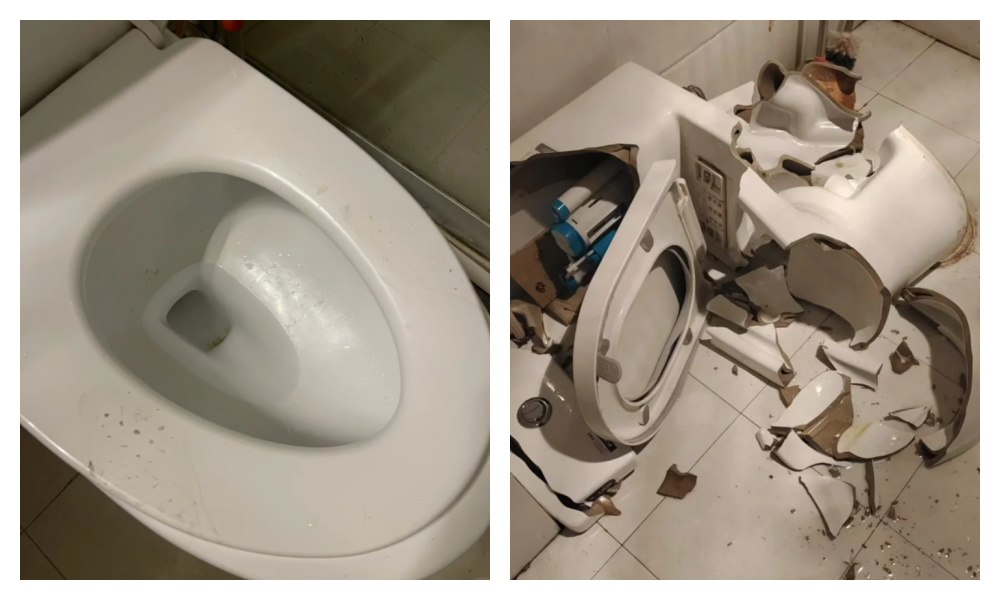

Squatting on toilets makes the seat dirty and can even break the toilet.
Along with the rapid modernization of Chinese public facilities and the country’s “Toilet Revolution” over the past decade, sitting toilets have become more common in urban areas, and thus the sitting-toilet-used-as-squat-toilet problem is increasingly becoming topic of public debate within China.
The Toilet Committee and Preference for Sitting Toilets
Is China slowly shifting to sitting toilets? Especially in modern malls in cities like Beijing, or even at airports, you see an increasing number of Western-style sitting toilets (坐厕) rather than squatting toilets (蹲厕).
This shift is due to several factors:
🚽📌 First, one major reason for the rise in sitting toilets in Chinese public places is to accommodate (foreign) tourists.
In 2015, China Daily reported that one of the most common complaints among international visitors was the poor condition of public toilets — a serious issue considering tourists are estimated to use public restrooms over 27 billion times per year.
That same year, China’s so-called “Toilet Revolution” (厕所革命) began gaining momentum. While not a centralized campaign, it marked a nationwide push to upgrade toilets across the country and improve sanitation systems to make them cleaner, safer, and more modern.
This movement was largely led by the tourism sector, with the needs of both domestic and international travelers in mind. These efforts, and the buzzword “Toilet Revolution,” especially gained attention when Xi Jinping publicly endorsed the campaign and connected it to promoting civilized tourism.
In that sense, China’s toilet revolution is also a “tourism toilet revolution” (旅游厕所革命), part of improving not just hygiene, but the national image presented to the world (Cheng et al. 2018; Li 2015).
🚽📌 Second, the growing number of sitting toilets in malls and other (semi)public spaces in Beijing relates to the idea that Western-style toilets are more sanitary.
Although various studies comparing the benefits of squatting and sitting toilets show mixed outcomes, sitting toilets — especially in shared restrooms — are generally considered more hygienic as they release fewer airborne germs after flushing and reduce the risk of infection (Ali 2022).
There are additional reasons why sitting toilets are favored in new toilet designs. According to Liang Ji (梁骥), vice-secretary of the Toilet Committee of the China Urban Environmental Sanitation Association (中国城市环境卫生协会厕所专业委员会), sitting toilets are also increasingly being introduced in public spaces due to practical concerns.
🚽📌 Squatting is not always easy, and can pose a safety risk, particularly for the elderly, pregnant women, and people with disabilities.
🚽📌 Then there are economic reasons: building squat toilets in malls (or elsewhere) requires a deeper floor design due to the sunken space needed below the fixture, which increases both construction time and cost.
🚽📌 Liang also points to an aesthetic factor: sitting toilets simply look more “high-end” and are easier to clean, which is why many consumer-oriented spaces prefer to install Western-style toilets.
So although there are plenty of reasons why sitting toilets are becoming a norm in newly built public spaces and trendy malls, they also lead to footprints on toilet seats — and all the problems that come with it.
The Catch 22 of Sitting vs Squad Toilets
This week, the issue became a trending topic on Weibo after Beijing News published an investigative report on it. The report suggested that most shopping malls in Beijing now have restrooms with sitting toilets, which should, in theory, be cleaner than the squat toilets of the past — but in reality, they’re often dirtier because people stand on them. This issue is more common in women’s restrooms, as men’s restrooms typically include urinals.
In researching the issue, a reporter visited several Beijing malls. In one women’s restroom, the reporter observed 23 people entering within five minutes. Although the restroom had only three squat toilets versus seven sitting ones, around 70% of the users opted for the squat toilets.
Upon inspection, most of the seven sitting toilets were dirty — despite being equipped with disposable seat covers — showing clear signs of urine stains and footprints. They found that sitting toilets being used as squat toilets is extremely common.
It’s a bit of a Catch-22. People generally prefer clean toilets, and there’s also a widespread preference for squat toilets. This leads to sitting toilets being used as squat toilets, which makes them dirty — reinforcing the preference for squat toilets, since the sitting toilets, though meant to be cleaner, end up dirtier.
In interviews with 20 women, nearly 80% said they either hover in a squat or directly squat on the toilet seat. One woman said, “I won’t sit unless I absolutely have to.” While some of those quoted in the article said that sitting toilets are more comfortable, especially for elderly people, they are still not preferred when the seats are not clean.
In the Beijing News article, the Toilet Committee’s Liang Ji suggested that while a balanced ratio of squat and sitting toilets is necessary, a gradual shift toward sitting toilets is likely the future for public restrooms in China.

