China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
China’s XR Development 101: How Chinese Tech Giants are Navigating Towards the Metaverse
Chinese tech giants are massively investing in virtual reality and in the technologies that are building up the Chinese metaverse.
Published
2 years agoon
By
Jialing Xie
Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Reality technologies are blurring the lines between the real and digital worlds and are powering the metaverse. Chinese tech giants are at the forefront of the latest developments on the mainland market, including XR, that are making the metaverse possible. Time for a round-up of what China’s key players are focusing on and which virtual initiatives are already live.
2021 is the year in which the concept of ‘metaverse’ has blossomed. In March of last year, the hugely successful online multiplayer game and game creation system Roblox went public with a market value of over $41 billion at the time, earning its reputation as the world’s first metaverse IPO.
Following the release of the 2021 sci-fi comedy Free Guy – which is set in a fictional metaverse-like video game, – and Facebook’s rebranding to ‘Meta’ last fall, ‘metaverse’ became one of the hottest buzzwords on the internet.
The term metaverse is actually decades old. In the 1981 novel True Names, the American computer scientist Vernor Steffen Vinge already envisioned a virtual world that could be accessed through a brain-computer interface, and the term ‘metaverse’ was first mentioned in the 1992 Snow Crash science fiction novel by Neal Stephenson.
Now, 5G, AI, VR, Blockchain, 3D modeling, and other new technologies converged on the concept of the metaverse industry are seeing an explosive growth in China.
At the recent 20th Party Congress, it became clear once again that the digital economy is key in China’s long-term strategies, with Chinese leader Xi Jinping promoting digitalization as one of the new “engines” of future growth.
About Metaverse (元宇宙) in China
In Chinese, ‘metaverse’ is referred to as yuányǔzhòu (元宇宙), which is a literal translation of ‘meta-verse’ – meaning ‘transcending universe’ (超越宇宙). Chinese tech sources also describe the year 2021 as “the metaverse year” (元宇宙元年).
Metaverse is a collective, shared virtual realm that can interact with the real world and where people can interact with each other and the spaces around them. There is not just one single metaverse – there can be many digital living spaces referred to as the ‘metaverse.’
Metaverse is a fluid concept or virtual experience that is still developing and due to the differences in cyber regulations, digital ecosystems, and strict control on online information flows, the Chinese metaverse will unquestionably be very different from the metaverse spheres that companies such as Facebook are working on.
The metaverse is made possible through a wide range of technologies including AI, IoT, Blockchain, Interaction Technology, computer games, and network computing. XR is key to the rise of the metaverse. XR, or Extended Reality, is an umbrella term for a range of immersive technologies including VR (Virtual Reality 虚拟现实), AR (Augmented Reality 增强现实), and MR (Mixed Reality 混合现实). A 2020 Deloitte report suggests that the global XR market consists of mainly VR technologies (48% of market share), followed by AR (34%) and MR (18%).
In December of 2020, Tencent’s CEO Ma Huateng (马化腾) announced the concept of the “All-real Internet” (全真互联网) in a special internal publication regarding the company’s growth and major changes. Ma proposed that the deep integration of the virtual and real world, the “All-real Internet,” is the future opportunity to focus on as the next stage of the (mobile) internet. Although there are some subtle differences, Ma’s idea of the “All-real Internet” overlaps with the concept of the metaverse.
The metaverse, XR, and related technologies are not just a hot issue for Chinese tech companies, they are also an important theme for Chinese authorities. The 20th Party Congress was by no means the first time for China’s leadership to stress the country’s focus on the latest digital innovations. In October 2021, President Xi Jinping also spoke about evolving China’s digital economy during the 19th CPC Central Committee. He asserted that one of the focal points within the development strategy of China’s digital economy is the further integration of digital technologies and real-world economies.
This idea was further clarified in the outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan issued by the State Council at the end of 2021, which listed VR and AR as one of the seven key industries of China’s digital economy along with cloud computing, IoT, AI, and others.
Subsequently, many local governments incorporated metaverse (“元宇宙”) and related relevant terms into their respective 14th Five-Year Plans. For example, Shanghai authorities stated it will focus on the further developments of industries related to quantum computing, 3rd-gen semiconductors, 6G communications, and metaverse.
Here, we will provide an overview of XR industry development in present-day China, going over the key players Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent (BAT) along with the younger Chinese tech giant ByteDance. We provide an overview of what they are investing in, what their respective strategies are when it comes to XR, and give examples of the kind of initiatives that they have already launched. To limit the scope of this article, we have left out Netease, Huawei, Bilibili, and some other relevant Chinese players for now (we might still make a part two later on!).
Key Players and Strategies
▶︎ BAIDU
As one of the leading artificial intelligence (AI) and internet companies in the world, Baidu specializes in internet and AI-related products and services. Baidu is mostly known as China’s number one search engine, but its ambitions go far beyond that. “We want to be like Amazon Web Services (AWS) for the metaverse,” Ma Jie (马杰), vice president at Baidu, recently said.
The company has taken a special interest in building the infrastructure to support metaverse-related projects, deviating from the strategies that focus more on the XR-related content development and distribution that you see at Tencent or Bytedance.
What’s Happening?
Investments
◼︎ iQiyi (爱奇艺), one of China’s top media streaming platforms (sometimes also referred to as the ‘Chinese Netflix’), released its all-in-one virtual reality headset ‘Adventure Dream’ in December 2021 powered by Snapdragon XR2. Baidu owns 53% of iQiyi and holds more than 90% of its shareholder voting rights.
Research & Development
◼︎ Baidu launched the ‘Baidu VR Browser’ on July 15, 2016, becoming China’s first browser powered by webVR technology.

