China and Covid19
Panic over Wuhan Coronavirus Leads to Online Backlash against Consumption of Wild Animals in China
Amid the coronavirus outbreak panic, the majority of Chinese netizens say it’s time for wild game to be game over.
Published
5 years agoon

First published
It is by far the number one topic dominating Chinese online media: the coronavirus. The source of the virus is suspected to be an illegal wild animal market in Wuhan. Calls for stricter outlawing of the trafficking and consumption of wild game are dominating Weibo this week.
Fears are mounting over a new strain of coronavirus that first appeared at a wet market in Wuhan in late December and has spread to four countries, killed 17, and infected almost 600 in China, with new cases being reported at time of writing.
The number of infected is expected to balloon as the annual Chinese New Year holiday begins on Friday and hundreds of millions of Chinese travelers move about the country.
The Wuhan coronavirus was first transmitted to humans in a wet market in Wuhan where many kinds of wild animals are sold illegally. While the source has yet to be conclusively identified, coronavirus is typically transmitted to humans via animals such as civet cats and bats. This has led to an outcry online and widespread condemnation of the consumption of wild game in China.
Known as the Wuhan Coronavirus internationally, domestically the virus is simply called “new pneumonia” (新型肺炎) in most Chinese media coverage. It is a type of respiratory illness causing mild to moderate cold-like symptoms that can potentially lead to complications from pneumonia.
So far, the virus seems to be milder than the previous two big global coronavirus outbreaks (SARS and MERS), but health officials caution that not enough is known as of yet, and also that the risk of mutation could mean far greater danger than first anticipated.
As of 10 am today, authorities have sealed off travel to and from Wuhan in an effort to prevent further spread of the disease. News of other cities in Hubei province also halting train operations came in later today, with Ezhou Station and Huangguang station both suspending services as of Thursday.
The Chinese government’s response to the Wuhan virus has been markedly different from the coverup of the SARS outbreak in 2003, and authorities have been swift to track the disease and to sequence its genome.
On January 20, Beijing confirmed that the virus can be spread between humans, and on January 22 it announced a full accounting of all cases in China and abroad in a press conference given by the State Council Information Office.
Backlash against the Consumption of Wild Game
As global and domestic concern mounts about the new virus, it has become the almost exclusive focus of Chinese social media this week, dominating the vast majority of trending topics on Weibo and Wechat.

A snapshot of the top trending topics on Weibo taken on January 23. The only topic not about the virus is about Taiwanese singer Chen Linong 陈立农 playing whack-a-mole.
The Wuhan virus is believed to have originated at the Wuhan Huanan Wholesale Seafood Market (武汉华南海鲜批发市场) and was most likely first transferred to humans from one of the many wild animals being illegal bought and sold there.
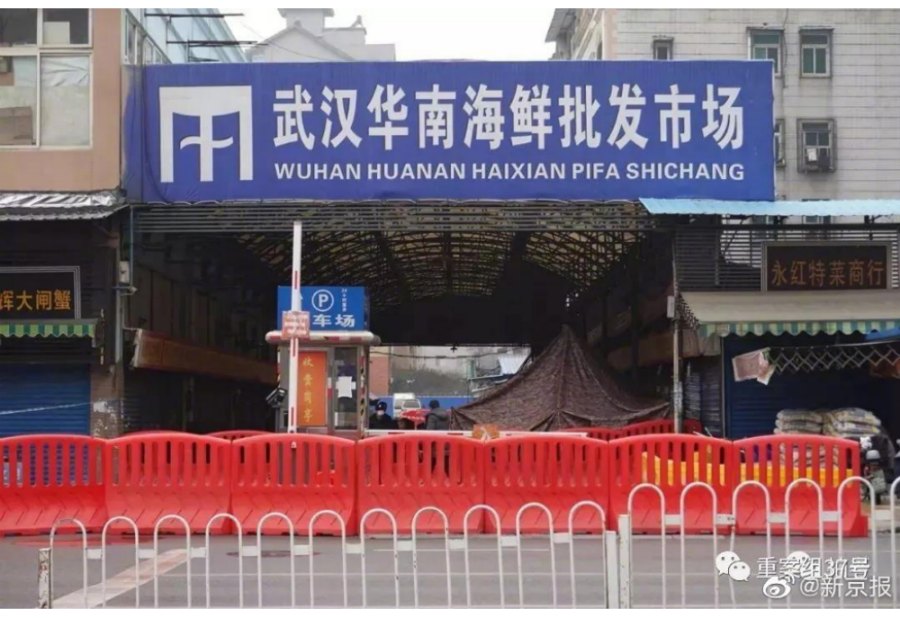

