China Insight
Pregnancy Discrimination in the Workplace: Three Major Problems Faced by Chinese Female Workers
Weibo discussions about a woman from Wuhan who was fired after sharing news of her pregnancy for “inability” to do her job.
Published
1 year agoon
By
Zilan Qian
Workplace pregnancy and maternity discrimination is a deep-rooted problem that has recently triggered online discussions in China, where netizens highlight common ways in which companies still try to avoid dealing with pregnant workers.
The official Weibo account of Legal Daily (法治日报), a Chinese state-owned newspaper, recently launched a social media hashtag about employers not being allowed to terminate female employees because they are pregnant (#不得因怀孕辞退女职工#).
Legal Daily reported that a female employee in Wuhan was fired from her job due to her pregnancy earlier this year (#武汉一女子怀孕后遭公司辞退#). After returning to work after the Spring Festival break, the woman informed the company about her pregnancy. In early February, the company asked her to accept a demotion and salary reduction, which she declined. Later that month, she received a termination letter from the company, stating that the employee was being terminated due to her “inability to do her job.”

A screenshot of a video posted on Weibo reporting the news about the female Wuhan employee terminated from her job because of her pregnancy. In the video, the woman disagreed with the company’s statement that she could not perform her duties.
Legal Daily‘s Weibo account cited Article 5 of the “Special Provisions on Labor Protection for Female Employees,” which prohibits employers from reducing the wages of female employees or terminating their employment contract due to them being pregnant, giving birth, or breastfeeding. It also stipulates a basic maternity leave of 98 days.
The female employee in question is currently suing the company for terminating her job. While this case may have a positive outcome, the issue of workplace discrimination against female employees due to pregnancy is more complicated than it appears, regardless of the Chinese laws designed to protect female workers.
Despite legal prohibitions against pregnancy discrimination in employment, some employers still circumvent the rules in various ways and in doing so, continue to engage in discrimination against female workers. This topic has recently also generated discussions on Chinese social media about the problems women face in the workplace.
Problem #1: Companies Not Hiring Female Workers At All
“It [the law] is not very useful,” one Weibo user wrote under the related hashtag: “Companies do not usually fire female workers who are pregnant. They will solve the problem from the beginning by not hiring female workers at all.”
Some smaller private companies do not want to take the risk of dealing with potentially prolonged maternity leave and pregnant workers that they cannot fire nor reduce their wages.
They also fear that workers who are pregnant or are taking care of young children will have reduced energy and might face challenges in the workplace. To avoid the presumed risk that comes with hiring a female worker, Weibo commenters discuss how many companies would “rather hire men directly” to evade the issue of dealing with pregnant workers altogether.

Weibo users commenting that small companies would rather hire men than afford the potential cost of female workers’ maternity leave.
Some voices note how female job-seekers are facing gender discrimination in hiring, regardless of their marital status or the number of children they have.
Another post under the same hashtag (#不得因怀孕辞退女职工#) mentioned:
“It is so hard for females to find jobs. [From the company’s perspective:] 1. Unmarried female: they’re here for the marriage leave; 2. Married but no children yet: they’re here for the pregnancy leave; 3. Married and have one child: here to have their second child (and the maternity leave); 4. Married and have two children: here to have their third child (and the maternity leave); 5. Married and have three children: they have no time for work because need to take care of the family; 6. Do not want to marry: they are having problematic thoughts [思想有问题].”
Problem #2: Going to Extremes to Avoid Paying for Maternity Leave
Despite Chinse labor law prohibiting companies from reducing wages or terminating the contracts of pregnant employees, some companies still attempt to circumvent paying for maternity leave through various means, as was the case with the Wuhan company.
One extreme way to avoid dealing with maternity leave pay is to cancel the company’s registration altogether, which is also called “dying together” (“同归于尽”, also: “to perish together with one’s foe”).
A recent news story about a boss who canceled his company’s registration overnight due to a female employee’s pregnancy received widespread attention on the internet.
According to a March 5 report by Netease (网易), the woman informed her boss that she was three months pregnant right after signing her work contract. The boss was so afraid of the potential costs for maternity leave pay and other benefits that he decided to immediately cancel the company’s registration.
While the boss claimed that the cancellation was due to the fact that the company was operating at a loss for the past two years, he reportedly spoke with each employee and compensated them accordingly. However, the pregnant female employee in question refused to leave. After the cancellation, the boss formed a new company including all the former employees – except for the pregnant one.
While some netizens expressed concerns over the extreme actions of the company, others also blamed the woman for “blackmailing” the company into supporting her pregnancy and childbirth. Additionally, many netizens argued that the woman’s actions also make it more difficult for other job-seeking females to find employment, especially with small companies that may become more cautious about hiring female workers.
Problem #3: Maternity Harassment on the Workfloor
“Dying together” is not the only way for companies to get rid of “troublesome” pregnant workers. There are many other low-cost ways to avoid dealing with pregnant employees and working mothers, such as making life in the workplace so difficult for them that they will voluntarily resign.
In Chinese, this kind of ‘maternity harassment’ is also called “chuān xiǎo xié” (穿小鞋), which literally means giving someone tight shoes to wear and making them uncomfortable. The phenomenon is also widespread in Japan, where the word ‘matahara‘ was coined as an abbreviated form of the words ‘maternity’ and ‘harassment’ to describe the unfair treatment of pregnant women and young mothers in the workforce.

