Backgrounder
Mainstream, Underground, and Online: Electronic Dance Music in China
A peek into China’s electronic dance music scene, from Jean Michel Jarre to the country’s post-covid club scene.
Published
3 years agoon
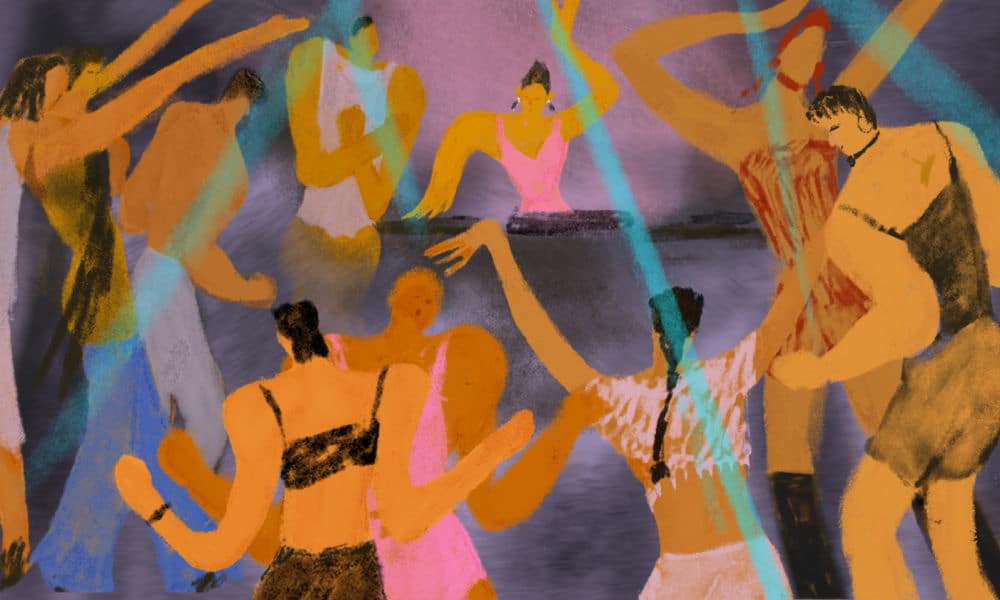
China has been called the “promised land for electronic dance music,” but some critics say the industry is negatively affected by those prioritizing money over music. Still, the country’s mainstream and underground dance scenes are thriving and the pandemic has brought increased recognition of local artists. This is a peek into China’s electronic music scene, from Jean Michel Jarre to the country’s post-covid dance scene.
This is the “WE…WEI…WHAT?” column by Manya Koetse, original publication in German by Goethe Institut China, visit Yi Magazin: WE…WEI…WHAT? Manya Koetse erklärt das chinesische Internet.
More DJs, more festivals, more fans, more online communities. Over the past few years, China’s dance music scene has seen enormous growth in popularity, and electronic music now appears wherever people go, both online and offline, from live music events, night clubs, and fashion shows to reality shows, movies, and social media.
Following the continued explosion of electronic music culture in China’s major cities, DJMag, a renowned UK-based platform dedicated to electronic dance music, even launched a special China Awards section in 2021. In this year’s Top 100 DJ list there are eight Chinese DJs, the highest number ever since a DJ from China first made the list in 2017.
As an unexpected consequence of the pandemic, China’s local dance community has seen heightened popularity of local DJs. While Covid19 has seriously affected the global dance music scene, it has been an ongoing opportunity to shine for local talents in mainland China.
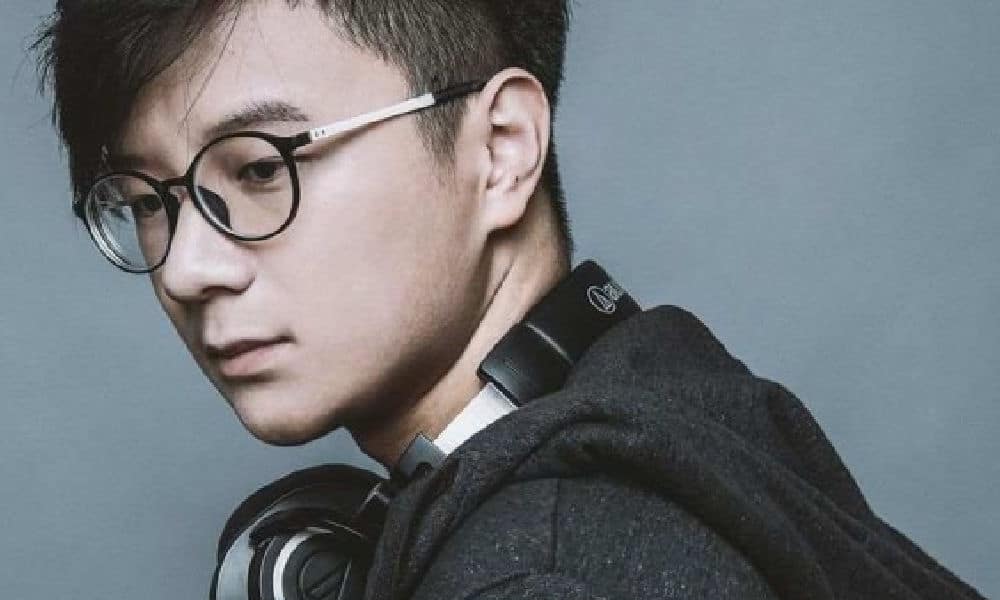

This was the first year for Chinese DJ Panta Q to enter the renowned DJMag Top 100 DJs list (image via DJMag).
Just five years ago, China-based DJ Spencer Tarring discussed the huge potential of China as “the rising promised land for electronic dance music.” But what’s the status quo of China’s dance and DJ culture? Here we’ll explore China’s electronic music scene, from mainstream to underground and the online community.
From ‘EDM’ to ‘Haoshi’
Let’s first explain some terminology. ‘Electronic dance music’ is actually a huge umbrella term for percussion-based electronic music produced primarily for nightclubs, raves, and festivals, and performed/presented by DJs. In Europe, electronic dance music is often simply called ‘dance’ or ‘dance music,’ with subgenres including techno, house, trance, and many others (deBoni 2018).
There’s also the acronym ‘EDM.’ Although it literally stands for ‘Electronic Dance Music,’ it is not the same as the overarching ‘electronic dance music’ genre, as it was adopted in the US to label commercial dance music. It has since been commonly used to solely describe the mainstream electronic dance music that is represented by world-famous DJs such as Tiësto, Martin Garrix, Armin van Buuren, or David Guetta (see Androids 2017; Jori 2021; Magnetic 2021).
In Mandarin Chinese, the term Diànzǐ yīnyuè (电子音乐), often abbreviated as Diànyīn (电音), literally means ‘electronic music’ and is used as a catch-all term for any music made using electronic instruments or involving electronic processing.

DJ Lizzy, a popular female DJ in China, image via Lizzy Wang Weibo account.
EDM is translated as Diànzǐ wǔqǔ (电子舞曲) (‘Electronic Dance Music’), and also refers to commercial dance music. House is generally translated as Hàoshì yīnyuè (浩室音乐), techno as Tiěkènuò yīnyuè (铁克诺音乐), and trance as Chūshén yīnyuè (出神音乐).
Rewind: A Very Short History of Electronic Music in China
The history of electronic dance music in China brings us back to the early 1980s. In the decades and years before, there was strict music censorship under Mao’s rule and the influx of Western music was limited. After Mao’s death and the start of the Open Door policy, modern music from outside of mainland China became increasingly popular among young Chinese, inspiring local musicians to start writing and recording their own pop, rock, and modern music (Holm 1983; Latham 2007: 336).
China’s ‘New Wave’ movement was partly triggered by ‘The Concerts in China‘ by the French electronic music pioneer Jean Michel Jarre in 1981, who performed in Beijing and Shanghai in October-November of that year for a combined audience of 150,000 people (Billboard 1982).

“Electronic music visits China for the first time” – Jean-Michel Jarre performs in China in 1981 (让-米歇尔·雅尔).
Following the Jarre concerts, the New Wave movement also became visible at conservatories and music schools across China in the early 1980s when Chinese composers started to experiment with electronic music. While influenced by Western music, many examples of Chinese electronic music created in these years featured Chinese traditional musical elements (Li 2018).
Many Chinese people became more familiar with modern Western music in the 1980s and 1990s through cassette tapes that were shared and copied hundreds of times, and the so-called dakou culture which emerged in the mid-90s.
Dakou (打口) CDs were dumped by Western countries and imported into China as plastic garbage, intended to be recycled, but then flowed into Chinese cities and became available for listeners to buy from black markets.
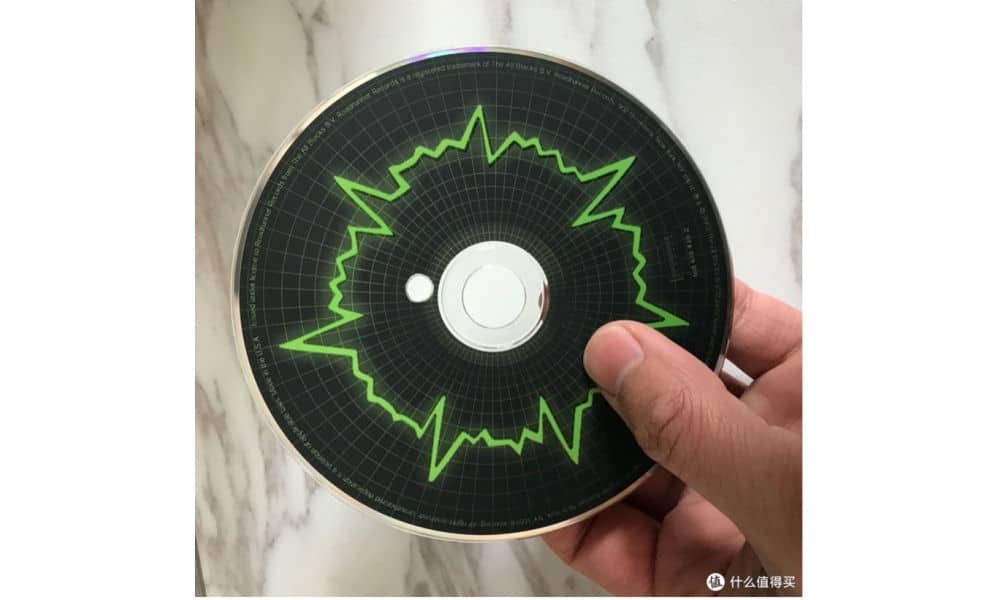