The Wuhan wet market where the Wuhan coronavirus is thought to have first been transferred to humans.
The market has since been shut down, but online criticism of such markets has been fierce on social media.
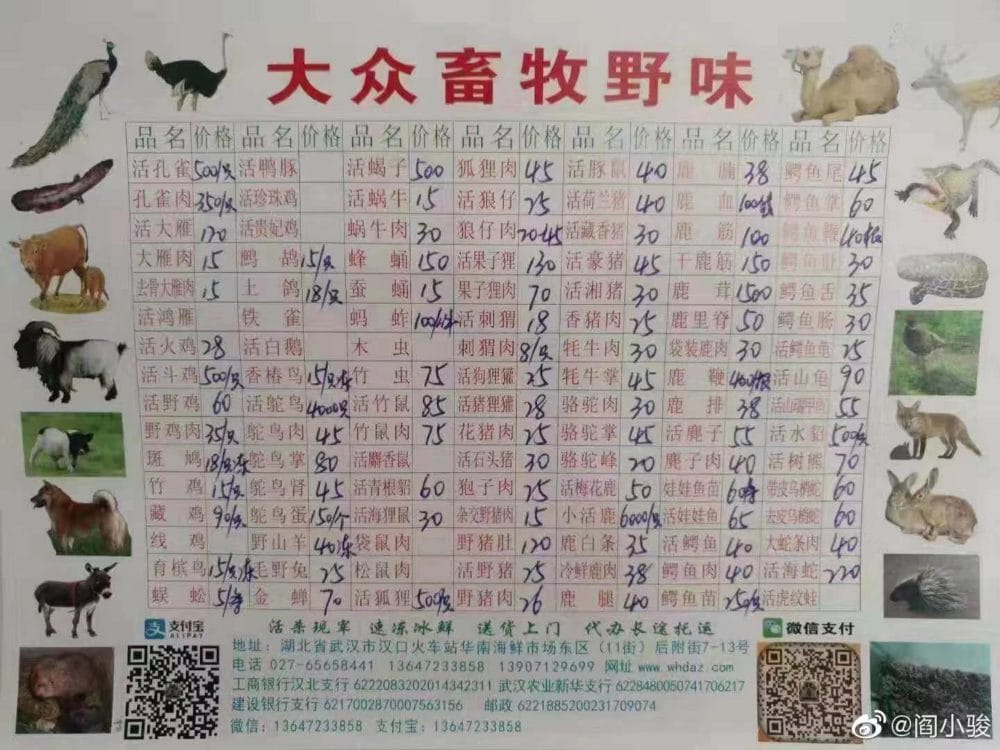
A price list for wild animals sold at the Wuhan wet market, including hedgehog, fox, and camel.
The hashtag “Support the banning of wild game markets” (#支持禁绝野味市场#) was topping the list of trending topics for much of Thursday and was viewed 270 million times.
Another hashtag, “The source of the new coronavirus is wild animals” (#新型冠状病毒来源是野生动物#), topped the list on Wednesday and has been viewed 990 million times.
Online commenters are lambasting the practice of eating illegal wild game such as civet cats, the cause of the 2003 SARS virus, and bats, the suspected cause of the Wuhan coronavirus (snakes have also been suggested as a possible source of the coronavirus outbreak).
“The only outcome of eating wild game is disease! SARS came from civet cats and bats. Ebola came from chimpanzees, monkeys, wild boar, and bats. MERS came from camels. The Avian Flu came from wild birds and poultry. AIDS came from chimps. Is it really that delicious? Is this really the way you want to eat?” one Weibo user questioned.
Comments viciously attacking those who eat wild animals can be seen across a variety of posts and topics.
“Let me say something malicious: Eating wild game is fine, just please remember to kill yourself immediately after,” said one much-upvoted commenter on a post about virus facts released by the State Council.
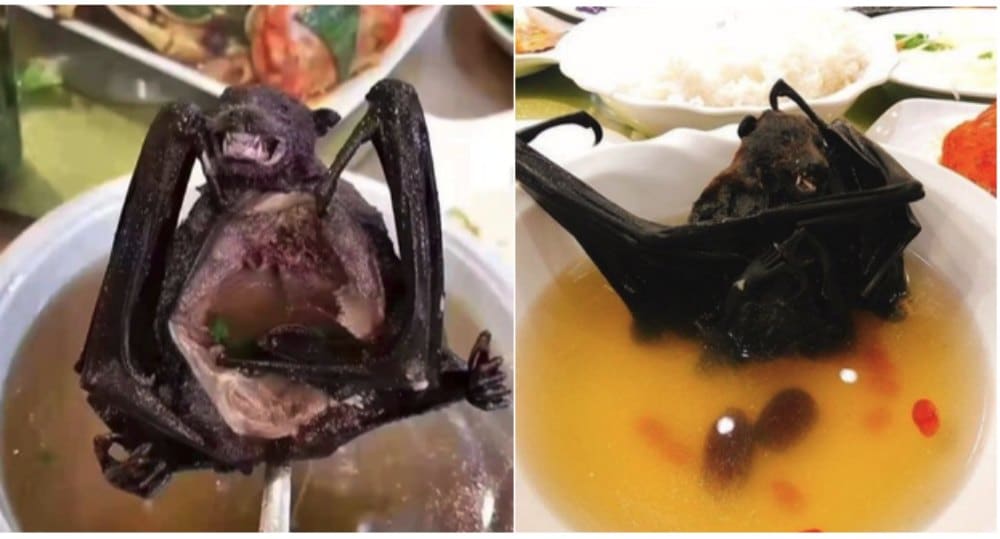

Images circulating on Weibo showing dishes featuring bats, the suspected source of the Wuhan coronavirus.
Various photos and a video of people eating bats have been going around WeChat and Weibo these days. The word for ‘bat’ in Chinese (蝙蝠) is ‘bianfu.‘ The ‘fu’ sound being the same as ‘fu’ (福) for ‘happiness,’ it is believed that superstition is one of the reasons for people to consume bat.
It is by far the number one topic dominating Chinese online media today: the #coronavirus. Since the source of the virus is suspected to be a wild animal market in Wuhan, the majority of Chinese netizens say it's time for wild game to be game over. Read: https://t.co/w3BZS5UfNq pic.twitter.com/gnLTGYDRdy
— What's on Weibo (@WhatsOnWeibo) January 23, 2020
“If humans don’t live in harmony with nature, the inevitable consequence is that nature bites back. We need to regulate our hungry mouths!” complained one Weibo user.
Another trending view of the issue is that eating wild game flies in the face of thousands of years of human domestication of animals. Said one Weibo comment: “Our ancestors spent thousands of years domesticating the tastiest, most nutritious, safest poultry and livestock for us, but people are still stupid enough to go and provoke wild animals! I’m so furious I can barely speak. Only human beings can destroy human beings, and it’s the worst and most stupid of us who are doing it.”

“We spent thousands of years domesticating super nutritious animals and you don’t even want to eat them! You just want wild game!”
A video circulating on Weibo made by the cast of My Own Swordsman (武林外传) educates viewers on the risks of eating wild animals, breaking the third wall to tell their audience that there’s really no nutritional difference between domestic and wild animals, and that wild animals may carry disease because they haven’t been subject to the same kinds of hygiene requirements.

