China Health & Science
Beijing Changfeng Hospital Fire: Five Things To Know
29 people lost their lives due to the devastating fire that occurred in Beijing’s Changfeng Hospital on Tuesday. These are 5 things to know.
Published
1 year agoon
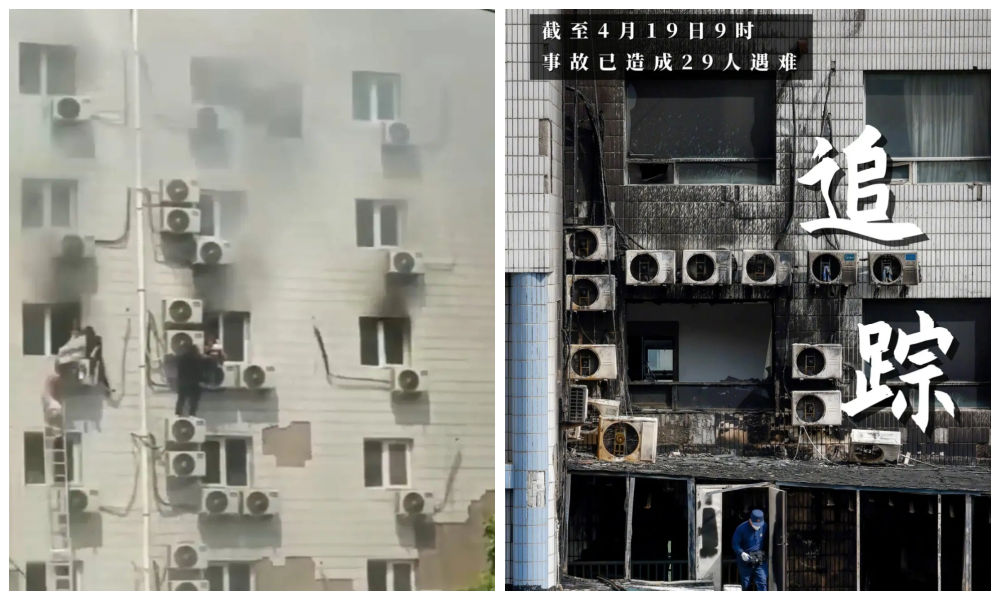

On Tuesday, April 18, a big fire broke out inside Changfeng Hospital, a private hospital located in Beijing’s Fengtai District. The incident, which killed 29 people, is now known as the “4.18 Beijing Changfeng Hospital Fire Incident” (4•18北京长峰医院火灾事故).
Videos of the incident that circulated on Chinese social media (see here) showed smoke coming out of the hospital windows on different floors, with patients hanging on to air conditioning units outside of the windows. The footage also showed patients falling down the building from higher floors.
This is the timeline of the incident as reported by Chinese official media:
• April 18 / 13:00-15:00
At 12:57 on April 18, the Fengtai District fire and emergency services received an alert that a fire had broken out in the east building of the inpatient department of Beijing Changfeng Hospital. The fire, which was extinguished at 13:33, killed 21 people. The cause of the incident was still under investigation.
• April 18 / 15:30
At 15:30, the rescue work was finished and a total of 71 patients were evacuated and transferred to other hospitals in Beijing.
• April 18 / Evening
Changfeng Hospital closed its doors and only allowed immediate family members of inpatients to still enter the hospital. The Chinese Non-government Medical Institutions Association, the largest association of private hospitals in China, later also announced that they had canceled the membership of Beijing Changfeng Hospital in light of the incident.
• April 19 / 9:00
As of 9:00 local time, official sources reported that the death toll of the fire incident had risen to 29 people. 27 of them were patients who were treated at the hospital, and some of them died after their transfer to another hospital. The average age was 71.2 according to China Youth Daily.
• April 19 / 12:00
In a briefing held by Beijing authorities, it was said that the fire originated from sparks that arose during renovation and construction work at the hospital, according to Chinese media reports. Authorities stated that the Changfeng Hospital director, along with 11 others (including the hospital’s Vice President, the construction company’s leader, and one construction workers on site), had been detained for their criminal liability in the fire incident.
