China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
‘Carpet Pacific’: A Timeline of the Cathay Pacific Scandal Through Weibo Hashtags
Cathay Pacific flight attendants mocking non-English speaking passengers by saying, “If you can’t say blanket, you can’t have it,” has sparked a major controversy and caused a marketing catastrophe.
Published
1 year agoon

Last week, Xiamen Airlines was the focus of attention on Chinese social media after one of their pilots was caught secretly filming a female staff members in the ladies room. This week, the focus has shifted to Cathay Pacific, as the Hong Kong-based airline faced accusations of discrimination against travelers from mainland China.
The incident gained significant attention on May 22 when a user of the Xiaohongshu (Little Red Book) app shared a public complaint about the Hong Kong airline. In the post, the author, who claimed to have resided in Hong Kong for eleven years, expressed their inability to remain silent after witnessing overt discrimination on a Cathay Pacific CX987 flight from Chengdu to Hong Kong.
The passenger said they were seated near the area where the flight attendants rest and prepare meals, and that they could hear the cabin crew making fun of passengers who could not speak English. Passengers who tried to ask them for help in English about filling out immigration cards allegedly also received impatient responses. The passenger recorded some of their conversation, and later posted the audio clip online.
In one clip, you can hear the staff laughing about a passenger who wanted a blanket but could not properly say it in English. “If you cannot say blanket, you cannot have it,” they joked. Since some passengers allegedly had used the word ‘carpet’ instead of ‘blanket’, the cabin crew can be heard saying: “A carpet is on the floor.”
The biggest China social story of the past few days started with one passenger exposing Cathay cabin crew mocking & discriminating against non-English speaking (Mainland) passengers. His complaint and this 30 second audio snippet led to them being fired, and a social media storm. pic.twitter.com/BDuabQcm0S
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) May 27, 2023
Since the incident was first exposed on social media, it turned into a major controversy and a marketing crisis for the Cathay Pacific company. As Cathay was condemned by million of netizens, many also vowed to boycott the airline.
Cathay Pacific has been hit hard by the pandemic, and was seeing an increased demand for travel into the Chinese Mainland since quarantine-free travel between Hong Kong the Mainland was finally resumed on January 8 of this year. Cathay is heavily dependent on the Chinese market, and approximately 70% of its revue reportedly comes from China (#国泰航空近七成营收来自中国#).
The incident has ignited anger due to the discriminatory treatment of mainland customers by a Hong Kong company, leading to further discussions on anti-Chinese sentiments in Hong Kong and the role of language in fostering (or hindering) national unity between mainland China and Hong Kong.
This is a timeline of the incident through Weibo hashtags that have gone trending over the past few days.
▶︎ The Cathay Discrimination Audio Leaked Online #国泰空乘歧视乘客录音曝光# (260 million views)
After a netizen posted about supposed discrimination against non-English speaking passengers by cabin crew members on the Cathay Pacific CX987 flight, the incident soon garnered widespread attention on Chinese social media, especially when the 30-second audio was also shared online (hear the audio snippet here).
▶︎ Cathay Pacific Apologizes #国泰航空致歉# (210 million views)
On May 22, Cathay Pacific soon issued a response apologizing for the passenger’s experience and promised a thorough investigation. However, their initial apology was considered inadequate by many netizens, and only sparked more debates about the discrimination against mainland Chinese passengers within Cathay’s work environment.
On May 23, Cathay Pacific issued a second apology via social channels, mentioning that they had contacted the passenger and that they had suspended the flight attendants involved.
▶︎ Cathay Pacific Uses Standard Mandarin to Apologize #国泰航空行政总裁用普通话道歉# (10 million views)
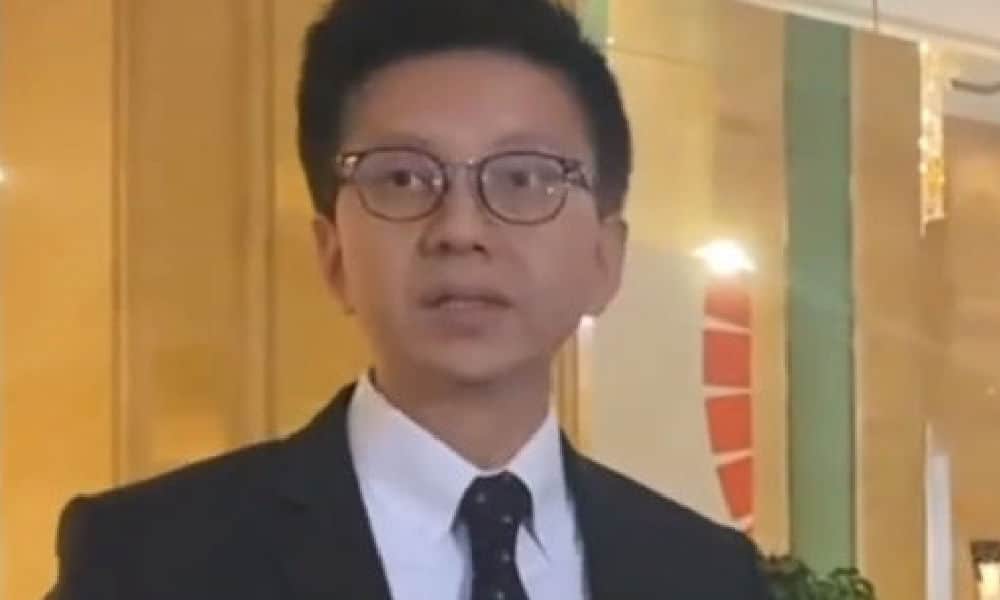