One Red Cross volunteer commented on the video: “I recommend that we immediately crackdown on all wild game markets, we cannot allow the cravings of a small group of people to affect our country as a whole. This kind of behavior disrupts the order of the food chain, and the rest of us are paying for the ridiculous and selfish behavior of these people.”
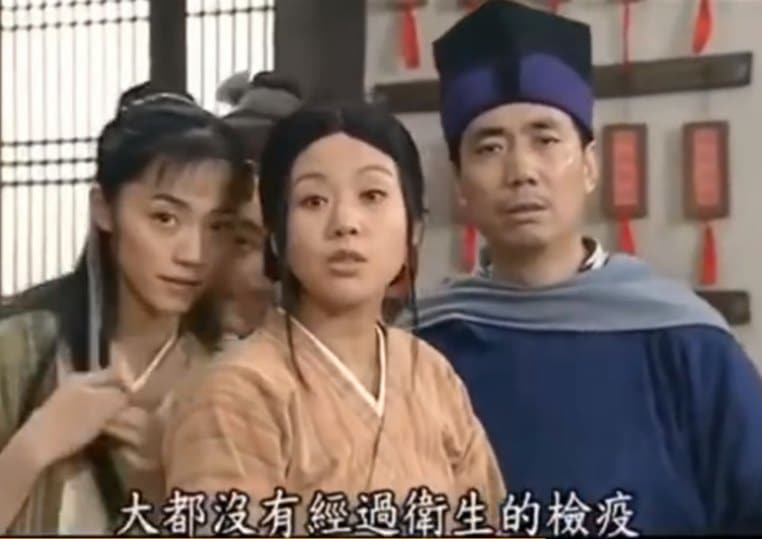

Jay Chou, an ambassador for Wild Aid, took the opportunity to reiterate his opposition to eating wild animals, and to repost his video discouraging the consumption of pangolin, highlighting the risk of disease transmission.

Perhaps the Wuhan Coronavirus will lead to a broader sea change among the Chinese population and their views towards – and tolerance of – the trafficking and consumption of wild animals.
By Jessica Colwell
Follow @whatsonweibo
With contributions from Miranda Barnes
Read more articles by Jessica Colwell here.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2020 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Jessica Colwell is a freelance writer currently living in Hong Kong. She is a former editor of Shanghaiist and has lived and worked in China since 2009. She has a love for everything Chinese internet and a soft spot for televised galas and Chinese pageantry.

China and Covid19
Sick Kids, Worried Parents, Overcrowded Hospitals: China’s Peak Flu Season on the Way
“Besides Mycoplasma infections, cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
Published
8 months agoon
November 22, 2023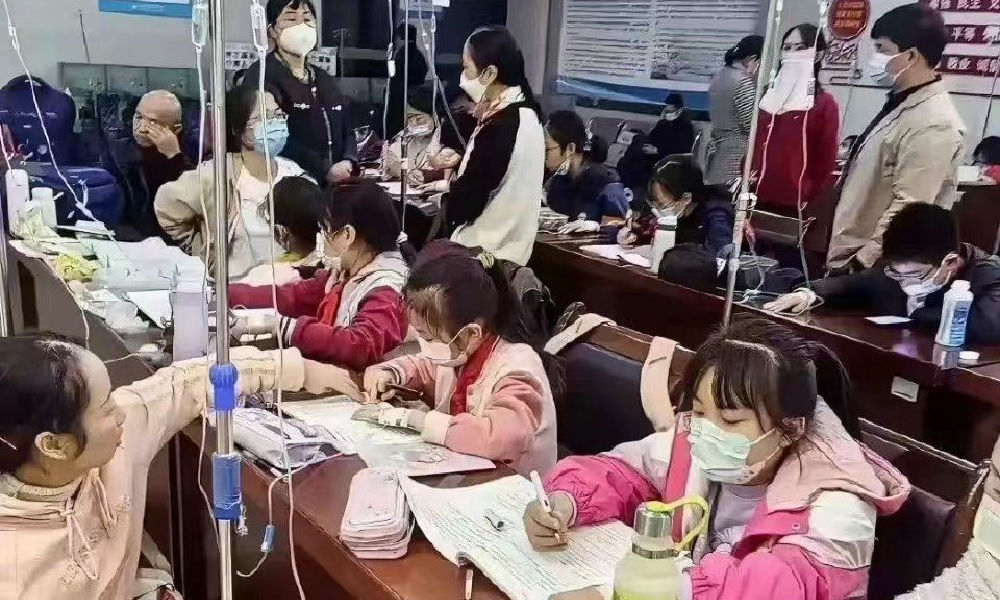
In the early morning of November 21, parents are already queuing up at Xi’an Children’s Hospital with their sons and daughters. It’s not even the line for a doctor’s appointment, but rather for the removal of IV needles.
The scene was captured in a recent video, only one among many videos and images that have been making their rounds on Chinese social media these days (#凌晨的儿童医院拔针也要排队#).

One photo shows a bulletin board at a local hospital warning parents that over 700 patients are waiting in line, estimating a waiting time of more than 13 hours to see a doctor.

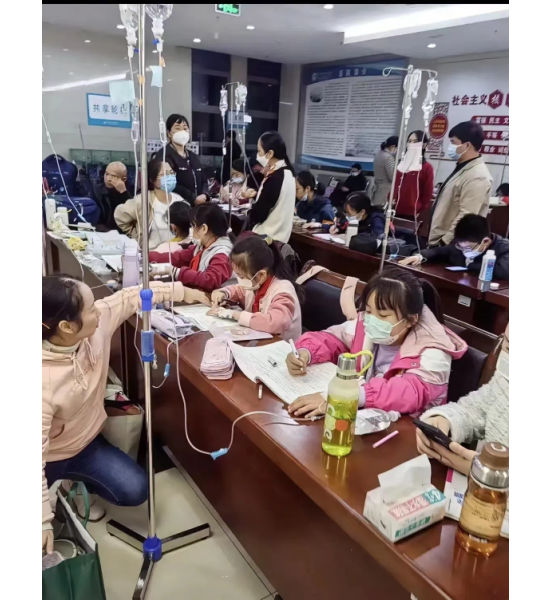
Another image shows children doing their homework while hooked up on an IV.

