Most Read
Girl is Dumped by Boyfriend for Being Too Fat, Takes Revenge Through Weibo
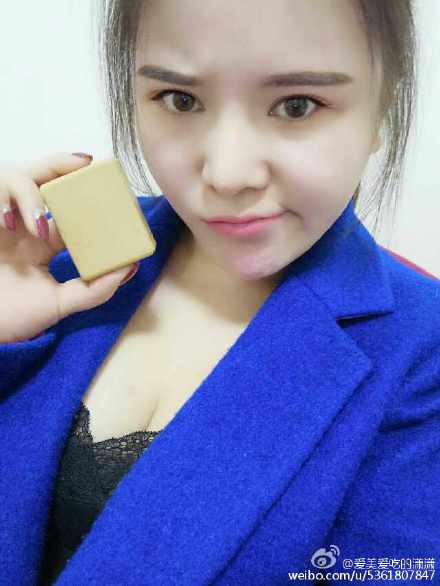
A girl named Xiaoxiao became trending on Weibo when she posted a public message to her former beau on the social media platform. After her boyfriend broke up with her for being too fat, she underwent liposuction and presented him with a piece of soap made from her removed fat.
Published
9 years agoon

A girl named Xiaoxiao became trending on Weibo when she posted a public message to her former beau on the social media platform. After her boyfriend broke up with her for being too fat, she underwent liposuction and presented him with a piece of soap made from her removed fat.
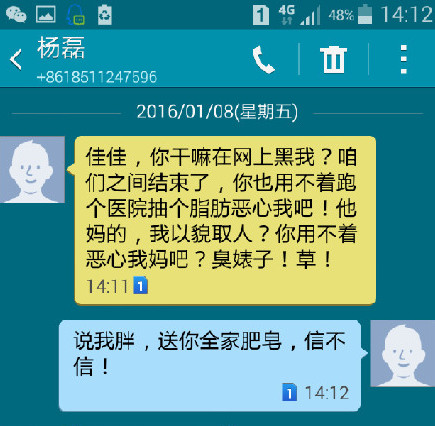
A young woman from Zhengzhou, Henan Province, posted a picture of herself on her Weibo account with a text saying: “Yang Xiaolei, do you remember last year’s Spring Festival? Since I cannot go home with you this year, I’ve made a piece of soap from my own fat to give to your mum for washing up. Chinese New Year – the time to surprise those low men who can only judge a book by its cover!”
The post has been shared over 5400 times and received over 3500 comments in a day.
[showad block=2]
‘Xiaoxiao’ also posted before & after pictures:
She also shared a screenshot with a recent message from her ex-boyfriend, that says:
“Why are you making me look bad on the Internet?! It was already over between us, you didn’t need to go to the hospital to suck out fat and disgust me! Damn, do I judge people solely by their appearances? You didn’t need to disgust my mum, or what? F*ck you b****!”
Underneath, she responds: “You said I was fat. I’m sending your entire family some soap, believe it or not!”
Although Xiaoxiao’s post got a lot of attention, most netizens do not agree with the girl’s actions. “Sometimes being ugly simply has nothing to do with being fat or not,” one person comments. “Being ugly inside is what being ugly really is,” another netizen says. “From this I can tell he really didn’t dump you because of your looks,” someone else responds.
Whether or not the girl really turned her body fat into soap remains unclear. It technically would be possible to do so. In 2013, Miami artist De La Paz kept the 3 liters of fat that was removed from his body during liposuction, and turned it into soap (source).
©2015 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Zibo had its BBQ moment. Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine with its special take on malatang. Tourism marketing in China will never be the same again.
Published
4 months agoon
April 1, 2024
Since the early post-pandemic days, Chinese cities have stepped up their game to attract more tourists. The dynamics of Chinese social media make it possible for smaller, lesser-known destinations to gain overnight fame as a ‘celebrity city.’ Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine.
During this Qingming Festival holiday, there is one Chinese city that will definitely welcome more visitors than usual. Tianshui, the second largest city in Gansu Province, has emerged as the latest travel hotspot among domestic tourists following its recent surge in popularity online.
Situated approximately halfway along the Lanzhou-Xi’an rail line, this ancient city wasn’t previously a top destination for tourists. Most travelers would typically pass through the industrial city to see the Maiji Shan Grottoes, the fourth largest Buddhist cave complex in China, renowned for its famous rock carvings along the Silk Road.
But now, there is another reason to visit Tianshui: malatang.
Gansu-Style Malatang
Málàtàng (麻辣烫), which literally means ‘numb spicy hot,’ is a popular Chinese street food dish featuring a diverse array of ingredients cooked in a soup base infused with Sichuan pepper and dried chili pepper. There are multiple ways to enjoy malatang.
When dining at smaller street stalls, it’s common to find a selection of skewered foods—ranging from meats to quail eggs and vegetables—simmering in a large vat of flavorful spicy broth. This communal dining experience is affordable and convenient for solo diners or smaller groups seeking a hotpot-style meal.
In malatang restaurants, patrons can usually choose from a selection of self-serve skewered ingredients. You have them weighed, pay, and then have it prepared and served in a bowl with a preferred soup base, often with the option to choose the level of spiciness, from super hot to mild.
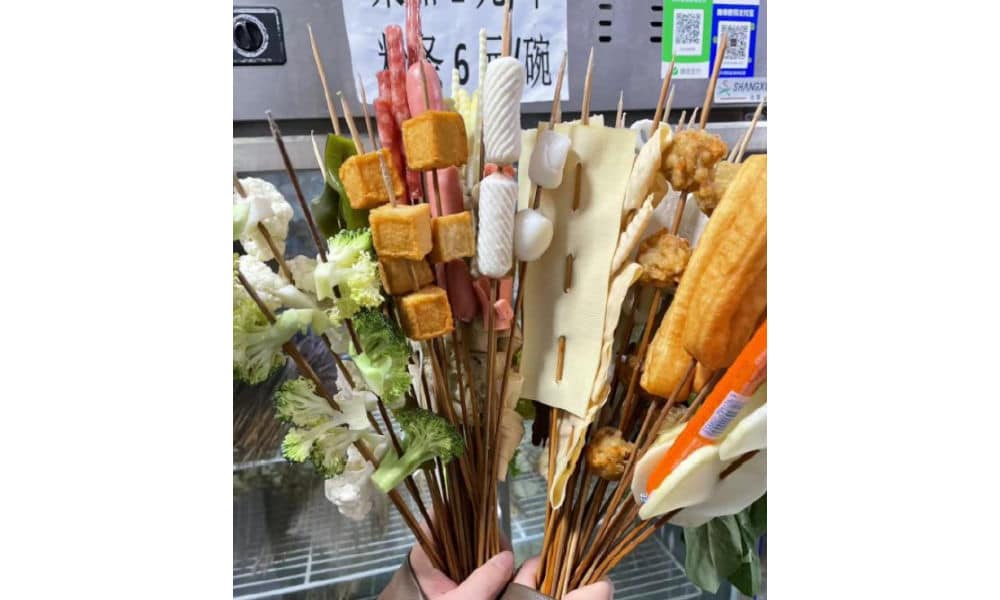