How NOT to use the sitting toilet. Sign photographed by Xiaohongshu user @FREAK.00.com.
Liang also highlighted the importance of correct toilet use and the need to consider public habits in toilet design.
In Squatting We Trust
On Chinese social media, however, the majority of commenters support squatting toilets. One popular comment said:
💬 “Please make all public toilets squat toilets, with just one sitting toilet reserved for people with disabilities.”

Squatting toilets in a public toilet in a Beijing hutong area, image by Xiaohongshu user @00后饭桶.
The preference for squatting, however, doesn’t always come down to bowel movements or tradition. Many cite a lack of trust in how others use public toilets:
💬 “When it comes to things for public use, it’s best to reduce touching them directly. Honestly, I don’t trust other people…”
💬 “Squatting is the most hygienic. At least I don’t have to worry about touching something others touched with their skin.”
💬 “I hate it when all the toilets in the women’s restroom at the mall are sitting toilets. I’m almost mastering the art of doing the martial-arts squat (蹲马步).”
Others view the gradual shift toward sitting toilets as a result of Westernization:
💬 “Sitting toilets are a product of widespread ‘Westernization’ back in the day — the further south you go, the worse it gets.”
But some come to the defense of sitting toilets:
💬 “Are there really still people who think squat toilets are cleaner? The chances of stepping in poop with squat toilets are way higher than with sitting ones. Sitting toilet seats can be wiped with disinfectant or covered with paper. Some people only care about keeping themselves ‘clean’ without thinking about whether the next person might end up stepping in their mess.”
💬 One reply bluntly said: “I don’t use sitting toilets. If that’s all there is, I’ll just squat on top of it. Not even gonna bother wiping it.”
It’s clear this debate is far from over, and the issue of people standing on toilet seats isn’t going away anytime soon. As China’s toilet revolution continues, various Toilet Committees across the country may need to rethink their strategies — especially if they continue leaning toward installing more sitting toilets in public spaces.
As always, Taobao has a solution. For just 50 RMB (~$6.70), you can order an anti-slip sitting-to-squatting toilet aid through the popular e-commerce platform.
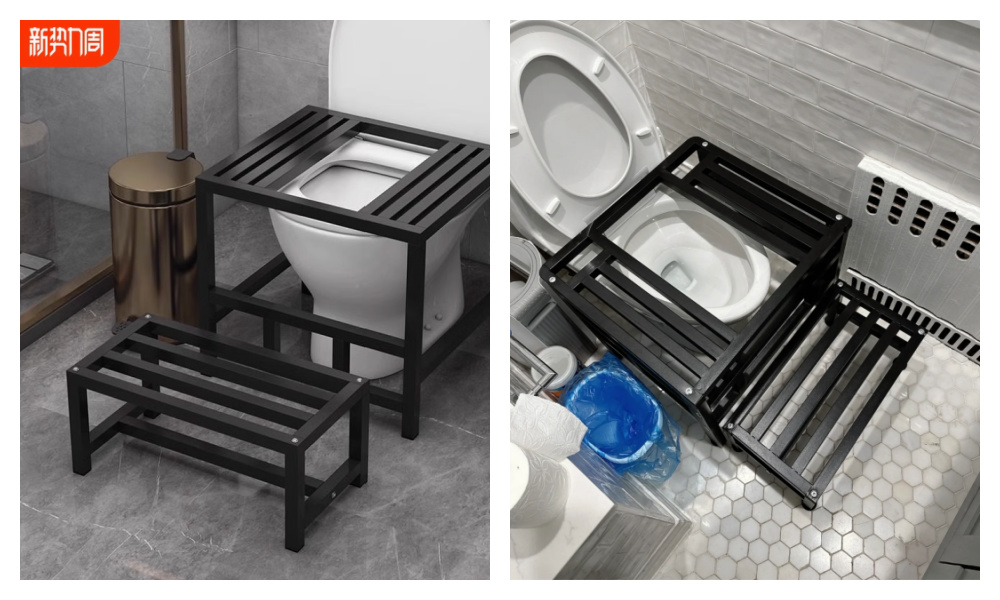