Recent discussions on Chinese social media platforms have highlighted a notable surge in flu cases. The ongoing flu season is particularly impacting children, with multiple viruses concurrently circulating and contributing to a high incidence of respiratory infections.
Among the prevalent respiratory infections affecting children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, influenza, and Adenovirus infection.
The spike in flu cases has resulted in overcrowded children’s hospitals in Beijing and other Chinese cities. Parents sometimes have to wait in line for hours to get an appointment or pick up medication.
According to one reporter at Haibao News (海报新闻), there were so many patients at the Children’s Hospital of Capital Institute of Pediatrics (首都儿科研究所) on November 21st that the outpatient desk stopped accepting new patients by the afternoon. Meanwhile, 628 people were waiting in line to see a doctor at the emergency department.
Reflecting on the past few years, the current flu season marks China’s first ‘normal’ flu peak season since the outbreak of Covid-19 in late 2019 / early 2020 and the end of its stringent zero-Covid policies in December 2022. Compared to many other countries, wearing masks was also commonplace for much longer following the relaxation of Covid policies.
Hu Xijin, the well-known political commentator, noted on Weibo that this year’s flu season seems to be far worse than that of the years before. He also shared that his own granddaughter was suffering from a 40 degrees fever.
“We’re all running a fever in our home. But I didn’t dare to go to the hospital today, although I want my child to go to the hospital tomorrow. I heard waiting times are up to five hours now,” one Weibo user wrote.
“Half of the kids in my child’s class are sick now. The hospital is overflowing with people,” another person commented.
One mother described how her 7-year-old child had been running a fever for eight days already. Seeking medical attention on the first day, the initial diagnosis was a cold. As the fever persisted, daily visits to the hospital ensued, involving multiple hours for IV fluid administration.
While this account stems from a single Weibo post within a fever-advice community, it highlights a broader trend: many parents swiftly resort to hospital visits at the first signs of flu or fever. Several factors contribute to this, including a lack of General Practitioners in China, making hospitals the primary choice for medical consultations also in non-urgent cases.
There is also a strong belief in the efficacy of IV infusion therapy, whether fluid-based or containing medication, as the quickest path to recovery. Multiple factors contribute to the widespread and sometimes irrational use of IV infusions in China. Some clinics are profit-driven and see IV infusions as a way to make more money. Widespread expectations among Chinese patients that IV infusions will make them feel better also play a role, along with some physicians’ lacking knowledge of IV therapy or their uncertainty to distinguish bacterial from viral infections (read more here)
To prevent an overwhelming influx of patients to hospitals, Chinese state media, citing specialists, advise parents to seek medical attention at the hospital only for sick infants under three months old displaying clear signs of fever (with or without cough). For older children, it is recommended to consult a doctor if a high fever persists for 3 to 5 days or if there is a deterioration in respiratory symptoms. Children dealing with fever and (mild) respiratory symptoms can otherwise recover at home.
One Weibo blogger (@奶霸知道) warned parents that taking their child straight to the hospital on the first day of them getting sick could actually be a bad idea. They write:
“(..) pediatric departments are already packed with patients, and it’s not just Mycoplasma infections anymore. Cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. And then, of course, those with bad luck are cross-infected with multiple viruses at the same time, leading to endless cycles. Therefore, if your child experiences mild coughing or a slight fever, consider observing at home first. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
The hashtag for “fever” saw over 350 million clicks on Weibo within one day on November 22.
Meanwhile, there are also other ongoing discussions on Weibo surrounding the current flu season. One topic revolves around whether children should continue doing their homework while receiving IV fluids in the hospital. Some hospitals have designated special desks and study areas for children.
Although some commenters commend the hospitals for being so considerate, others also remind the parents not to pressure their kids too much and to let them rest when they are not feeling well.
Opinions vary: although some on Chinese social media say it's very thoughtful for hospitals to set up areas where kids can study and read, others blame parents for pressuring their kids to do homework at the hospital instead of resting when not feeling well. pic.twitter.com/gnQD9tFW2c
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) November 22, 2023
By Manya Koetse, with contributions from Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China and Covid19
Repurposing China’s Abandoned Nucleic Acid Booths: 10 Innovative Transformations
Abandoned nucleic acid booths are getting a second life through these new initiatives.
Published
1 year agoon
May 19, 2023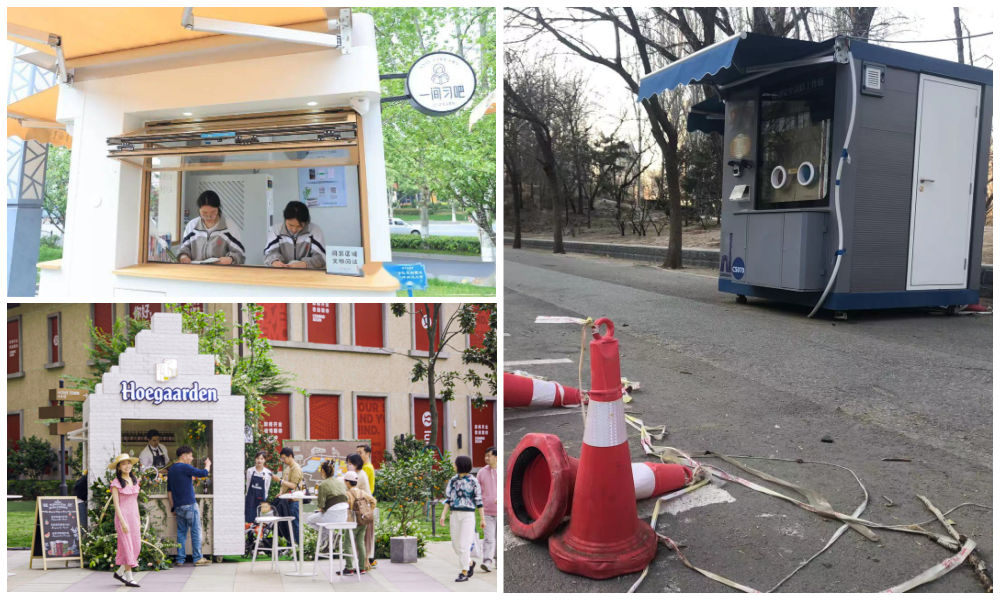
During the pandemic, nucleic acid testing booths in Chinese cities were primarily focused on maintaining physical distance. Now, empty booths are being repurposed to bring people together, serving as new spaces to serve the community and promote social engagement.
Just months ago, nucleic acid testing booths were the most lively spots of some Chinese cities. During the 2022 Shanghai summer, for example, there were massive queues in front of the city’s nucleic acid booths, as people needed a negative PCR test no older than 72 hours for accessing public transport, going to work, or visiting markets and malls.
The word ‘hésuān tíng‘ (核酸亭), nucleic acid booth (also:核酸采样小屋), became a part of China’s pandemic lexicon, just like hésuān dìtú (核酸地图), the nucleic acid test map lauched in May 2022 that would show where you can get a nucleic test.
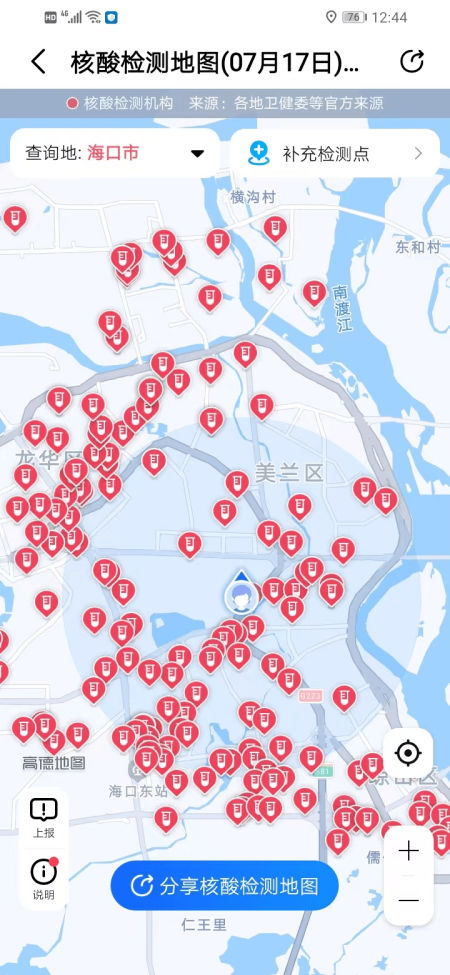
Example of nucleic acid test map.
During Halloween parties in Shanghai in 2022, some people even came dressed up as nucleic test booths – although local authorities could not appreciate the creative costume.