• April 19 / Late afternoon
According to CCTV, Beijing’s Fengtai District has set up a community working group (群众工作组) to provide assistance and support to patient’s families and help with any practical problems at the scene.
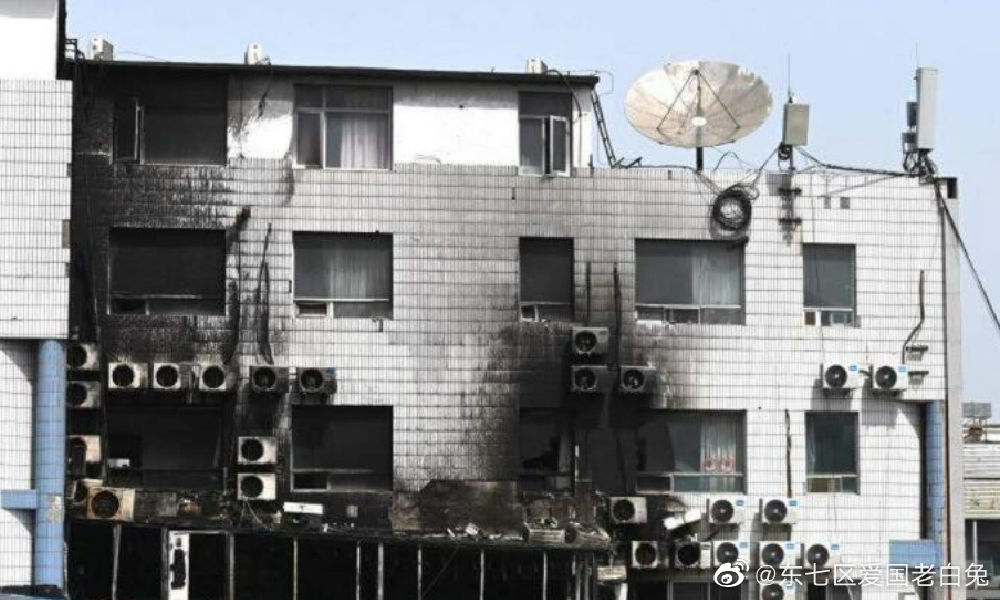

Here are five important things to know regarding the deadly fire at Beijing’s Changfeng Hospital:
1. The Patients Were Especially Vulnerable
The fire reportedly broke out at the 5th floor of the Changfeng Hospital, which is a private hospital specializing in neurology, vascular tumors, and arteriovenous malformations.
The patients that were staying at the higher floors at the affected building were especially weak, as they were mostly elderly patients and those receiving critical or end-of-life care. Many of them were mobility-limited patients who could not easily get out of bed and escape the fire by themselves.
2. There Were No Adequate Fire Evacuation Measures in Place
There were no adequate fire evacuation measures in place at the hospital, where hospital rooms were crowded with multiple patients. According to one nurse who was quoted by China Youth Daily, she had to climb down a water pipe from the 8th floor of the hospital, which is the building’s top floor. The videos that circulated also showed the lack of fire stairs, as patients fled from windows and held on to air conditioning units.
Because the fire occurred during daylight hours, emergency responders were able to act quickly, the hospital building had only 8 floors, and rescue efforts were not hindered by road obstructions, the high death toll resulting from the Changfeng fire is all the more surprising and tragic.
In late February of this year, Changfeng Hospital had released news about strictly implementing fire prevention and control measures. The hospital reportedly also held a fire prevention and control meeting according to government regulator requirements, but the April 18 fire showed that these measures were not actively implemented.
3. The Construction Work on the Hospital Seemed Unregulated
Chinese media source The Time Weekly (时代周报) reported that residents in the hospital’s neighborhood stated that the renovation of the building had been going on for some time and that many wires could be seen outside of the building where the fire occurred, expected to be illegal power lines (私拉电线) without proper safety measures.