Lin Shaobo apologizes using Standard Mandarin, image via Weibo.com.
During a media briefing in Guangzhou on May 24, Cathay Pacific CEO Lin Shaobo (林绍波) once again expressed his sincere apologies on behalf of Cathay for the incident. In doing so, he used Standard Mandarin, the national language of mainland China.
▶︎ Three Employers Fired for Discriminating Against Passengers #国泰航空3名歧视乘客空乘被解聘# (460 million views)
At this time, it was also announced that Cathay had completed their investigation into the matter and, in accordance with the company’s regulations, had dismissed the three involved cabin crew members. Lin Shaobo clarified that the airline maintains a “zero tolerance” approach towards any employees who violate the company’s rules and ethical standards.
▶︎ Cathay Pacific’s Flight Attendant Union Regrets the Incident #国泰空乘工会对空姐被解聘感到遗憾# (180 million views)
On May 24, there was some online turmoil over a statement issued by Cathay Pacific’s Flight Attendant Union (FAU). In the statement, the union expressed that Cathay is “facing a shortage of both manpower and resources, a significant increase in workload and low salaries.” Because these problems are ignored, Cathay is seeing an “extremely low” morale among cabin crew and more complaints regarding cabin service. “Nothing comes from nothing,” the statement said. The Union was criticized for “whitewashing” the cabin crew’s discrimination against non-English-speakers.
▶︎ No Official Support for The Union #国泰航空称空中服务员工会不代表国泰# (130 million views)
On May 25, Cathay Pacific issued a statement in which they clarified that The Union is an independent labor union and does not represent the company. They also clarified that did not support the union’s position nor agreed with it.
▶︎ Hu Xijin Recommends Mainland Passengers to Speak Mandarin #胡锡进建议乘国泰航空只讲普通话# (910,000 views)
Chinese political & social commentator Hu Xijin (@胡锡进) also responded to the Cathay incident in multiple posts. In one of them, he suggested that mainland passengers should primarily speak Mandarin when they fly Cathay in the future. Since so much of their customer base is from mainland, Cathay should have enough cabin crew speaking Mandarin, he argued. Hu also reflected on how Cathay also caused controversy in 2019, when it would not stop staff from joining the Kong Kong pro-democracy protests. According to Hu, the company should pay attention to “correcting the values” of their employees.