Halloween 2022: dressed up as nucliec acid booths. Via @manyapan twitter.
In December 2022, along with the announced changed rules in China’s ‘zero Covid’ approach, nucleic acid booths were suddenly left dismantled and empty.
With many cities spending millions to set up these booths in central locations, the question soon arose: what should they do with the abandoned booths?
This question also relates to who actually owns them, since the ownership is mixed. Some booths were purchased by authorities, others were bought by companies, and there are also local communities owning their own testing booths. Depending on the contracts and legal implications, not all booths are able to get a new function or be removed yet (Worker’s Daily).
In Tianjin, a total of 266 nucleic acid booths located in Jinghai District were listed for public acquisition earlier this month, and they were acquired for 4.78 million yuan (US$683.300) by a local food and beverage company which will transform the booths into convenience service points, selling snacks or providing other services.
Tianjin is not the only city where old nucleic acid testing booths are being repurposed. While some booths have been discarded, some companies and/or local governments – in cooperation with local communities – have demonstrated creativity by transforming the booths into new landmarks. Since the start of 2023, different cities and districts across China have already begun to repurpose testing booths. Here, we will explore ten different way in which China’s abandoned nucleic test booths get a second chance at a meaningful existence.
1: Pharmacy/Medical Booths
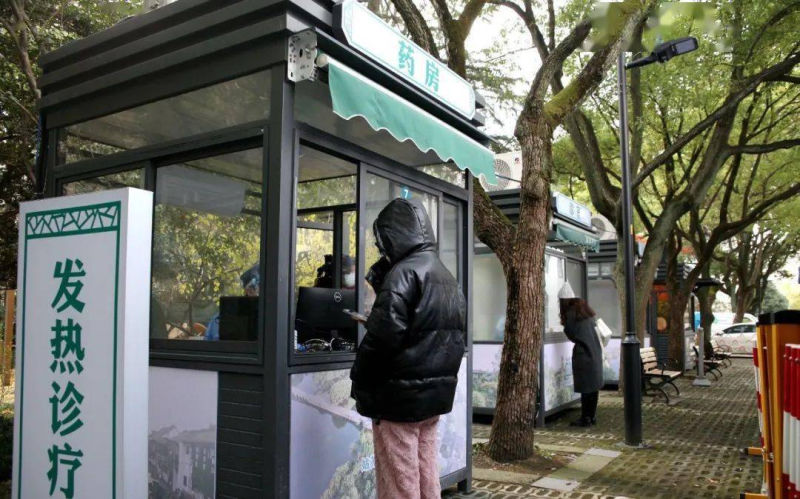

Via ‘copyquan’ republished on Sohu.
Blogger ‘copyquan’ recently explored various ways in which abandoned PCR testing points are being repurposed.
One way in which they are used is as small pharmacies or as medical service points for local residents (居民医疗点). Alleviating the strain on hospitals and pharmacies, this was one of the earliest ways in which the booths were repurposed back in December of 2022 and January of 2023.
Chongqing, Tianjin, and Suzhou were among earlier cities where some testing booths were transformed into convenient medical facilities.
2: Market Stalls
In Suzhou, Jiangsu province, the local government transformed vacant nucleic acid booths into market stalls for the Spring Festival in January 2022, offering them free of charge to businesses to sell local products, snacks, and traditional New Year goods.
The idea was not just meant as a way for small businesses to conveniently sell to local residents, it was also meant as a way to attract more shoppers and promote other businesses in the neighborhood.
3: Community Service Center
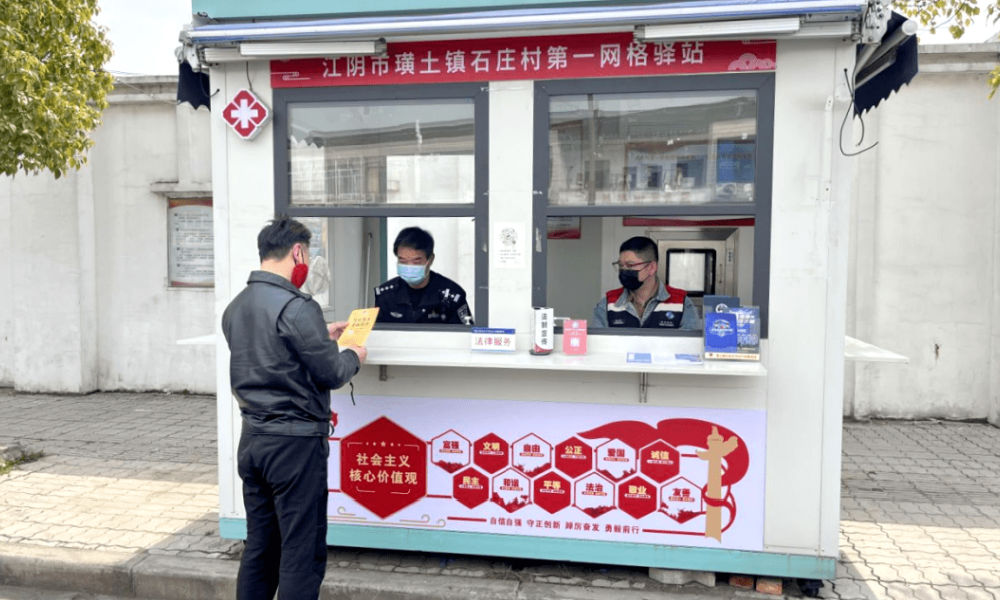