The cause of the fire can be traced back to sparks that were generated during renovations on the inside of the hospital, at the inpatient department, and they reportedly ignited volatile fumes from combustible paint on the site.
This also suggests that the construction workers and the renovation procedures in general did not follow proper safety or risk assessment protocols that could have prevented the fire from breaking out.
4. Media Coverage of the Fire Was Initially Limited, Comments Censored
Although the Changfeng Hospital fire is now all over Chinese social media, news about the fire was strictly controlled in the direct aftermath of the incident.
On Twitter, VOA News reporter Wen Hao (@ThisIsWenhao) noted how public anger erupted across Chinese social media on Tuesday as videos and social media posts about the fire were taken down. Wen states that it was not until 20:49 that local official media first announced the fire and the number of deaths.
Reporter Vivian Wu (@vivianwubeijing) also noted how it was not until about 21:00 before Chinese news outlets received the “green light” to report on the incident.
All the big reports about the incident only were released eight hours after the fire started, suggesting that local authorities wanted to make sure the fire was under control and that there was enough information on the incident – and how to communicate it to family members and the general audience – before further news was released and went viral on social media.
In a blog that has now been censored on socials titled “5 Facts the News Conference Didn’t Tell You About the Changfeng Hospital Fire that Killed 29 People” (“长峰医院火灾致29人死亡,发布会没告诉你的5条真相”)* – still online at iFeng – the author called it “a mystery” that such a major fire in Beijing could stay under wraps for eight hours until the official announcement came out. The author, along with other sources, also claimed that some family members did not know about the fire until they saw the news pop up.
In 2022, a fire that occurred in Urumqi city, Xinjiang, triggered waves of mourning and anger on Chinese social media. On Weibo, there were many questions and rumors surrounding the incident at a particularly sensitive zero-Covid time, when frustrations were already building (read all about the aftermath here).
Although the context and location of the Urumqi fire is very different from the Changfeng one, it seems clear that there was a government-orchestrated media strategy following the direct aftermath of the April 18 fire to keep information flows under control.
5. The Incident Reignited Scrutiny on Private Hospitals in China
The fire at Changfeng Hospital has reignited scrutiny on the role of private hospitals in China, which have been previously also been criticized for prioritizing financial gain over the well-being of patients.
In light of this incident, some netizens mention Putian Medical Group, a powerful player in China’s healthcare industry that has set up private hospitals all over the country. Putian has previously been criticized for overpricing patients, working together with Baidu to lead patients to their clinics, and fraudulent affairs (read more here).
Now, Changfeng Hospital – which runs a number of hospitals in twenty cities across the country – is also facing backlash for spending hundreds of millions of yuan on advertising their medical services while suffering financial losses. At the same time, they were clearly not allocating enough resources for proper fire control and safety measures in their buildings.
Chinese media outlet The Observer wrote that the hospital actually shows similarities with the Putian Medical Group, as various clinics or hospitals led by Changfeng were previously also reported for medical scams. The Fengtai branch itself was penalized a total of 11 times since 2016 for various reasons (#长峰医院7年间至少被罚11次#).
For now, many people are still questioning how the incident could have happened and why its outcome is so tragic. While further investigations are still underway, some of these questions will hopefully be answered in the near future.
By Manya Koetse
Follow @whatsonweibo
* The five questions that the news conference did not answer according to the blogger relate to: 1. Why family members and the general audience only learnt about the fire at such a relatively late time; 2. Why the death toll of the incident was so high considering the circumstances; 3. Why the hospital was allowed to do interior construction work while also resuming normal operations; 4. Why the owner of the Changfeng Hospital group is not among the 12 people detained after the fire; 5. Why Hunan patients who were treated at the hospital were allegedly transferred to private secondary hospitals in Beijing.
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

Also Read
China Food & Drinks
Chinese Woman with Heartbreak Passes Away after Drinking Bottle of Baijiu
Three friends are held partially responsible for not intervening when the woman consumed 500ml of baijiu.
