China and Covid19
Shanghai Residents Protest as Pudong Apartments Turn Into Quarantine Site
Shanghai residents at Zhangjiang Nashi International are angered about their community turning into a Covid quarantine site.
Published
2 years agoon
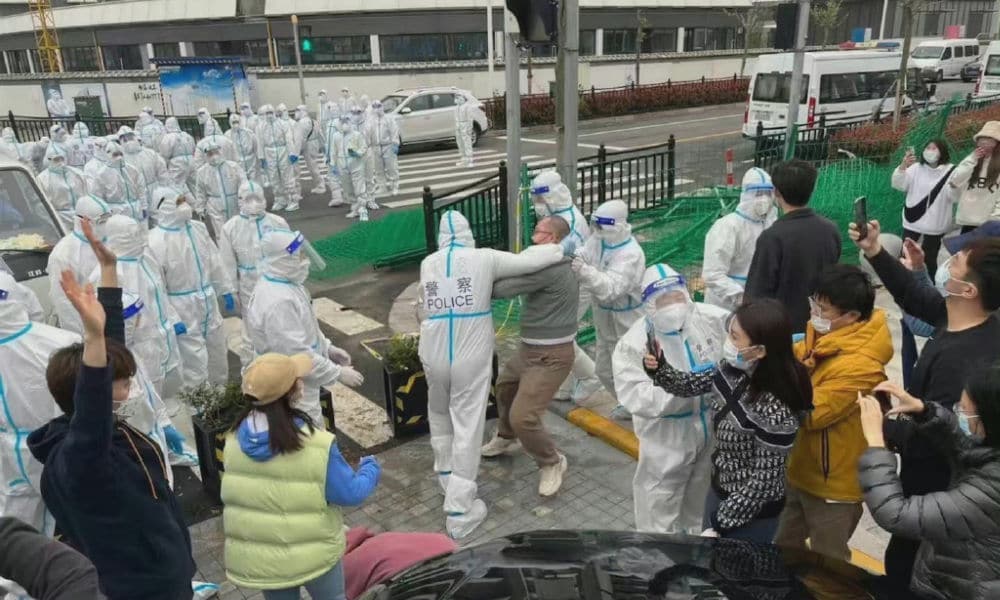

A local protest in a Shanghai neighborhood where residents are angry about their community buildings being taken over and used as a quarantine site has now moved from the streets to the internet.
On Thursday, April 14, videos showing how Shanghai residents were dragged off by officers in medical suits went viral on Chinese social media. The footage allegedly shows a situation taking place at the Zhangjiang Nashi International apartment complex in Shanghai’s New Pudong Area (张江纳仕国际社区), where residents were notified on Thursday that several buildings within their community would be taken over and used as a quarantine isolation site for Covid-19 patients.

Videos showed members of police dressed in hazmat suits clashing with angry residents while a crowd of people stood by screaming and filming the chaotic scenes unfolding around them. Some images also showed residents on their knees, seemingly pleading with the officers.
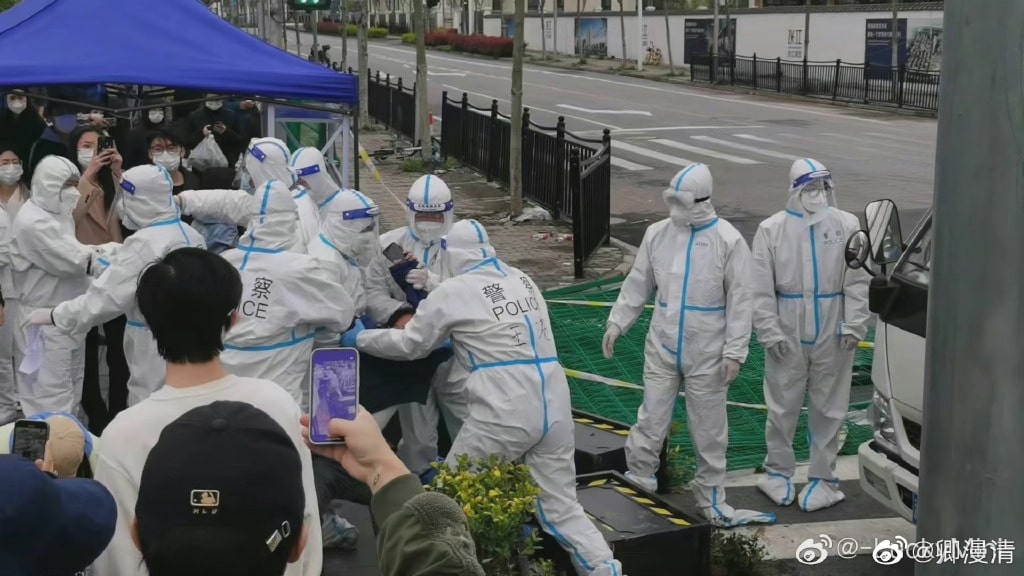

Other videos also showed residents being dragged away.
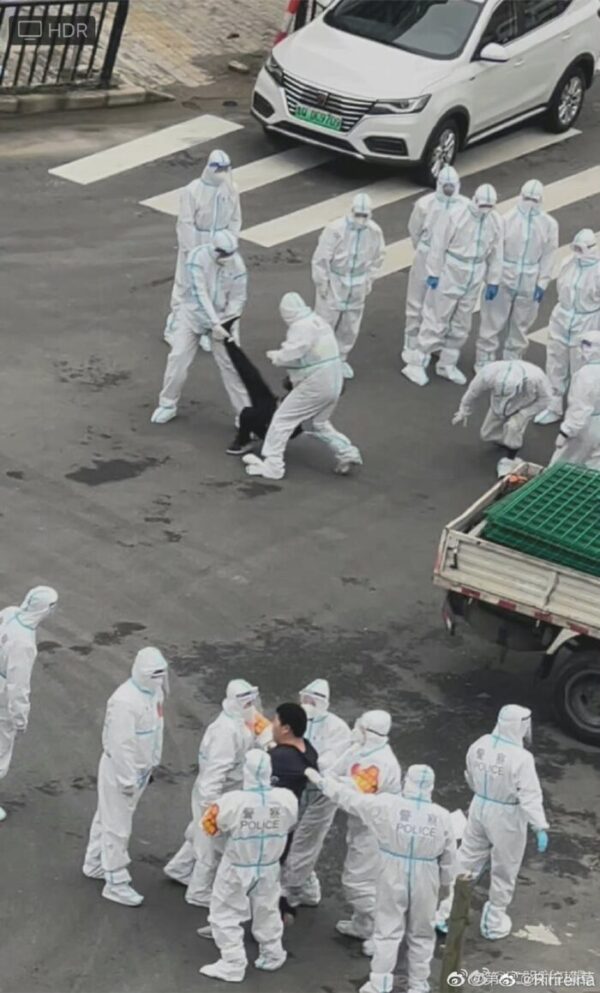