Xirang
◼︎ In 2017, Baidu launched ‘Baidu VR’ platform, which is now offering a wide range of VR-related software and hardware products and services, including the Baidu VR Headset, VR Creation Center, AI app, and XiRang (希壤), which is referred to as China’s “first metaverse platform.”
What’s Live?
Retail
◼︎ In 2018, Baidu VR and UXin Limited, a Chinese online used car marketplace, jointly developed VR 360° interior panoramas that put viewers in the driver’s seat to see how interior details come together and to better understand the details of each vehicle such as scratches, wheels and engine models.
◼︎ Baidu’s ‘Meta Ziwu’ (元宇宙誌屋Meta ZiWU), a virtual space within XiRang, hosts various fashion shows for international brands. In August of 2022, Italian luxury fashion house Prada livestreamed its Fall 2022 collection within the interactive realms of ‘Meta Ziwu,’ and so did Dior, the French fashion house which has also launched its first-ever metaverse exhibition “On the Road” (在路上) via Meta Ziwu.
Social Networking
◼︎ In late 2021, Baidu launched its metaverse project XiRang (希壤, ‘the land of hope’) as “the first Chinese-made metaverse product.” In December, Baidu held ‘Baidu Create 2021′, a three-day annual developers’ conference in a virtual world generated by the XiRang platform, hosting 100,000 people on one set of servers at the same time. Baidu’s Vice President Ma Jie, also Head of the Metaverse XiRang project, shared that the main goal behind this project is to lay the infrastructure of the metaverse by providing developers and content creators with the tools to build their metaverse projects.

Chinese architect Ma Yansong (马岩松), founder of MAD architects, also works together with Meta Ziwu as a virtual architect.
▶︎ALIBABA
Founded in 1999, Alibaba is one of the world’s largest e-commerce and cloud computing companies in Asia Pacific. Its massive success in e-commerce also established Alibaba’s leading position in artificial intelligence and other key technologies that have supported e-commerce, as well as in the future of metaverse.
As one of the biggest venture capital firms and investment corporations in the world, Alibaba struck several deals with prominent XR companies including Magic Leap and Nreal to gain footing in the Extended Reality industry.
As for R&D, Alibaba’s ambition in becoming the world’s fifth-largest economy led to a strong emphasis on technological research and XR-focused innovation and the founding of DAMO Academy.
Within the field of XR, Alibaba primarily focuses on two aspects: underlying technology solutions (e.g. cloud computing) and XR application in its own core business model (e-commerce).
What’s Happening?
Investments
◼︎ In February 2016 and October 2017, Alibaba led the investment rounds in Magic Leap, an augmented reality firm headquartered in Florida.
◼︎ In March of this year, Alibaba led a $60 million investment round of Beijing-based augmented reality glasses maker Nreal. Nreal, founded in 2017, has since launched two AR glasses for the Chinese market: Nreal X for developers and content creators and Nreal Air for regular consumers. Nreal Air glasses have been released in Japan and the UK in February and May of this year. In addition to AR glasses, Nreal also cooperated with iQiyi, China Mobile Migu, Weilai, and Kuaishou to develop AR content.
Research & Development
◼︎ In March 2016, Alibaba announced its own VR research lab, GM LAB ( ‘GnomeMagic’ Lab), which aims to power its e-commerce platform and other subsidiary businesses such as the VR content production for its film and music platforms.
◼︎ Alibaba registered several metaverse-related trademarks, including “Ali Metaverse.”
◼︎ In 2021, Alibaba’s DAMO Academy, a global research program in cutting-edge technologies, launched ‘X Lab’ that focuses on research in key areas related to the metaverse industry, including quantum computing, XR, and xG Technology. Tan Ping (谭平), the former Head of XR Lab, shared several of their ongoing projects at the time. One example he mentioned is the virtual character Xiaomo (小莫), who is very versatile and can, among other things, convert textual information into sign language to enable smoother communication for the hearing impaired.