Small grid community center in Shizhuang Village, image via Sohu.
Some residential areas have transformed their local nucleic acid testing booths into community service centers, offering all kinds of convenient services to neighborhood residents.
These little station are called wǎnggé yìzhàn (网格驿站) or “grid service stations,” and they can serve as small community centers where residents can get various kinds of care and support.
4: “Refuel” Stations
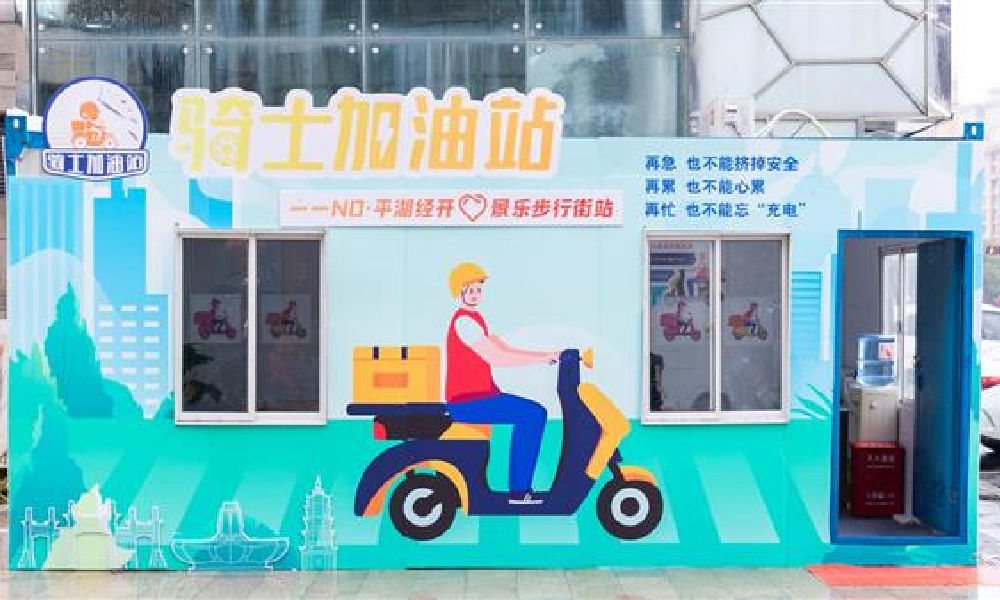

In February of this year, 100 idle nucleic acid sampling booths were transformed into so-called “Rider Refuel Stations” (骑士加油站) in Zhejiang’s Pinghu. Although it initially sounds like a place where delivery riders can fill up their fuel tanks, it is actually meant as a place where they themselves can recharge.
Delivery riders and other outdoor workers can come to the ‘refuel’ station to drink some water or tea, warm their hands, warm up some food and take a quick nap.
5: Free Libraries
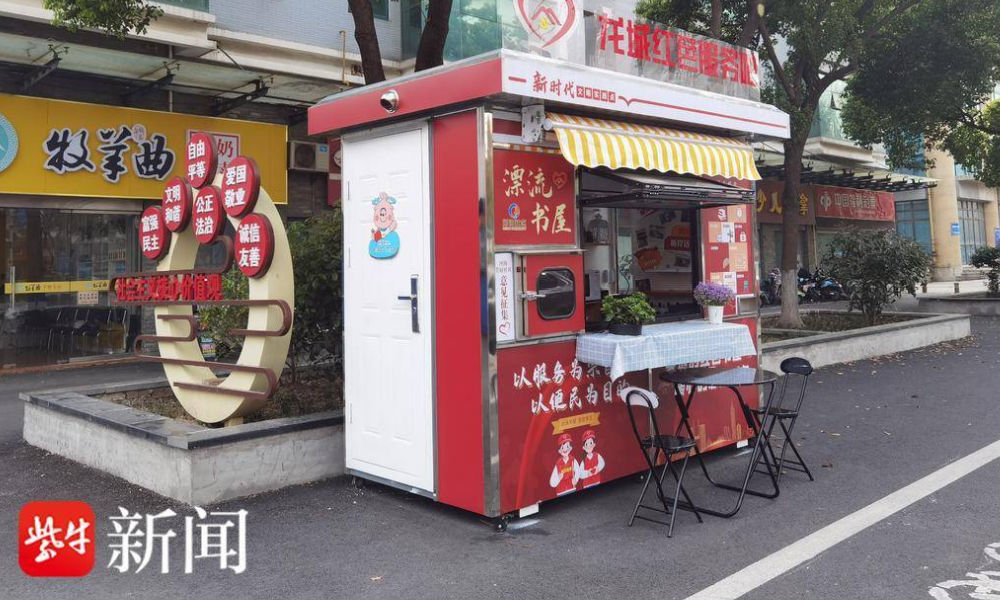