The Taobao solution.
For Chinese malls, offering these might be cheaper than dealing with broken toilets and the never-ending battle against footprints on toilet seats…
Best,
Manya
(@manyapan)
References:
Ali, Wajid, Dong-zi An, Ya-fei Yang, Bei-bei Cui, Jia-xin Ma, Hao Zhu, Ming Li, Xiao-Jun Ai, and Cheng Yan. 2022. “Comparing Bioaerosol Emission after Flushing in Squat and Bidet Toilets: Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment for Defecation and Hand Washing Postures.” Building and Environment 221: 109284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109284.
Bhattacharya, Sudip, Vijay Kumar Chattu, and Amarjeet Singh. 2019. “Health Promotion and Prevention of Bowel Disorders Through Toilet Designs: A Myth or Reality?” Journal of Education and Health Promotion 8 (40). https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_198_18.
Cao, Jingrui 曹晶瑞, and Tian Jiexiong 田杰雄. 2025. “城市微调查|商场女卫生间,坐厕为何频频变“蹲坑”? [In Shopping Mall Women’s Restrooms, Why Do Sitting Toilets Frequently Turn into ‘Squat Toilets’?]” Beijing News, March 20. https://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309405146044773302810. Accessed March 19, 2025.
Cheng, Shikun, Zifu Li, Sayed Mohammad Nazim Uddin, Heinz-Peter Mang, Xiaoqin Zhou, Jian Zhang, Lei Zheng, and Lingling Zhang. 2018. “Toilet Revolution in China.” Journal of Environmental Management 216: 347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.043.
Dai, Wangyun. 2018. “Seats, Squats, and Leaves: A Brief History of Chinese Toilets.” Sixth Tone, January 13. https://www.sixthtone.com/news/1001550. Accessed March 22, 2025.
Li, Jinzao. 2015. “Toilet Revolution for Tourism Evolution.” China Daily, April 7. https://europe.chinadaily.com.cn/opinion/2015-04/07/content_20012249_2.htm. Accessed March 22, 2025.
China’s Online Discourse on the Russia-Ukraine War