Xiaomo by Alibaba can turn spoken text into sign language.
‘X Lab’ is also experimenting with making history come alive through virtual initiatives. Recently, Alibaba’s cloud gaming platform Yuanjing made it possible for visitors at their Alibaba Cloud’s Apsara conference to virtually visit the Xi’an Museum and check out its artifacts via mobile phone or laptop, or to have an immersive experience of the Tang dynasty’s imperial palace complex, powered by automatic 3D space creation and visual localization technology.
What’s Live?
eCommerce
◼︎ In November 2016, Alibaba launched the Mobile BUY+ feature in Taobao mobile apps in light of its annual Single’s Day Global Shopping Festival. With VR headsets and the app, China-based Taobao shoppers could experience shopping in-store at Target, Macy’s, or Costco in the US and other malls located in countries such as Japan and Australia.

◼︎ As Alibaba constantly keeps innovating its e-commerce landscape, its research institute DAMO Academy, in collaboration with its licensing platform Alifish, rolled out an XR-powered marketplace on Alibaba’s e-commerce platforms Tmall and Taobao for its November 2022 Single’s Day festival that allows consumers to visit virtual shopping streets and shop for merchandise as their own customizable avatars.
Entertainment
◼︎ In 2021, Alibaba led a $20 million Series A financing round of DGene, a virtual reality and immersive entertainment developer. Among others, DGene creates digital influencers or can even recreate historical figures based on its AI-driven technologies.
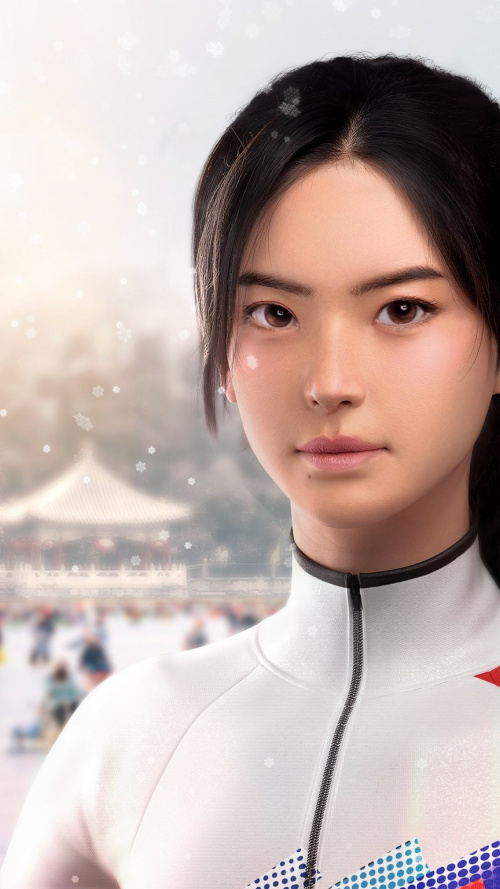