Published
7 months agoon
December 15, 2023
An incident that happened on the night of May 21, 2023, has become a trending topic on Chinese social media today after a local court examined the case.
A woman named ‘Xiao Qiu’ (alias), a resident of Jiangxi’s Nanchang, apparently attempted to drink her sorrows away after a heartbreaking breakup.
She spent the night at a friend’s house, where she drank about 50cl of baijiu (白酒), a popular Chinese spirit distilled from fermented sorghum that contains between 35% and 60% alcohol. One entire bottle of baijiu, such as Moutai, is usually 50cl.
She was together with three female friends. One of them also consumed baijiu, although not as much, and the two other friends did not drink at all.
As reported by Jiupai News, the intoxicated Xiao Qu ended up sleeping in her car, while one of her sober friends stayed with her. However, at about 5 AM, her friend discovered that Xiao Qiu was no longer breathing. Just about an hour later, she was declared dead at the local Emergency Center. The cause of death was ruled as cardiac and respiratory failure due to alcohol poisoning.
The court found that Xiao Qu’s friends were partly responsible for her death, citing their failure to prevent her excessive drinking and inadequate assistance following her baijiu binge drink session. Each friend was directed to contribute to the compensation for medical expenses and pain and suffering incurred by Qiu’s family.
The friend who also consumed baijiu was assigned a 6% compensation responsibility, while the other two were assigned 3% each.
On Weibo, many commenters do not agree with the court’s decision, asserting that adult individuals should not be held accountable when a friend goes on a drinking spree. Some commenters wrote: “You can tell someone not to drink, but what if they don’t listen?” “Should we record ourselves telling friends not to drink too much from now on?”
This is not the first time for friends to be held liable for an alcohol-related death in China. In 2018, multiple stories went viral involving people who died after excessive drinking at social gatherings.
One case involved a 30-year-old Chinese man who was found dead in his hotel room bathtub in Yangzhou after a formal dinner with friends where he allegedly drank heavily. The man reportedly died of a heart attack. His friends reached a 1 million yuan (±US$157,000) settlement with his family, with the cost shared among the friends who were present during the night.

Surveillance cameras in Jinhua captured how the man was unable to stand or walk after drinking with his friends.
Another case involved a man who died when he was left by his friends at a hotel in Jinhua, Zhejiang province, after heavily drinking at a banquet. Surveillance cameras captured how the man was unable to stand or walk after drinking with his friends. Those friends also paid a compensation together of 610,000 yuan (US$96,000) to the man’s family.
Organisers of an alcohol drinking contest in Henan province were also ordered to pay a compensation of over US$70,000 after one participant died due to excessive alcohol intake in July of 2017.
These cases also triggered online discussions about how Chinese traditional drinking culture often encourages people at the table to drink as much as they can or to exceed their limits; the goal sometimes is to literally “take someone to the ground by drinking.” When someone proposes a toast, everyone at the table is required to finish their glasses, sometimes at a very high pace.
In light of the latest news, some commenters write on Weibo: “No matter what kind of drinking gathering it is, for someone who is already drunk, others should intervene to prevent them from continuing to drink. Even if they invite, provoke, or insist on drinking themselves, they should not be allowed to continue. Otherwise, it not only harms them, you might end up facing legal responsibility yourself.”
Others remind people that overindulging in alcohol when you’re in a state of distress is never a good idea, and that no heartbreak is worth getting drunk over: “There are plenty of other fish in the sea.”
By Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Health & Science
‘Sister Blood Points’ Controversy: Shanghai Woman’s Tibet Blood Donations Ignite Privilege Debate
Dozens of local public officials in Tibet donated blood to rescue a Shanghainese woman. Netizens believe it’s a matter of privilege.