A dakou cd with a punch hole (source).
Dakou CDs (and tapes) have a cut-out, a punch hole, or crack in them to mark them as waste and prevent them from being resold, but people were still able to restore them and listen to most of the music. The dakou culture greatly influenced China’s music scene.1
Proper nightclubs first started to open up in big Chinese cities in the early 1990s, a time in which many people in the electronic music scene were more focused on the music rather than the money.
This is also when Ben Huang, who would become one of China’s most well-known DJs, started his career. The Shanghai-born Huang was a student of modern dance and fine arts before he became active in the Beijing music scene and kick-started China’s club culture.
Other big names emerging around this time are the so-called “godfather of Chinese dance music” Mickey Zhang, DJ Youdai (Zhang Youdai), Yang Bing, and famous electronic musician Weng Weng. They later also started organizing dance parties or setting up their own labels.
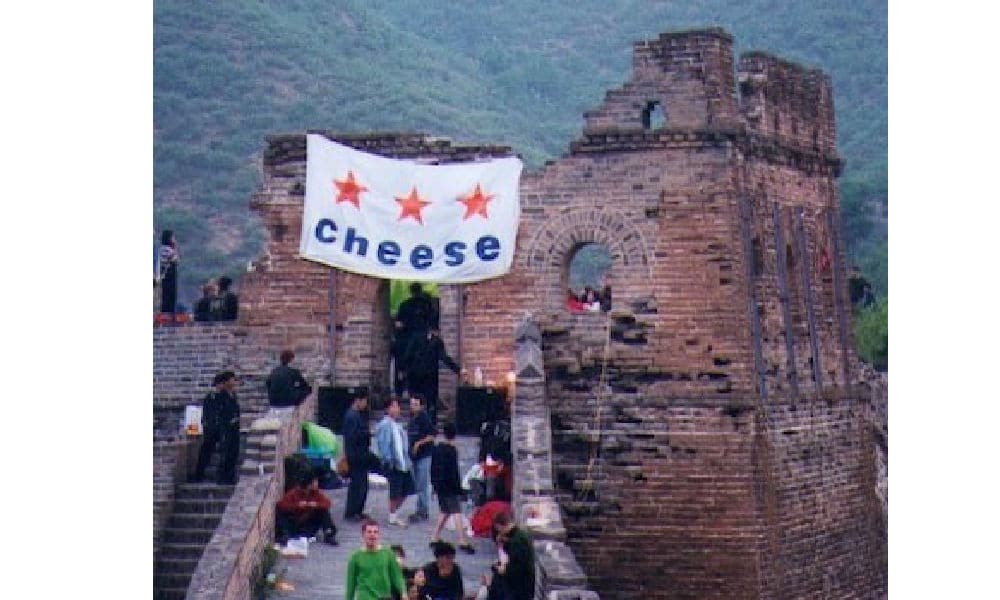

1998 saw the first rave party named ‘Cheese’ at the Great Wall. Image via The Beijinger.
Although illegal rave parties emerged in various cities across the country since the mid-90s, China’s first big rave party took place in the late 1990s at the Great Wall, organized by the Swiss collective ‘Cheese’ (Grefer 2016; Yiu & Charrieras 2021: 233). Vice China (2019) writes:
“What was most magical about China’s party culture in the 1990s, is that it miraculously united all participants of any subculture. The people coming to these rave parties could come from completely different communities, from doctors to lawyers, from hoodlums to diplomats, local punks and sightseeing exchange students (..), on the dance floor surrounded by electronic music, nobody would talk about ideals and doctrines, actions and problems, everyone put all their conflicts aside and danced.”
Nevertheless, much of the scene remained underground and many people in China had not been exposed to electronic dance music yet or did not understand it.
When the renowned British-Canadian electronic musician Richie Hawtin performed in Shanghai at some of the city’s earliest techno events in the 1990s, some people wondered if the CD was stuck and if the mixer needed to be fixed.2
The Mainstream Scene: “Tuhai” and Rock Music Envy
Starting in the 2000s, more money-driven clubs started to open and the electronic dance music scene in China started to develop into two separate worlds; the underground with its underground scene and the mainstream with its mainstream scene.
“And there I am in the middle,” DJ Ben Huang said in a 2009 interview.
Huang’s comment is telling for a market where electronic music has become the second most popular music genre, while the ‘real’ Chinese fans of electronic dance still complain that there has been too little progress in the scene in recent years.
Online discussions indicate that many think that electronic dance music in China has become too commercialized too quickly and has become all about the money rather than the music – leaving little space for the underground scene to flourish, and lacking breeding ground to boost a stronger development of the local electronic music scene.
In 2016, Jiangsu television aired China’s first-ever variety show featuring Electronic Dance Music (EDM) titled Heroes of Remix (盖世英雄remix). The show introduced international electronic dance music genres to a mainstream audience, mixing it with Chinese traditional influences. Two years later, the talent reality show Rave Now (即刻电音) premiered on Tencent Video, further promoting the popularity of EDM in China.
Against the backdrop of an ever-growing EDM industry in China with numerous nightclubs opening up all over the country, the release of the 2021 movie Upcoming Summer (盛夏未来), which focuses on electronic music, further assimilated dance music into China’s mainstream pop culture. A hashtag dedicated to the movie on Chinese social media received over 650 million views (#电影盛夏未来#). (Note: the movie can now also be viewed through Netflix.)

The film Upcoming Summer, where EDM plays a major role.
While electronic music is divided into many genres, commercial EDM is by far the most popular type of electronic music in China. Some of the music played by Chinese local DJs that is deemed to be of lower quality than ‘legitimate’ EDM is also called ‘Tuhai’ (土嗨), a wordplay on ‘too high’ that refers to unoriginal bounce music with whistles and repetitive melodies.
The more the popularity of electric dance music is growing among the masses, the more music fans speak out, saying that China’s mainstream electronic music does not represent authentic electronic dance music, even arguing it that it negatively influences the development of the entire genre; excessive commercialization has neglected the music itself.
The recent surge of Tuhai in Chinese clubs is also a side-effect of the pandemic, during which clubs have started booking far more local DJs with little experience to keep the shows going. To counter the so-called ‘Tuhai virus’, China’s top DJ Carta launched the ‘Chinese Bounce Mafia’ alias together with trance DJ Luminn and DJ/producer Unity to mock the repetitive music genre.

‘Chinese Bounce Mafia’ promo poster from 2020.
In an interview with MixMag (Wycech 2020), Carta says:
“We started Chinese Bounce Mafia after seeing the number of shows these guys were doing and what was happening to the market. We all hated the music, so we said ‘fuck these guys, if they can get all these shows, so can we’. So Chinese Bounce Mafia is our stand against what we see as a problem within the market. The name is a troll because people thought we’ve all sold out and given into bounce but we actually play anything from house to trance to big room to techno.”
It is not easy to counter the Tuhai trend, which is not just ubiquitous in China’s clubs but is also everywhere in the Chinese online music environment, triggering online discussions on how the low-standard music is negatively impacting the overall music quality in the online libraries of platforms such as QQ Music, Kugou, and Tencent Music.
Some Chinese electronic music fans even say they envy China’s rock music scene. One article by the Music Economy Official Weibo Account (@音乐财经官方微博) on Sina said:
“As a fan of electronic music, I feel envious [of the rock music scene]. I envy their music festivals, I envy their good musicians, I envy their good fans, and this isn’t the first time for me to admire China’s rock scene in this way.”
The Music Economy author argues that although it’s been a bumpy ride for rock music in China, the genre has come a long way over the past four decades and has since been embraced by the general public.
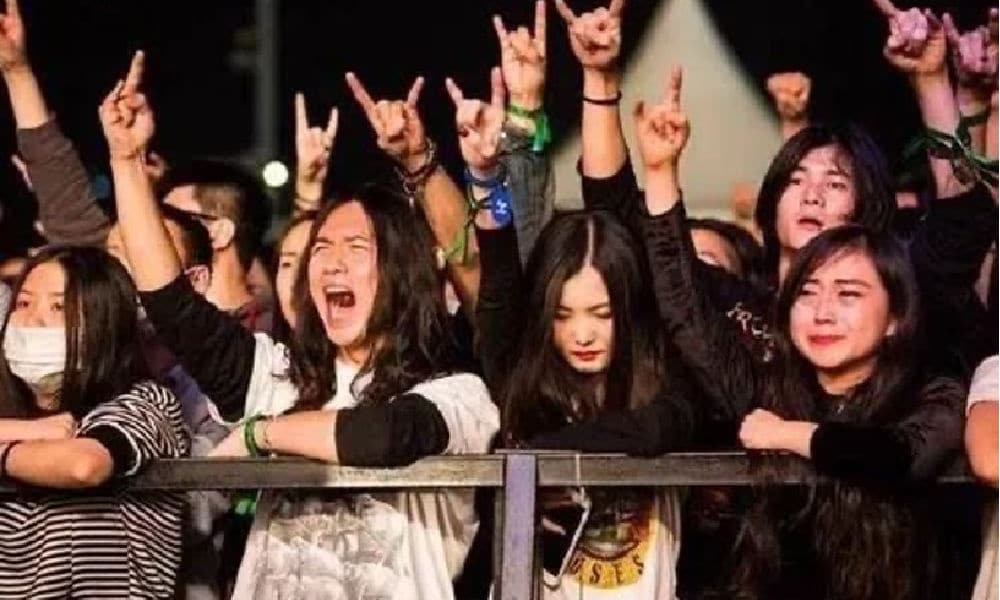