▶︎”Leaked” Internal Email Labeled as Fake News #国泰航空称网传英文内部信件为伪造# (77 million views)
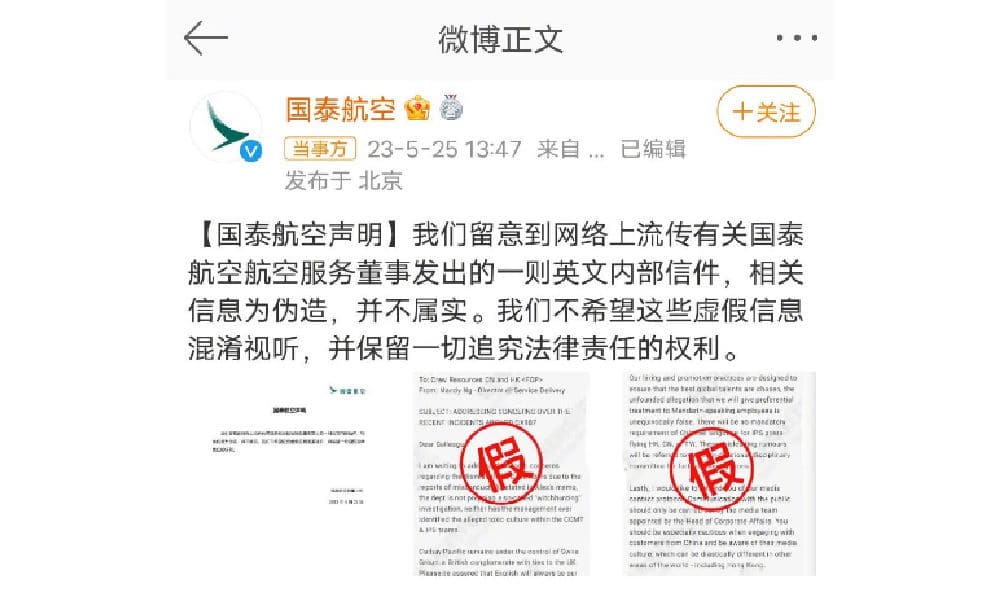
Post by Cathay in which they deny that this “leaked memo” is authentic. Screenshot by What’s on Weibo.
In the meantime, some images circulated online that allegedly showed an internal Cathay Pacific memo by the company’s HK Express CEO Mandy Ng in which a warning was issued to be “cautious when engaging with customers from China and be aware of their media culture.” That memo was labeled as being false by Cathay Pacific.
▶︎ Hong Kong Perfomer Condemns Cathay for Incident #香港演员怒斥国泰空乘歧视乘客# (170 million views)
Hong Kong celebrity Maria Cordero, nicknamed ‘Fat Mama’ (肥妈) went trending on Weibo for condemning the Cathay Pacific crew members in a recent interview. “Is speaking English that important?” she wondered: “The whole world is learning Chinese!” She also expressed that the primary duty of flight attendants is to look after passengers and help solve their problems. If they are incapable of fulfilling their duty, they should be sacked.
▶︎ Blankets for Everyone #旅客称现在国泰的航班挨个发毛毯# (6.5 million views)
According to passengers flying Cathay after the ‘blanket incident,’ the cabin crew went around explicitly asking all passengers if they needed any blankets, making announcements in English, Mandarin, and Cantonese.
▶︎ Follow-up to the Incident #国泰航空空乘歧视乘客后续# (26 million views)
As the Cathay scandal keeps fermenting online, one commenter expressed a common viewpoint by stating: “If Cathay Pacific is so unwilling to serve Chinese people and they refuse to speak Mandarin, why don’t they clearly state that they don’t welcome Chinese passengers? They can’t have it both ways by earning money from Chinese tickets without providing the same level of service.”
Meanwhile, an online meme has gained popularity, depicting ‘Cathay Pacific’ as ‘Carpet Pacific’ in reference to the controversial comments made by the cabin crew.