Published
8 months agoon
December 9, 2023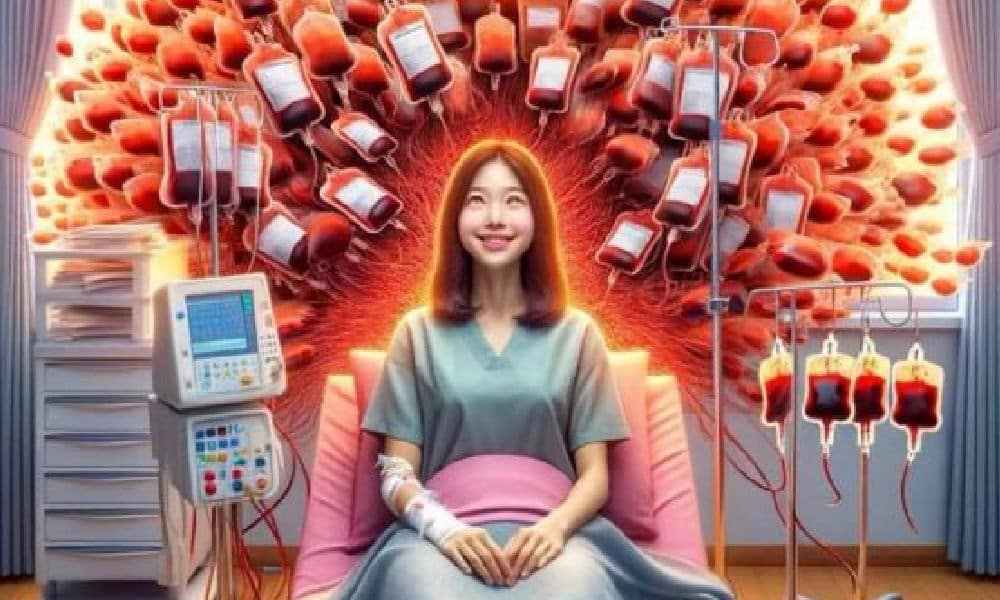
The medical rescue of a critically injured Shanghai woman in Tibet has recently triggered major controversy on Chinese social media after netizens suspected that the woman’s treatment may have been facilitated through the abuse of power.
What was supposed to be a romantic honeymoon getaway turned into a nightmare for newlyweds Yu Yanyan (27, 余言言) and her husband Tao Li (29, 陶立).
On October 14, just two weeks after their wedding, the couple from Shanghai was driving on China’s National Highway 219. Their destination was Ngari Prefecture in Tibet’s far west, where the average elevation is 4500 meters.
As they drove by the famous mountain pass Jieshan Daban (界山達阪), situated at an altitude of 5347 meters, they suddenly realized that the altitude was affecting them. Soon, Tao Li, who was driving the car, lost consciousness and crashed the car. Yu Yanyan, on the passenger side, was badly injured in the crash.
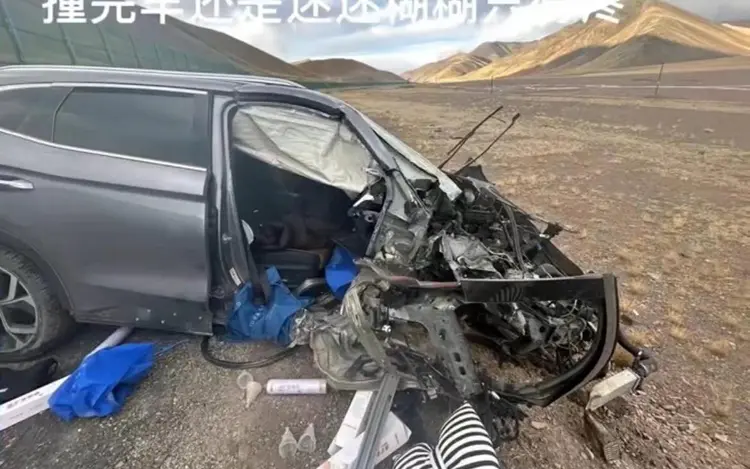

The crashed car, image via Beijing News/Xinjinbao (source).