Dong Dong was launched as the first virtual brand ambassador for the Winter Olympics in 2022.
◼︎ For the Olympic Winter Olympics in 2022, Alibaba launched Dong Dong, a digital persona developed by Damo Academy using cloud-based digital technologies. Dong Dong was able to engage with fans and online viewers through livestreams, respond to questions in real time, and she even hosted online talkshows.
▶︎TENCENT
As a multinational technology and entertainment conglomerate with the highest-grossing revenue in the world, Tencent has the financial resources to gain an upper hand in technological innovation through acquisition and investment. In 2021 alone, Tencent made a total of 76 investments in Gaming, accounting for 25.2% of Tencent’s total investment throughout the year – a 9.3% increase compared to 2020. Tencent is now the biggest gaming company in the world.
Tencent also ramped up the company’s total headcount working in R&D department by 41%, accounting for 68% of its total workforce in 2021.
Although XR is used to create immersive experiences in different industries including healthcare, manufacturing, or education, its primary fields are still gaming and social – which just so happen to be Tencent’s main focus areas. It is therefore perhaps unsurprising that Tencent, as the country’s Gaming & Social giant, has made XR part of its core business.
What’s Happening?
Investments
◼︎ In 2012, Tencent made an investment in Epic Games, the owner of Unreal Engine which powers well-known video games such as Fortnite, purchasing approximately 40% of the total Epic capital, making it the second largest shareholder. Epic Games’ major businesses span across RT3D game engine (Unreal), in-house developed games (Fortnite), and platform games. This investment is one of the reasons why Tencent conquered a leading position in the metaverse realm when it comes to games.
◼︎ As early as 2014, Tencent already tapped into the VR market by investing in social VR platform AltspaceVR, which was later acquired by Microsoft in 2017.
◼︎ In May 2019, Tencent and Roblox announced a joint venture in which Tencent holds a 49% controlling stake.
◼︎ In September of 2021, Tencent became the new investor behind Beijing-based VR game developer Vanimals (威魔纪元), known for its flagship games Undying and Eternity Warriors VR.
◼︎ In November 2021, Tencent joined the $82M Series D fundraising of Ultraleap, the world leader in mid-air haptics and 3D hand tracking. Ultraleap’s hand-tracking platform has been built into multiple platforms including Qualcomm’s XR and VR devices.
◼︎ In March 2022, Tencent invested in the Chinese AR glasses manufacturer SUPERHEXA (蜂巢科技) holding 7.3% of its shares.
Research & Development
◼︎ In 2015, Tencent announced its avant-garde VR Project ‘Tencent VR,’ a plan consisting of building its own VR games and releasing Tencent Virtual reality software development kits (VR SDKs) to support other VR game developers.
◼︎ As of September 2021, Tencent applied for registration of nearly 100 trademarks related to the metaverse, including “Tencent Music Metaverse” (腾讯音乐元宇宙).
◼︎ In June 2022, Tencent officially set up its XR department led by its Interactive Entertainment Division (IEG) game developer NExT Studios. During Tencent’s annual gaming conference SPARK 2022, the Head of IEG, Ma Xiaoyi (马晓轶), shared Tencent’s ambitions in charting all segments of the VR industry in the next 5 years, from developer software tools and SDKs to VR hardware, to consumer-facing content.
◼︎ NExT Studios, which is the youngest studio within the Tencent Games family, has partnered with the Shenzhen-based FACEGOOD, a 3D content generation technology company that is focused on building metaverse infrastructure.
What’s Live?
Gaming
◼︎ At ChinaJoy 2019, the largest gaming and digital entertainment exhibition across Asia, Tencent launched its cloud gaming solution on its WeGame client, allowing users to play several games instantly without a download. In December of that year, Tencent Games and global leader AI hardware & software leader Nvidia announced a new partnership to launch the START (云游戏) cloud gaming service for PC and console titles.

◼︎ Following the Sino-American joint venture with Roblox in May 2021, Tencent officially launched the Chinese version of Roblox (罗布乐思) topping the App Store free game list in July of 2021.
Social Networking
◼︎ In November 2021, Tencent led a $25 million Series A funding in the British developer Lockwood Publishing best known for the metaverse app Avakin Life, which allows users to create 3D characters and socialize in the virtual community.
◼︎ During the Lunar New Year in February 2022, Tencent’s instant messaging software QQ launched a new feature called “Super QQ Show” (超级QQ秀), which is an upgrade of its ‘QQ Show’ service that’s been running since 2003. Super QQ Show allows users to create their own 3D avatars and use them in an interactive context. It added AI face recognition and rendering. The platform is an interesting one for brands. Fast-food chain KFC even has its own restaurant in this virtual world.
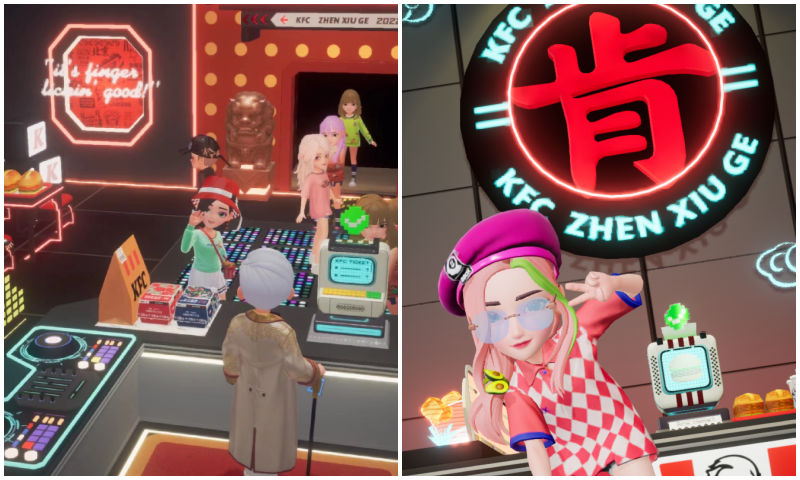