According to various Weibo users from the area, the people from the complex, where some 500 people live, already had parts of their building being used as a quarantine site in March of this year. When they were notified that the makeshift quarantine location within their compound would be expanded, they protested the decision.
“I live in the Nashi complex (..) and like many of my neighbors, we have returned from abroad and we’re very patriotic. But anyone who would have this happening to them would be disillusioned.”
The incident was discussed on Weibo using various hashtags but was also heavily censored, with videos and images of the situation suddenly going offline. One video received over 15,000 likes before it was taken offline.
Videos showing chaotic scenes are circulating on Weibo now from one Shanghai community where residents protested their buildings being taken over and used as a quarantine location. Videos are uploaded, censored, and reuploaded again. Read more here: https://t.co/iYdX4Mipc5 pic.twitter.com/yKD9f4F2ug
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) April 14, 2022
“Shanghai government, can you please be reasonable?!” some pleaded, while others posted images of the incident covered with red scribbles to avoid automated censorship: “If you delete this, I’ll post again! I’ll just post again!”
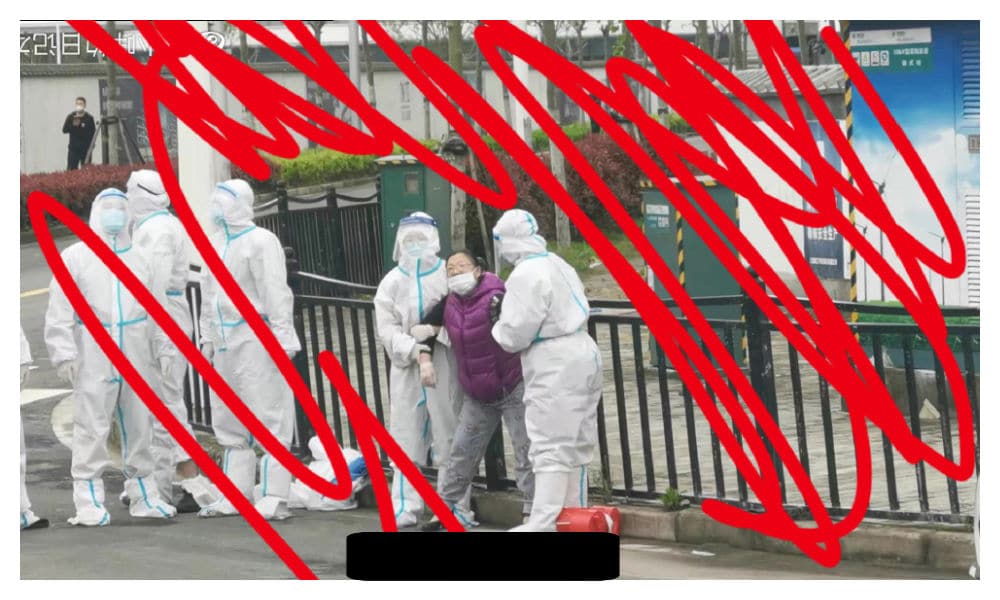


“Most police officers now are not helping people solve their problems, they are just maintaining social stability,” one Weibo commenter said.
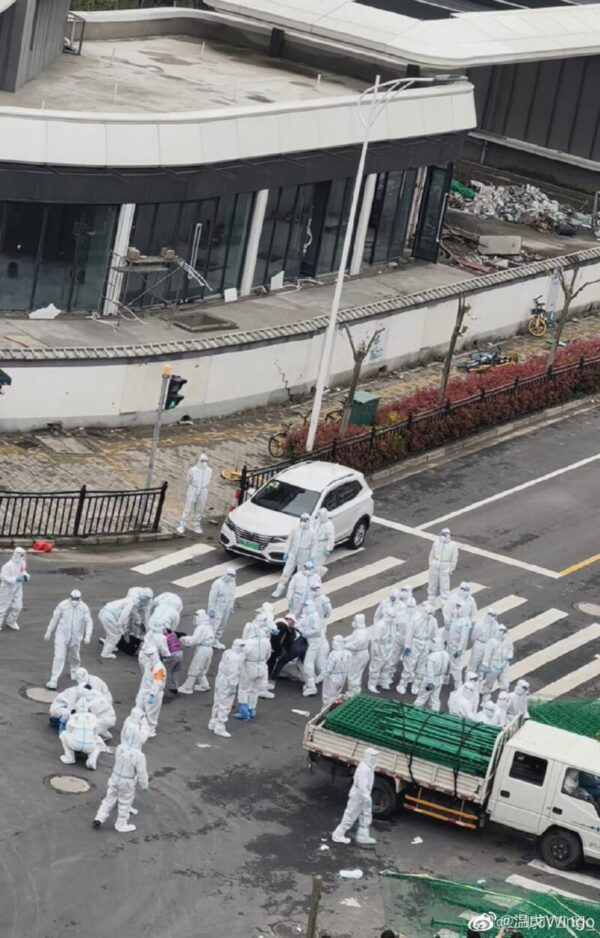