What followed was a complicated, time-sensitive, and costly rescue operation. At the Ngari People’s Hospital (阿里地区人民医院), Yu was diagnosed with a ruptured liver, abdominal bleeding, hemorrhagic shock, and thoracic trauma. She was losing a lot of blood in a short time and required surgery, but there was not enough blood available for a blood transfusion at the time in the sparsely populated region, as reported by Beijing News.
Tibetan Civil Servants to the Rescue
While the hospital made efforts to secure donations, specifically requiring an adequate supply of A+ type blood, Yu’s husband was reportedly advised to reach out to the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (上海卫健委) to inquire about potential assistance. One of his aunts, or his ‘auntie’, allegedly helped him to contact them.
These efforts appeared to be fruitful. Between October 16-17, just days following the crash, numerous members of the public and dozens of local civil servants in Tibet, including firefighters, policemen, and military personnel, stepped forward to donate blood, contributing to over 7000 mL of A-type Rh-positive blood that ultimately saved Yu’s life.
Allegedly thanks to the Tibet office of the Shanghai Municipal People’s Government, a medical specialist from Shanghai was even sent to assist in the medical treatment of Yu at the Ngari hospital.
As Yu later required more advanced medical care and surgeries, she was advised to go to a bigger hospital. She was then transferred via a specially arranged chartered plane. The total costs of this medical chartered plane flight from Ngari to Sichuan’s Huaxi hospital (四川华西医院), arranged by Yu’s father, allegedly cost 1,2 million yuan (US$169.230).

After receiving surgery at the Huaxi Hospital, Yu was in stable condition and was transferred to Shanghai.
An Abuse of Power?
Yu’s story began drawing notice, eventually garnering nationwide media coverage, after Yu herself posted a video on her social media account (Douyin) in which she recounted her experiences. Yu, who only had a relatively small group of followers, told about her rescue operation and her recovery. But instead of garnering sympathy, it led to many questions from netizens and went viral. The video was later deleted.

Screenshots from the since deleted Douyin video.
Who was the ‘auntie’ who reached out to the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission? How were Tibet public officials made to donate blood for this Shanghai patient? What power dynamics were in play that facilitated the mobilization of people in this manner by the family?