Other memes include the quote: “If you cannot say blanket, you cannot have it,” or include the phrase “no zuo no die” – a popular internet meme that basically means ‘what goes around comes around.’
Those flying China Southern Airlines or Eastern Airlines are posting about their warm on-board blankets, joking: “I didn’t even have to say ‘blanket’ and still got it!”

By Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

Also Read
China Books & Literature
Why Chinese Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Shopping Festival
Bookworms love to get a good deal on books, but when the deals are too good, it can actually harm the publishing industry.
Published
2 months agoon
June 8, 2024By
Ruixin Zhang
JD.com’s 618 shopping festival is driving down book prices to such an extent that it has prompted a boycott by Chinese publishers, who are concerned about the financial sustainability of their industry.
When June begins, promotional campaigns for China’s 618 Online Shopping Festival suddenly appear everywhere—it’s hard to ignore.
The 618 Festival is a product of China’s booming e-commerce culture. Taking place annually on June 18th, it is China’s largest mid-year shopping carnival. While Alibaba’s “Singles’ Day” shopping festival has been taking place on November 11th since 2009, the 618 Festival was launched by another Chinese e-commerce giant, JD.com (京东), to celebrate the company’s anniversary, boost its sales, and increase its brand value.
By now, other e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and Pinduoduo have joined the 618 Festival, and it has turned into another major nationwide shopping spree event.
For many book lovers in China, 618 has become the perfect opportunity to stock up on books. In previous years, e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Dangdang (当当) would roll out tempting offers during the festival, such as “300 RMB ($41) off for every 500 RMB ($69) spent” or “50 RMB ($7) off for every 100 RMB ($13.8) spent.”
Starting in May, about a month before 618, the largest bookworm community group on the Douban platform, nicknamed “Buying Like Landsliding, Reading Like Silk Spinning” (买书如山倒,看书如抽丝), would start buzzing with activity, discussing book sales, comparing shopping lists, or sharing views about different issues.