In case you missed it in our earlier newsletter, we recently published the article “US-Russia Rapprochement and ‘Saint Zelensky’: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Shake-Up” as part of our What’s on Weibo Chapters. For more insights into how the war is discussed on Chinese social media, you can catch up here.
Stay tuned — we’re publishing another article on this topic later this week, exploring the unexpected connection between the Russia-Ukraine war and Chinese cosplayers.
What’s Trending
🍏 Chinese Netizens Turn to Tim Cook Over Factory’s Illegal Overtime
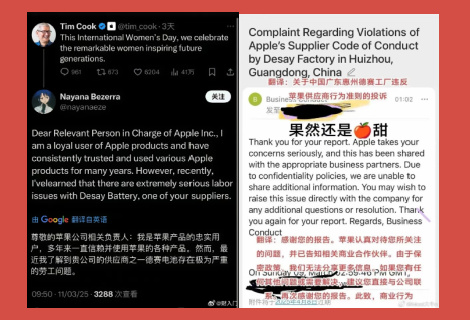
Netizens have recently started reaching out to Apple and its CEO Tim Cook in order to put pressure on a Chinese battery factory accused of violating labor laws. The controversy involves the Huizhou factory of Desay Battery (德赛电池), known for producing lithium batteries for the high-end smartphone market, including Apple and Samsung. The factory caught netizens’ attention after a worker exposed in a video that his superiors were deducting three days of wages because he worked an 8-hour shift instead of the company’s “mandatory 10-hour on-duty.” Compulsory overtime violates China’s labor laws.
In response, the worker and other netizens started to let Apple know about the situation through email and social media, trying to put pressure on the factory by highlighting its position in the Apple supply chain. By now, Desay Battery issued an official statement, admitting to “management oversights regarding employee rights protection” (“保障员工权益的管理上存在疏漏”) and promising to do better in safeguarding employee rights.
It’s an interesting story, and some commentators suggest that it shows that Chinese workers can effectively expose labor violations by reporting them to Western suppliers or EU regulators. But opinions vary. Others are less optimistic about the effectiveness, arguing that companies like Apple would be quick to drop suppliers over product quality issues but more willing to turn a blind eye to labor violations—since cheap labor remains a key competitive advantage in Chinese manufacturing.
💸 From Patriotic Influencer to Tax Evader: Sima Nan Fined More Than Nine Million Yuan

China’s well-known nationalist blogger Sima Nan (司马南) became a trending topic on Friday after being hit with a 9 million RMB ($1.2 million) fine for tax evasion. According to state media, from 2019 to 2023, he underpaid millions of yuan in personal income tax and other taxes by concealing income and submitting false declarations.
Sima responded to media, saying he fully admits guilt. At the same time he’s also blaming the multi-channel network that allegedly was in charge of paying taxes on his behalf at the time.
📌 Noteworthy: Sima Nan promised that- if he’ll still be allowed to have his social media presence – he would in detail explain how he ended up becoming a tax evader. This is kind of funny, because it shows just how good he is in what he does, turning his PR crisis into an opportunity for clicks and views 📈 (yes we do want to know how he went from patriotic influencer to becoming a multi-million tax dodger).
📌Public reaction: The most recurring comments I’ve seen on Weibo is that people are amazed at his high income. They note the hypocrisy of a nationalist, patriotic influencer who’s always preaching truth & justice evading taxes himself, and also conclude that being a nationalist is truly a money-making business🤑🇨🇳
💔 Tragedy at Hubei University: Zhang Yuzhen’s Disappearance and Aftermath

The disappearance of 19-year-old Chinese student Zhang Yuzhen (张钰臻) has captured nationwide attention this week. Zhang did not return after leaving her campus at Hubei University around 5 p.m. on March 15. Her phone remained traceable until 5:54 p.m., about one kilometer from campus. The case became a hot topic as millions of netizens turned into online sleuths, searching for clues that might lead to Zhang’s whereabouts.
On the afternoon of March 20, it was reported that Zhang’s personal items — including her keys and glasses — were discovered by a passerby next to a lake near the university. Police then began searching the lake. By that evening, her remains were found. The case is still under investigation.
There has been some online criticism regarding how the university handled Zhang’s disappearance. Although she was last seen on March 15, it wasn’t until March 18 that her parents were notified by a school counselor. They then reported her missing to the police, after which the school began cooperating with the investigation.
Now, there is also much discussion surrounding the behavior of Zhang’s mother, who has been publicly expressing her grief and anger on Douyin. After learning of her daughter’s death, she became emotionally distraught — screaming, crying, and demanding answers. She seemingly caused some public disturbance when she was prevented from immediately seeing her daughter’s remains, and was also not allowed to leave her hotel (perhaps due to concerns over her emotional state, though details remain unclear at this time). While some online voices have criticized her behavior, many are calling for empathy, arguing that any mother who has just lost her child would be desperate and distraught.
What’s Noteworthy