People became upset, as they suspected Yu’s life had only been saved because of an abuse of power, and that ordinary Chinese patients would never have never received a similar treatment.
They started referring to Yu as ‘Sister Blood Points.’ The Chinese term is xuè cáo jiě 血槽姐, with xuè cáo 血槽 (lit. blood groove) often being used in the world of gaming to refer to the health bar, an image in video games that shows the player how much energy or blood or strength they have left before it’s game over.
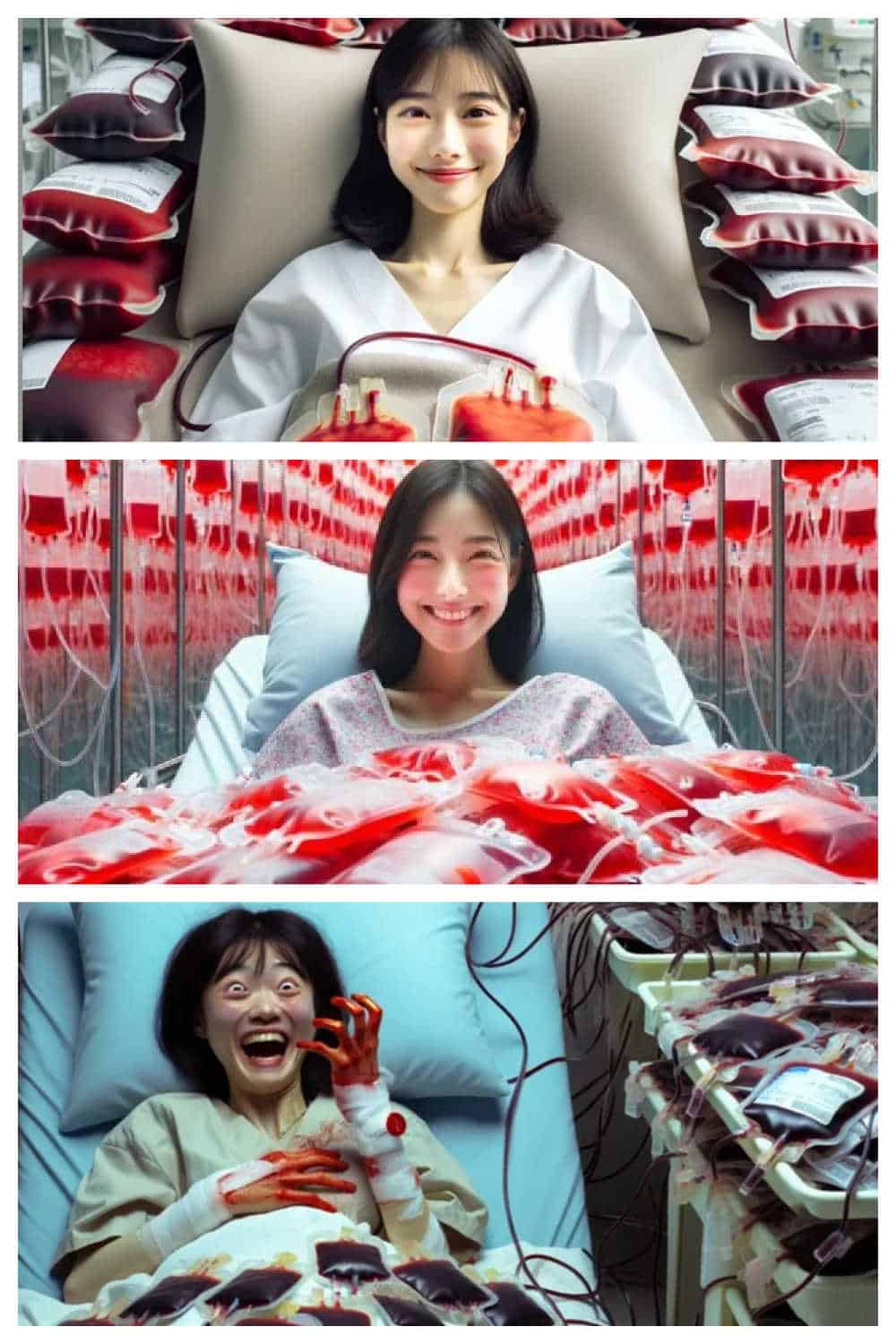

Various online AI-generated images featuring a portrayal of “Sister Blood Points.”
There were also various digital (AI-generated) images showing Yu surrounded by bags of donated blood, portraying her as a privileged, blood-sucking Shanghai ‘princess’ in Tibet.
Following the online commotion, the Ngari Propaganda Department issued a statement on November 29 promising to look into the issue. Additionally, in the first week of December, various Chinese media outlets also started to investigate the case.
An Ordinary Patient in Extraordinary Circumstances
On December 6, online newspaper The Paper (澎湃新闻) published an article together with Shangguan News (上观新闻) which answered some of the most pressing questions surrounding the case.
The Paper reported that they found no officially organized mobilization of public officials or members of the public to donate blood. Instead, local workers and individuals donated blood after learning about the woman’s situation through various channels, including from the hospital staff. Yu Yanyan’s husband Tao called the successful blood donation campaign a result of “multi-party mobilization” (“这是我们多方动员的结果,确实不是有组织的。”)
The Shanghai Municipal Health Commission also denied that they had contacted health authorities in Tibet to ask civil servants to donate blood. They claimed their members of staff did not personally know the patient nor any members of her or her husband’s family.
Furthermore, the article says that the woman known as ‘auntie’ is a 60-year-old retired woman who previously worked at a crafts factory. Upon learning about Yu’s predicament, she forwarded the information to her daughter-in-law, who works at a bank and also did all she could to spread the news and ask for help. This eventually led to the Tibet office of the Shanghai Municipal People’s Government being updated on the situation.