Social media users share lists of which books to buy during the 618 shopping festivities.
This year, however, the mood within the group was different. Many members posted that before the 618 season began, books from various publishers were suddenly taken down from e-commerce platforms, disappearing from their online shopping carts. This unusual occurrence sparked discussions among book lovers, with speculations arising about a potential conflict between Chinese publishers and e-commerce platforms.
A joint statement posted in May provided clarity. According to Chinese media outlet The Paper (@澎湃新闻), eight publishers in Beijing and the Shanghai Publishing and Distribution Association, which represent 46 publishing units in Shanghai, issued a statement indicating they refuse to participate in this year’s 618 promotional campaign as proposed by JD.com.
The collective industry boycott has a clear motivation: during JD’s 618 promotional campaign, which offers all books at steep discounts (e.g., 60-70% off) for eight days, publishers lose money on each book sold. Meanwhile, JD.com continues to profit by forcing publishers to sell books at significantly reduced prices (e.g., 80% off). For many publishers, it is simply not sustainable to sell books at 20% of the original price.
One person who has openly spoken out against JD.com’s practices is Shen Haobo (沈浩波), founder and CEO of Chinese book publisher Motie Group (磨铁集团). Shen shared a post on WeChat Moments on May 31st, stating that Motie has completely stopped shipping to JD.com as it opposes the company’s low-price promotions. Shen said it felt like JD.com is “repeatedly rubbing our faces into the ground.”
Nevertheless, many netizens expressed confusion over the situation. Under the hashtag topic “Multiple Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Book Promotions” (#多家出版社抵制618图书大促#), people complained about the relatively high cost of physical books.
With a single legitimate copy often costing 50-60 RMB ($7-$8.3), and children’s books often costing much more, many Chinese readers can only afford to buy books during big sales. They question the justification for these rising prices, as books used to be much more affordable.
Book blogger TaoLangGe (@陶朗歌) argues that for ordinary readers in China, the removal of discounted books is not good news. As consumers, most people are not concerned with the “life and death of the publishing industry” and naturally prefer cheaper books.
However, industry insiders argue that a “price war” on books may not truly benefit buyers in the end, as it is actually driving up the prices as a forced response to the frequent discount promotions by e-commerce platforms.
China News (@中国新闻网) interviewed publisher San Shi (三石), who noted that people’s expectations of book prices can be easily influenced by promotional activities, leading to a subconscious belief that purchasing books at such low prices is normal. Publishers, therefore, feel compelled to reduce costs and adopt price competition to attract buyers. However, the space for cost reduction in paper and printing is limited.
Eventually, this pressure could affect the quality and layout of books, including their binding, design, and editing. In the long run, if a vicious cycle develops, it would be detrimental to the production and publication of high-quality books, ultimately disappointing book lovers who will struggle to find the books they want, in the format they prefer.
This debate temporarily resolved with JD.com’s compromise. According to The Paper, JD.com has started to abandon its previous strategy of offering extreme discounts across all book categories. Publishers now have a certain degree of autonomy, able to decide the types of books and discount rates for platform promotions.
While most previously delisted books have returned for sale, JD.com’s silence on their official social media channels leaves people worried about the future of China’s publishing industry in an era dominated by e-commerce platforms, especially at a time when online shops and livestreamers keep competing over who has the best book deals, hyping up promotional campaigns like ‘9.9 RMB ($1.4) per book with free shipping’ to ‘1 RMB ($0.15) books.’
This year’s developments surrounding the publishing industry and 618 has led to some discussions that have created more awareness among Chinese consumers about the true price of books. “I was planning to bulk buy books this year,” one commenter wrote: “But then I looked at my bookshelf and saw that some of last year’s books haven’t even been unwrapped yet.”
Another commenter wrote: “Although I’m just an ordinary reader, I still feel very sad about this situation. It’s reasonable to say that lower prices are good for readers, but what I see is an unfavorable outlook for publishers and the book market. If this continues, no one will want to work in this industry, and for readers who do not like e-books and only prefer physical books, this is definitely not a good thing at all!”
By Ruixin Zhang, edited with further input by Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Chinese Sun Protection Fashion: Move over Facekini, Here’s the Peek-a-Boo Polo
From facekini to no-face hoodie: China’s anti-tan fashion continues to evolve.
Published
2 months agoon
June 6, 2024
It has been ten years since the Chinese “facekini”—a head garment worn by Chinese ‘aunties’ at the beach or swimming pool to prevent sunburn—went international.
Although the facekini’s debut in French fashion magazines did not lead to an international craze, it did turn the term “facekini” (脸基尼), coined in 2012, into an internationally recognized word.

The facekini went viral in 2014.
In recent years, China has seen a rise in anti-tan, sun-protection garments. More than just preventing sunburn, these garments aim to prevent any tanning at all, helping Chinese women—and some men—maintain as pale a complexion as possible, as fair skin is deemed aesthetically ideal.
As temperatures are soaring across China, online fashion stores on Taobao and other platforms are offering all kinds of fashion solutions to prevent the skin, mainly the face, from being exposed to the sun.

One of these solutions is the reversed no-face sun protection hoodie, or the ‘peek-a-boo polo,’ a dress shirt with a reverse hoodie featuring eye holes and a zipper for the mouth area.

This sun-protective garment is available in various sizes and models, with some inspired by or made by the Japanese NOTHOMME brand. These garments can be worn in two ways—hoodie front or hoodie back. Prices range from 100 to 280 yuan ($13-$38) per shirt/jacket.

The no-face hoodie sun protection shirt is sold in various colors and variations on Chinese e-commerce sites.
Some shops on Taobao joke about the extreme sun-protective fashion, writing: “During the day, you don’t know which one is your wife. At night they’ll return to normal and you’ll see it’s your wife.”