Although malatang originated in Sichuan, it is now common all over China. What makes Tianshui malatang stand out is its “Gansu-style” take, with a special focus on hand-pulled noodles, potato, and spicy oil.
An important ingredient for the soup base is the somewhat sweet and fragrant Gangu chili, produced in Tianshui’s Gangu County, known as “the hometown of peppers.”
Another ingredient is Maiji peppercorns (used in the sauce), and there are more locally produced ingredients, such as the black fungi from Qingshui County.
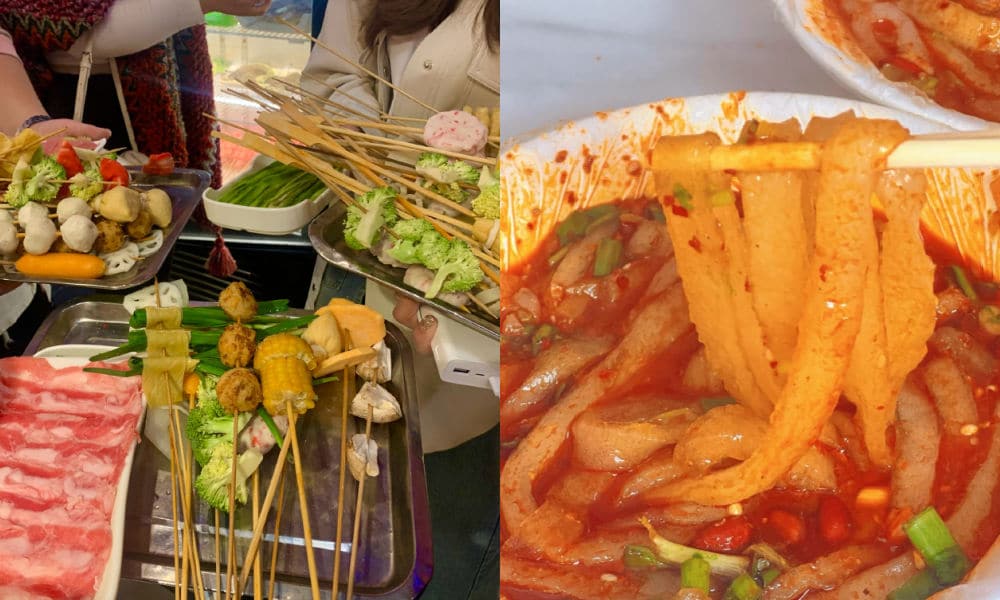