The Tibet office has refuted any suggestion that personal relationships influenced the procedures that resulted in the dispatch of a Shanghai medical expert to assist at Ngari People’s Hospital. A Shanghai medical team stationed in Tibet received a request for urgent support at the hospital and, following their ethical work guidelines, dispatched an expert to provide assistance.
The Paper further stated that nor Yu, nor her husband or their family were officials. In order to pay for the medical flight, Yu’s parents used family savings and borrowed money from others.
All of the information that was coming out about the entire ordeal seemed to indicate that Yu was just an ordinary patient in extraordinary circumstances.
A Sign of Distrust
While certain commenters believe that the latest information has put an end to weeks of speculation, others continue to harbor suspicions that there might be more to the story – they are not satisfied with the answers provided on December 6.
As some netizens dug up screenshots of online calls for help from Tao, Yu’s husband, some commenters responded: “This only makes it clearer that there’s no special status (特殊身份) here. Real influential officials wouldn’t go so low as to seek help online. A simple phone call would have quickly resolved their issue.”
In the end, the entire ordeal, now labeled “The Civil Servant Blood Donation Incident” (公务员献血事件) on Chinese social media, reveals more about public distrust in the transparency of China’s healthcare system than it does about Yu, her family, or the situation in Tibet.
While frustrations regarding privilege and power abuse within China’s healthcare system have existed for years, this issue has gained significant public attention this year in light of the launch of a top-down anti-corruption campaign targeting the healthcare industry.
This issue is especially important due to China’s longstanding struggle with public mistrust in the medical care sector. Some studies even suggest that China’s healthcare system has suffered from a “trust crisis among the public” since the 1990s (Chen & Cheng 2022, 2).
Multiple factors contribute to the relatively low trust in the Chinese healthcare system, but access and costs both play major roles. The sentence “Getting medical attention is difficult, getting medical attention is expensive” (Kànbìng nán, kànbìng guì 看病难,看病贵) has become a well-known expression among Chinese patients dissatisfied with the challenges they encounter in both accessibility and affordability when seeking medical treatments.
Most medical providers in China have become increasingly commercialized and profit-driven since the 1980s, leading to problems with crime and corruption within the medical system as medical professionals are expected to balance both a focus on patient well-being and financial gain. With doctors contending with low pay and incentive-based labor, bribery has emerged as a well-known problem, often considered somewhat of an “open secret” (Fun & Yao 2017, 30-31).
The prevalence of such issues has fueled public frustration, making individual cases like Yu Yanyan’s a source of intense controversy. In an environment where “getting medical attention is difficult, getting medical attention is expensive,” and where corruption is a notorious problem, many people simply do not think it is possible for one young woman to receive so much medical assistance from doctors and civil servants without the involvement of connections, power abuse, and bribery in the process.
Now that more details about the ‘blood point sister’ story have come to light, most netizens have started to question the truth behind this story and realize that Yu might just be an ordinary citizen, while some bloggers are still demanding more answers. In the end, most agree that it is not really about Miss Yu at all, but about whether or not they could expect similar medical treatment if they would end up in such a terrible situation.
“Is there currently an emergency response system in place that allows ordinary people to seek help in equally urgent crises?” (“当前是否存在一个紧急响应机制,可以让普通人在遇到同样紧急的危机时,能寻求帮助?”) one Sina blogger wonders.
“It is actually not important to know if they had special privileges or not,” one Weibo commenter writes: “I just hope that if patients need donated blood in the future, they will get the same treatment.”
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
References:
Chen, Lu, and Miaoting Cheng. 2022. “Exploring Chinese Elderly’s Trust in the Healthcare System: Empirical Evidence from a Population-Based Survey in China.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19 (24): 16461-.
Fun, Yujing & Zelin Yao. 2017. “A State of Contradiction: Medical Corruption and Strain in Beijing Public Hospitals. In: Børge Bakken (Ed.), Crime and the Chinese Dream, Hong Kong University Press: 20–39.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?