Over the past week, frustrations have been building in Shanghai, where millions of households have been in lockdown since March 28 or earlier. Despite the stringent measures, the city’s total Covid-19 cases soared to another daily record of 27,719 on Thursday.
According to China’s dynamic zero-covid policy, people who test positive for Covid-19 are sent to centralized facilities for a mandatory quarantine. While locked-down residents have struggled to get food, medications, and urgent medical care amid China’s zero-infection policy, many also face difficulties in getting basic medical care or adequate supplies at these centralized quarantine centers, leading to growing anger about how the city is handling the current outbreak.
People spreading photos and videos of the Shanghai Zhangjiang community upheaval express anger, not just about the situation there but about the lockdown management in general (including some stories such as this one, or this one) and the censorship of issues reported by Shanghai residents.
While images, posts, and videos are censored at full speed, one person posts a screenshot of a WeChat conversation about the Zhangjiang incident.
– “Is this really Shanghai?”
– “I saw this. In the afternoon. Weibo won’t allow you to see anything anymore now.”
– “How could Shanghai have changed into this?”
As another person posted a new hashtag about the incident, there was just one thread left on Weibo by Thursday night shortly after 10pm Beijing time. “We just have this one thread,” commenters replied: “Everything is censored, this one won’t stick around for long either.”
“I wonder how long this post will last,” another Weibo blogger wondered, publishing photos of today’s incident. Their post has since been deleted.
Update April 15, 13:45 China Standard Time:
Shortly after this report, BBC also reported about the incident, after which Shanghai Daily reporter Andy Boreham provided some details on Twitter surrounding the protest, claiming that the buildings in questions are talent apartments (人才公寓) – discounted rental sites provided by the city for ‘talented’ people, usually in special areas hoping to attract highly skilled workers.
Boreham also claims that these apartments were provided to tenants on the basis that could be relocated at any time, which is also stated in their contracts. Although the tenants allegedly agreed on April 12 to be moved to another part of the complex, a group of them decided to resist when it came to relocating and tried to stop police from putting up barriers to isolate the building as a quarantine site. See the Twitter thread below.
Here’s some background facts for your followers: This is filmed at a talent apartment (人才公寓)which is basically heavily discounted rental sites provided by the gov’t for “talented” people, usually in special areas hoping to attract highly skilled workers. (2/9)
— Andy Boreham 安柏然 (@AndyBxxx) April 15, 2022
The topic “Zhangjiang Nashi International Community” (张江纳仕国际社区) still comes up with zero results in Weibo’s search function after yesterday’s online turmoil. There is, however, one hashtag about the issue today, namely that initiated by China Real Estate News (@中国房地产报) about the Shanghai Zhangjiang Group responding to the use of talent apartments for quarantine housing (#上海张江集团回应人才公寓被征用为隔离房:疫情防控需要#). Chinese media outlet The Paper also published the brief statement.
The statement explains that the Zhangjiang Nashi Talent Apartment buildings are state-owned property rental housing built by the Zhangjiang real estate group, and that the talent apartments started to be used in August 2021. Since Shanghai’s Covid crisis, the city used five (unoccupied) buildings as a makeshift isolation site.
On April 12, the local government reportedly notified the Zhangjiang Group that it would also expropriate an additional nine buildings and use them as a central quarantine site. According to the Zhangjiang Group, they immediately notified the 39 tenants who needed to be relocated and gave compensation for lease changes.
But during the afternoon of April 14, when the planned quarantine site plans were set into motion, some tenants obstructed the construction site, and “relevant departments dealt with the situation on the spot.” The statement further said that the situation has since calmed down.
“I’d also recommend the houses of the people who make these decisions to be taken over and used as a quarantine site,” one commenter said: “So they can experience what it feels like to be driven out of your own home.”
Meanwhile, one anonymous contributor claiming to be one of the residents living in the Zhangjiang Nashi International community published a lengthy thread on the Chinese Q&A platform Zhihu.com, where they suggested that the statement by the Zhangjiang Group was misleading. The post was published in the early morning of April 15 just before 3am, but no longer shows up in Zhihu search function at time of writing.
“Firstly, Zhangjiang Nashi International is NOT a talent apartment! It’s NOT a talent apartment! It’s NOT!,” the author writes. The uploader claims that the community they live in is a regular residential area that only rents out apartments at a high price, and does not sell them.
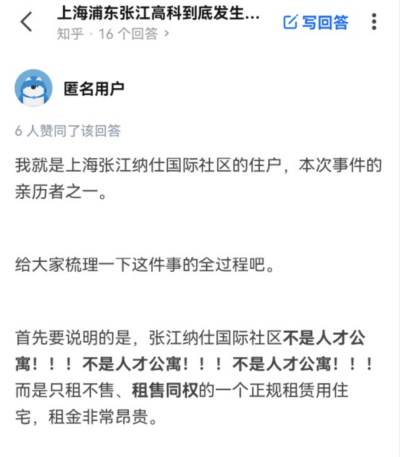
The uploader suggested that, since the rent of the apartments is quite high (lowest rent prices for a one bedroom apartment start at 7950 yuan/month, which is $1250, highest are priced at 11350 yuan/month, which is $1781), the tenants would not accept an alleged ‘subletting’ agreement.
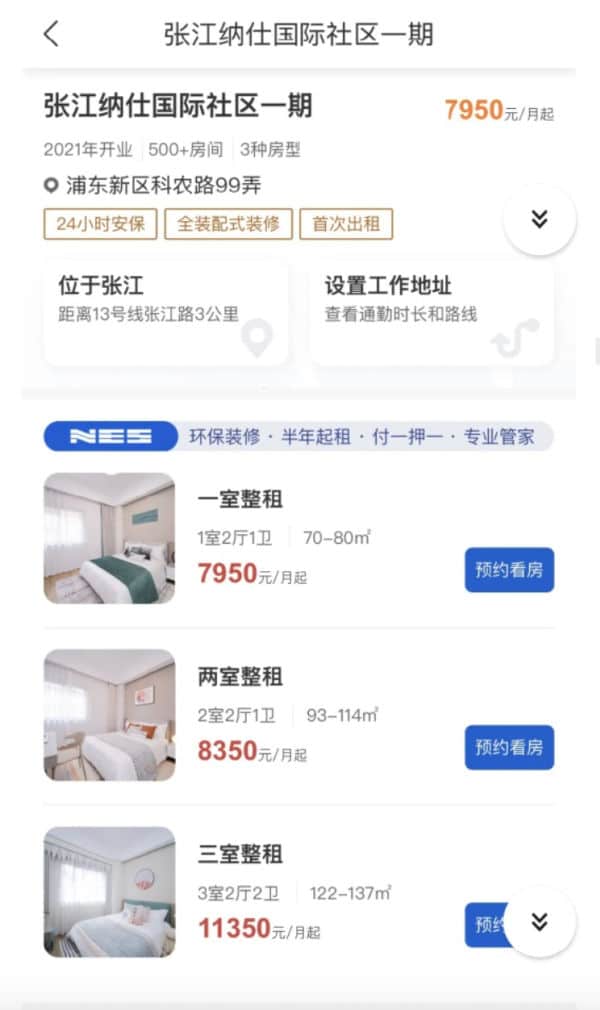
The uploader said that they were notified by the Zhangjiang Group that four of the buildings in their complex would be used as quarantine sites on March 15 of this year.
Because the four buildings were vacant and far removed from the buildings with the most residents, the decisions were not objected by tenants.
Not long after, the entire community went into lockdown mode starting on March 18. Until the incident of April 14, the residents had been inside their homes for 27 days while cooperating with mass testing campaigns and managing to test negative for Covid-19 throughout.
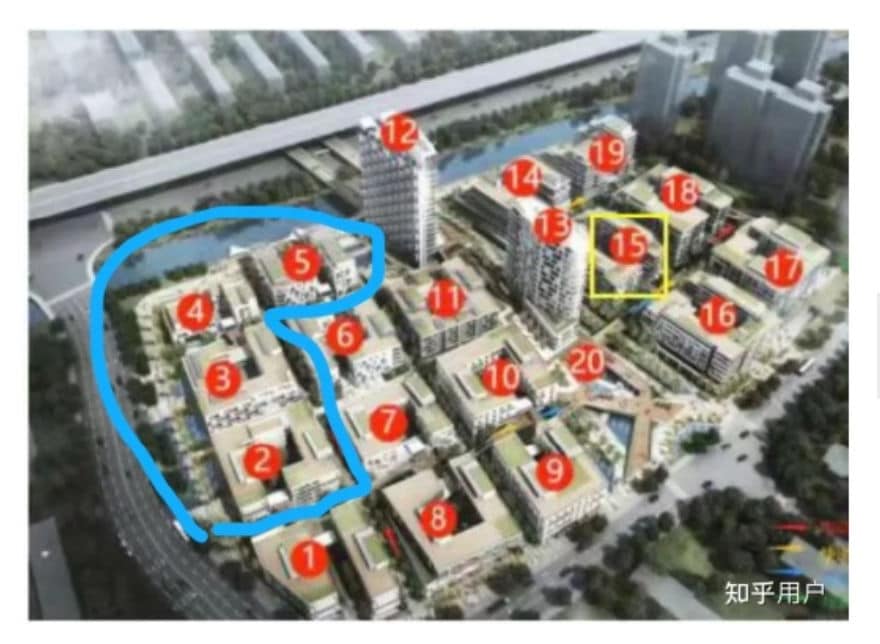
On April 11, the residents were informed that an additional building, building 6, would also be used as a quarantine location.
This decision made residents living in building number 7 and 11 more nervous, since they were in close proximity of building number 6 – less than 20 meters away. The close proximity of the quarantine building and the quick spread of Omicron made residents fear that they could easily also be infected.
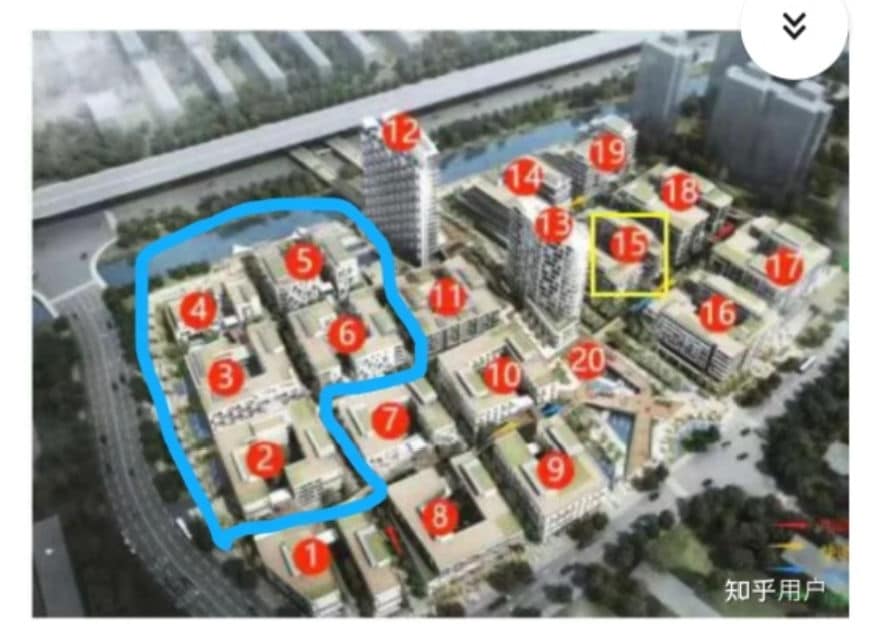
The Zhihu author then explains that on April 12, the community was informed that an additional eight buildings would also be used as quarantine locations, namely 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 18, 19. Of these buildings, 7, 11, and 14 were all occupied and for the residents at 14 all of their furniture and electrical appliances is self-bought and was not provided to them. The residents were expected to move out.