One restaurant that made Tianshui’s malatang particularly famous is Haiying Malatang (海英麻辣烫) in the city’s Qinzhou District. On February 13, the tiny restaurant, which has been around for three decades, welcomed an online influencer (@一杯梁白开) who posted about her visit.
The vlogger was so enthusiastic about her taste of “Gansu-style malatang,” that she urged her followers to try it out. It was the start of something much bigger than she could have imagined.
Replicating Zibo
Tianshui isn’t the first city to capture the spotlight on Chinese social media. Cities such as Zibo and Harbin have previously surged in popularity, becoming overnight sensations on platforms like Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin.
This phenomenon of Chinese cities transforming into hot travel destinations due to social media frenzy became particularly noteworthy in early 2023.
During the Covid years, various factors sparked a friendly competition among Chinese cities, each competing to attract the most visitors and to promote their city in the best way possible.
The Covid pandemic had diverse impacts on the Chinese domestic tourism industry. On one hand, domestic tourism flourished due to the pandemic, as Chinese travelers opted for destinations closer to home amid travel restrictions. On the other hand, the zero-Covid policy, with its lockdowns and the absence of foreign visitors, posed significant challenges to the tourism sector.
Following the abolition of the zero-Covid policy, tourism and marketing departments across China swung into action to revitalize their local economy. China’s social media platforms became battlegrounds to capture the attention of Chinese netizens. Local government officials dressed up in traditional outfits and created original videos to convince tourists to visit their hometowns.
Zibo was the first city to become an absolute social media sensation in the post-Covid era. The old industrial and mining city was not exactly known as a trendy tourist destination, but saw its hotel bookings going up 800% in 2023 compared to pre-Covid year 2019. Among others factors contributing to its success, the city’s online marketing campaign and how it turned its local BBQ culture into a unique selling point were both critical.

Zibo crowds, image via 163.com.
Since 2023, multiple cities have tried to replicate the success of Zibo. Although not all have achieved similar results, Harbin has done very well by becoming a meme-worthy tourist attraction earlier in 2024, emphasizing its snow spectacle and friendly local culture.
By promoting its distinctive take on malatang, Tianshui has emerged as the next city to captivate online audiences, leading to a surge in visitor numbers.
Like with Zibo and Harbin, one particular important strategy used by these tourist offices is to swiftly respond to content created by travel bloggers or food vloggers about their cities, boosting the online attention and immediately seizing the opportunity to turn online success into offline visits.
A Timeline
What does it take to become a Chinese ‘celebrity city’? Since late February and early March of this year, various Douyin accounts started posting about Tianshui and its malatang.
They initially were the main reason driving tourists to the city to try out malatang, but they were not the only reason – city marketing and state media coverage also played a role in how the success of Tianshui played out.
Here’s a timeline of how its (online) frenzy unfolded:
- July 25, 2023: First video on Douyin about Tianshui’s malatang, after which 45 more videos by various accounts followed in the following six months.
- Feb 5, 2024: Douyin account ‘Chuanshuo Zhong de Bozi’ (传说中的波仔) posts a video about malatang streetfood in Gansu
- Feb 13, 2024: Douyin account ‘Yibei Liangbaikai’ (一杯梁白开) posts a video suggesting the “nationwide popularization of Gansu-style malatang.” This video is an important breakthrough moment in the success of Tianshui as a malatang city.
- Feb – March ~, 2024: The Tianshui Culture & Tourism Bureau is visiting sites, conducting research, and organizing meetings with different departments to establish the “Tianshui city + malatang” brand (文旅+天水麻辣烫”品牌) as the city’s new “business card.”
- March 11, 2024: Tianshui city launches a dedicated ‘spicy and hot’ bus line to cater to visitors who want to quickly reach the city’s renowned malatang spots.
- March 13-14, 2024: China’s Baidu search engine witnesses exponential growth in online searches for Tianshui malatang.
- March 14-15, 2024: The boss of Tianshui’s popular Haiying restaurant goes viral after videos show him overwhelmed and worried he can’t keep up. His facial expression becomes a meme, with netizens dubbing it the “can’t keep up-expression” (“烫不完表情”).