Chinese rock music fans enjoying a concert, image via Music Economy.
One of the reasons why the author argues that China’s dance music community has reason to envy the rock music scene is that there is an alleged pure love for music that draws people into the rock scene, while many people coming to the DJ culture enter the market for the money, not for the music. Because people are prioritizing money over music, too many compromises are often made, resulting in low-effort productions or mediocre festivals.
Another difference between China’s dance and DJ culture compared to the rock scene, is that many rock music fans have grown up listening to the music and have followed their favorite musicians for years. China does not (yet) have a greater electronic music history to build on.
The author writes:
“I know it’s not very scientific to compare rock to electronic music, but they are both imported products and when I see how rock is finally flourishing after having been through so much, I can’t help feeling envious. Electronic dance music and electronic music in China still need to build on more experience. I hope more musicians can stop worrying about income and focus on the music, following their own dreams. I also hope more people will really start caring about electronic music and dance, and that they will start spending money on tickets and records to support their organizers and favorite musicians.”
What also plays a role in this, is that DJ culture mostly takes place inside nightclubs and entertainment venues, where drinks and socializing are often considered more important by Chinese clubgoers than whoever is standing behind the DJ table. China’s current commercial club culture is not a fruitful breeding ground for the further development of China’s electronic dance music scene, the author claims.
Underground & Online Electronic Dance in Post-Covid China
Despite all negative consequences of Covid19 for the music industry, the pandemic has also had an unexpected positive influence on China’s dance culture. With no international DJs allowed to travel into China, local DJ talents are getting increased recognition and there is more interest in the domestic dance scene.
As clubs were shutting down across the world in the spring of 2020, China entered its post-lockdown phase and nightclubs came back to life, with more people ready to explore the club scene.
Despite those voices expressing concern about the lower-quality EDM that is dominating China’s club scene, there are also those who think it is not necessarily bad for electronic dance to go mainstream this way because it also indirectly creates more acceptance for non-mainstream sub-genres and electronic music at large.
In recent years, new underground nightclubs, festivals and independent labels have mushroomed in China. There is now a flourishing club music scene in various cities across the country: Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Wuhan, Kunming, and Guangzhou have all played a pivotal role in the development of China’s electro dance music culture, with Chengdu leading the way (Neocha 2021).

Partying at TAG, image via Tag Changdu Weibo account.
Among Chengdu’s many electronic music clubs, there’s .TAG (‘To Another Galaxy’). The club, located on the 21st floor of Chengdu’s Poly Centre, was founded by a small group of Chinese and Dutch music lovers and entrepreneurs, taking inspiration from clubs in Amsterdam and Berlin. TAG has become a city hotspot for underground house and techno, with local DJs such as Cora and HAO attracting a young and free-spirited clubbing crowd.
TAG was founded in 2013, the same year in which renowned record label SVBKVLT was established in Shanghai. SVBKVLT has pushed works from many local talents, including the Beijing-based electronic music duo Zaliva-D and Shanghai producer and artist 33EMYBW (Wu Shanmin).
Chengdu’s .TAG and Shanghai’s SVBKVLT are just some examples of China’s thriving underground scene, as there are many other important players, including Beijing’s underground techno club Zhao Dai, Shanghai’s 3NTRY, club Elevator and ALL, or OIL in Shenzhen, featuring Chinese DJs and electronic music artists such as Slowcook, Yang Yang, Temple Rat, Knopha, Chuan, Max Shen, Luna Li, and many, many more.

Image via Weibo account of 33EMYBW.
China’s electro music culture goes beyond clubs and festivals – the online environment is a big part of it. Although the 2021 shutdown of the Xiami Music app from the Chinese market created a vacuum for online electronic music streaming, other online music libraries such as QQ Music, Netease Cloud Music, Kuwo and Kugou are now competing over listeners.
On social media platforms Weibo and Wechat, there are various electronic music blogging accounts with thousands of followers but there are also hundreds of festival accounts, club accounts, label accounts, and DJ/creator accounts.
More in-depth discussions on China’s electronic music scene can also be found on Chinese Q&A platform Zhihu.com, the social networking sites QQ and Douban, and on Bilibili. Over the past few years, other smaller online communities, from Moresound to Abletive, have also arrived at the scene for people to discuss the development of Chinese dance music.
Although many online discussions about the state of China’s electronic dance music scene are quite critical of how the scene is evolving, it could still be seen as a sign of how the industry and its audience are maturing – growth comes with growing pains.
Despite all hurdles, new China-based talents are gaining traction and electronic music labels are popping up one after another. Covid has posed a major challenge to the scene but has also injected new energy into the domestic market.
Electronic music in China has come a long way since Jean Michel Jarre first made waves in the country, and after all these years, the genre is entering a new era. The next few years will show which direction Chinese electronic music is moving in, but one thing is certain: electronic music is part of China’s music scene today and, whether or not everyone agrees on the quality of the beats that are booming, the music is here to stay.
On one online discussion page about Chinese electronic music, someone asked how others feel about Chinese DJ PantaQ arriving in the DJMag Top 100 DJ list. One commenter answered: “This is only the beginning. Chinese electronic music will start to shine on the international stage.”
By Manya Koetse
Follow @whatsonweibo
1 Professor Jeroen de Kloet did extensive research into China’s dakou culture. For more on China’s dakou generation, we recommend reading: Jeroen de Kloet, China with a Cut: Globalisation, Urban Youth and Popular Music (Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press, 2010).
2 This scene was described by Chinese DJ / producer Ma Haiing (MHP) in the book by Matthew Collin, Rave On: Global Adventures in Electronic Dance Music (London: Profile Books, 2018), Chapter 6.
References
– Androids. 2017. “An Idiot’s Guide to EDM Genres.” Complex.com, October 13: https://www.complex.com/music/an-idiots-guide-to-edm-genres/ [Oct 11, 2021].
– Billboard. 1982. “Jarre Fame Spreads – Even to China.” Billboard Magazine (March 13): page 22.
– Collin, Matthew. 2018. Rave On: Global Adventures in Electronic Dance Music, London: Profile Books.
– De Boni, Luka. 2018. “The Rise of China’s Electronic Dance Music Scene: From Underground Culture to Online Communities.” What’s on Weibo, August 26
https://www.whatsonweibo.com/the-rise-of-chinas-electronic-dance-music-scene-from-underground-culture-to-online-communities/ [Nov 1, 2021].
– De Kloet, Jeroen. 2010. China with a Cut: Globalisation, Urban Youth and Popular Music. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press
– Grefer, Philipp. 2016. “Disco(s), Techno and the EDM Storm: A Brief (and Personal) History of Electronic Music in China.” The Beijinger, Nov 16 https://www.thebeijinger.com/blog/2016/11/04/discos-techno-and-edm-storm-brief-and-personal-history-electronic-music-china [Nov 12, 2021].
– Holm, David. 1983. “The Difficulty of ‘Walking on Two Legs.’” Index on Censorship: 12 (1): 34-37.
– Jori, Anita. 2021 “The Meanings of ‘electronic dance music’ and EDM.” In: The Evolution of Electronic Dance Music , edited by Ewa Mazierska, Tony Rigg and Les Gillon, Chapter 1. New York: Bloomsbury Academic.
– Latham, Kevin. 2007. Pop Culture China! Media, Arts, and Lifestyle. California: ABC-CLIO.
– Li, Qiuxiao. 2018. “Characteristics of Early Electronic Music Composition in China’s Mainland,” Contemporary Music Review 37:1-2.
– Magnetic. 2021. “STOP CALLING EDM EDM – HERE IS A PROPER DEFINITION.” Magnetic Magazine, Jan 13 https://www.magneticmag.com/2015/10/stop-calling-edm-edm-here-is-a-proper-definition/ [Oct 12, 2021].
– Music Economy Official Weibo Account 音乐财经官方微博.2020. “电音圈有什么资格羡慕滚圈.” Sina News, August 20 https://k.sina.com.cn/article_5255791141_13945022501900poao.html [Nov 27, 2021].
– Neocha. 2021. “Sleepless in Chengdu.” July 5, https://neocha.com/magazine/sleepless-in-chengdu/ [Nov 27, 2021].
– Yiu, Alex and Damien Charrieras. 2021. “On the Fence: Electronic Dance Music Cultures in Hong Kong and Shenzhen.” In: Sébastien Darchen, Damien Charrieras, John Willsteed (eds), Electronic Cities – Music, Policies and Space in the 21st Century, 223-243. Singapore: Palgrave Macmillan.
– Vice China. 2019. “触电中国 EP1:从荷东到锐舞,中国电音的起源与脉络.” Tencent News, July 30 https://new.qq.com/omn/20190730/20190730A0CTCB00.html?pc [Oct 12, 2021].
– Wycech, Olivia. 2020. “An Edm Club In Taipei Has Unabashedly Banned Bounce Music…But What Even Is Bounce Music?” MixMag, October 20 https://mixmag.asia/feature/what-is-chinese-bounce-music [Nov 17, 2021].
Featured image by Ama for Yi Magazin.
This text was written for Goethe-Institut China under a CC-BY-NC-ND-4.0-DE license (Creative Commons) as part of a monthly column in collaboration with What’s On Weibo.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