On Xiaohongshu, fashion commenters note how Chinese sun protective clothing has become more extreme over the past few years, with “sunburn protection warriors” (防晒战士) thinking of all kinds of solutions to avoid a tan.
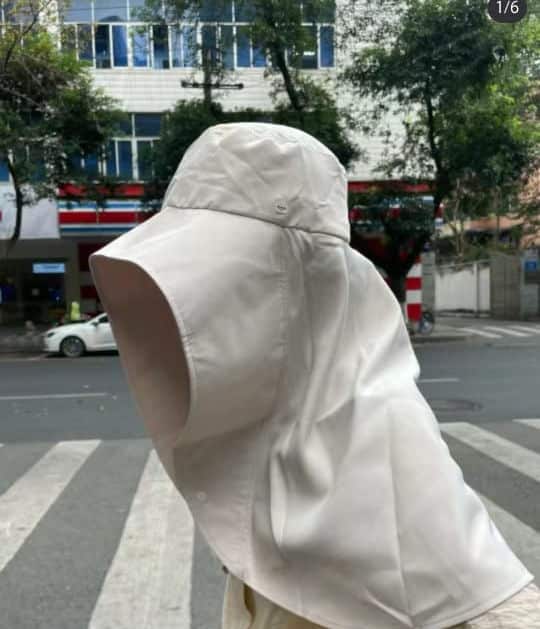




Although there are many jokes surrounding China’s “sun protection warriors,” some people believe they are taking it too far, even comparing them to Muslim women dressed in burqas.
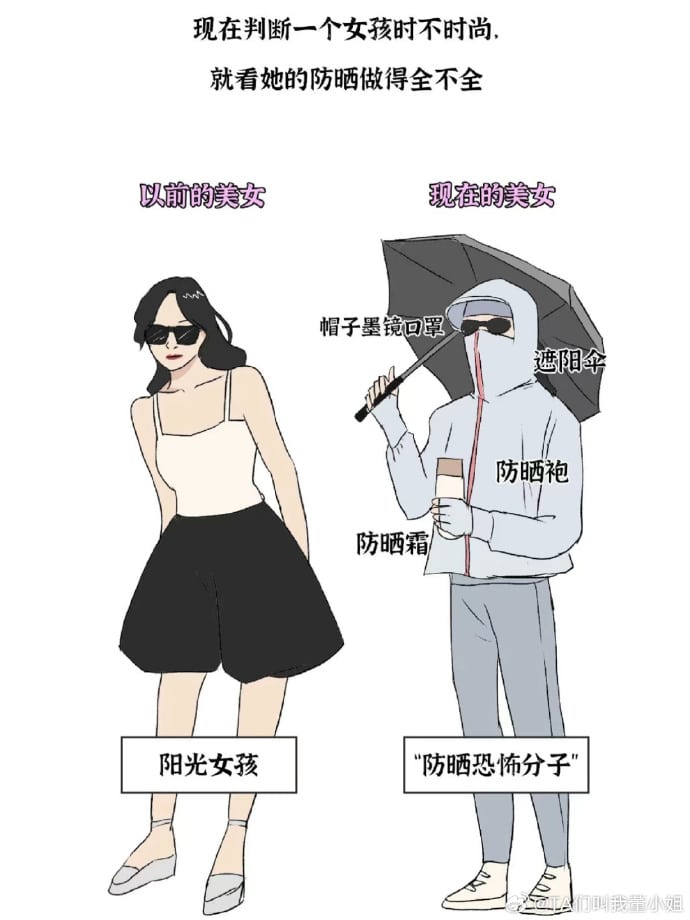
Image shared on Weibo by @TA们叫我董小姐, comparing pretty girls before (left) and nowadays (right), also labeled “sunscreen terrorists.”
Some Xiaohongshu influencers argue that instead of wrapping themselves up like mummies, people should pay more attention to the UV index, suggesting that applying sunscreen and using a parasol or hat usually offers enough protection.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?