The worried and stressed expression of this malatang diner boss went viral overnight.
- March 17, 2024: Chinese media report about free ‘Tianshui malatang’ wifi being offered to visitors as a special service while they’re standing in line at malatang restaurants.
- March 18, 2024: Tianshui opens its first ‘Malatang Street’ where about 40 stalls sell malatang.
- March 18, 2024: Chinese local media report that one Tianshui hair salon (Tony) has changed its shop into a malatang shop overnight, showing just how big the hype has become.
- March 21, 2024: A dedicated ‘Tianshui malatang’ train started riding from Lanzhou West Station to Tianshui (#天水麻辣烫专列开行#).
- March 21, 2024: Chinese actor Jia Nailiang (贾乃亮) makes a video about having Tianshui malatang, further adding to its online success.
- March 30, 2024: A rare occurrence: as the main attraction near Tianshui, the Maiji Mountain Scenic Area announces that they’ve reached the maximum number of visitors and don’t have the capacity to welcome any more visitors, suspending all ticket sales for the day.
- April 1, 2024: Chinese presenter Zhang Dada was spotted making malatang in a local Tianshui restaurant, drawing in even more crowds.
A New Moment to Shine
Fame attracts criticism, and that also holds true for China’s ‘celebrity cities.’
Some argue that Tianshui’s malatang is overrated, considering the richness of Gansu cuisine, which offers much more than just malatang alone.
When Zibo reached hype status, it also faced scrutiny, with some commenters suggesting that the popularity of Zibo BBQ was a symptom of a society that’s all about consumerism and “empty social spectacle.”
There is a lot to say about the downsides of suddenly becoming a ‘celebrity city’ and the superficiality and fleetingness that comes with these kinds of trends. But for many locals, it is seen as an important moment as they see their businesses and cities thrive.
Even after the hype fades, local businesses can maintain their success by branding themselves as previously viral restaurants. When I visited Zibo a few months after its initial buzz, many once-popular spots marketed themselves as ‘wanghong’ (网红) or viral celebrity restaurants.
For the city itself, being in the spotlight holds its own value in the long run. Even after the hype has peaked and subsided, the gained national recognition ensures that these “trendy” places will continue to attract visitors in the future.
According to data from Ctrip, Tianshui experienced a 40% increase in tourism spending since March (specifically from March 1st to March 16th). State media reports claim that the city saw 2.3 million visitors in the first three weeks of March, with total tourism revenue reaching nearly 1.4 billion yuan ($193.7 million).
There are more ripple effects of Tianshui’s success: Maiji Shan Grottoes are witnessing a surge in visitors, and local e-commerce companies are experiencing a spike in orders from outside the city. Even when they’re not in Tianshui, people still want a piece of Tianshui.
By now, it’s clear that tourism marketing in China will never be the same again. Zibo, Harbin, and Tianshui exemplify a new era of destination hype, requiring a unique selling point, social media success, strong city marketing, and a friendly and fair business culture at the grassroots level.
While Zibo’s success was largely organic, Harbin’s was more orchestrated, and Tianshui learned from both. Now, other potential ‘celebrity’ cities are preparing to go viral, learning from the successes and failures of their predecessors to shine when their time comes.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Travel
Chinese Tourists in Europe: Getting Robbed Is Part of the Experience
“The Best Anti-Theft Strategy in Europe”? Chinese netizens are sharing tips how not to get robbed during their Europe trip.
Published
12 months agoon
August 11, 2023
PREMIUM CONTENT
My bag was stolen in Amsterdam, my phone was snatched in Paris, and my camera was robbed in Rome. Chinese social media is brimming with accounts from Chinese travelers sharing their unfortunate experiences of falling prey to theft during their trips to Europe. Getting robbed in Europe has become so common that Chinese apps like Xiaohongshu and Douyin are now flooded with numerous “Europe Anti-Theft Strategies” and “How Not To Get Robbed in Europe” guides.
In this post-pandemic days, a growing number of Chinese tourists are making their way to Europe, some for the first time in years. As the practice of chronicling one’s journey on social media has become part of the travel experience, Chinese platforms like Xiaohongshu, Douyin, and WeChat have witnessed a surge in posts capturing Europe trip adventures.
Unfortunately, many of these posts are about Chinese tourists getting their phone stolen, their wallet nicked, or being robbed of their travel bags.
When it comes to European destinations, Paris stands out as one of the most notorious places where Chinese travelers frequently report incidents of robbery. However, social media is also filled with posts recounting unfortunate experiences in cities like Barcelona, Rome, Venice, Amsterdam, and London.
The average Chinese tourist is often a vulnerable target for thieves and pickpockets in Europe for several reasons. They are often equipped with premium gadgets, wear designer’s clothes, and are frequently engrossed in their smartphones. Many Chinese tourists also find handling wallets, cards, and physical currency unfamiliar due to their background in a cashless society.
Additionally, the challenges of using China Unionpay cards for payments in many European locations, coupled with difficulties in withdrawing money from conventional ATMs, lead Chinese travelers in Europe to carry substantial amounts of cash. This, combined with a general lack of awareness about potential dangers, makes Chinese travelers in Europe more susceptible to theft.
Getting robbed in Europe is now so commonplace among Chinese tourists, that some argue that “if you haven’t been robbed, you didn’t get the full Europe experience.”
“The Europe Experience”
So what is that ‘Europe experience’ people are talking about?
Of course, many posts concerning Europe travel among Chinese tourists center on savoring delightful cuisine, admiring beautiful architecture, and exploring world-famous sites. Yet, a significant portion of these posts is focused on sharing personal experiences of becoming victims of theft in European cities.
Below, we have highlighted the most-mentioned cities on Chinese social media when it comes to getting robbed and what kind of experiences are shared for these locations.
◼︎ Amsterdam: Subtle and Sudden
Many who share their unfortunate experiences of falling victim to theft in Amsterdam or other parts of the Netherlands often recount having their valuables stolen on trains or at train stations, frequently right after arriving in the country from Schiphol Airport or traveling from other European destinations via international trains. Numerous accounts emphasize how a mere moment of distraction can lead to the sudden discovery that their bags have disappeared. The same vulnerability applies to stolen phones – some people share how one moment their smartphone was in their hand, only to be gone the next minute, without even realizing they had somehow let go of it.
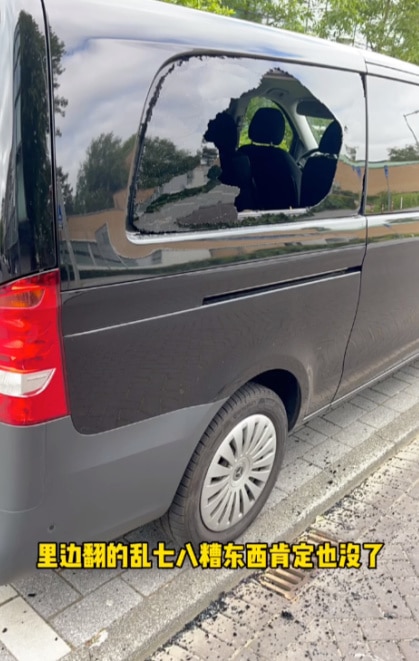