Backgrounder
“Oppenheimer” in China: Highlighting the Story of Qian Xuesen
Qian Xuesen is a renowned Chinese scientist whose life shares remarkable parallels with Oppenheimer’s.
Published
10 months agoon
September 16, 2023By
Zilan Qian
They shared the same campus, lived in the same era, and both played pivotal roles in shaping modern history while navigating the intricate interplay between science and politics. With the release of the “Oppenheimer” movie in China, the renowned Chinese scientist Qian Xuesen is being compared to the American J. Robert Oppenheimer.
In late August, the highly anticipated U.S. movie Oppenheimer finally premiered in China, shedding light on the life of the famous American theoretical physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer (1904-1967).
Besides igniting discussions about the life of this prominent scientist, the film has also reignited domestic media and public interest in Chinese scientists connected to Oppenheimer and nuclear physics.
There is one Chinese scientist whose life shares remarkable parallels with Oppenheimer’s. This is aerospace engineer and cyberneticist Qian Xuesen (钱学森, 1911-2009). Like Oppenheimer, he pursued his postgraduate studies overseas, taught at Caltech, and played a pivotal role during World War II for the US.
Qian Xuesen is so widely recognized in China that whenever I introduce myself there, I often clarify my last name by saying, “it’s the same Qian as Qian Xuesen’s,” to ensure that people get my name.
Some Chinese blogs recently compared the academic paths and scholarly contributions of the two scientists, while others highlighted the similarities in their political challenges, including the revocation of their security clearances.
The era of McCarthyism in the United States cast a shadow over Qian’s career, and, similar to Oppenheimer, he was branded as a “communist suspect.” Eventually, these political pressures forced him to return to China.
Although Qian’s return to China made his later life different from Oppenheimer’s, both scientists lived their lives navigating the complex dynamics between science and politics. Here, we provide a brief overview of the life and accomplishments of Qian Xuesen.
Departing: Going to America
Qian Xuesen (钱学森, also written as Hsue-Shen Tsien), often referred to as the “father of China’s missile and space program,” was born in Shanghai in 1911,1 a pivotal year marked by a historic revolution that brought an end to the imperial dynasty and gave rise to the Republic of China.
Much like Oppenheimer, who pursued further studies at Cambridge after completing his undergraduate education, Qian embarked on a journey to the United States following his bachelor’s studies at National Chiao Tung University (now Shanghai Jiao Tong University). He spent a year at Tsinghua University in preparation for his departure.
The year was 1935, during the eighth year of the Chinese Civil War and the fourth year of Japan’s invasion of China, setting the backdrop for his academic pursuits in a turbulent era.
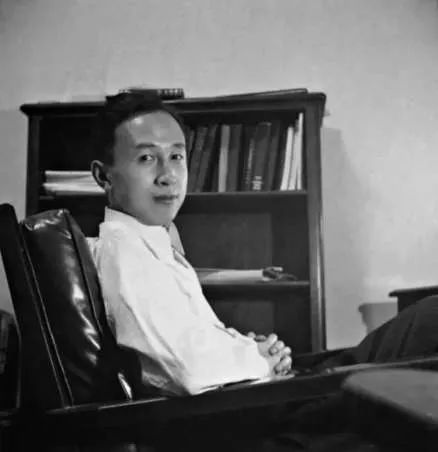

Qian in his office at Caltech (image source).
One year after arriving in the U.S., Qian earned his master’s degree in aeronautical engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Three years later, in 1939, the 27-year-old Qian Xuesen completed his PhD at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), the very institution where Oppenheimer had been welcomed in 1927. In 1943, Qian solidified his position in academia as an associate professor at Caltech. While at Caltech, Qian helped found NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
When World War II began, while Oppenheimer was overseeing the Manhattan Project’s efforts to assist the U.S. in developing the atomic bomb, Qian actively supported the U.S. government. He served on the U.S. government’s Scientific Advisory Board and attained the rank of lieutenant colonel.
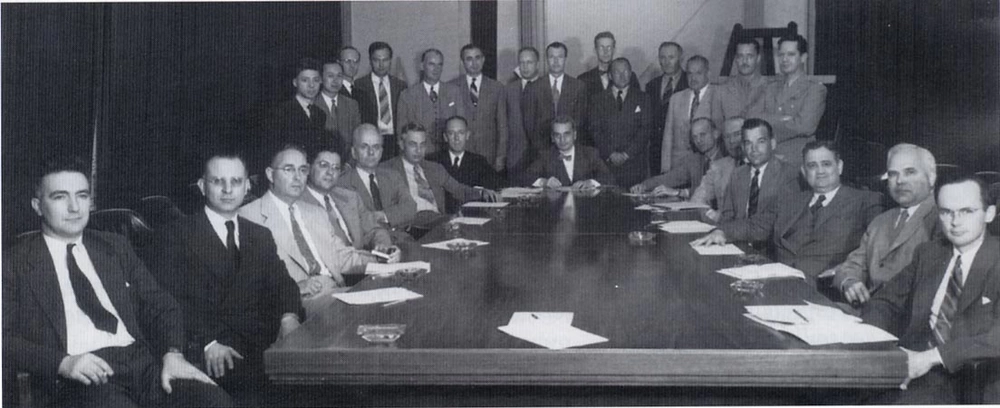

The first meeting of the US Department of the Air Force Scientific Advisory Board in 1946. The predecessor, the Scientific Advisory Group, was founded in 1944 to evaluate the aeronautical programs and facilities of the Axis powers of World War II. Qian can be seen standing in the back, the second on the left (image source).
After the war, Qian went to teach at MIT and returned to Caltech as a full-time professor in 1949. During that same year, Mao Zedong proclaimed the establishment of the People’s Republic of China (PRC). Just one year later, the newly-formed nation became involved in the Korean War, and China fought a bloody battle against the United States.
Red Scare: Being Labeled as a Communist
Robert Oppenheimer and Qian Xuesen both had an interest in Communism even prior to World War II, attending communist gatherings and showing sympathy towards the Communist cause.
Qian and Oppenheimer may have briefly met each other through their shared involvement in communist activities. During his time at Caltech, Qian secretly attended meetings with Frank Oppenheimer, the brother of J. Robert Oppenheimer (Monk 2013).
However, it was only after the war that their political leanings became a focal point for the FBI.
Just as the FBI accused Oppenheimer of being an agent of the Soviet Union, they quickly labeled Qian as a subversive communist, largely due to his Chinese heritage. While the government did not succeed in proving that Qian had communist ties with China during that period, they did ultimately succeed in portraying Qian as a communist affiliated with China a decade later.
During the transition from the 1940s to the 1950s, the Cold War was underway, and the anti-communist witch-hunts associated with the McCarthy era started to intensify (BBC 2020).
In 1950, the Korean War erupted, with the People’s Republic of China (PRC) joining North Korea in the conflict against South Korea, which received support from the United States. It was during this tumultuous period that the FBI officially accused Qian of communist sympathies in 1950, leading to the revocation of his security clearance despite objections from Qian’s colleagues. Four years later, in 1954, Robert Oppenheimer went through a similar process.
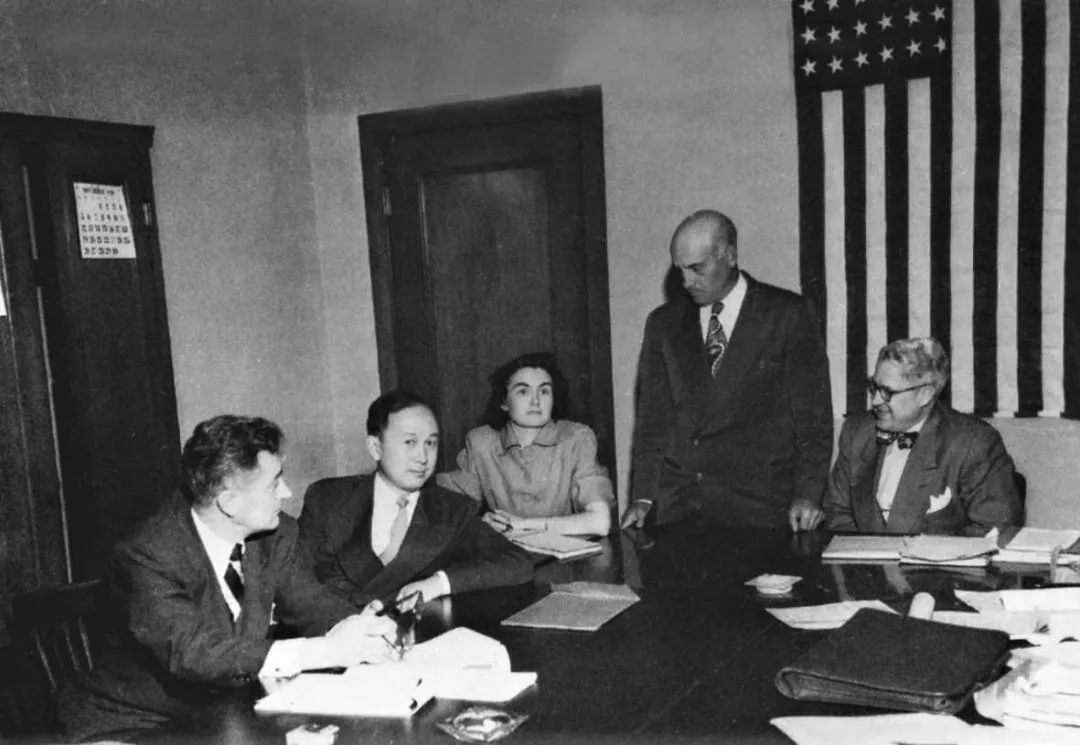

The 1950’s security hearing of Qian (second left). (Image source).
After losing his security clearance, Qian began to pack up, saying he wanted to visit his aging parents back home. Federal agents seized his luggage, which they claimed contained classified materials, and arrested him on suspicion of subversive activity. Although Qian denied any Communist leanings and rejected the accusation, he was detained by the government in California and spent the next five years under house arrest.
Five years later, in 1955, two years after the end of the Korean War, Qian was sent home to China as part of an apparent exchange for 11 American airmen who had been captured during the war. He told waiting reporters he “would never step foot in America again,” and he kept his promise (BBC 2020).