image via sohu.
In various Chinese cities, abandoned nucleic acid booths have been transformed into little free libraries where people can grab some books to read, donate or return other books, and sit down for some reading.
Changzhou is one of the places where you’ll find such “drifting bookstores” (漂流书屋) (see video), but similar initiatives have also been launched in other places, including Suzhou.
6: Study Space
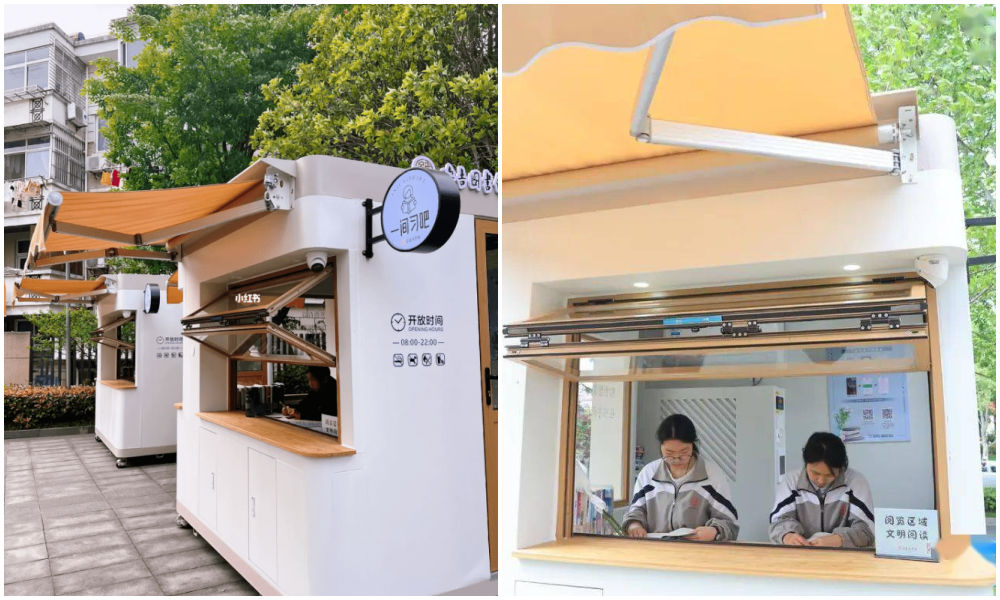

Photos via Copyquan’s article on Sohu.
Another innovative way in which old testing points are being repurposed is by turning them into places where students can sit together to study. The so-called “Let’s Study Space” (一间习吧), fully airconditioned, are opened from 8 in the morning until 22:00 at night.
Students – or any citizens who would like a nice place to study – can make online reservations with their ID cards and scan a QR code to enter the study rooms.
There are currently ten study booths in Anji, and the popular project is an initiative by the Anji County Library in Zhejiang (see video).
7: Beer Kiosk
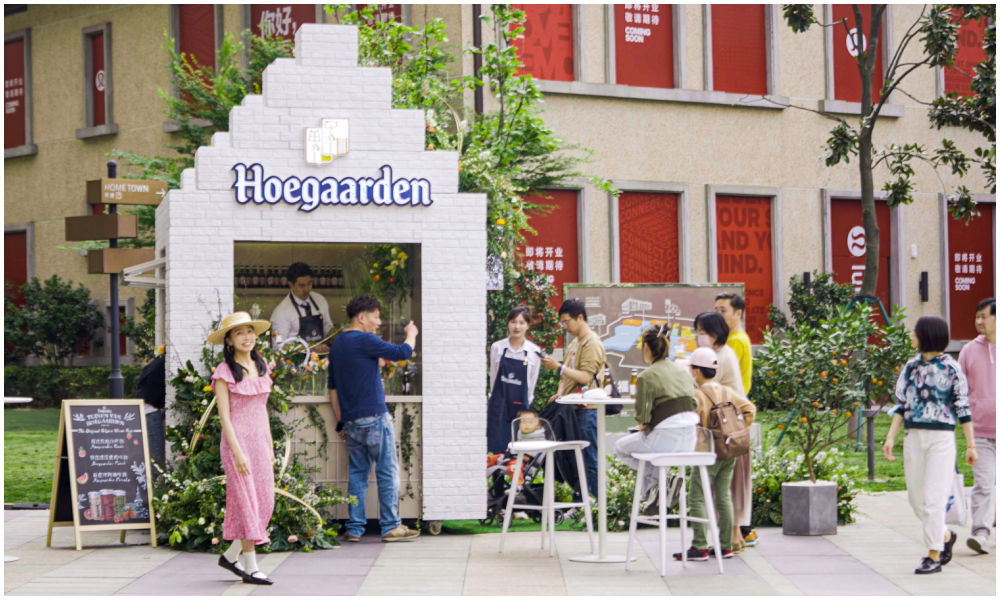

Hoegaarden beer shop, image via Creative Adquan.
Changing an old nucleic acid testing booth into a beer bar is a marketing initiative by the Shanghai McCann ad agency for the Belgium beer brand Hoegaarden.
The idea behind the bar is to celebrate a new spring after the pandemic. The ad agency has revamped a total of six formr nucleic acid booths into small Hoegaarden ‘beer gardens.’
8: Police Box
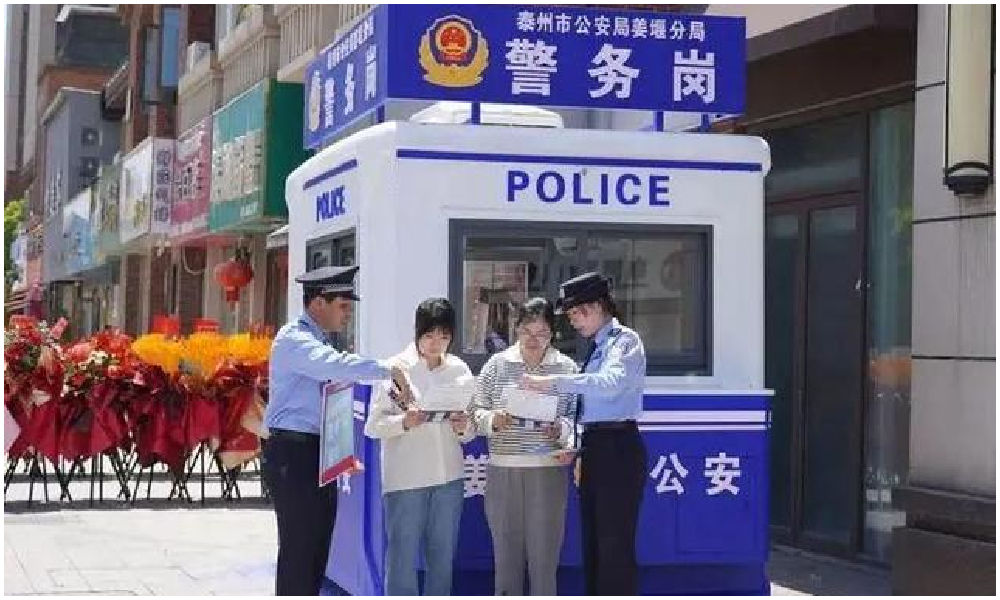

In Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province, authorities have repurposed old testing booths and transformed them into ‘police boxes’ (警务岗亭) to enhance security and improve the visibility of city police among the public.
Currently, a total of eight vacant nucleic acid booths have been renovated into modern police stations, serving as key points for police presence and interaction with the community.
9: Lottery Ticket Booths
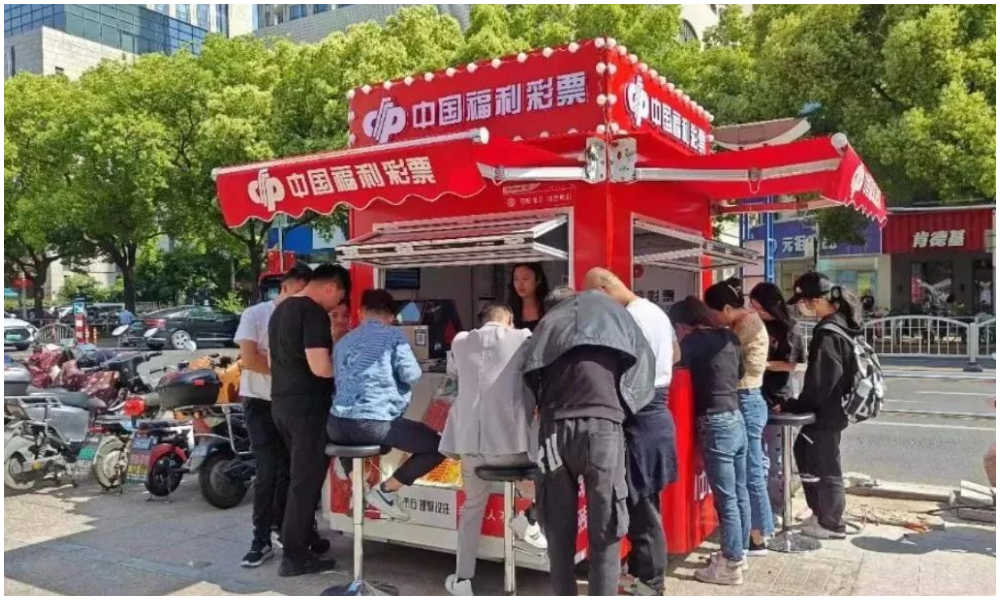

Image via The Paper
Some nucleic acid booths have now been turned into small shops selling lottery tickets for the China Welfare Lottery. One such place turning the kiosks into lottery shops is Songjiang in Shanghai.
Using the booths like this is a win-win situation: they are placed in central locations so it is more convenient for locals to get their lottery tickets, and on the other hand, the sales also help the community, as the profits are used for welfare projects, including care for the elderly.
10: Mini Fire Stations
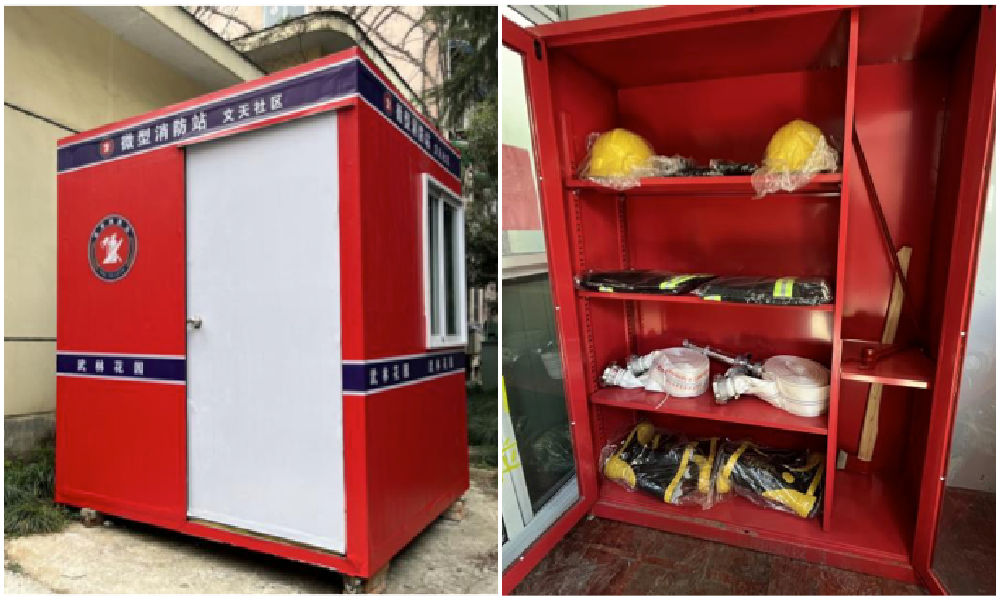

Micro fire stations, images via ZjNews.
Some communities decided that it would be useful to repurpose the testing points and turn them into mini fire kiosks, just allowing enough space for the necessary equipment to quickly respond to fire emergencies.
Want to read more about the end of ‘zero Covid’ in China? Check our other articles here.
By Manya Koetse,
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?






John Wang
February 6, 2020 at 10:49 am
Hello Jessica,
great article and good collection of stories. Corona is the only topic of social media this Chinese new year… the only topic, start to be boring for people to stay at home.
I was hoping to start to work to think something else