Furthermore, alongside incidents involving theft on trains or at train stations, another common way tourists experience robbery in Amsterdam is through valuables being stolen from parked cars. A recent account highlights an incident where an individual’s parked car, situated near a hotel, had its windows smashed, resulting in the loss of all items except their Van Gogh museum souvenirs.
◼︎ Barcelona: Bold and Brazen
Barcelona is also infamous for tourists becoming victims of theft. In July of this year, the Chinese Consulate General in Barcelona even issued a warning to Chinese nationals about the risks. Accounts shared by Chinese travelers on social media highlight that theft experiences in this city lack subtlety compared to those in Amsterdam; thieves in Barcelona tend to employ bolder and rougher tactics.
Several Chinese tourists recount incidents where, upon exiting the subway, they encountered individuals who deliberately splashed paint, ketchup, or other substances on their bags or clothes to create a distraction. Caught off guard and attempting to clean off the mess, they became vulnerable to pickpocketing and subsequently lost their phones and wallets.
There are exceptionally audacious thieves who won’t hesitate to snatch bags or phones from tourists right within the subway or even on bustling streets like the Ramblas. They make a swift getaway with the stolen items. Certain Chinese bloggers have shared their experiences of attempting to fend off thieves who targeted their crossbody bags or other belongings, only to feel a sense of regret afterward, realizing that the thieves might have been armed with knives.
◼︎ Brussels: With Love and Chocolates
There are also reports coming from Chinese tourists in Brussels who are warning others of their experiences with thieves there. Some of these thieves seem surprisingly sweet-toothed and romantic, like the thief who first told his victim “I love you” before trying to snatch their phone.
Compared to other theft experiences, another man’s encounter in Brussels took on a somewhat amusing tone. He shared his exasperation over an incident where a man unexpectedly reached into the bag of chocolates he had just purchased in the Belgian capital and snatched a piece of chocolate.1
◼︎ Paris: Nowhere is Safe?
Paris is renowned as one of the most infamous destinations for theft, with many Chinese tourists labeling the city as “unsafe.” From minor pickpocketing incidents to brazen daytime carjackings, a variety of crimes pose challenges for travelers in the French capital.
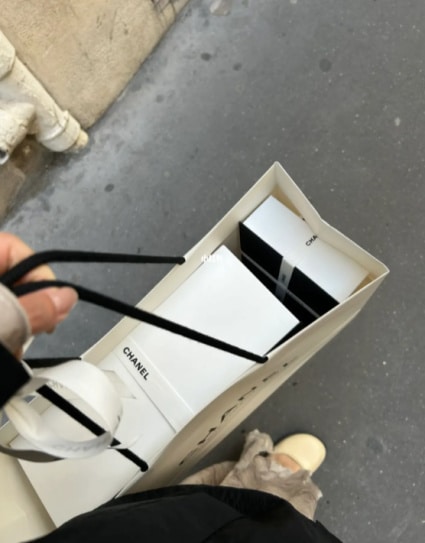

Paris is a favored destination among Chinese travelers who frequently indulge in shopping sprees, purchasing luxury items like Chanel or Louis Vuitton handbags, which increases their vulnerability to theft. Many shoppers bring their bags back to their hotel for safekeeping, and, as an extra measure of caution, opt to store their most valuable things inside the hotel room’s safety box. However, some Chinese tourists recently recounted the unsettling experiences where even their own rooms weren’t secure havens for their valuables. Upon returning to their accommodations, they were dismayed to find everything missing. When raising their concerns with the hotel management, they received the response that the hotel claimed no responsibility for the incident.
The notion that ‘nowhere is safe’ is further underscored by accounts from travelers, including those with rental cars, who have encountered incidents of smashed windows and theft of bags even while inside their vehicles.
Another aspect worth noting about Paris is that certain Chinese nationals, particularly those who are residing in the city temporarily rather than just visiting briefly, have reported experiencing theft for the second time. A user on Xiaohongshu recounted an incident where they were assaulted and robbed near Porte de Clignancourt. Additionally, there are accounts of multiple thieves collaborating to target unsuspecting commuters on the subway.
◼︎ London: Picky Pickpockets
London thieves are infamous for targeting phones, often using aggressive tactics. “Gangs” on scooters or bicycles speed by and snatch phones from people’s hands, especially when they’re using them by the roadside, such as at bus stops or traffic lights.