Visiting KFC in the Super QQ Show.
◼︎ In the summer of 2022, the Tencent-backed app developer company Soulgate Inc., which operates the social networking app Soul, applied to be listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Tencent is the largest shareholder holding 49.9% of the shares. Soul is a virtual social playground with the mission of “building a ‘Soul’cial Metaverse for young generations” where users can connect with other users through the virtual identity they develop in the app. The majority of its users, nearly 75%, belong to Gen-Z.
Entertainment
◼︎ On New Year’s Eve of 2021, Tencent Music Entertainment (TME) Group launched China’s first virtual social music platform TMELAND, where users can create their own avatars and interact with each other through their “digital identity.” It’s worth mentioning that TMELAND was powered by the ‘Hybrid Edge-Cloud Platform Solution’ developed by XVERSE (元象科技), which was founded by a former Tencent executive committed to building a one-stop shop for 3D content development.
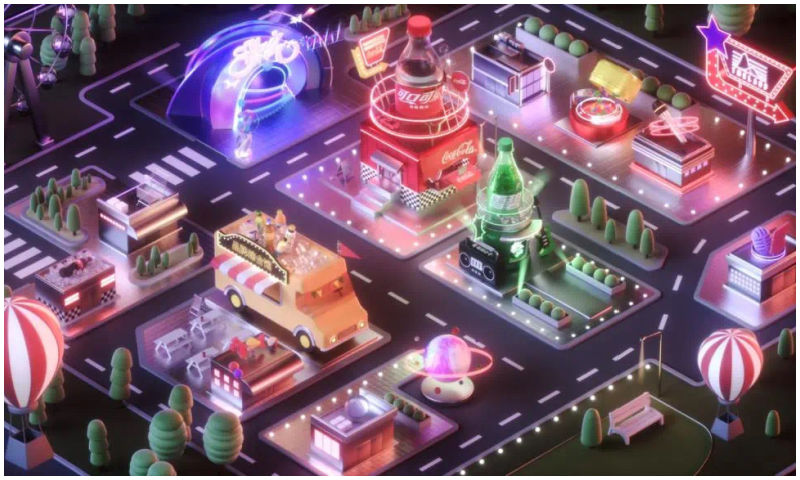

Coca Cola zone in TMLAND.
Recently, Coca-Cola partnered up with TMELAND to open a new metaverse zone, accessible via the TMELAND mini-programme on WeChat.
▶︎BYTEDANCE
Known as “the world’s most valuable startup,” the Bytedance success story started with the algorithm-powered Toutiao (头条 ‘Headlines’) in 2012, a news and content platform that personalizes content for each user based on their own preferences. The Bytedance app TikTok (Douyin in China) conquered the world as one of most successful Chinese apps internationally.
Bytedance is a social networking leader, but is also focused on its in-house development in VR/AR. By 2021, Bytedance had completed at least 76 investment events, more than the previous two years combined.
From ByteDance’s activities in the XR industry, the company seems to have its strategy primarily focused on hardware, content development, and distribution across gaming, social networking, and entertainment industries.
What’s Happening?
Investments
◼︎ As early as 2018, Toutiao (Bytedance’s core product) acquired VSCENE (维境视讯) a Beijing-based solution provider for VR Live streaming.
◼︎ In July 2020, Bytedance participated in Series A funding of Seizet (熵智科技), an industrial automation company that provides a 3D industrial camera and software.
◼︎ In February 2021, Bytedance invested in Moore Threads (摩尔线程), a company that specialized in visual computing and artificial intelligence fields. In November last year, Moore Threads announced it has developed China’s first domestic full-fledged graphic processing unit (GPU) chip. Along with 5G communications, Wi-Fi 6, cloud computing, and chip technology, GPU is considered one of the main infrastructure technologies of the metaverse.
◼︎ In August 2021, ByteDance acquired Chinese VR hardware maker & software platform Pico for approximately $771 million to support its long-term investment in the VR ecosystem. By the end of Q1 2022, Pico is estimated to hold a 4.5% share of the global VR market, following Meta which is the dominant global player (90%). This year, Bytedance has set a higher sales target for Pico headsets to reach 1.6 million device output. To meet its VR industry goals, Bytedance is investing more into promotion and hiring more staff for Pico to catch up with or even surpass Meta’s Quest.
◼︎ In June 2022, ByteDance acquired PoliQ (波粒子), a team specialized in making virtual social platforms that allow users to interact with one another using their self-invented avatars in the virtual world. Jiesi Ma, the founder of PoliQ, is appointed to lead the VR Social department at ByteDance.
Research & Development
◼︎ To boost its entire VR ecosystem, Pico is engaging in more partnerships with Hollywood’s major film studios and leading streaming media companies in China (iQiyi, Youku, Tencent Video, Bilibili, and so on). In July 2022, Pico hosted Pico WangFeng@VR Music + Drifting Fantasy concert which leveraged 3D 8K VR Live Streaming technology to create a “magical” and immersive visual musical experience. By wearing Pico’s VR headsets, the audience can enjoy Wang’s performance from 5 different angles and as close as a meter away.
What’s Live?
Gaming
◼︎ On February 22, 2021, Bytedance released its game development and publishing brand Nuverse (朝夕光年). To date, Nuverse has launched several successful games through APAC and the western markets including “Burning Streetball” (热血街篮), “Houchi Shoujo” (放置少女), “Ragnarok X: Next Generation” (RO仙境传说:新世代的诞生), “Mobile Legends: Bang Bang”, and “Warhammer 40,000: Lost Crusade.”
◼︎ In April 2021, Bytedance put another US$15 million into Chinese Roblox competitor Reworld (代码乾坤), a platform for creating game worlds and playing games using the company’s own simulation engine.
Social Networking
◼︎ In September 2021, Bytedance launched its avatar app Pixsoul in Southeast Asian markets and Brazil. Users can create personalized avatars and use them to socialize.
◼︎ In January 2022, Bytedance launched a beta version of its virtual social app “Party Island” (派对岛) where users can make friends with people sharing similar interests and hang out with avatars in various virtual settings such as parks and movie theaters. However, the app was reportedly removed from app stores again and its date of relaunching is unknown.
Entertainment
◼︎ In September 2021, TikTok introduced its creator-led NFT collection titled “TikTok Top Moments” where TikTok will feature a selection of culturally-significant TikTok videos from some of the most beloved creators on the platform. Powered by Immutable X, users can ‘own’ a moment on TikTok that broke the internet and trade the TikTok Top Moments NFTs.