The residents complained that it was not easy to move their entire household in times of epidemic, and the building number 14 residents also worried about their furniture and appliances being used by Covid19 patients. They were therefore also offered compensation for relocating.
But, as explained in the lengthy Zhihu post, not all of the residents received their compensation and it was unclear when and if they would. Residents also demanded to see official proof that the government was really demanding that their apartment buildings were to be made into quarantine sites. A meeting between Zhangjiang Group and the residents took place and was also recorded, but did not lead to a solution.

A second negotiation between residents and the real estate group on April 13 also did not settle the matter, and the residents of building 7, 11, and 14 were required to move out immediately unless they wanted to live together with Covid-19 patients.
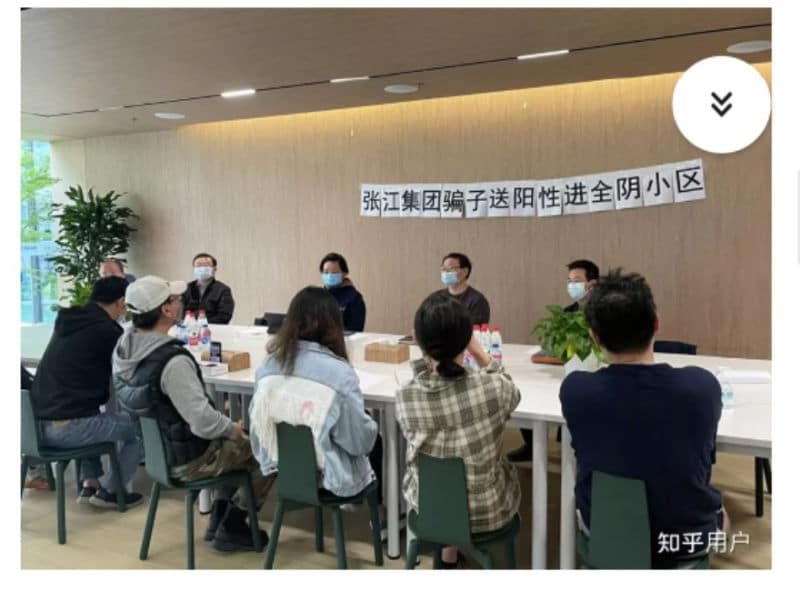

But a new problem also emerged, as the residents would allegedly be relocated to building number 15, which is surrounded on all sides by the buildings used as quarantine locations – at distance less than 20 meters away. The anxiety over becoming infected, the stress over the community being taken over, and the doubts over whether or not the decision was actually legal or not eventually led to the altercations of April 14.
The protests themselves did not turn out to be fruitful for the residents. It was a moment to document what was happening to them and to express their sadness and anger. Now, the author says, the residents are sharing their community with the Covid-19 patients and the residents are still not sure whether or not the entire ordeal is legal or not.
The social media user also warns others not to spread rumors and not to mix up other videos with what happened on April 14.
For more articles on the Covid-19 topics on Chinese social media, check here.
By Manya Koetse
With contributions by Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our weekly newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

Also Read
China and Covid19
Sick Kids, Worried Parents, Overcrowded Hospitals: China’s Peak Flu Season on the Way
“Besides Mycoplasma infections, cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
Published
8 months agoon
November 22, 2023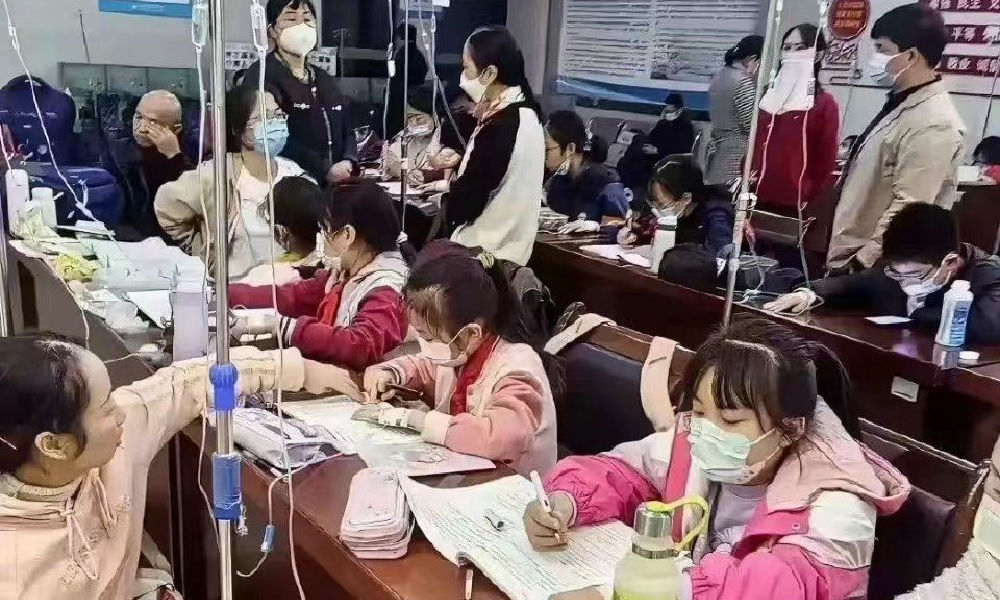
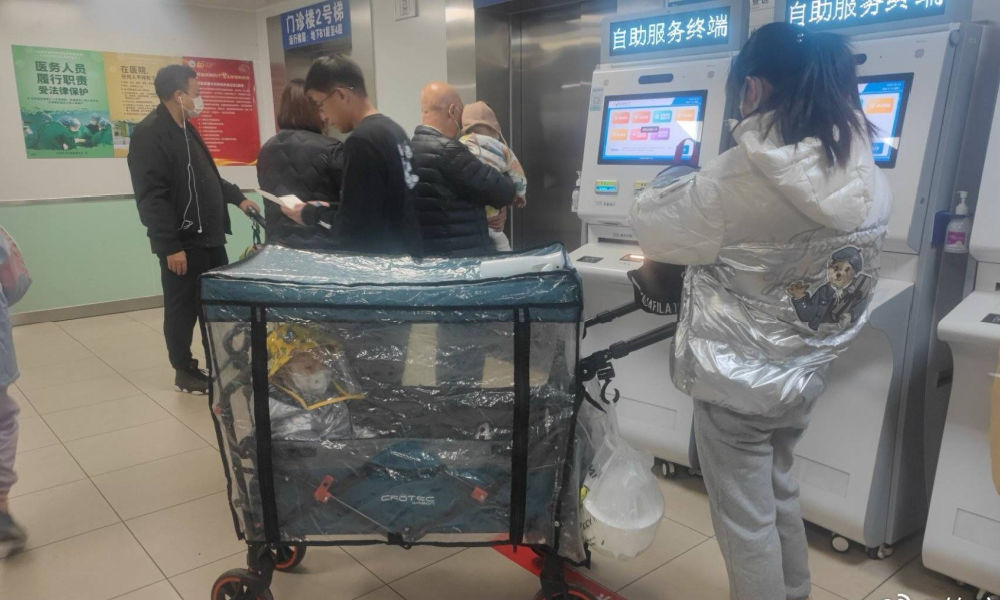
In the early morning of November 21, parents are already queuing up at Xi’an Children’s Hospital with their sons and daughters. It’s not even the line for a doctor’s appointment, but rather for the removal of IV needles.
The scene was captured in a recent video, only one among many videos and images that have been making their rounds on Chinese social media these days (#凌晨的儿童医院拔针也要排队#).