Some Chinese in London have shared their experiences of thieves attempting to steal their phones, only to realize they were Huawei devices and then tossing them back, seemingly disappointed since they were expecting iPhones. Another Xiaomi user recounted a similar incident. In a separate older post, a Chinese young man recalled a 2022 incident where a duo of thieves snatched his bracelet and watch near Bond Street. Interestingly, they returned his belongings later (with the second person pretending to assist) after realizing they held no significant value and weren’t worth the effort.

Xiahongshu user Alex Ya Yulun shares a nasty experience near Bond Street.
Another person shared how they discovered that a thief had somehow gotten into their wallet at Euston Station and only took their creditcard, leaving his cash and debit card. The idea behind this – of only stealing one credit card instead of the entire wallet – is that it buys the thief time to go and spend money on the card before it is canceled, as it might take a while for tourists to discover it missing. In this case, the victim was quick to discover and cancel his card via his bank. Just seconds later, he received a notification that someone had attempted to make a purchase worth of 3000 pounds (US$3820) with his card. “That’s how sneaky they are,” he wrote: “They just take one card to buy themselves time.”
◼︎ Milan: Distracted by Pigeons
How nice it is to have dinner outside and enjoy the vibrant citylife. But in Milan, Chinese travelers warn about groups of young people who will come up to your table, pretending to promote something and hand out flyers. While distracting you, they will nick the phone they have spotted on the table.
Distraction seems to be a popular tactic among Milan thieves. Another female Xiaohongshu user shares how she was waiting for someone at a high-end hotel in Milan center, when a man called out to her in English. She turned around to see why, and before she knew it another man had grabbed the purse that was right to her.
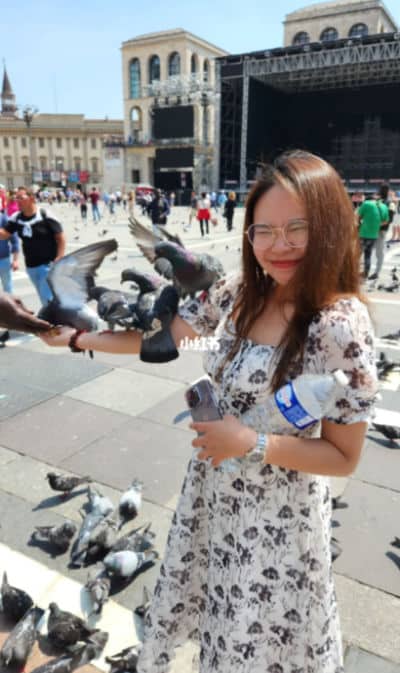

Xiaohongshu user BoomerXu shares their experience of the pigeon scam in Milan.
What better distraction than pigeons fluttering around near the Duomo di Milano? A popular Milan tactic involves thieves and scammers coming up to people admiring the view and the many pigeons near the square, and then handing them birdseed causing the pigeons to all come over at the same time – a perfect picture moment. The scammers will then use this as an opportunity to suddenly surround tourists with multiple people and demand money in a forceful and aggressive manner.
◼︎ Rome: Don’t Judge by Appearance
Rome is another notorious place for getting robbed. Some experiences shared on Chinese social media about becoming a victim of theft in the Italian capital are less subtle than those of others. One female solo traveler shared how she walked back to her hotel at night while listening to some music on her headphones, not far Roma Termini, when someone suddenly grabbed her by her throat from behind and robbed her of her camera before running off.
In August 2023, a Chinese PhD student shared a previous incident involving the theft of her belongings in Italy. While enjoying a moment at a cafe in Rome with a group of four women, they engaged in conversation, casually placing their bags on two vacant chairs beside them. Shortly thereafter, they were met with the shocking realization that their belongings had disappeared. This incident was particularly distressing for the PhD student, as her stolen bag contained not only her passport but also her laptop housing valuable research materials and papers.
The circumstances leading to the ladies not noticing the perpetrator’s proximity can be attributed to the deceptive nature of appearances. As fellow travelers emphasize, it is vital not to judge Roman thieves based on their looks. That stylishly attired, elegantly tall woman seated adjacent to you on the subway might very well be a pickpocket.
◼︎ Returning Home
Chinese tourists have also reported instances of theft during their return journey to China. When travelers need to make transfers within Europe on their way back to China, there’s a risk of items being stolen from their suitcases, including valuable possessions like stylish handbags.
Some online users share that the locks they use on their suitcases seem ineffective, as airport thieves seem knowledgeable about opening them. The combination of a Chinese name, a destination in China, and a relatively nice suitcase appears to be an opportunity for thieves. One traveler even recounted the surprising discovery that their box of chocolates had been opened during transfer and partially eaten!
The Anti-Theft Strategy
With so many people getting robbed in Europe, it is only natural for netizens to actively search for content on how to protect themselves.
Those who have had the unlucky experience of getting robbed share advice on how not to become a victim of theft while traveling, but many of these online “Preventing Theft and Robbery Guides” (防偷防抢指南/欧洲防小偷指南) or “Anti-Theft Strategy” posts (欧洲最强防盗) are also written by Chinese nationals studying or working in cities like London, Amsterdam, Paris, who have become adept at spotting theft tactics and protecting their belongings.