Li Weike, image via Pandaily.
◼︎ In January 2022, ByteDance bought a 20% stake in Hangzhou Li Weike Technology Co., Ltd. (Li Weike, 李未可). The company aspires to build China’s first AI+AR-powered glasses that connect users with the virtual idol Li Weike, a digital character built by the company to help users with various tasks and essentially provide users with social and emotional support.
By Jialing Xie and Manya Koetse
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get unlimited access to all of our articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Jialing is a Baruch College Business School graduate and a former student at the Beijing University of Technology. She currently works in the US-China business development industry in the San Francisco Bay Area. With a passion for literature and humanity studies, Jialing aims to deepen the general understanding of developments in contemporary China.

Also Read
China Books & Literature
Why Chinese Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Shopping Festival
Bookworms love to get a good deal on books, but when the deals are too good, it can actually harm the publishing industry.
Published
2 months agoon
June 8, 2024By
Ruixin Zhang
JD.com’s 618 shopping festival is driving down book prices to such an extent that it has prompted a boycott by Chinese publishers, who are concerned about the financial sustainability of their industry.
When June begins, promotional campaigns for China’s 618 Online Shopping Festival suddenly appear everywhere—it’s hard to ignore.
The 618 Festival is a product of China’s booming e-commerce culture. Taking place annually on June 18th, it is China’s largest mid-year shopping carnival. While Alibaba’s “Singles’ Day” shopping festival has been taking place on November 11th since 2009, the 618 Festival was launched by another Chinese e-commerce giant, JD.com (京东), to celebrate the company’s anniversary, boost its sales, and increase its brand value.
By now, other e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and Pinduoduo have joined the 618 Festival, and it has turned into another major nationwide shopping spree event.
For many book lovers in China, 618 has become the perfect opportunity to stock up on books. In previous years, e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Dangdang (当当) would roll out tempting offers during the festival, such as “300 RMB ($41) off for every 500 RMB ($69) spent” or “50 RMB ($7) off for every 100 RMB ($13.8) spent.”
Starting in May, about a month before 618, the largest bookworm community group on the Douban platform, nicknamed “Buying Like Landsliding, Reading Like Silk Spinning” (买书如山倒,看书如抽丝), would start buzzing with activity, discussing book sales, comparing shopping lists, or sharing views about different issues.