One photo shows a bulletin board at a local hospital warning parents that over 700 patients are waiting in line, estimating a waiting time of more than 13 hours to see a doctor.

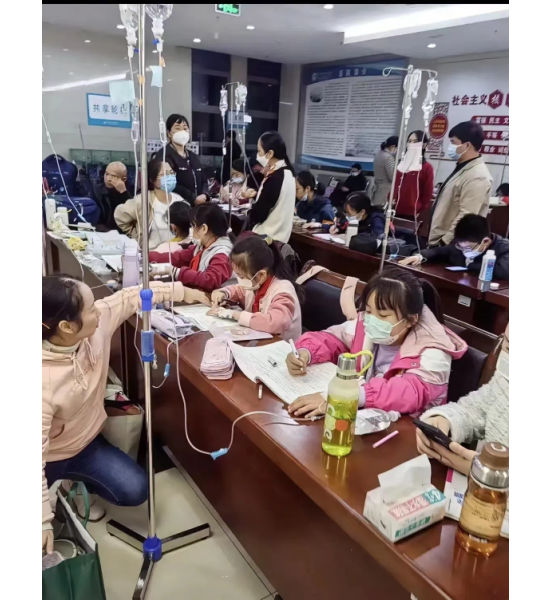
Another image shows children doing their homework while hooked up on an IV.

Recent discussions on Chinese social media platforms have highlighted a notable surge in flu cases. The ongoing flu season is particularly impacting children, with multiple viruses concurrently circulating and contributing to a high incidence of respiratory infections.
Among the prevalent respiratory infections affecting children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, influenza, and Adenovirus infection.
The spike in flu cases has resulted in overcrowded children’s hospitals in Beijing and other Chinese cities. Parents sometimes have to wait in line for hours to get an appointment or pick up medication.
According to one reporter at Haibao News (海报新闻), there were so many patients at the Children’s Hospital of Capital Institute of Pediatrics (首都儿科研究所) on November 21st that the outpatient desk stopped accepting new patients by the afternoon. Meanwhile, 628 people were waiting in line to see a doctor at the emergency department.
Reflecting on the past few years, the current flu season marks China’s first ‘normal’ flu peak season since the outbreak of Covid-19 in late 2019 / early 2020 and the end of its stringent zero-Covid policies in December 2022. Compared to many other countries, wearing masks was also commonplace for much longer following the relaxation of Covid policies.
Hu Xijin, the well-known political commentator, noted on Weibo that this year’s flu season seems to be far worse than that of the years before. He also shared that his own granddaughter was suffering from a 40 degrees fever.
“We’re all running a fever in our home. But I didn’t dare to go to the hospital today, although I want my child to go to the hospital tomorrow. I heard waiting times are up to five hours now,” one Weibo user wrote.
“Half of the kids in my child’s class are sick now. The hospital is overflowing with people,” another person commented.
One mother described how her 7-year-old child had been running a fever for eight days already. Seeking medical attention on the first day, the initial diagnosis was a cold. As the fever persisted, daily visits to the hospital ensued, involving multiple hours for IV fluid administration.
While this account stems from a single Weibo post within a fever-advice community, it highlights a broader trend: many parents swiftly resort to hospital visits at the first signs of flu or fever. Several factors contribute to this, including a lack of General Practitioners in China, making hospitals the primary choice for medical consultations also in non-urgent cases.
There is also a strong belief in the efficacy of IV infusion therapy, whether fluid-based or containing medication, as the quickest path to recovery. Multiple factors contribute to the widespread and sometimes irrational use of IV infusions in China. Some clinics are profit-driven and see IV infusions as a way to make more money. Widespread expectations among Chinese patients that IV infusions will make them feel better also play a role, along with some physicians’ lacking knowledge of IV therapy or their uncertainty to distinguish bacterial from viral infections (read more here)
To prevent an overwhelming influx of patients to hospitals, Chinese state media, citing specialists, advise parents to seek medical attention at the hospital only for sick infants under three months old displaying clear signs of fever (with or without cough). For older children, it is recommended to consult a doctor if a high fever persists for 3 to 5 days or if there is a deterioration in respiratory symptoms. Children dealing with fever and (mild) respiratory symptoms can otherwise recover at home.
One Weibo blogger (@奶霸知道) warned parents that taking their child straight to the hospital on the first day of them getting sick could actually be a bad idea. They write:
“(..) pediatric departments are already packed with patients, and it’s not just Mycoplasma infections anymore. Cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. And then, of course, those with bad luck are cross-infected with multiple viruses at the same time, leading to endless cycles. Therefore, if your child experiences mild coughing or a slight fever, consider observing at home first. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
The hashtag for “fever” saw over 350 million clicks on Weibo within one day on November 22.
Meanwhile, there are also other ongoing discussions on Weibo surrounding the current flu season. One topic revolves around whether children should continue doing their homework while receiving IV fluids in the hospital. Some hospitals have designated special desks and study areas for children.
Although some commenters commend the hospitals for being so considerate, others also remind the parents not to pressure their kids too much and to let them rest when they are not feeling well.
Opinions vary: although some on Chinese social media say it's very thoughtful for hospitals to set up areas where kids can study and read, others blame parents for pressuring their kids to do homework at the hospital instead of resting when not feeling well. pic.twitter.com/gnQD9tFW2c
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) November 22, 2023
By Manya Koetse, with contributions from Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China and Covid19
Repurposing China’s Abandoned Nucleic Acid Booths: 10 Innovative Transformations
Abandoned nucleic acid booths are getting a second life through these new initiatives.
Published
1 year agoon
May 19, 2023
During the pandemic, nucleic acid testing booths in Chinese cities were primarily focused on maintaining physical distance. Now, empty booths are being repurposed to bring people together, serving as new spaces to serve the community and promote social engagement.
Just months ago, nucleic acid testing booths were the most lively spots of some Chinese cities. During the 2022 Shanghai summer, for example, there were massive queues in front of the city’s nucleic acid booths, as people needed a negative PCR test no older than 72 hours for accessing public transport, going to work, or visiting markets and malls.
The word ‘hésuān tíng‘ (核酸亭), nucleic acid booth (also:核酸采样小屋), became a part of China’s pandemic lexicon, just like hésuān dìtú (核酸地图), the nucleic acid test map lauched in May 2022 that would show where you can get a nucleic test.
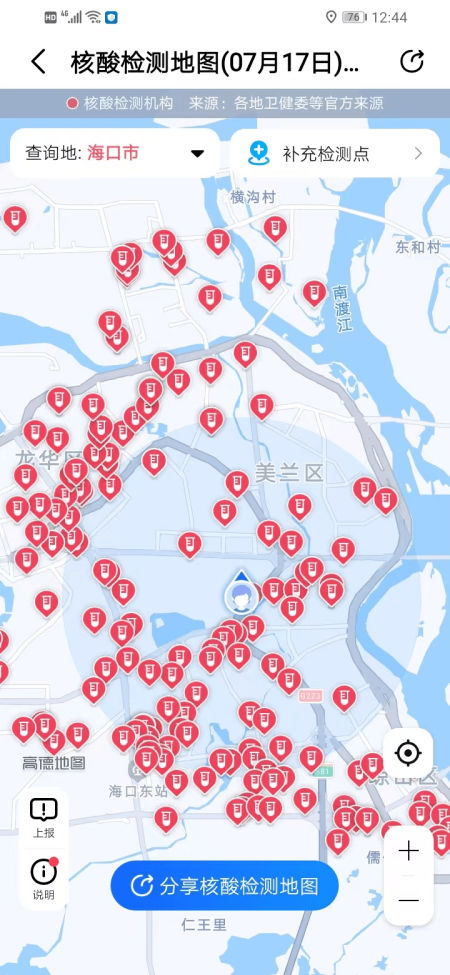
Example of nucleic acid test map.
During Halloween parties in Shanghai in 2022, some people even came dressed up as nucleic test booths – although local authorities could not appreciate the creative costume.

Halloween 2022: dressed up as nucliec acid booths. Via @manyapan twitter.
In December 2022, along with the announced changed rules in China’s ‘zero Covid’ approach, nucleic acid booths were suddenly left dismantled and empty.
With many cities spending millions to set up these booths in central locations, the question soon arose: what should they do with the abandoned booths?
This question also relates to who actually owns them, since the ownership is mixed. Some booths were purchased by authorities, others were bought by companies, and there are also local communities owning their own testing booths. Depending on the contracts and legal implications, not all booths are able to get a new function or be removed yet (Worker’s Daily).
In Tianjin, a total of 266 nucleic acid booths located in Jinghai District were listed for public acquisition earlier this month, and they were acquired for 4.78 million yuan (US$683.300) by a local food and beverage company which will transform the booths into convenience service points, selling snacks or providing other services.
Tianjin is not the only city where old nucleic acid testing booths are being repurposed. While some booths have been discarded, some companies and/or local governments – in cooperation with local communities – have demonstrated creativity by transforming the booths into new landmarks. Since the start of 2023, different cities and districts across China have already begun to repurpose testing booths. Here, we will explore ten different way in which China’s abandoned nucleic test booths get a second chance at a meaningful existence.
1: Pharmacy/Medical Booths
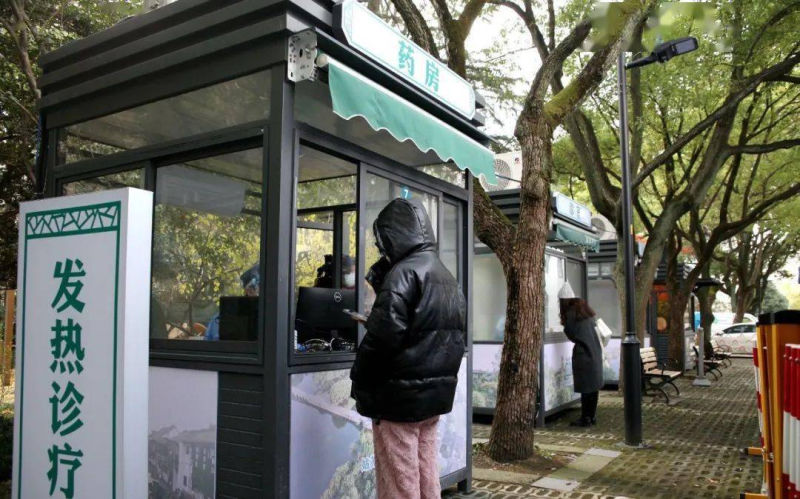

Via ‘copyquan’ republished on Sohu.
Blogger ‘copyquan’ recently explored various ways in which abandoned PCR testing points are being repurposed.
One way in which they are used is as small pharmacies or as medical service points for local residents (居民医疗点). Alleviating the strain on hospitals and pharmacies, this was one of the earliest ways in which the booths were repurposed back in December of 2022 and January of 2023.
Chongqing, Tianjin, and Suzhou were among earlier cities where some testing booths were transformed into convenient medical facilities.
2: Market Stalls
In Suzhou, Jiangsu province, the local government transformed vacant nucleic acid booths into market stalls for the Spring Festival in January 2022, offering them free of charge to businesses to sell local products, snacks, and traditional New Year goods.
The idea was not just meant as a way for small businesses to conveniently sell to local residents, it was also meant as a way to attract more shoppers and promote other businesses in the neighborhood.
3: Community Service Center
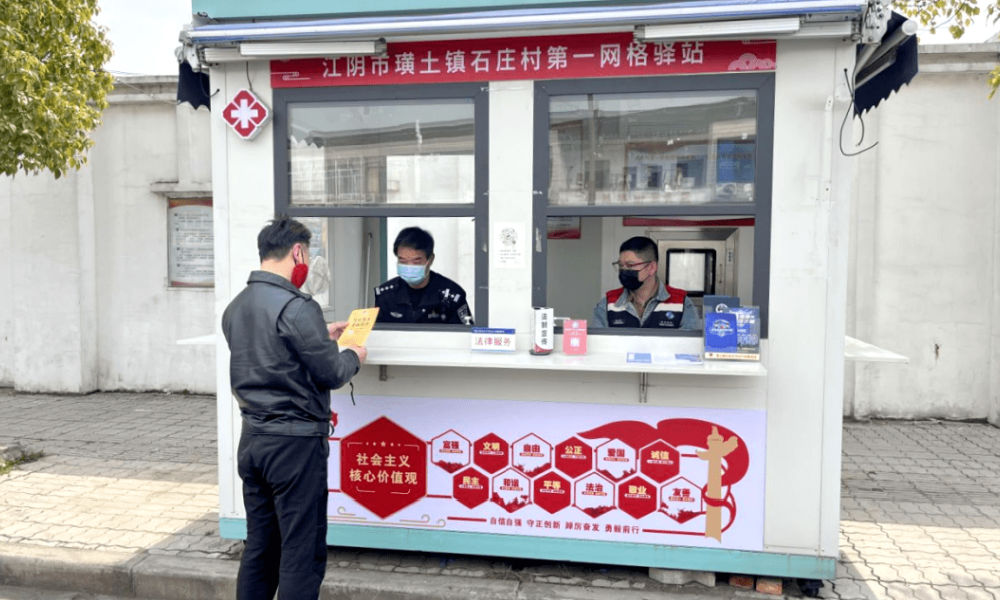

Small grid community center in Shizhuang Village, image via Sohu.
Some residential areas have transformed their local nucleic acid testing booths into community service centers, offering all kinds of convenient services to neighborhood residents.
These little station are called wǎnggé yìzhàn (网格驿站) or “grid service stations,” and they can serve as small community centers where residents can get various kinds of care and support.
4: “Refuel” Stations
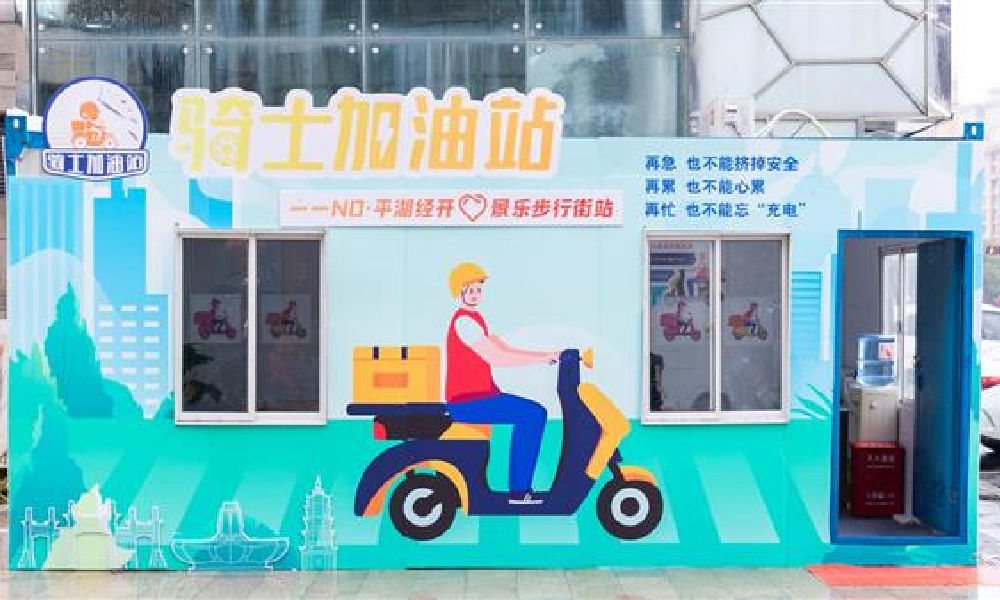

In February of this year, 100 idle nucleic acid sampling booths were transformed into so-called “Rider Refuel Stations” (骑士加油站) in Zhejiang’s Pinghu. Although it initially sounds like a place where delivery riders can fill up their fuel tanks, it is actually meant as a place where they themselves can recharge.
Delivery riders and other outdoor workers can come to the ‘refuel’ station to drink some water or tea, warm their hands, warm up some food and take a quick nap.
5: Free Libraries
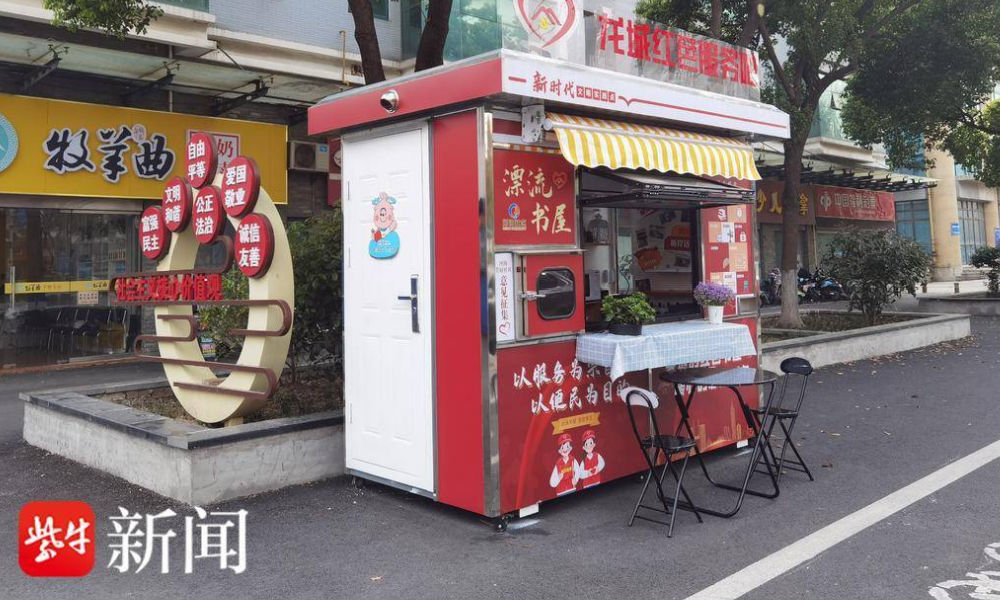

image via sohu.
In various Chinese cities, abandoned nucleic acid booths have been transformed into little free libraries where people can grab some books to read, donate or return other books, and sit down for some reading.
Changzhou is one of the places where you’ll find such “drifting bookstores” (漂流书屋) (see video), but similar initiatives have also been launched in other places, including Suzhou.
6: Study Space
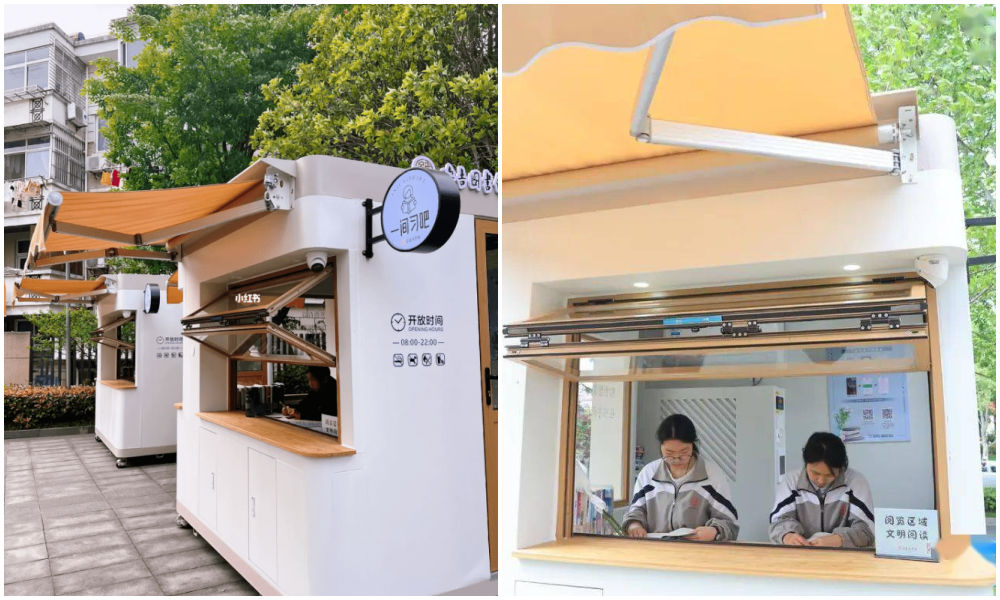

Photos via Copyquan’s article on Sohu.
Another innovative way in which old testing points are being repurposed is by turning them into places where students can sit together to study. The so-called “Let’s Study Space” (一间习吧), fully airconditioned, are opened from 8 in the morning until 22:00 at night.
Students – or any citizens who would like a nice place to study – can make online reservations with their ID cards and scan a QR code to enter the study rooms.
There are currently ten study booths in Anji, and the popular project is an initiative by the Anji County Library in Zhejiang (see video).
7: Beer Kiosk
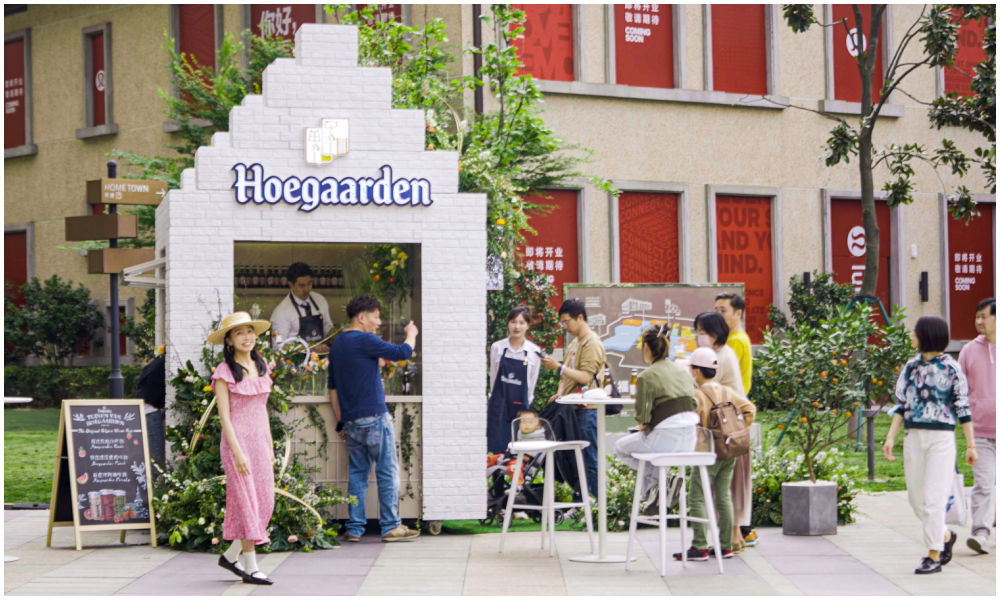

Hoegaarden beer shop, image via Creative Adquan.
Changing an old nucleic acid testing booth into a beer bar is a marketing initiative by the Shanghai McCann ad agency for the Belgium beer brand Hoegaarden.
The idea behind the bar is to celebrate a new spring after the pandemic. The ad agency has revamped a total of six formr nucleic acid booths into small Hoegaarden ‘beer gardens.’
8: Police Box
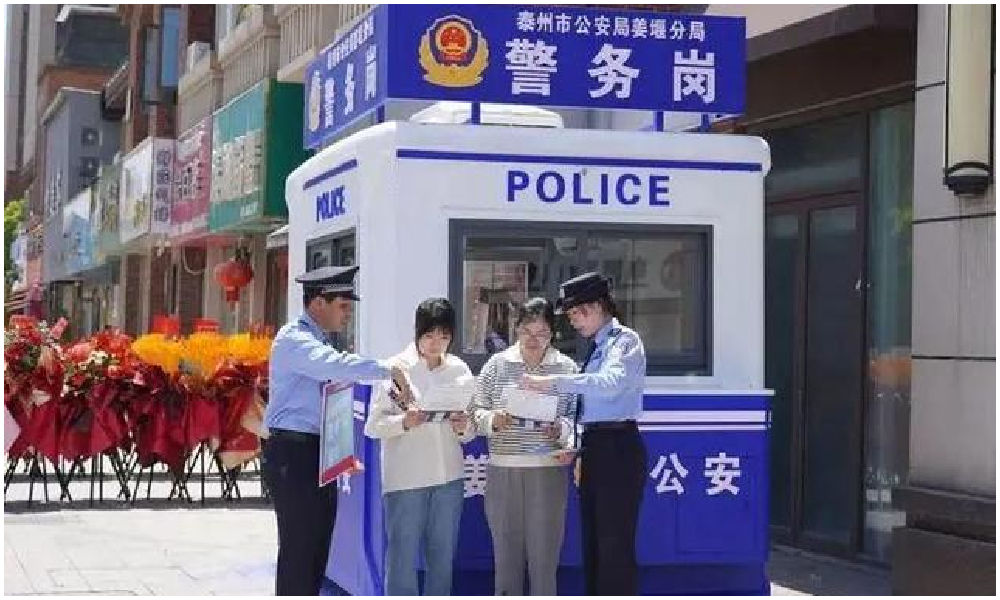

In Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province, authorities have repurposed old testing booths and transformed them into ‘police boxes’ (警务岗亭) to enhance security and improve the visibility of city police among the public.
Currently, a total of eight vacant nucleic acid booths have been renovated into modern police stations, serving as key points for police presence and interaction with the community.
9: Lottery Ticket Booths
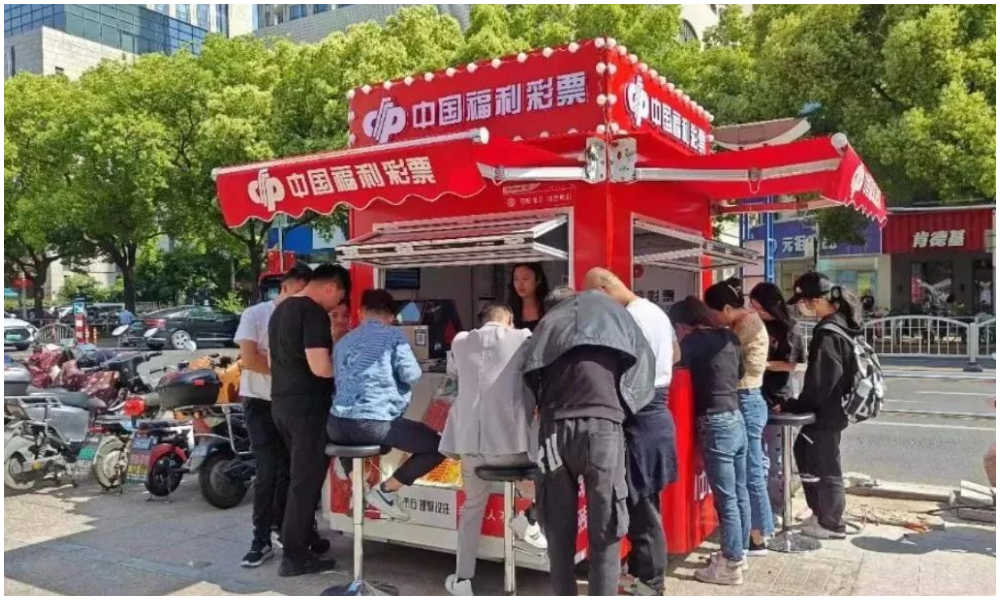

Image via The Paper
Some nucleic acid booths have now been turned into small shops selling lottery tickets for the China Welfare Lottery. One such place turning the kiosks into lottery shops is Songjiang in Shanghai.
Using the booths like this is a win-win situation: they are placed in central locations so it is more convenient for locals to get their lottery tickets, and on the other hand, the sales also help the community, as the profits are used for welfare projects, including care for the elderly.
10: Mini Fire Stations
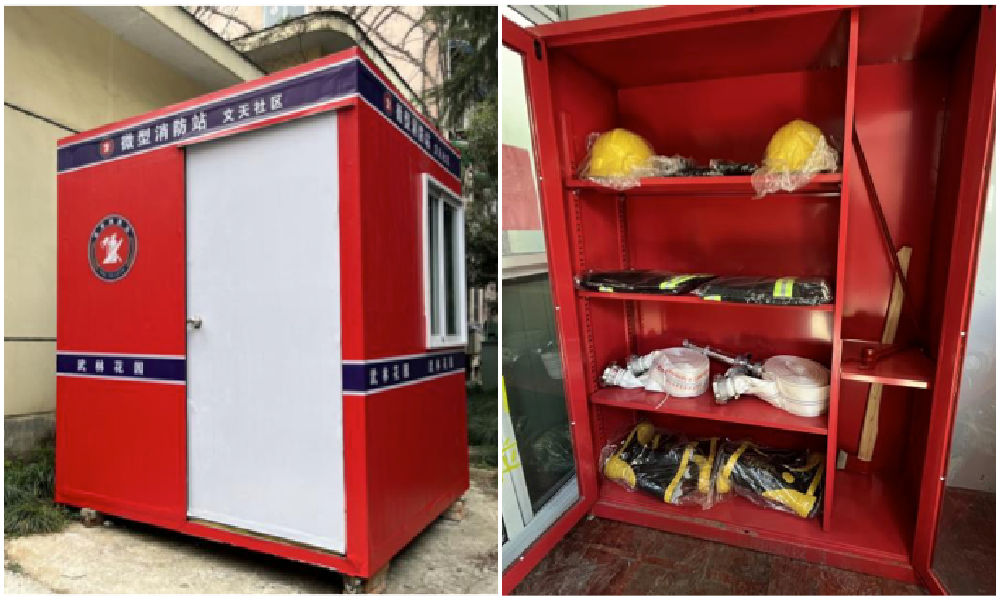

Micro fire stations, images via ZjNews.
Some communities decided that it would be useful to repurpose the testing points and turn them into mini fire kiosks, just allowing enough space for the necessary equipment to quickly respond to fire emergencies.
Want to read more about the end of ‘zero Covid’ in China? Check our other articles here.
By Manya Koetse,
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?