Anti-theft products recommended by Xiaohongshu user 一只小卷卷🍓.
Here is a compilation of recurring tips gathered from various Chinese netizens, vloggers, and bloggers on avoiding theft and safeguarding your belongings while in Europe:
◼︎ Wear an anti-theft waist bag / waist belt (防盜腰包) to store valuables such as cash, phones, passport, or creditcards.
◼︎ Other Chinese social media users go a step further and even recommend special underpants with pockets to store valuables such as passport and cash money.

◼︎ Try to maintain a low profile while traveling. Refrain from wearing designer clothing, don’t wear expensive watches, and leave your jewelry at home. This is a tip that is repeated by most anti-theft guides.
◼︎ When going out, it’s best to carry minimal valuables and leave the rest in your hotel room. Given existing concerns about hotel room safety, it’s advisable to use the hotel’s safety box to store your belongings.
◼︎ Some people suggest using phones with lanyards attached to your body to prevent the phone from being snatched while you’re distracted. (However, there’s a potential drawback to this approach – if a thief employs aggressive tactics and snatches the phone while running or on a motorcycle, it could lead to injury.)
◼︎ Many posts also recommend purchasing different strong locks for Europe travels: S-locks for handbags to prevent zippers from being easily opened, a strong anti-theft lock for the suitcase, and even door locks to prevent (hotel)doors from being opened from outside.

Images showing variou lock to prevent theft, by Xiaohongshu user 岛屿啊.
◼︎ Stay vigilant about your surroundings: who is walking in front of you, who is walking behind you, who is at your left and right, and is anyone getting too close?
◼︎ Since public transport and stations are a pickpocket hotspot, it is better to walk to your destination if possible instead. At night, go by taxi.
◼︎ When traveling by train, it’s crucial to keep your luggage within sight at all times. For many Chinese tourists, this might be an unfamiliar practice, as on high-speed trains, luggage can be conveniently stored in designated compartments, allowing travelers to relax until their destination is reached. However, the situation is quite different in Europe.
◼︎ A thief only needs a small window of opportunity to snatch your phone. When you’re outside, try to minimize the frequency of looking at your phone or having your phone in your hand, and always stay vigilant. Never put your phone in the outer pockets of your coat.
◼︎ When renting a car in Europe, it’s imperative to never leave valuables behind inside the vehicle.
◼︎ Stay vigilant against distraction tactics. Whether you’re on the street or dining at a restaurant, if someone approaches you to ask questions, hand out flyers, display a paper or sign, be mindful of your phone and wallet. While they engage you in conversation or divert your attention, another individual could take advantage and attempt to steal from you.
◼︎ Don’t accept any items from strangers. For instance, in Rome or Paris, some people might try to offer you a bracelet, claiming it’s free, but then demand money if you take it.
◼︎ When using a taxi during your travels, ensure that you keep valuable items near you. Also, make sure to personally place your luggage in the back of the taxi or watch the driver stow it for you. One Chinese tourist shared her experience on Xiaohongshu, where she entered the taxi while the driver loaded her luggage into the trunk. Unfortunately, upon reaching her destination, her luggage was nowhere to be found.
◼︎ When purchasing luxury items such as Chanel or Louis Vuitton bags, make sure to take your purchases out of the original luxury shopping bags and carry them in normal tote bags. Walking around with a Vuitton or Chanel shop bag just screams: ‘I just bought a super expensive designer product’ and not only street thieves will know, but people working in and around the hotel will also notice.

◼︎ Using a simple canvas tote bag is a recurring tip in the online Europe anti-theft guides. However, a controversial tip advises travelers to use frog-themed bags to ward off Roma thieves because they think that they see frogs as signs of bad luck.
Disappointed, Disillusioned
The changing view of Europe as a potentially hazardous destination for Chinese tourists signifies shifting times. Instead of a dream destination, Europe is increasingly described as a place that is “chaotic” or that is “lacking law and order.” Many people who share their experiences online suggest that they are “disappointed” or “won’t be coming back.”
Partly, this phenomenon could be labeled as the “Paris syndrome,” an extreme sense of disillusionment experienced by certain individuals during their visit to Paris, where they find the city not aligning with their expectations. This condition is often seen as an acute form of culture shock.
However, this trend also signifies changing times. In the present context, many Chinese citizens consider their home country a secure haven, largely free from concerns like robbery or personal safety on the streets; their major cities are considered much more secure. As mentioned by some bloggers, this disparity has seemingly become more noticeable after the pandemic. At the same time, due to all the warnings about theft in Europe, Chinese travelers are more conscious of how they are being perceived as attractive targets for thieves while traveling abroad.
Besides the risks of getting robbed, one factor seemingly influencing this portrayal of a “chaotic” Europe, particularly among Chinese travelers who have fallen victim to theft in Europe and reported such incidents, is their perception of local law enforcement as unresponsive or inadequate when addressing such thefts.
From Italy to the Netherlands, Chinese netizens express frustration about police merely making police reports for insurance purposes, but otherwise not actively chasing thieves, even if there is security footage or if the perpetators were caught on camera. “The chances of ever getting your stuff back are very, very low,” one Xiaohongshu user said. One Weibo user reiterated this idea, sharing how the police responded after their Rimowa suitcase with all their belongings was stolen on a Munich train station: “They were actually very quick in providing a written case report, but it was clear that no measures would be taken to actually solve the case. When we told them there were surveillance cameras on the platform recording the incident, the police officer stated that they didn’t have the authority to view the surveillance footage according to the law.”2
Another person shared how their laptop was stolen inside a train in Amsterdam and that even though they could show the police the exact location of their stolen laptop due to the ‘Find my Apple’ function, the police officer seemed “lethargic” and told them to try and find the laptop themselves. “I was simply stupefied, more upset by this response than the actual theft,” they wrote.3

Xiaohongshu user (一只虎虎酱) shares experiences of reporting a theft at Dutch police station.
Besides the lack of police actionability, immigration and lack of border security are also often mentioned as additional factors that contribute to Europe being perceived as a ‘messy place.’
“Is Europe really that chaotic?” one person recently asked on Xiaohongshu, getting over 3000 likes and more than 160 replies. “In Europe, many illegal immigrants resort to stealing money for survival because they don’t have jobs,” one person replied, with others explaining: “Sigh, insisting on whatever humanitarian efforts, they’ve let in a large influx of African refugees, as well as Roma people. When you travel or have a tour guide, they’ll always remind you about this. Additionally, we Chinese are relatively wealthy and tend to flaunt luxury purchases, which makes us targets for theft.”
“Although countries in Europe are mostly very developed, the public order is not safe at all,” one Chinese vlogger reports: “The thieves aren’t necessarily strictly locals; many are outsiders. Because in Europe, you know, there are no borders or security checks, so getting in is quite easy and straightforward.”4
For individuals who have not yet traveled to Paris or other places in Europe, the abundance of negative posts detailing incidents of theft may not exactly serve as an encouragement to visit.
“I’ve decided not to return to Paris or visit Europe for the time being. I’ll see how it is next year,” wrote one commenter: “If a city cannot guarantee my safety, what’s the point of traveling there?”5
“God please make sure I don’t get robbed in Europe this time around,” another Weibo user wrote: “I’m just a poor guy. If anything, give me some money instead of stealing it from me.”
“You should just assume that everyone around you is a thief,” some travelers on Xiaohongshu recommend: “That’s the only way to prepare yourself for your upcoming Europe trip.”
By Manya Koetse, co-author & initiator Miranda Barnes
1 我和我朋友走回家的路上,大概下午6点左右,走到Primark那条街上(人挺多挺杂的),我俩买了一袋散装的巧克力,因为拿了两块吃,所以袋口是打开的。刚走出店门,一个男的迎面走来,要把手伸进巧克力袋子,给我朋友吓懵了,等她反应过来,那男的手已经伸进袋子了,而且直接伸到最底下抽出一块,然后离开,我真的崩溃了。听描述好像觉得我们完全可以拒绝或者立刻离开之类的,但实际上事情发生的太突然了,估计也就3到5秒。我们最后把整袋巧克力都扔了。
2 发现箱子被盗后,立即做了报警处理。警方倒是痛快,很快出具了书面的立案报告,却显然并不想采取任何有助于破案的措施。当我们提供站台上有监控录像的信息时,接待的警察表示,根据法律其无权查看监控录像。
3 “偷东西的不见得是非常本地人了,很多都是外来人,因为欧洲这边嘛,他没有边境也没有安检,所以想进来很容易很简单”
4 我直接惊呆了,这比小偷偷我包还气愤,一个关键的交通枢纽大机场的警察竟然让我们(我和我男朋友)自己去找。然后我质问说,如果我们找到了,小偷要攻击我们怎么办?
5 如果一个城市无法确保我的安全,还有什么谈论的旅行可言呢?
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Featured Eiffel tower in main image shot by Valentin B. Kremer on Unsplash.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?








Jason Lan
March 25, 2016 at 11:28 pm
I love what she did. Creative and twisted. <3
xfeng
January 6, 2018 at 7:20 pm
Whatsonweibo is on Weibo:
http://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309404193212775410609