Social media users share lists of which books to buy during the 618 shopping festivities.
This year, however, the mood within the group was different. Many members posted that before the 618 season began, books from various publishers were suddenly taken down from e-commerce platforms, disappearing from their online shopping carts. This unusual occurrence sparked discussions among book lovers, with speculations arising about a potential conflict between Chinese publishers and e-commerce platforms.
A joint statement posted in May provided clarity. According to Chinese media outlet The Paper (@澎湃新闻), eight publishers in Beijing and the Shanghai Publishing and Distribution Association, which represent 46 publishing units in Shanghai, issued a statement indicating they refuse to participate in this year’s 618 promotional campaign as proposed by JD.com.
The collective industry boycott has a clear motivation: during JD’s 618 promotional campaign, which offers all books at steep discounts (e.g., 60-70% off) for eight days, publishers lose money on each book sold. Meanwhile, JD.com continues to profit by forcing publishers to sell books at significantly reduced prices (e.g., 80% off). For many publishers, it is simply not sustainable to sell books at 20% of the original price.
One person who has openly spoken out against JD.com’s practices is Shen Haobo (沈浩波), founder and CEO of Chinese book publisher Motie Group (磨铁集团). Shen shared a post on WeChat Moments on May 31st, stating that Motie has completely stopped shipping to JD.com as it opposes the company’s low-price promotions. Shen said it felt like JD.com is “repeatedly rubbing our faces into the ground.”
Nevertheless, many netizens expressed confusion over the situation. Under the hashtag topic “Multiple Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Book Promotions” (#多家出版社抵制618图书大促#), people complained about the relatively high cost of physical books.
With a single legitimate copy often costing 50-60 RMB ($7-$8.3), and children’s books often costing much more, many Chinese readers can only afford to buy books during big sales. They question the justification for these rising prices, as books used to be much more affordable.
Book blogger TaoLangGe (@陶朗歌) argues that for ordinary readers in China, the removal of discounted books is not good news. As consumers, most people are not concerned with the “life and death of the publishing industry” and naturally prefer cheaper books.
However, industry insiders argue that a “price war” on books may not truly benefit buyers in the end, as it is actually driving up the prices as a forced response to the frequent discount promotions by e-commerce platforms.
China News (@中国新闻网) interviewed publisher San Shi (三石), who noted that people’s expectations of book prices can be easily influenced by promotional activities, leading to a subconscious belief that purchasing books at such low prices is normal. Publishers, therefore, feel compelled to reduce costs and adopt price competition to attract buyers. However, the space for cost reduction in paper and printing is limited.
Eventually, this pressure could affect the quality and layout of books, including their binding, design, and editing. In the long run, if a vicious cycle develops, it would be detrimental to the production and publication of high-quality books, ultimately disappointing book lovers who will struggle to find the books they want, in the format they prefer.
This debate temporarily resolved with JD.com’s compromise. According to The Paper, JD.com has started to abandon its previous strategy of offering extreme discounts across all book categories. Publishers now have a certain degree of autonomy, able to decide the types of books and discount rates for platform promotions.
While most previously delisted books have returned for sale, JD.com’s silence on their official social media channels leaves people worried about the future of China’s publishing industry in an era dominated by e-commerce platforms, especially at a time when online shops and livestreamers keep competing over who has the best book deals, hyping up promotional campaigns like ‘9.9 RMB ($1.4) per book with free shipping’ to ‘1 RMB ($0.15) books.’
This year’s developments surrounding the publishing industry and 618 has led to some discussions that have created more awareness among Chinese consumers about the true price of books. “I was planning to bulk buy books this year,” one commenter wrote: “But then I looked at my bookshelf and saw that some of last year’s books haven’t even been unwrapped yet.”
Another commenter wrote: “Although I’m just an ordinary reader, I still feel very sad about this situation. It’s reasonable to say that lower prices are good for readers, but what I see is an unfavorable outlook for publishers and the book market. If this continues, no one will want to work in this industry, and for readers who do not like e-books and only prefer physical books, this is definitely not a good thing at all!”
By Ruixin Zhang, edited with further input by Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Chinese Sun Protection Fashion: Move over Facekini, Here’s the Peek-a-Boo Polo
From facekini to no-face hoodie: China’s anti-tan fashion continues to evolve.
Published
2 months agoon
June 6, 2024
It has been ten years since the Chinese “facekini”—a head garment worn by Chinese ‘aunties’ at the beach or swimming pool to prevent sunburn—went international.
Although the facekini’s debut in French fashion magazines did not lead to an international craze, it did turn the term “facekini” (脸基尼), coined in 2012, into an internationally recognized word.

The facekini went viral in 2014.
In recent years, China has seen a rise in anti-tan, sun-protection garments. More than just preventing sunburn, these garments aim to prevent any tanning at all, helping Chinese women—and some men—maintain as pale a complexion as possible, as fair skin is deemed aesthetically ideal.
As temperatures are soaring across China, online fashion stores on Taobao and other platforms are offering all kinds of fashion solutions to prevent the skin, mainly the face, from being exposed to the sun.

One of these solutions is the reversed no-face sun protection hoodie, or the ‘peek-a-boo polo,’ a dress shirt with a reverse hoodie featuring eye holes and a zipper for the mouth area.

This sun-protective garment is available in various sizes and models, with some inspired by or made by the Japanese NOTHOMME brand. These garments can be worn in two ways—hoodie front or hoodie back. Prices range from 100 to 280 yuan ($13-$38) per shirt/jacket.

The no-face hoodie sun protection shirt is sold in various colors and variations on Chinese e-commerce sites.
Some shops on Taobao joke about the extreme sun-protective fashion, writing: “During the day, you don’t know which one is your wife. At night they’ll return to normal and you’ll see it’s your wife.”

On Xiaohongshu, fashion commenters note how Chinese sun protective clothing has become more extreme over the past few years, with “sunburn protection warriors” (防晒战士) thinking of all kinds of solutions to avoid a tan.
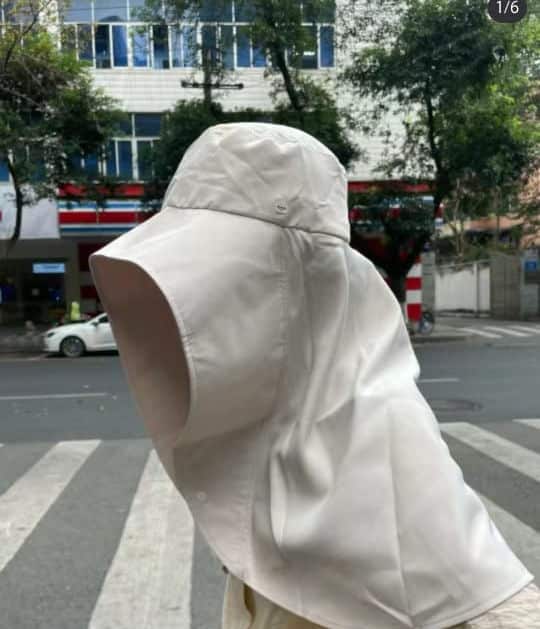




Although there are many jokes surrounding China’s “sun protection warriors,” some people believe they are taking it too far, even comparing them to Muslim women dressed in burqas.
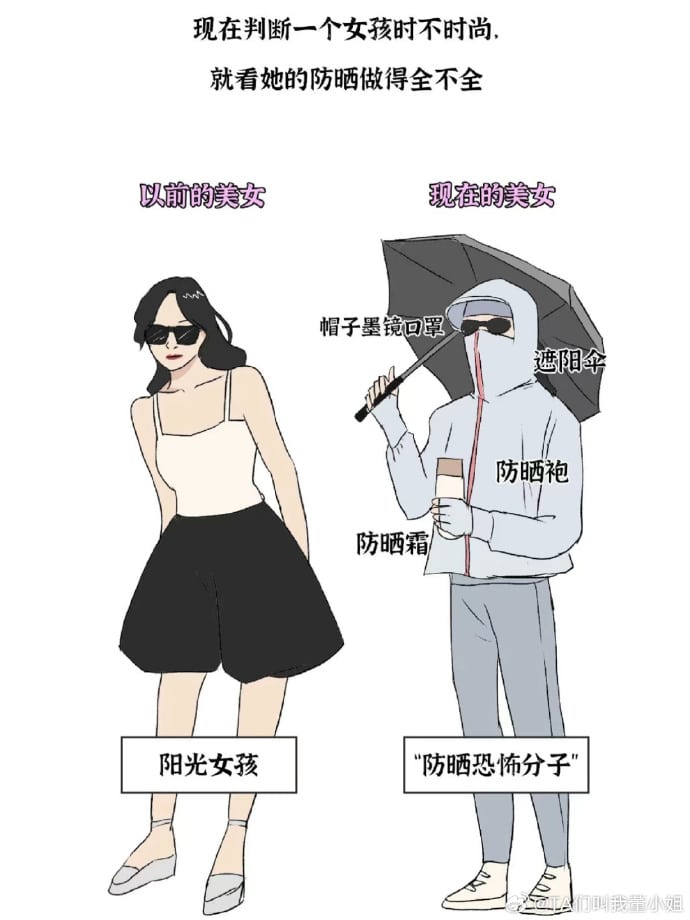
Image shared on Weibo by @TA们叫我董小姐, comparing pretty girls before (left) and nowadays (right), also labeled “sunscreen terrorists.”
Some Xiaohongshu influencers argue that instead of wrapping themselves up like mummies, people should pay more attention to the UV index, suggesting that applying sunscreen and using a parasol or hat usually offers enough protection.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?