A letter from the US Immigration and Naturalization Service to Qian Xuesen, dated August 4, 1955, in which he was notified he was allowed to leave the US. The original copy is owned by Qian Xuesen Library of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, where the photo was taken. (Caption and image via wiki).
Dan Kimball, who was the Secretary of the US Navy at the time, expressed his regret about Qian’s departure, reportedly stating, “I’d rather shoot him dead than let him leave America. Wherever he goes, he equals five divisions.” He also stated: “It was the stupidest thing this country ever did. He was no more a communist than I was, and we forced him to go” (Perrett & Bradley, 2008).
Kimball may have foreseen the unfolding events accurately. After his return to China, Qian did indeed assume a pivotal role in enhancing China’s military capabilities, possibly surpassing the potency of five divisions. The missile programme that Qian helped develop in China resulted in weapons which were then fired back on America, including during the 1991 Gulf War (BBC 2020).
Returning: Becoming a National Hero
The China that Qian Xuesen had left behind was an entirely different China than the one he returned to. China, although having relatively few experts in the field, was embracing new possibilities and technologies related to rocketry and space exploration.
Within less than a month of his arrival, Qian was welcomed by the then Vice Prime Minister Chen Yi, and just four months later, he had the honor of meeting Chairman Mao himself.

Qian and Mao (image source).
In China, Qian began a remarkably successful career in rocket science, with great support from the state. He not only assumed leadership but also earned the distinguished title of the “father” of the Chinese missile program, instrumental in equipping China with Dongfeng ballistic missiles, Silkworm anti-ship missiles, and Long March space rockets.
Additionally, his efforts laid the foundation for China’s contemporary surveillance system.
By now, Qian has become somewhat of a folk hero. His tale of returning to China despite being thwarted by the U.S. government has become like a legendary narrative in China: driven by unwavering patriotism, he willingly abandoned his overseas success, surmounted formidable challenges, and dedicated himself to his motherland.
Throughout his lifetime, Qian received numerous state medals in recognition of his work, establishing him as a nationally celebrated intellectual. From 1989 to 2001, the state-launched public movement “Learn from Qian Xuesen” was promoted throughout the country, and by 2001, when Qian turned 90, the national praise for him was on a similar level as that for Deng Xiaoping in the decade prior (Wang 2011).
Qian Xuesen remains a celebrated figure. On September 3rd of this year, a new “Qian Xuesen School” was established in Wenzhou, Zhejiang Province, becoming the sixth high school bearing the scientist’s name since the founding of the first one only a year ago.
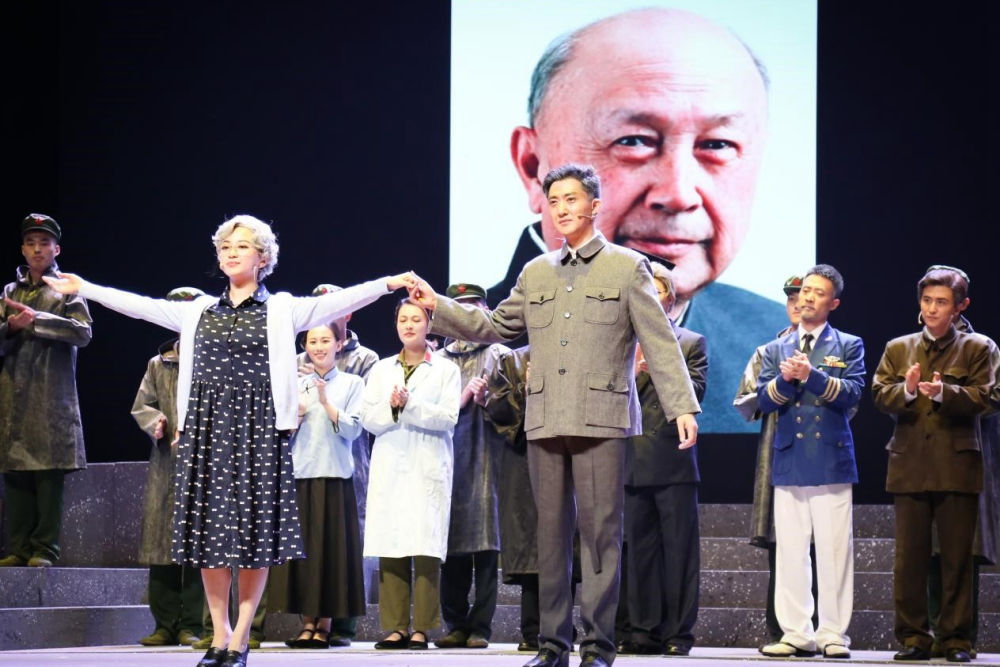

In 2017, the play “Qian Xuesen” was performed at Qian’s alma mater, Shanghai Jiaotong University. (Image source.)
Qian Xuesen’s legacy extends well beyond educational institutions. His name frequently appears in the media, including online articles, books, and other publications. There is the Qian Xuesen Library and a museum in Shanghai, containing over 70,000 artefacts related to him. Qian’s life story has also been the inspiration for a theater production and a 2012 movie titled Hsue-Shen Tsien (钱学森).2
Unanswered Questions
As is often the case when people are turned into heroes, some part of the stories are left behind while others are highlighted. This holds true for both Robert Oppenheimer and Qian Xuesen.
The Communist Party of China hailed Qian as a folk hero, aligning with their vision of a strong, patriotic nation. Many Chinese narratives avoid the debate over whether Qian’s return was linked to problems and accusations in the U.S., rather than genuine loyalty to his homeland.
In contrast, some international media have depicted Qian as a “political opportunist” who returned to China due to disillusionment with the U.S., also highlighting his criticism of “revisionist” colleagues during the Cultural Revolution and his denunciation of the 1989 student demonstrations.
Unlike the image of a resolute loyalist favored by the Chinese public, Qian’s political ideology was, in fact, not consistently aligned, and there were instances where he may have prioritized opportunity over loyalty at different stages of his life.
Qian also did not necessarily aspire to be a “flawless hero.” Upon returning to China, he declined all offers to have his biography written for him and refrained from sharing personal information with the media. Consequently, very little is known about his personal life, leaving many questions about the motivations driving him, and his true political inclinations.

The marriage photo of Qian and Jiang. (Image source).
We do know that Qian’s wife, Jiang Ying (蒋英), had a remarkable background. She was of Chinese-Japanese mixed race and was the daughter of a prominent military strategist associated with Chiang Kai-shek. Jiang Ying was also an accomplished opera singer and later became a professor of music and opera at the Central Conservatory of Music in Beijing.
Just as with Qian, there remain numerous unanswered questions surrounding Oppenheimer, including the extent of his communist sympathies and whether these sympathies indirectly assisted the Soviet Union during the Cold War.
Perhaps both scientists never imagined they would face these questions when they first decided to study physics. After all, they were scientists, not the heroes that some narratives portray them to be.
Also read:
■ Farewell to a Self-Taught Master: Remembering China’s Colorful, Bold, and Iconic Artist Huang Yongyu
■ “His Name Was Mao Anying”: Renewed Remembrance of Mao Zedong’s Son on Chinese Social Media
By Zilan Qian
Follow @whatsonweibo
1 Some sources claim that Qian was born in Hangzhou, while others say he was born in Shanghai with ancestral roots in Hangzhou.
2The Chinese character 钱 is typically romanized as “Qian” in Pinyin. However, “Tsien” is a romanization in Wu Chinese, which corresponds to the dialect spoken in the region where Qian Xuesen and his family have ancestral roots.
This article has been edited for clarity by Manya Koetse
References (other sources hyperlinked in text)
BBC. 2020. “Qian Xuesen: The man the US deported – who then helped China into space.” BBC.com, 27 October https://www.bbc.com/news/stories-54695598 [9.16.23].
Monk, Ray. 2013. Robert Oppenheimer: A Life inside the Center, First American Edition. New York: Doubleday.
Perrett, Bradley, and James R. Asker. 2008. “Person of the Year: Qian Xuesen.” Aviation Week and Space Technology 168 (1): 57-61.
Wang, Ning. 2011. “The Making of an Intellectual Hero: Chinese Narratives of Qian Xuesen.” The China Quarterly, 206, 352-371. doi:10.1017/S0305741011000300
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Backgrounder
Farewell to a Self-Taught Master: Remembering China’s Colorful, Bold, and Iconic Artist Huang Yongyu
Renowned Chinese artist and the creator of the ‘Blue Rabbit’ zodiac stamp Huang Yongyu has passed away at the age of 98. “I’m not afraid to die. If I’m dead, you may tickle me and see if I smile.”
Published
1 year agoon
June 15, 2023
The famous Chinese painter, satirical poet, and cartoonist Huang Yongyu has passed away. Born in 1924, Huang endured war and hardship, yet never lost his zest for life. When his creativity was hindered and his work was suppressed during politically tumultuous times, he remained resilient and increased “the fun of living” by making his world more colorful.
He was a youthful optimist at old age, and will now be remembered as an immortal legend. The renowned Chinese painter and stamp designer Huang Yongyu (黄永玉) passed away on June 13 at the age of 98. His departure garnered significant attention on Chinese social media platforms this week.
On Weibo, the hashtag “Huang Yongyu Passed Away” (#黄永玉逝世#) received over 160 million views by Wednesday evening.
Huang was a member of the China National Academy of Painting (中国国家画院) as well as a Professor at the Central Academy of Fine Arts (中央美术学院).
Huang Yongyu is widely recognized in China for his notable contribution to stamp design, particularly for his iconic creation of the monkey stamp in 1980. Although he designed a second monkey stamp in 2016, the 1980 stamp holds significant historical importance as it marked the commencement of China Post’s annual tradition of releasing zodiac stamps, which have since become highly regarded and collectible items.
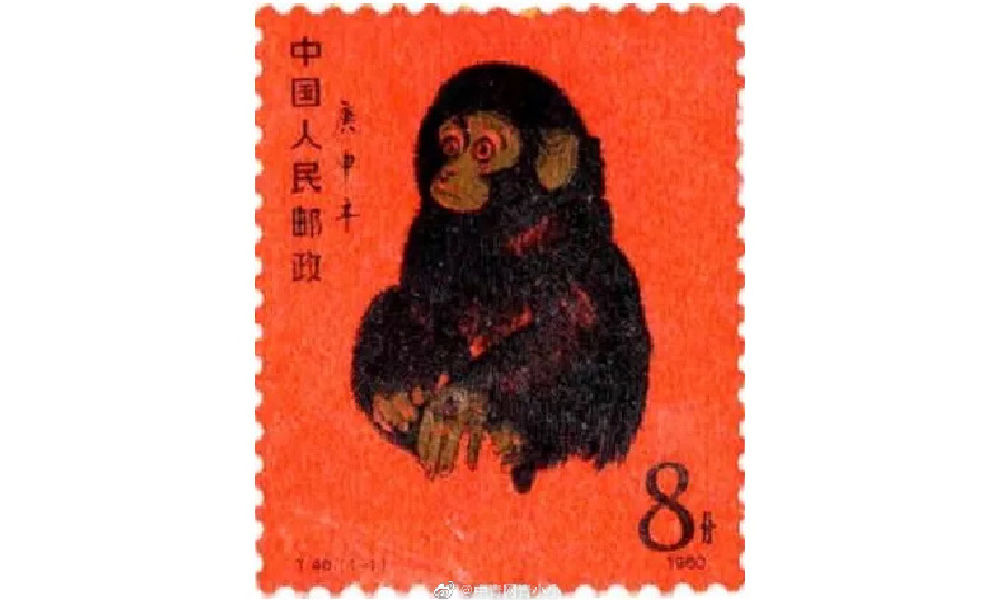

Huang’s famous money stamp that was issued by China Post in 1980.
The monkey stamp designed by Huang Yongyu has become a cherished collector’s item, even outside of China. On online marketplaces like eBay, individual stamps from this series are being sold for approximately $2000 these days.
Huang Yongyu’s latest most famous stamp was this year’s China Post zodiac stamp. The stamp, a blue rabbit with red eyes, caused some online commotion as many people thought it looked “horrific.”
Some thought the red-eyed blue rabbit looked like a rat. Others thought it looked “evil” or “monster-like.” There were also those who wondered if the blue rabbit looked so wild because it just caught Covid.
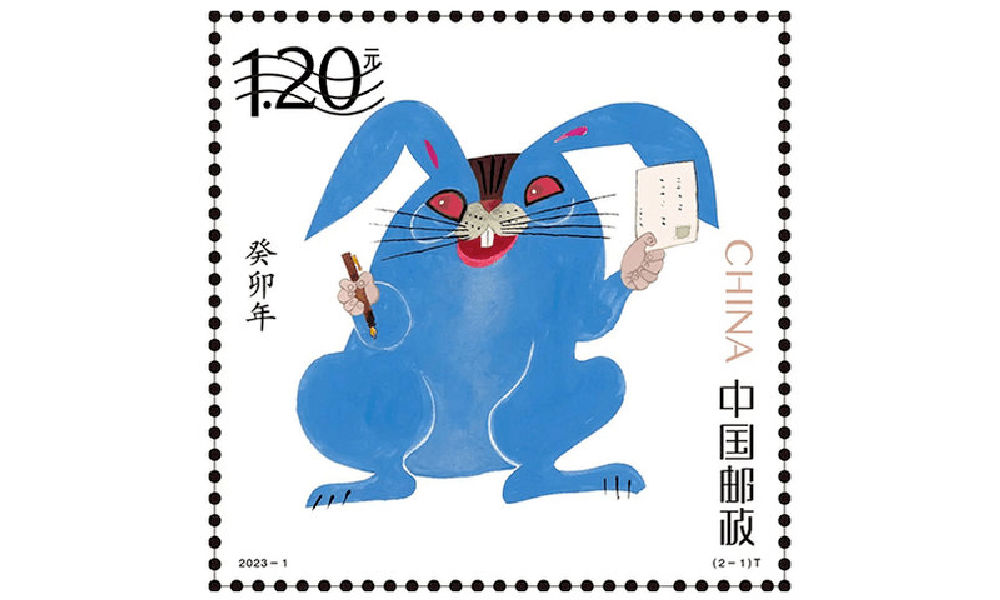

Huang’s (in)famous blue rabbit stamp.
Nevertheless, many people lined up at post offices for the stamps and they immediately sold out.
In light of the controversy, Huang Yongyu spoke about the stamps in a livestream in January of 2023. The 98-year-old artist claimed he had simply drawn the rabbit to spread joy and celebrate the new year, stating, “Painting a rabbit stamp is a happy thing. Everyone could draw my rabbit. It’s not like I’m the only one who can draw this.”
Huang’s response also went viral, with one Weibo hashtag dedicated to the topic receiving over 12 million views (#蓝兔邮票设计者直播回应争议#) at the time. Those defending Huang emphasized how it was precisely his playful, light, and unique approach to art that has made Huang’s work so famous.
A Self-Made Artist
“I’m ugly, but my mum likes me”
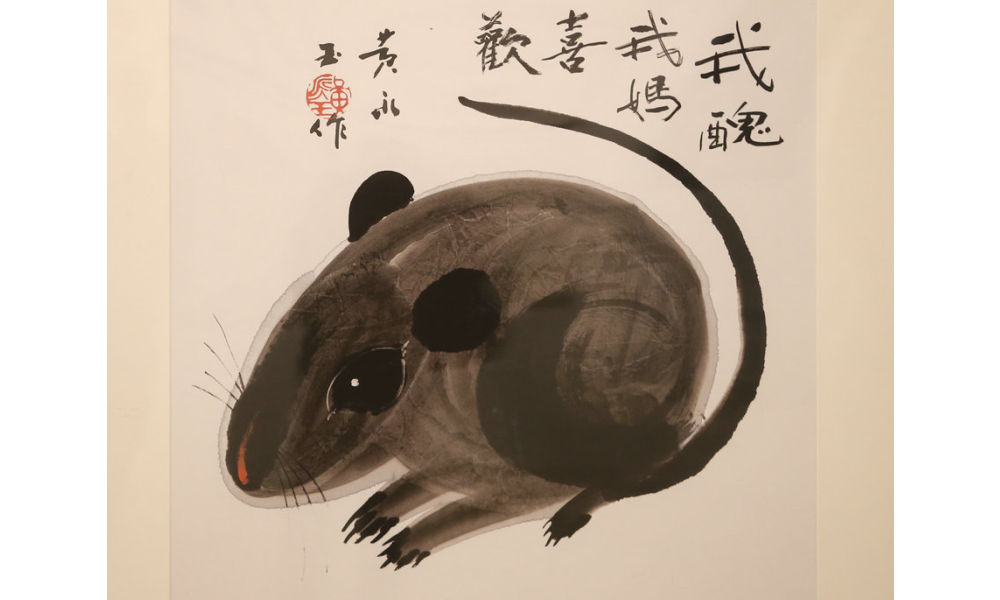

‘Ugly Mouse’ by Huang Yongyu [Image via China Daily].
Huang Yongyu was born on August 9, 1924, in Hunan’s Chengde as a native of the Tujia ethnic group.
He was born into an extraordinary family. His grandfather, Huang Jingming (黄镜铭), worked for Xiong Xiling (熊希齡), who would become the Premier of the Republic of China. His first cousin and lifelong friend was the famous Chinese novelist Shen Congwen (沈从文). Huang’s father studied music and art and was good at drawing and playing the accordion. His mother graduated from the Second Provincial Normal School and was the first woman in her county to cut her hair short and wear a short skirt (CCTV).
Born in times of unrest and poverty, Huang never went to college and was sent away to live with relatives at the age of 13. His father would die shortly after, depriving him of a final goodbye. Huang started working in various places and regions, from porcelain workshops in Dehua to artisans’ spaces in Quanzhou. At the age of 16, Huang was already earning a living as a painter and woodcutter, showcasing his talents and setting the foundation for his future artistic pursuits.
When he was 22, Huang married his first girlfriend Zhang Meixi (张梅溪), a general’s daughter, with whom he shared a love for animals. He confessed his love for her when they both found themselves in a bomb shelter after an air-raid alarm.
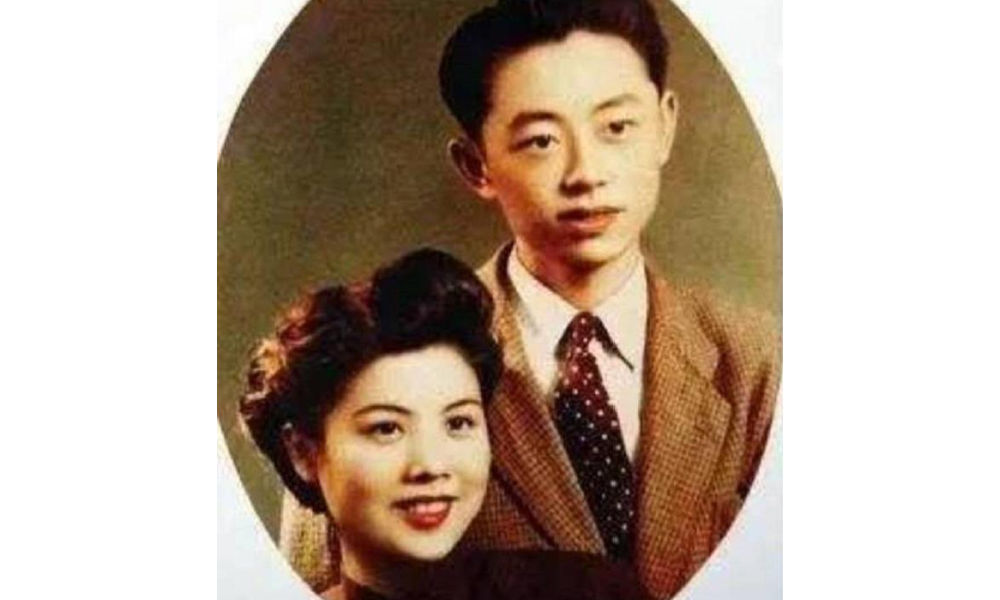

Huang and Zhang Meixi [163.com]
In his twenties, Huang Yongyu emerged as a sought-after artist in Hong Kong, where he had relocated in 1948 to evade persecution for his left-wing activities. Despite achieving success there, he heeded Shen Congwen’s advice in 1953 and moved to Beijing. Accompanied by his wife and their 7-month-old child, Huang took on a teaching position at the esteemed Central Academy of Fine Arts (中央美术学院).
The couple raised all kinds of animals at their Beijing home, from dogs and owls to turkeys and sika deers, and even monkeys and bears (Baike).
Throughout Huang’s career, animals played a significant role, not only reflecting his youthful spirit but also serving as vehicles for conveying satirical messages.
One recurring motif in his artwork was the incorporation of mice. In one of his famous works, a grey mouse is accompanied by the phrase ‘I’m ugly, but my mum likes me’ (‘我丑,但我妈喜欢’), reinforcing the notion that regardless of our outward appearance or circumstances, we remain beloved children in the eyes of our mothers.

As a teacher, Huang liked to keep his lessons open-minded and he, who refused to join the Party himself, stressed the importance of art over politics. He would hold “no shirt parties” in which his all-male studio students would paint in an atmosphere of openness and camaraderie during hot summer nights (Andrews 1994, 221; Hawks 2017, 99).
By 1962, creativity in the classroom was limited and there were far more restrictions to what could and could not be created, said, and taught.
Bright Colors in Dark Times
“Strengthen my resolve and increase the fun of living”
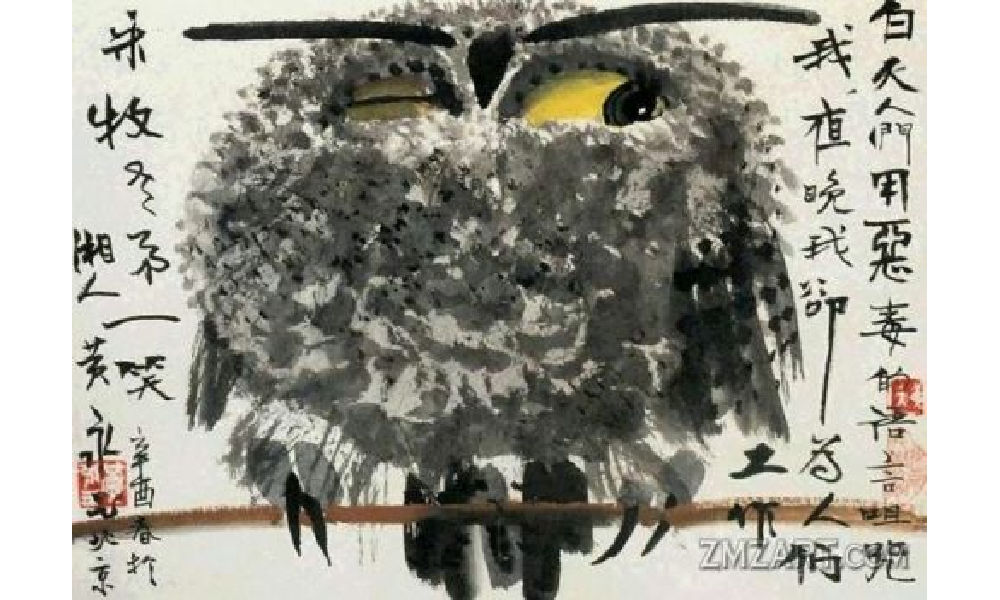

Huang Yongyu’s winking owl, 1973, via Wikiart.
In 1963, Huang was sent to the countryside as part of the “Four Cleanups” movement (四清运动, 1963-1966). Although Huang cooperated with the requirement to attend political meetings and do farm work, he distanced himself from attempts to reform his thinking. In his own time, and even during political meetings, he would continue to compose satirical and humorous pictures and captions centered around animals, which would later turn into his ‘A Can of Worms’ series (Hawks 2017, 99; see Morningsun.org).
Three years later, at the beginning of the Cultural Revolution, many Chinese major artists, including Huang, were detained in makeshift jails called ‘niupeng‘ (牛棚), cowsheds. Huang’s work was declared to be counter-revolutionary, and he was denounced and severely beaten. Despite the difficult circumstances, Huang’s humor and kindness would remind his fellow artist prisoners of the joy of daily living (2017, 95-96).
After his release, Huang and his family were relocated to a cramped room on the outskirts of Beijing. The authorities, thinking they could thwart his artistic pursuits, provided him with a shed that had only one window, which faced a neighbor’s wall. However, this limitation didn’t deter Huang. Instead, he ingeniously utilized vibrant pigments that shone brightly even in the dimly lit space.
During this time, he also decided to make himself an “extra window” by creating an oil painting titled “Eternal Window” (永远的窗户). Huang later explained that the flower blossoms in the paining were also intended to “strengthen my resolve and increase the fun of living” (Hawks 2017, 4; 100-101).
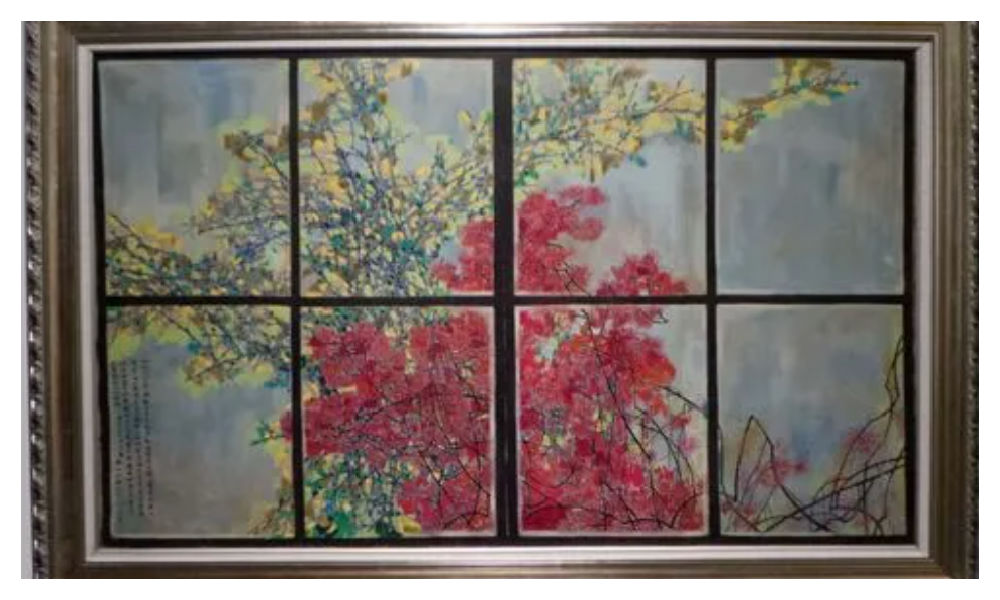

Huang Yongyu’s Eternal Window [Baidu].
In 1973, during the peak of the Cultural Revolution, Huang painted his famous winking owl. The calligraphy next to the owl reads: “During the day people curse me with vile words, but at night I work for them” (“白天人们用恶毒的语言诅咒我,夜晚我为他们工作”) (Matthysen 2021, 165).
The painting was seen as a display of animosity towards the regime, and Huang got in trouble for it. Later on in his career, however, Huang would continue to paint owls. In 1977, when the Cultural Revolution had ended, Huang Yongyu painted other owls to ridicules his former critics (2021, 174).

According to art scholar Shelly Drake Hawks, Huang Yongyu employed animals in his artwork to satirize the realities of life under socialism. This approach can be loosely compared to George Orwell’s famous novel Animal Farm.
However, Huang’s artistic style, vibrant personal life, and boundary-pushing work ethic also draw parallels to Picasso. Like Picasso, Huang embraced a colorful life, adopted an innovative approach to art, and challenged artistic norms.
An Optimist Despite All Hardships
“Quickly come praise me, while I’m still alive”
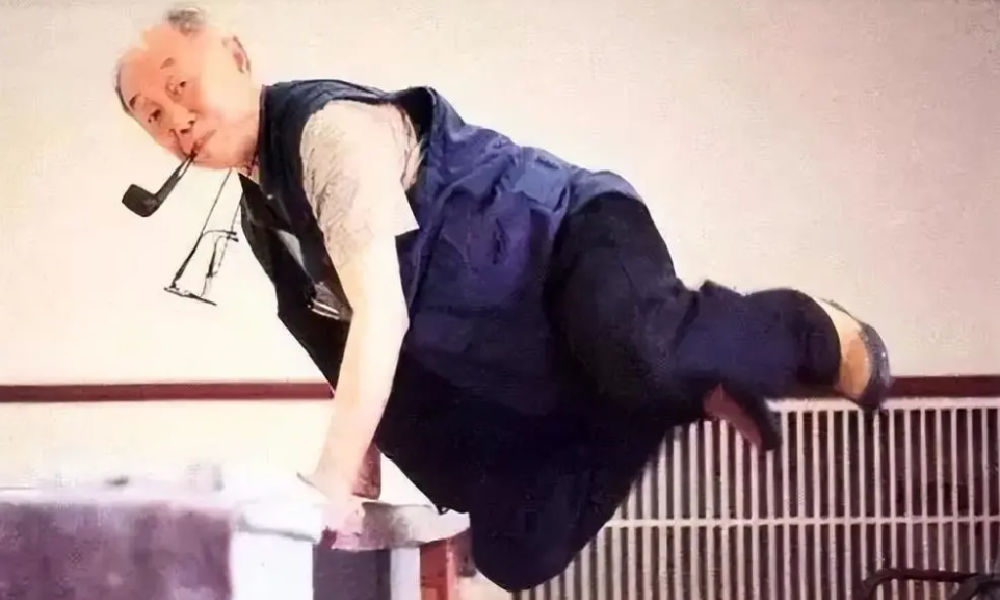

Huang Yongyu will be remembered in China with love and affection for numerous reasons. Whether it is his distinctive artwork, his mischievous smile and trademark pipe, his unwavering determination to follow his own path despite the authorities’ expectations, or his enduring love for his wife of over 75 years, there are countless aspects to appreciate and admire about Huang.
One things that is certainly admirable is how he was able to maintain a youthful and joyful attitude after suffering many hardships and losing so many friends.
“An intriguing soul. Too wonderful to describe,” one Weibo commenter wrote about Huang, sharing pictures of Huang Yongyu’s “Scenes of Pooping” (出恭图) work.
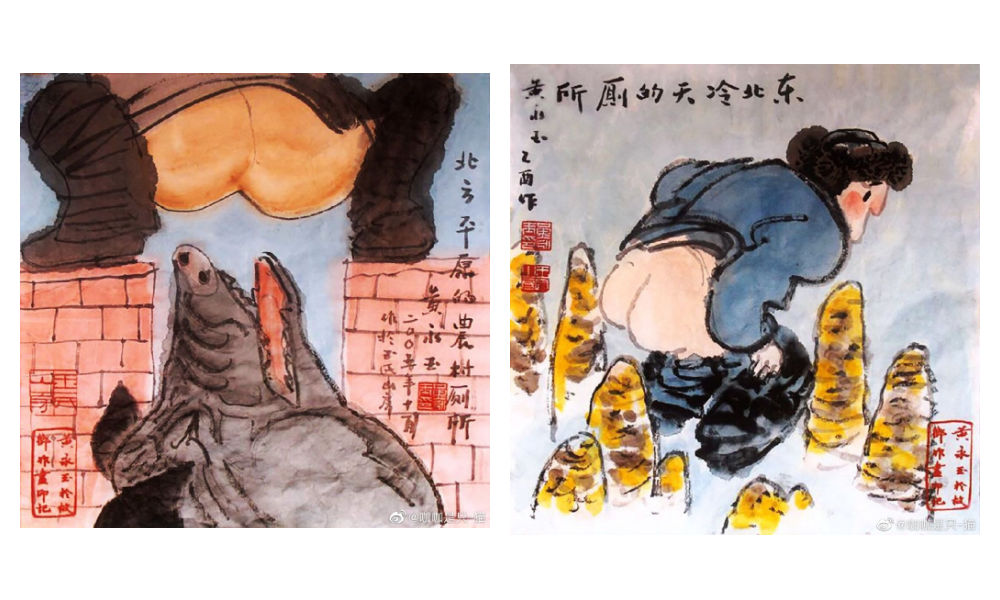
Old age did not hold him back. At the age of 70, his paintings sold for millions. When he was in his eighties, he was featured on the cover of Esquire (时尚先生) magazine.
At the age of 82, he stirred controversy in Hong Kong with his “Adam and Eve” sculpture featuring male and female genitalia, leading to complaints from some viewers. When confronted with the backlash, Huang answered, “I just wanted to have a taste of being sued, and see how the government would react” (Ora Ora).
I'm guessing the 98-year-old Huang loved the controversy. When confronted with backlash for his sculpture featuring male and female genitalia in 2007 Hong Kong, Huang answered, "I just wanted to have a taste of being sued, and see how the government would react." pic.twitter.com/kG0MVVM4SN
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) June 15, 2023
In his nineties, he started driving a Ferrari. He owned mansions in his hometown in Hunan, in Beijing, in Hong Kong, and in Italy – all designed by himself (Chen 2019).
Huang kept working and creating until the end of his life. “It’s good to work diligently. Your work may be meaningful. Maybe it won’t be. Don’t insist on life being particularly meaningful. If it’s happy and interesting, then that’s great enough.”

“Hometown Scenery” or rather “Hunan Scenery” (湘西风景) by Huang.
Huang did not dread the end of his life.
“My old friends have all died, I’m the only one left,” he said at the age of 95. He wrote his will early and decided he wanted a memorial service for himself before his final departure. “Quickly come praise me, while I’m still alive,” he said, envisioning himself reclining on a chair in the center of the room, “listening to how everyone applauds me” (CCTV, Sohu).
He stated: “I don’t fear death at all. I always joke that when I die, you should tickle me first and see if I’ll smile” (“对死我是一点也不畏惧,我开玩笑,我等死了之后先胳肢我一下,看我笑不笑”).
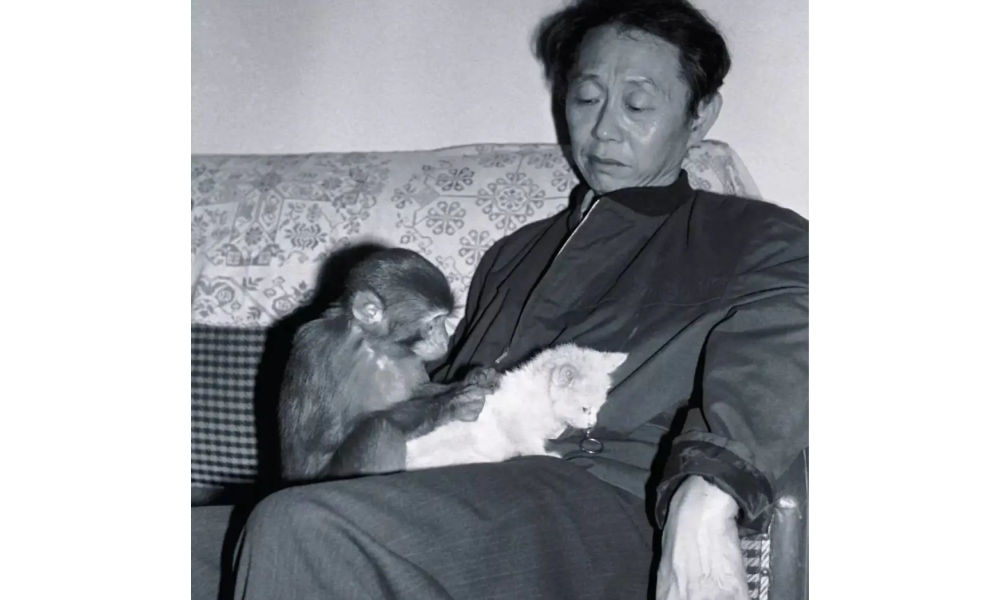

Huang with Yiwo (伊喔), the original model for the monkey stamp [Shanghai Observer].
Huang also was not sentimental about what should happen to his ashes. In a 2019 article in Guangming Daily, it was revealed that he suggested to his wife the idea of pouring his ashes into the toilet and flushing them away with the water.
However, his wife playfully retorted, saying, “No, that won’t do. Your life has been too challenging; you would clog the toilet.”
To this, Huang responded, “Then wrap my ashes into dumplings and let everyone [at the funeral] eat them, so you can tell them, ‘You’ve consumed Huang Yongyu’s ashes!'”
But she also opposed of that idea, saying that they would vomit and curse him forever.
Nevertheless, his wife expressed opposition to this idea, citing concerns that it would cause people to vomit and curse him indefinitely.
In response, Huang declared, “Then let’s forget about my ashes. If you miss me after I’m gone, just look up at the sky and the clouds.” Eventually, his wife would pass away before him, in 2020, at the age of 98, having spent 77 years together with Huang.
Huang will surely be missed. Not just by the loved ones he leaves behind, but also by millions of his fans and admirers in China and beyond.
“We will cherish your memory, Mr. Huang,” one Weibo blogger wrote. Others honor Huang by sharing some of his famous quotes, such as, “Sincerity is more important than skill, which is why birds will always sing better than humans” (“真挚比技巧重要,所以鸟总比人唱得好”).
Among thousands of other comments, another social media user bid farewell to Huang Yongyu: “Our fascinating Master has transcended. He is now a fascinating soul. We will fondly remember you.”
By Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
References
Andrews, Julia Frances. 1994. Painters and Politics in the People’s Republic of China, 1949-1979. Berkley: University of California Press.
Baike. “Huang Yongyu 黄永玉.” Baidu Baike https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%BB%84%E6%B0%B8%E7%8E%89/1501951 [June 14, 2023].
CCTV. 2023. “Why Everyone Loves Huang Yongyu [为什么人人都爱黄永玉].” WeChat 央视网 June 14.
Chen Hongbiao 陈洪标. 2019. “Most Spicy Artist: Featured in a Magazine at 80, Flirting with Lin Qingxia at 91, Playing with Cars at 95, Wants Memorial Service While Still Alive [最骚画家:80岁上杂志,91岁撩林青霞,95岁玩车,活着想开追悼会].” Sohu/Guangming Daily March 16: https://www.sohu.com/a/301686701_819105 [June 15, 2023].
Hawks, Shelley Drake. 2017. The Art of Resistance Painting by Candlelight in Mao’s China. Seattle: University of Washington Press.
Matthysen, Mieke. 2021. Ignorance is Bliss: The Chinese Art of Not Knowing. Palgrave Macmillan.
Ora Ora. “HUANG YONGYU 黃永玉.” Ora Ora https://www.ora-ora.com/artists/103-huang-yongyu/ [June 15, 2023].
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?