“The world is so big, I want to go out and see it” (Shìjiè nàme dà, wǒ xiǎng qù kànkan “世界那么大,我想去看看”).
This ten-character sentence became part of China’s collective social media memory after a teacher’s resignation note went viral in 2015. Now, a decade later, the phrase has gone viral once again.
In April 2015, the phrase caused a huge buzz on China’s social media when the female teacher Gu Shaoqiang (顾少强) at Zhengzhou’s Henan Experimental High School resigned from her job. Working as a psychology teacher for 11 years, she gave a class in which she made students write a letter to their future self. The exercise made her realize that she, too, wanted more from life. Despite having little savings, she submitted a simple resignation note that read: “The world is so big, I want to go out and see it.”
The resignation letter was approved, and she posted it to social media.
The letter resonated with millions of Chinese who felt they also wanted to do something different with their life, like go and travel, see the world, and escape the pressures and routines of their daily life. The phrase became so popular that it was adapted in all kinds of ways and manners, by meme creators, in books, by brands, and even by Xi Jinping, who said: “China’s market is so big, we welcome everyone to come and see it” (“中国市场这么大,欢迎大家都来看看”).
This week, Lěngshān Record (冷杉Record), the Wechat account under Chinese media outlet Phoenix Weekly (凤凰周刊), revisited the phrase and published a short documentary about Gu’s life after the resignation and the hype surrounding it.
An earlier news article about Gu’s life post-resignation already disclosed that Gu, despite receiving many sponsorship deals, never actually extensively traveled the world. In the short documentary, Gu explains that she chose to “return home after seeing the world.” By this, she doesn’t mean traveling extensively abroad, but rather gaining life experience in a broader sense. While she did travel, it was within China, including in Tibet and Qinghai.
What truly changed was her life path. She left Zhengzhou and relocated to Chengdu to be near Yu Fu (于夫), a man she had met just weeks earlier by chance during a trip to Yunnan. Six months after the resignation letter, she married him. Together, they ended up opening a hostel near Chengdu, married, and had a daughter.
Gu, now 45 years old, has been back in her hometown of Zhengzhou for the past years, caring for her aging mother and 9-year-old daughter. She is living separately from her husband, who manages their business in Chengdu. She also runs her own livestreaming and online parenting consultancy business.
Although the woman who wanted to “see the world” ended up back home, she has zero regrets about what she did, suggesting her courage to step out of the life she found limiting ultimately transformed her in a meaningful way.
On Chinese social media, the topic went trending on March 19. Most people cannot believe it’s already been ten years since the sentence went trending (“What? How could time fly like that?”). Others, however, wonder about the hopes and dreams behind the original message—and how it all turned out.
💬 “Seeing the world? She just escaped her old life, got married, and had a baby. How is that ‘seeing the world’?” one commenter wondered (@-NANA酱- ).
💬 “The world is so big—what did she end up seeing?” others questioned. “She went from Zhengzhou to Chengdu.”
💬 “Seeing the world takes money,” some pointed out.
💬 But others came to her defense, saying that “seeing the world” also means stepping out of your comfort zone and exploring a different life. In the end, Gu certainly did just that.
💬 “She was quite courageous,” another commenter wrote: “She gave up a stable job to go and see the world. Perhaps her life didn’t end up so rich, but the experiences she gained are priceless.”
The world is still big, though, and there’s plenty left for Gu Shaoqiang to see.
Also read what we wrote about this in 2015: In The Digital Age, ‘Handwritten Weibo’ Have Become All The Rage
What’s Memorable

📚 This pick from our archive is from last year, about Fan Zeng (范曾), the famous Chinese calligrapher, who is turning 87 soon and has a wife 50 years his junior.
This week, some videos featuring Chinese theoretical physicist & Nobel Prize winner Yang Chen-Ning (杨振宁) circulated on social media. Yang is turning 103 this year. Still sharp of mind, and he takes a walk every day.

Yang Chen-ning
In this interview here, when asked about the secret to his longevity, he points to one thing above all: luck.
🍀 Mostly, he suggests it’s the luck of good genes. On his father’s side, diabetes was common, but he was fortunate to inherit his mother’s genes in that regard.
🍚 He also mentions the luck of never experiencing extreme hunger during wartime — he lived in Kunming during those years.
💪 And then he stresses the importance of taking walks, every day, since he was about 70. Keep moving, keep the blood flowing!
What he doesn’t mention, however, is that his wife, Weng Fang (翁帆), is 54 years (!) his junior — I’m pretty sure she helps keep him young too…
Fan and Yang are good friends, and Yang’s good health might have inspired him to marry his 50-years-younger girlfriend last year. Read more 👇
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng






