China Insight
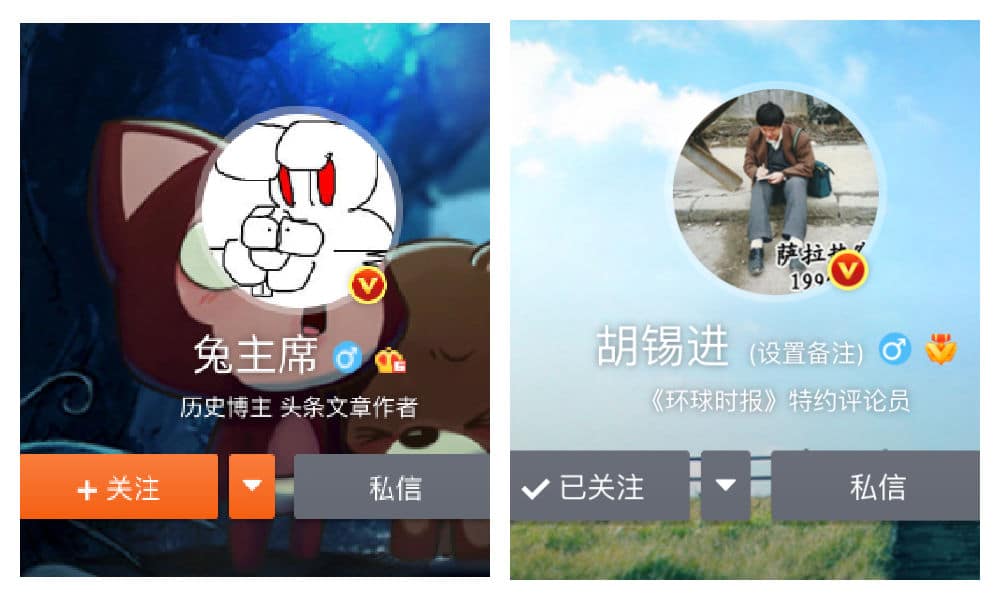
Chairman Rabbit vs Hu Xijin: Divided Nationalists on Weibo
Hu’s personal opinions should not be mistaken for China’s official stance nor guide Chinese online public opinion, Chairman Rabbit argues.
Published
2 years agoon
THIS IS A PREMIUM CONTENT ARTICLE
Political commentator Hu Xijin was an influential online voice in the days surrounding Pelosi’s visit to Taiwan. Chinese blogging account Chairman Rabbit lashed out against Hu, saying he misled public opinion at a time when his statements should have matched the official stance.
On August 3rd, a day after Nancy Pelosi’s visit to Taiwan, Chinese blogger Chairman Rabbit (兔主席) posted a long piece of text on Weibo rebuking political commentator Hu Xijin (胡锡进) for his overdosed hawkish claims leading up to Pelosi’s controversial visit.
Following the post by Chairman Rabbit, grandson of a former CCP leader, Chinese social media saw many discussions and a wave of criticism against Hu and his overaggressive position.
In his since-deleted post, Chairman Rabbit demanded stricter regulation of Hu’s public statements due to his perceived ties with the Chinese government.
Hu Xijin is a Chinese journalist and the former editor-in-chief and party secretary of Global Times, a Chinese and English-language media outlet under the auspices of the Chinese Communist Party’s official People’s Daily newspaper.
Although he retired from his job, Hu is still a very active commentator on political affairs via social media. With nearly 25 million fans on Weibo and over half a million followers on Twitter, his posts and statements often go trending and influence public opinions.
Chairman Rabbit argued that Hu has built a credible reputation in his field, both within China and abroad, where he is generally perceived as having certain authority to speak about China’s political affairs – with some foreign media almost regarding him as some sort of spokesman for the Chinese government. Meanwhile, according to Chairman Rabbit, Hu uses this credibility to promote his own personal views.
“He was too loud. It would make the people think that [China’s] actions are not enough, bringing about disappointment and distrust. This is damaging to the morale of the people and also to the credibility of the government,” Chairman Rabbit wrote.
Two Political Commentators “Protecting China’s National Interests”
Chairman Rabbit is the alias of Ren Yi (任意), a Harvard-educated Chinese blogger who currently has over 1.8 million followers on Weibo, where he calls himself a ‘history blogger.’ He is also the grandson of former Chinese politician Ren Zhongyi (任仲夷), who was a leader in China’s reform period since the late 1970s. ‘Chairman Rabbit’ is known as a nationalist, conservative political commentator who often comments on US-related issues and current affairs (for more on his background, check out this article by Tianyi Xu).
The Chinese blogger’s post came after a week in which Hu Xijin recurringly went trending for his strong condemnation of a potential visit to Taiwan by U.S. House Speaker Pelosi.
Hu suggested that a Taiwan visit by Pelosi would be a clear provocation of China, giving the PLA “good reason” for “waging a war.” One of Hu’s tweets, in which he voiced the view that U.S. military planes escorting Pelosi to Taiwan could potentially be shot down, was deleted by Twitter on July 30. Afterward, Hu reiterated his views on Weibo and criticized Western censorship.

Hu Xijin tweet which was deleted by Twitter on July 30.
Chairman Rabbit wrote about Hu:
“(..) as we can see time and again, he lacks judgment and accurate sources of information on some major issues (..), and he represents only his personal views, which may be misdirected. If his views were perceived as being purely personal, they would not receive nearly as much attention – his “authority figure” status is the key to everything, and he is perceived as having a special channel to represent authorities.”
In the post, Chairman Rabbit accuses Hu of using his status to promote his own views and to influence the public debate and the international view of China to gain clout.
Hu Xijin responded to the post himself on his Weibo account, suggesting he felt betrayed and “deeply puzzled” to be attacked by someone he considered a “friend who worked together [with me] to defend China’s national interests,” writing: “I originally saw them as allies, yet right in the heat of the moment, I was surprised to find that that they suddenly turned their guns to aim it at me.”
In the same post, Hu still defended his own words, arguing that despite his “limited power” he still does what he can to “protect China’s national interests.”
“Frisbee Hu”
The Chairman Rabbit vs Hu Xijin dispute caught the attention of Chinese netizens, including the liberals and conservatives on Chinese social media.
With his muscle-flexing language, Hu seemingly regained popularity amongst die-hard nationalists on Weibo after long being suspected of being a “gongzhi” (公知), a derogatory use of the term “public intellectual.” The latest controversy shows that the interests of online nationalists do not always align with the official government stances.
It also shows a division between populist nationalists and the more elite or ‘establishment’ nationalists on Chinese social media. The former operate independently and are willing to pressure the government toward a more hostile foreign policy, while the latter follow the decisions of the government and respond to them.
Hu is known for commenting on political issues and tuning into official narratives, which even led to him being nicknamed “Frisbee Hu” (胡叼盘), suggesting he can catch the ‘frisbees’ thrown by the Communist Party like a dog catches his toy.
However, it seems he did not catch their ‘frisbee’ this time. For the CCP, it arguably would be not a wise choice to engage in any kind of military conflict at this time, knowing the unpredictable societal changes it may bring to its regime, especially ahead of Xi Jinping’s bid for a third term in office at the 20th party congress later this year.
Authorities did emphasize that China would not “idly sit by” if Pelosi would visit Taiwan. Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Zhao Lijian warned the U.S. on August 1st that if the U.S. House speaker would visit Taipei, “the Chinese side will respond resolutely and take strong countermeasures to defend our sovereignty and territorial integrity.”
But the aggressiveness of Hu Xijin’s posts perhaps went beyond what the authorities had in mind. According to Chairman Rabbit, Hu “influenced public opinion, and China’s international image as well. What he got in the end was traffic for his own account.”
Instruments to Govern the Public Sphere
On social media, Hu still received a lot of support while others agreed with Chairman Rabbit that Hu was chasing clout and that his words have consequences. Although that is not necessarily bad – as his influence can mobilize and channel public rage in a time of strict Covid measures and a declining economy, – it can also backfire and reflect negatively on the government when they fail to meet the public’s expectations.
Chairman Rabbit suggests that it might be better for Hu to put a disclaimer and clarification at the top of any statement to make it clear that his views are personal and do not represent the official view.
This is not the first time Hu gets caught up in a conflict between Chinese populist and establishment nationalists. In 2021, Hu had a public spat with Shen Yi, a professor at Fudan University. When Shen Yi defended a controversial post by the CCP Central Political and Legal Affairs Commission which put an image of the Chinese rocket launch besides that of a mass cremation in India, Hu argued that official accounts should not ridicule India’s Covid deaths but “express sympathy for India, and place Chinese society firmly on the moral high ground” (read here).
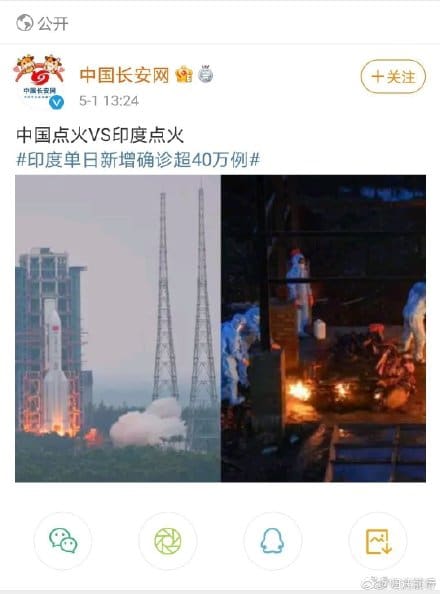
At that time, however, Hu sided with the so-called ‘establishment nationalists’ advocating for more decent public expressions from an official government account at a time when their neighboring country was mourning the victims of their Covid outbreak.
Disputes such as ‘Hu vs Shen’ and ‘Hu vs Chairman Rabbit’ could be seen as instruments to govern the public sphere, shifting the focus of attention amid online storms. The ‘Hu vs Shen’ public spat shifted the subject from whether it is moral to ridicule a neighboring country for its tragedy to whether it is good for an official government account to ridicule a neighboring country for its tragedy.
Similarly, the ‘Hu vs. Chairman Rabbit’ dispute shifted the subject from whether it is moral to wage a war over Pelosi’s visit to whether it would be in China’s best national interests to wage a war and to the influence of online public commentators within this matter.
Chairman Rabbit posted a second lengthy post regarding the dispute on August 4th, in which he again reiterated his stance that Hu Xijin’s tone on social media did not match the official stance, and that Hu, with limited diplomatic and military knowledge, miscalculated his response to the Pelosi issue and guided public opinion in the wrong direction.
The dispute between the two influential commentators triggered discussions, with some bloggers wondering when the next round of bickering is going to take place. In doing so, Chairman Rabbit has also been instrumental in channeling nationalist sentiments and creating some calm after the online storm following Pelosi’s visit.
“I think the Propaganda Department needs take responsibility, as they tacitly accepted Hu Xijin’s influence on public opinion. They can’t later shift all the blame to a person who’s already retired,” one popular comment said: “Those who are responsible should take responsibility! Our propaganda has always seen some problems, both internally as well as externally.”
Other commenters think Hu Xijin is getting too much credit for being held responsible for shifting public opinion. “My friends don’t even know who Hu Xijin is, yet they had also shifted in the ‘prepare for war’ direction,” one Weibo user writes, with another person adding: “He’s just saying out loud what I was thinking already. If everyone said it, it might be blocked, but he can speak for us.”
“Hindsight is 20/20,” others say: “And we might need hawkish expressions such as those published by Hu. I still support him.”
By Xiuyu Lian and Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our weekly newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Stories that are authored by the What's on Weibo Team are the stories that multiple authors contributed to. Please check the names at the end of the articles to see who the authors are.

Also Read
China Insight
The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
The story of ‘Fat Cat’ has become a hot topic in China, sparking widespread sympathy and discussions online.
Published
3 months agoon
May 9, 2024
The tragic story behind the recent suicide of a 21-year-old Chinese gamer nicknamed ‘Fat Cat’ has become a major topic of discussion on Chinese social media, touching upon broader societal issues from unfair gender dynamics to businesses taking advantage of grieving internet users.
The story of a 21-year-old Chinese gamer from Hunan who committed suicide has gone completely viral on Weibo and beyond this week, generating many discussions.
In late April of this year, the young man nicknamed ‘Fat Cat’ (胖猫 Pàng Māo, literally fat or chubby cat), tragically ended his life by jumping into the river near the Chongqing Yangtze River Bridge (重庆长江大桥) following a breakup with his girlfriend. By now, the incident has come to be known as the “Fat Cat Jumping Into the River Incident” (胖猫跳江事件).
News of his suicide soon made its rounds on the internet, and some bloggers started looking into what was behind the story. The man’s sister also spoke out through online channels, and numerous chat records between the young man and his girlfriend emerged online.
One aspect of his story that gained traction in early May is the revelation that the man had invested all his resources into the relationship. Allegedly, he made significant financial sacrifices, giving his girlfriend over 510,000 RMB (approximately 71,000 USD) throughout their relationship, in a time frame of two years.
When his girlfriend ended the relationship, despite all of his efforts, he was devastated and took his own life.
The story was picked up by various Chinese media outlets, and prominent social and political commentator Hu Xijin also wrote a post about Fat Cat, stating the sad story had made him tear up.
As the news spread, it sparked a multitude of hashtags on Weibo, with thousands of netizens pouring out their thoughts and emotions in response to the story.
Playing Games for Love
The main part of this story that is triggering online discussions is how ‘Fat Cat,’ a young man who possessed virtually nothing, managed to provide his girlfriend, who was six years older, with such a significant amount of money – and why he was willing to sacrifice so much in order to do so.
The young man reportedly was able to make money by playing video games, specifically by being a so-called ‘booster’ by playing with others and helping them get to a higher level in multiplayer online battle games.
According to his sister, he started working as a ‘professional’ video gamer as a means of generating money to satisfy his girlfriend, who allegedly always demanded more.
He registered a total of 36 accounts to receive orders to play online games, making 20 yuan per game (about $2.80). Because this consumed all of his time, he barely went out anymore and his social life was dead.
In order to save more money, he tried to keep his own expenses as low as possible, and would only get takeout food for himself for no more than 10 yuan ($1,4). His online avatar was an image of a cat saying “I don’t want to eat vegetables, I want to eat McDonald’s.”

The woman in question who he made so many sacrifices for is named Tan Zhu (谭竹), and she soon became the topic of public scrutiny. In one screenshot of a chat conversation between Tan and her boyfriend that leaked online, she claimed she needed money for various things. The two had agreed to get married later in this year.
Despite of this, she still broke up with him, driving him to jump off the bridge after transferring his remaining 66,000 RMB (9135 USD) to Tan Zhu.
As the story fermented online, Tan Zhu also shared her side of the story. She claimed that she had met ‘Fat Cat’ over two years ago through online gaming and had started a long distance relationship with him. They had actually only met up twice before he moved to Chongqing. She emphasized that financial gain was never a motivating factor in their relationship.
Tan additionally asserted that she had previously repaid 130,000 RMB (18,000 USD) to him and that they had reached a settlement agreement shortly before his tragic death.
Ordering Take-Out to Mourn Fat Cat
– “I hope you rest in peace.”
– “Little fat cat, I hope you’ll be less foolish in your next life.”
– “In your next life, love yourself first.”
These are just a few of the messages left by netizens on notes attached to takeout food deliveries near the Chongqing Yangtze River Bridge.

AI-generated image spread on Chinese social media in connection to the event.
As Fat Cat’s story stirred up significant online discussion, with many expressing sympathy for the young man who rarely indulged in spending on food and drinks, some internet users took the step of ordering McDonalds and other food delivery services to the bridge, where he tragically jumped from, in his honor.
This soon snowballed into more people ordering food and drinks to the bridge, resulting in a constant flow of delivery staff and a pile-up of take-out bags.

Delivery food on the bridge, photo via Weibo.
However, as the food delivery efforts picked up pace, it came to light that some of the deliveries ordered and paid for were either empty or contained something different; certain restaurants, aware of the collective effort to honor the young man, deliberately left the food boxes empty or substituted sodas or tea with tap water.
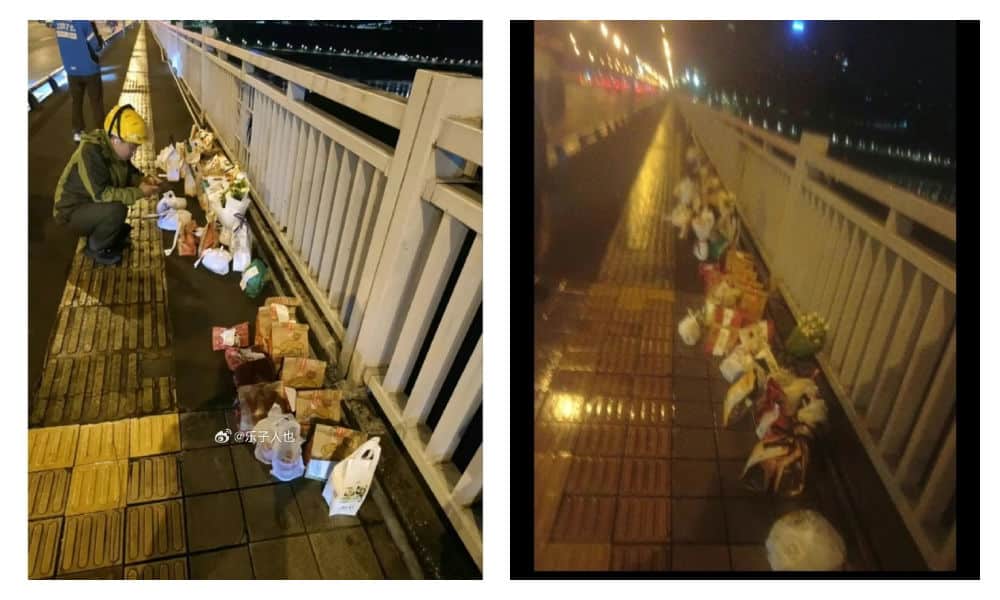

At least five restaurants were caught not delivering the actual orders. Chinese bubble tea shop ChaPanda was exposed for substituting water for milk tea in their cups. On May 3rd, ChaPanda responded that they had fired the responsible employee.
Another store, the Zhu Xiaoxiao Luosifen (朱小小螺蛳粉), responded on that they had temporarily closed the shop in question to deal with the issue. Chinese fast food chain NewYobo (牛约堡) also acknowledged that at least twenty orders they received were incomplete.
Fast food company Wallace (华莱士) responded to the controversy by stating they had dismissed the employees involved. Mixue Ice Cream & Tea (蜜雪冰城) issued an apology and temporarily closed one of their stores implicated in delivering empty orders.
In the midst of all the controversy, Fat Cat’s sister asked internet users to refrain from ordering take-out food as a means of mourning and honoring her brother.
Nevertheless, take-out food and flowers continued to accumulate near the bridge, prompting local authorities to think of ways of how to deal with this unique method of honoring the deceased gamer.
Gamer Boy Meets Girl
On Chinese social media, this story has also become a topic of debate in the context of gender dynamics and social inequality.
There are some male bloggers who are angry with Tan Zhu, suggesting her behaviour is an example of everything that’s supposedly “wrong” with Chinese women in this day and age.
Others place blame on Fat Cat for believing that he could buy love and maintain a relationship through financial means. This irked some feminist bloggers, who see it as a chauvinistic attitude towards women.
A main, recurring idea in these discussions is that young Chinese men such as Fat Cat, who are at the low end of the social ladder, are actually particularly vulnerable in a fiercely competitive society. Here, a gender imbalance and surplus of unmarried men make it easier for women to potentially exploit those desperate for companionship.
The story of Fat Cat brings back memories of ‘Mo Cha Official,’ a not-so-famous blogger who gained posthumous fame in 2021 when details of his unhappy life surfaced online.
Likewise, the tragic tale of WePhone founder Su Xiangmao (苏享茂) resurfaces. In 2017, the 37-year-old IT entrepreneur from Beijing took his own life, leaving behind a note alleging blackmail by his 29-year-old ex-wife, who demanded 10 million RMB (±1.5 million USD) (read story).
Another aspect of this viral story that is mentioned by netizens is how it gained so much attention during the Chinese May holidays, coinciding with the tragic news of the southern China highway collapse in Guangdong. That major incident resulted in the deaths of at least 48 people, and triggered questions over road safety and flawed construction designs. Some speculate that the prominence given to the Fat Cat story on trending topic lists may have been a deliberate attempt to divert attention away from this incident.
‘Fat Cat’ was cremated. His family stated their intention to take necessary legal steps to recover the money from his former girlfriend, but Tan Zhu reportedly already reached an agreement with the father and settled the case. Nevertheless, the case continues to generate discussions online, with some people wondering: “Is it over yet? Can we talk about something different now?”

Fat Cat images projected in Times Square
However, given that images of the ‘Fat Cat’ avatar have even appeared in Times Square in New York by now (Chinese internet users projected it on one of the big LED screens), it’s likely that this story will be remembered and talked about for some time to come.
UPDATE MAY 25
On May 20, local authorities issued a lengthy report to clarify the timeline of events and details surrounding the death of “Fat Cat,” which had attracted significant attention across China.
The report concluded that there was no fraud involved and that “Fat Cat” and his girlfriend were in a genuine relationship. Tan did not deceive “Fat Cat” for money; the transfers were voluntary. Furthermore, Tan returned most of the money to his parents.
The gamer’s sister is reportedly still being investigated for potentially infringing on Tan’s privacy by disclosing numerous private details to the public.
In the end, one thing is clear in this gamer’s tragic story, which is that there are no winners.
By Manya Koetse
– With contributions by Miranda Barnes and Ruixin Zhang
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea
Chinese tea brand LELECHA faced backlash for using the iconic literary figure Lu Xun to promote their “Smoky Oolong” milk tea, sparking controversy over the exploitation of his legacy.
Published
3 months agoon
May 3, 2024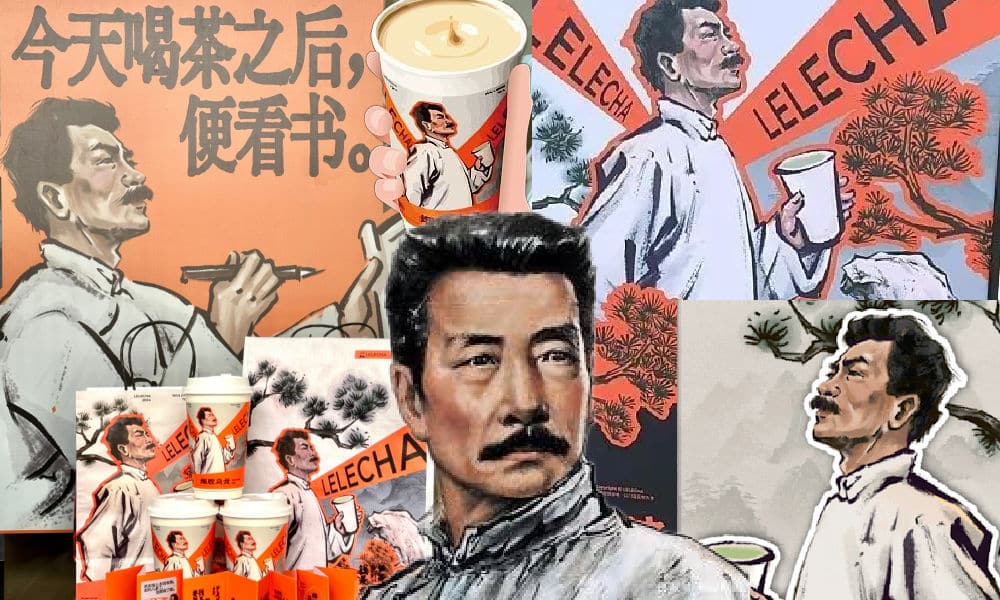
It seemed like such a good idea. For this year’s World Book Day, Chinese tea brand LELECHA (乐乐茶) put a spotlight on Lu Xun (鲁迅, 1881-1936), one of the most celebrated Chinese authors the 20th century and turned him into the the ‘brand ambassador’ of their special new “Smoky Oolong” (烟腔乌龙) milk tea.
LELECHA is a Chinese chain specializing in new-style tea beverages, including bubble tea and fruit tea. It debuted in Shanghai in 2016, and since then, it has expanded rapidly, opening dozens of new stores not only in Shanghai but also in other major cities across China.
Starting on April 23, not only did the LELECHA ‘Smoky Oolong” paper cups feature Lu Xun’s portrait, but also other promotional materials by LELECHA, such as menus and paper bags, accompanied by the slogan: “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” (“老烟腔,新青年”). The marketing campaign was a joint collaboration between LELECHA and publishing house Yilin Press.

Lu Xun featured on LELECHA products, image via Netease.
The slogan “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” is a play on the Chinese magazine ‘New Youth’ or ‘La Jeunesse’ (新青年), the influential literary magazine in which Lu’s famous short story, “Diary of a Madman,” was published in 1918.
The design of the tea featuring Lu Xun’s image, its colors, and painting style also pay homage to the era in which Lu Xun rose to prominence.
Lu Xun (pen name of Zhou Shuren) was a leading figure within China’s May Fourth Movement. The May Fourth Movement (1915-24) is also referred to as the Chinese Enlightenment or the Chinese Renaissance. It was the cultural revolution brought about by the political demonstrations on the fourth of May 1919 when citizens and students in Beijing paraded the streets to protest decisions made at the post-World War I Versailles Conference and called for the destruction of traditional culture[1].
In this historical context, Lu Xun emerged as a significant cultural figure, renowned for his critical and enlightened perspectives on Chinese society.
To this day, Lu Xun remains a highly respected figure. In the post-Mao era, some critics felt that Lu Xun was actually revered a bit too much, and called for efforts to ‘demystify’ him. In 1979, for example, writer Mao Dun called for a halt to the movement to turn Lu Xun into “a god-like figure”[2].
Perhaps LELECHA’s marketing team figured they could not go wrong by creating a milk tea product around China’s beloved Lu Xun. But for various reasons, the marketing campaign backfired, landing LELECHA in hot water. The topic went trending on Chinese social media, where many criticized the tea company.
Commodification of ‘Marxist’ Lu Xun
The first issue with LELECHA’s Lu Xun campaign is a legal one. It seems the tea chain used Lu Xun’s portrait without permission. Zhou Lingfei, Lu Xun’s great-grandson and president of the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation, quickly demanded an end to the unauthorized use of Lu Xun’s image on tea cups and other merchandise. He even hired a law firm to take legal action against the campaign.
Others noted that the image of Lu Xun that was used by LELECHA resembled a famous painting of Lu Xun by Yang Zhiguang (杨之光), potentially also infringing on Yang’s copyright.
But there are more reasons why people online are upset about the Lu Xun x LELECHA marketing campaign. One is how the use of the word “smoky” is seen as disrespectful towards Lu Xun. Lu Xun was known for his heavy smoking, which ultimately contributed to his early death.
It’s also ironic that Lu Xun, widely seen as a Marxist, is being used as a ‘brand ambassador’ for a commercial tea brand. This exploits Lu Xun’s image for profit, turning his legacy into a commodity with the ‘smoky oolong’ tea and related merchandise.
“Such blatant commercialization of Lu Xun, is there no bottom limit anymore?”, one Weibo user wrote. Another person commented: “If Lu Xun were still alive and knew he had become a tool for capitalists to make money, he’d probably scold you in an article. ”
On April 29, LELECHA finally issued an apology to Lu Xun’s relatives and the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation for neglecting the legal aspects of their marketing campaign. They claimed it was meant to promote reading among China’s youth. All Lu Xun materials have now been removed from LELECHA’s stores.

Statement by LELECHA.
On Chinese social media, where the hot tea became a hot potato, opinions on the issue are divided. While many netizens think it is unacceptable to infringe on Lu Xun’s portrait rights like that, there are others who appreciate the merchandise.
The LELECHA controversy is similar to another issue that went trending in late 2023, when the well-known Chinese tea chain HeyTea (喜茶) collaborated with the Jingdezhen Ceramics Museum to release a special ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ (佛喜) latte tea series adorned with Buddha images on the cups, along with other merchandise such as stickers and magnets. The series featured three customized “Buddha’s Happiness” cups modeled on the “Speechless Bodhisattva” (无语菩萨), which soon became popular among netizens.
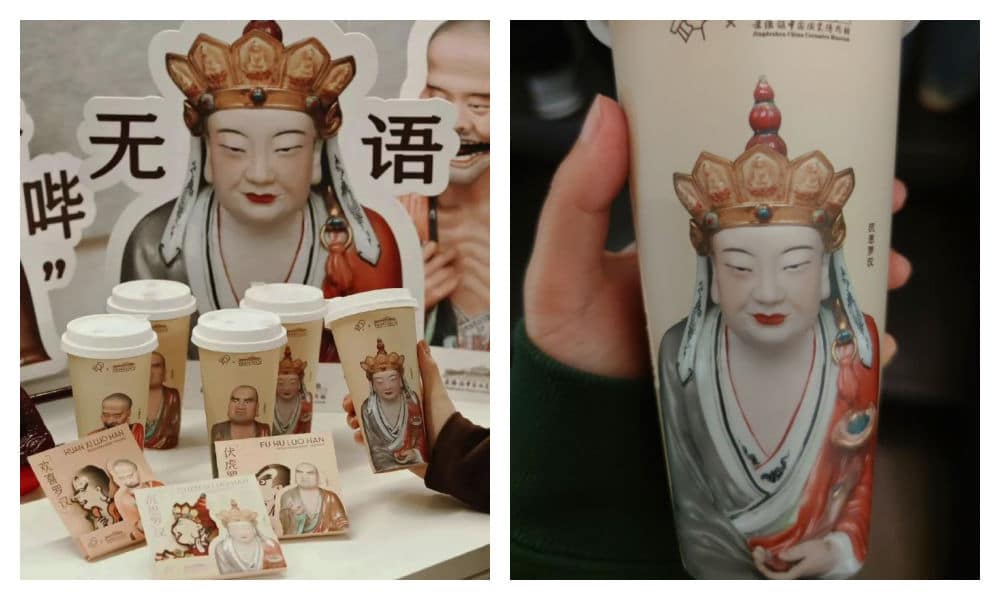

The HeyTea Buddha latte series, including merchandise, was pulled from shelves just three days after its launch.
However, the ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ success came to an abrupt halt when the Ethnic and Religious Affairs Bureau of Shenzhen intervened, citing regulations that prohibit commercial promotion of religion. HeyTea wasted no time challenging the objections made by the Bureau and promptly removed the tea series and all related merchandise from its stores, just three days after its initial launch.
Following the Happy Buddha and Lu Xun milk tea controversies, Chinese tea brands are bound to be more careful in the future when it comes to their collaborative marketing campaigns and whether or not they’re crossing any boundaries.
Some people couldn’t care less if they don’t launch another campaign at all. One Weibo user wrote: “Every day there’s a new collaboration here, another one there, but I’d just prefer a simple cup of tea.”
By Manya Koetse
[1]Schoppa, Keith. 2000. The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. New York: Columbia UP, 159.
[2]Zhong, Xueping. 2010. “Who Is Afraid Of Lu Xun? The Politics Of ‘Debates About Lu Xun’ (鲁迅论争lu Xun Lun Zheng) And The Question Of His Legacy In Post-Revolution China.” In Culture and Social Transformations in Reform Era China, 257–284, 262.
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?