Image showing Chinese comedian Papi Jiang talking about women in the workplace being afraid to get pregnant as it might cost them their career.
By pushing employees to resign voluntarily, the company not only saves on the costs of female workers’ maternity leave pay but also avoids paying for a severance package.
Under the report by Jingshi Live-Streaming (经视直播) about the woman in Wuhan who was fired from her job due to her pregnancy, one Weibo user commented that many companies fire female workers who are pregnant, but they usually do not state it upfront and instead secretly force them to leave.
This comment received over 1500 likes, with many sharing their own similar experiences. One person wrote: “I was in that situation. The company explicitly persuaded me to resign and covertly marginalized me.”
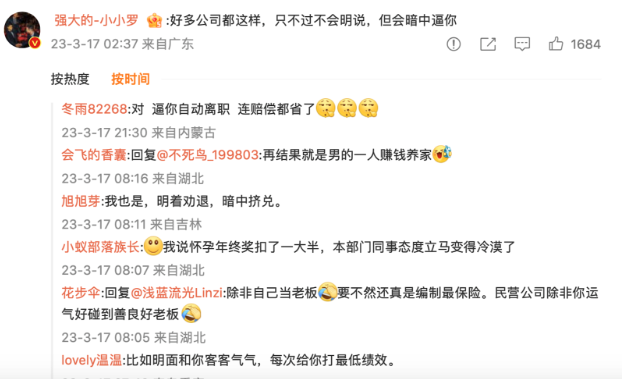
Weibo users sharing their experiences of being forced to “voluntarily resign.”
Another person shared: “After I announced my pregnancy, my year-end bonus was reduced by more than half, and my colleagues immediately treated me with coldness.” One woman mentioned that “companies overtly use polite language while covertly giving the lowest performance evaluation to force employees to resign.”
One Weibo user complained about how female workers first face nagging questions about their future plans to have children, then face criticism from employees and colleagues after announcing their pregnancy and then have to worry about getting fired or seeing their salary reduced after giving birth.
No Way Out?
Despite laws and regulations requiring companies to provide maternity leave for female employees, there are still loopholes that are used by businesses to avoid responsibility. This leaves women in a vulnerable position in the workplace and limits economic opportunities. Weibo users come up with several suggestions in recent online discussions on how to solve the problems female workers face.
Some suggest that women should “just be realistic” and settle for a second-best option (“退而求其次”). One Weibo post argued that since it is difficult for women to secure permanent positions in both government institutions and big private companies, they should consider becoming temporary workers in government departments as a secondary option.
Others disagreed with this hot take, stating that the average wages and benefits for temporary workers in government departments are not enough to make a living.
Another suggestion raised to combat pregnancy discrimination is to offer equal parental leave to both men and women. However, this proposal was also met with resistance from some who argued that it does not solve anything since fathers have the option to forgo paternity leave, but women do not have that choice. They also cited examples of male colleagues who voluntarily waived their 15-day paternity leave.
Some are skeptical about finding a solution to the problem of women facing pregnancy discrimination in the workplace, and also raise the issue of this problem decreasing women’s willingness to have babies at all. Some netizens jokingly comment: “Do women need to provide their certificate of sterilization from the hospitals?” or “I suggest females just remove the uterus [as a solution].”
Facing low fertility rates and a large aging population, boosting birthrates is a priority for Chinese authorities. While Chinese experts look for ways to motivate couples to have (more) children at an earlier age, combating pregnancy discrimination in the workplace is also more important than ever.
One Weibo user bitterly joked about the apparent contradiction of boosting national birth rates while also promoting equal positions in the workplace:
“Women say: “If I get pregnant, I will face workplace discrimination.”
The government says: “How dare companies discriminate against women? I will fine them.”
Companies say: “You’re good at playing tricks. I won’t hire women anymore.”
Women say: “If I have a child, I can’t even find a job. I won’t have children in the future.”
Society says: “China is getting old before it gets rich. What should we do?”
The media says: “There is news every day. It’s great!”
By Zilan Qian
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles. Follow us on Twitter here.
◼︎ 同归于尽 Tóng guī yú jìn
Dying together; suffering a downfall together; perishing together with one’s foe
◼︎ 穿小鞋 Chuān xiǎo xié
Giving someone tight shoes to wear; making things hard for someone by abusing one’s power
◼︎ 退而求其次 Tuì ér qíu qí cì
To settle for the second best thing
Images in featured image:
http://www.xinqtech.com/startup/201806/291055.html
https://www.maxlaw.cn/n/20220316/10379852097730.shtml
https://www.maxlaw.cn/n/20180823/923419931554.shtml
https://www.sohu.com/a/325722786_120156585
http://k.sina.com.cn/article_2090512390_7c9ab00602000n007.html
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
Zilan Qian is a China-born undergraduate student at Barnard College majoring in Anthropology. She is interested in exploring different cultural phenomena, loves people-watching, and likes loitering in supermarkets and museums.

China Insight
The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
The story of ‘Fat Cat’ has become a hot topic in China, sparking widespread sympathy and discussions online.
Published
3 months agoon
May 9, 2024
The tragic story behind the recent suicide of a 21-year-old Chinese gamer nicknamed ‘Fat Cat’ has become a major topic of discussion on Chinese social media, touching upon broader societal issues from unfair gender dynamics to businesses taking advantage of grieving internet users.
The story of a 21-year-old Chinese gamer from Hunan who committed suicide has gone completely viral on Weibo and beyond this week, generating many discussions.
In late April of this year, the young man nicknamed ‘Fat Cat’ (胖猫 Pàng Māo, literally fat or chubby cat), tragically ended his life by jumping into the river near the Chongqing Yangtze River Bridge (重庆长江大桥) following a breakup with his girlfriend. By now, the incident has come to be known as the “Fat Cat Jumping Into the River Incident” (胖猫跳江事件).
News of his suicide soon made its rounds on the internet, and some bloggers started looking into what was behind the story. The man’s sister also spoke out through online channels, and numerous chat records between the young man and his girlfriend emerged online.
One aspect of his story that gained traction in early May is the revelation that the man had invested all his resources into the relationship. Allegedly, he made significant financial sacrifices, giving his girlfriend over 510,000 RMB (approximately 71,000 USD) throughout their relationship, in a time frame of two years.
When his girlfriend ended the relationship, despite all of his efforts, he was devastated and took his own life.
The story was picked up by various Chinese media outlets, and prominent social and political commentator Hu Xijin also wrote a post about Fat Cat, stating the sad story had made him tear up.
As the news spread, it sparked a multitude of hashtags on Weibo, with thousands of netizens pouring out their thoughts and emotions in response to the story.
Playing Games for Love
The main part of this story that is triggering online discussions is how ‘Fat Cat,’ a young man who possessed virtually nothing, managed to provide his girlfriend, who was six years older, with such a significant amount of money – and why he was willing to sacrifice so much in order to do so.
The young man reportedly was able to make money by playing video games, specifically by being a so-called ‘booster’ by playing with others and helping them get to a higher level in multiplayer online battle games.
According to his sister, he started working as a ‘professional’ video gamer as a means of generating money to satisfy his girlfriend, who allegedly always demanded more.
He registered a total of 36 accounts to receive orders to play online games, making 20 yuan per game (about $2.80). Because this consumed all of his time, he barely went out anymore and his social life was dead.
In order to save more money, he tried to keep his own expenses as low as possible, and would only get takeout food for himself for no more than 10 yuan ($1,4). His online avatar was an image of a cat saying “I don’t want to eat vegetables, I want to eat McDonald’s.”

The woman in question who he made so many sacrifices for is named Tan Zhu (谭竹), and she soon became the topic of public scrutiny. In one screenshot of a chat conversation between Tan and her boyfriend that leaked online, she claimed she needed money for various things. The two had agreed to get married later in this year.
Despite of this, she still broke up with him, driving him to jump off the bridge after transferring his remaining 66,000 RMB (9135 USD) to Tan Zhu.
As the story fermented online, Tan Zhu also shared her side of the story. She claimed that she had met ‘Fat Cat’ over two years ago through online gaming and had started a long distance relationship with him. They had actually only met up twice before he moved to Chongqing. She emphasized that financial gain was never a motivating factor in their relationship.
Tan additionally asserted that she had previously repaid 130,000 RMB (18,000 USD) to him and that they had reached a settlement agreement shortly before his tragic death.
Ordering Take-Out to Mourn Fat Cat
– “I hope you rest in peace.”
– “Little fat cat, I hope you’ll be less foolish in your next life.”
– “In your next life, love yourself first.”
These are just a few of the messages left by netizens on notes attached to takeout food deliveries near the Chongqing Yangtze River Bridge.

AI-generated image spread on Chinese social media in connection to the event.
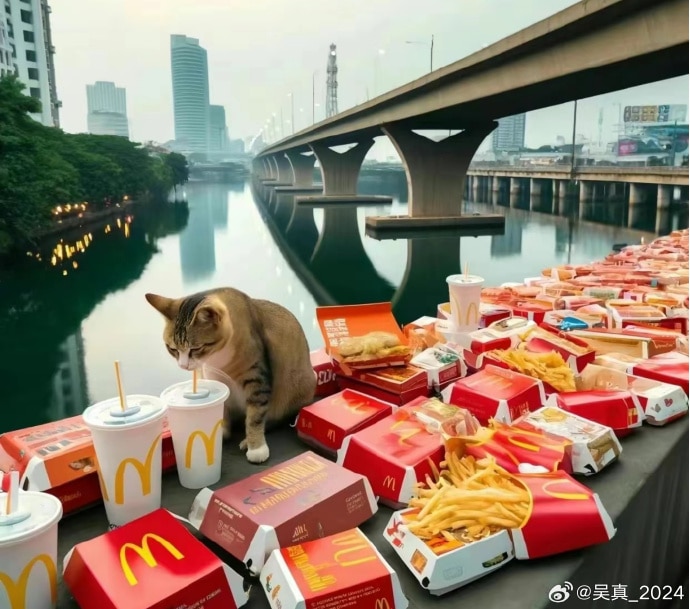
As Fat Cat’s story stirred up significant online discussion, with many expressing sympathy for the young man who rarely indulged in spending on food and drinks, some internet users took the step of ordering McDonalds and other food delivery services to the bridge, where he tragically jumped from, in his honor.
This soon snowballed into more people ordering food and drinks to the bridge, resulting in a constant flow of delivery staff and a pile-up of take-out bags.

Delivery food on the bridge, photo via Weibo.
However, as the food delivery efforts picked up pace, it came to light that some of the deliveries ordered and paid for were either empty or contained something different; certain restaurants, aware of the collective effort to honor the young man, deliberately left the food boxes empty or substituted sodas or tea with tap water.
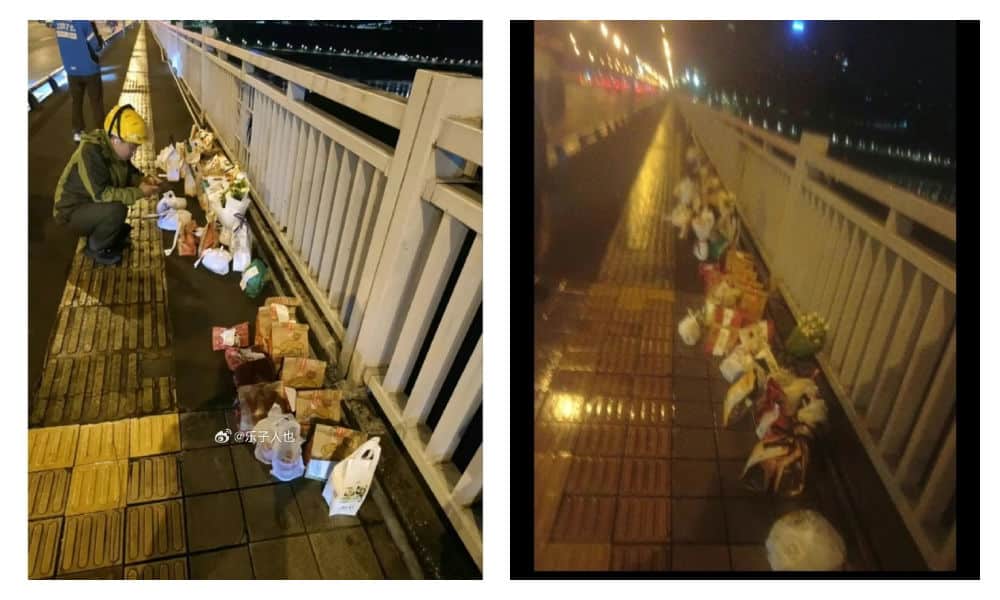

At least five restaurants were caught not delivering the actual orders. Chinese bubble tea shop ChaPanda was exposed for substituting water for milk tea in their cups. On May 3rd, ChaPanda responded that they had fired the responsible employee.
Another store, the Zhu Xiaoxiao Luosifen (朱小小螺蛳粉), responded on that they had temporarily closed the shop in question to deal with the issue. Chinese fast food chain NewYobo (牛约堡) also acknowledged that at least twenty orders they received were incomplete.
Fast food company Wallace (华莱士) responded to the controversy by stating they had dismissed the employees involved. Mixue Ice Cream & Tea (蜜雪冰城) issued an apology and temporarily closed one of their stores implicated in delivering empty orders.
In the midst of all the controversy, Fat Cat’s sister asked internet users to refrain from ordering take-out food as a means of mourning and honoring her brother.
Nevertheless, take-out food and flowers continued to accumulate near the bridge, prompting local authorities to think of ways of how to deal with this unique method of honoring the deceased gamer.
Gamer Boy Meets Girl
On Chinese social media, this story has also become a topic of debate in the context of gender dynamics and social inequality.
There are some male bloggers who are angry with Tan Zhu, suggesting her behaviour is an example of everything that’s supposedly “wrong” with Chinese women in this day and age.
Others place blame on Fat Cat for believing that he could buy love and maintain a relationship through financial means. This irked some feminist bloggers, who see it as a chauvinistic attitude towards women.
A main, recurring idea in these discussions is that young Chinese men such as Fat Cat, who are at the low end of the social ladder, are actually particularly vulnerable in a fiercely competitive society. Here, a gender imbalance and surplus of unmarried men make it easier for women to potentially exploit those desperate for companionship.
The story of Fat Cat brings back memories of ‘Mo Cha Official,’ a not-so-famous blogger who gained posthumous fame in 2021 when details of his unhappy life surfaced online.
Likewise, the tragic tale of WePhone founder Su Xiangmao (苏享茂) resurfaces. In 2017, the 37-year-old IT entrepreneur from Beijing took his own life, leaving behind a note alleging blackmail by his 29-year-old ex-wife, who demanded 10 million RMB (±1.5 million USD) (read story).
Another aspect of this viral story that is mentioned by netizens is how it gained so much attention during the Chinese May holidays, coinciding with the tragic news of the southern China highway collapse in Guangdong. That major incident resulted in the deaths of at least 48 people, and triggered questions over road safety and flawed construction designs. Some speculate that the prominence given to the Fat Cat story on trending topic lists may have been a deliberate attempt to divert attention away from this incident.
‘Fat Cat’ was cremated. His family stated their intention to take necessary legal steps to recover the money from his former girlfriend, but Tan Zhu reportedly already reached an agreement with the father and settled the case. Nevertheless, the case continues to generate discussions online, with some people wondering: “Is it over yet? Can we talk about something different now?”

Fat Cat images projected in Times Square
However, given that images of the ‘Fat Cat’ avatar have even appeared in Times Square in New York by now (Chinese internet users projected it on one of the big LED screens), it’s likely that this story will be remembered and talked about for some time to come.
UPDATE MAY 25
On May 20, local authorities issued a lengthy report to clarify the timeline of events and details surrounding the death of “Fat Cat,” which had attracted significant attention across China.
The report concluded that there was no fraud involved and that “Fat Cat” and his girlfriend were in a genuine relationship. Tan did not deceive “Fat Cat” for money; the transfers were voluntary. Furthermore, Tan returned most of the money to his parents.
The gamer’s sister is reportedly still being investigated for potentially infringing on Tan’s privacy by disclosing numerous private details to the public.
In the end, one thing is clear in this gamer’s tragic story, which is that there are no winners.
By Manya Koetse
– With contributions by Miranda Barnes and Ruixin Zhang
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea
Chinese tea brand LELECHA faced backlash for using the iconic literary figure Lu Xun to promote their “Smoky Oolong” milk tea, sparking controversy over the exploitation of his legacy.
Published
3 months agoon
May 3, 2024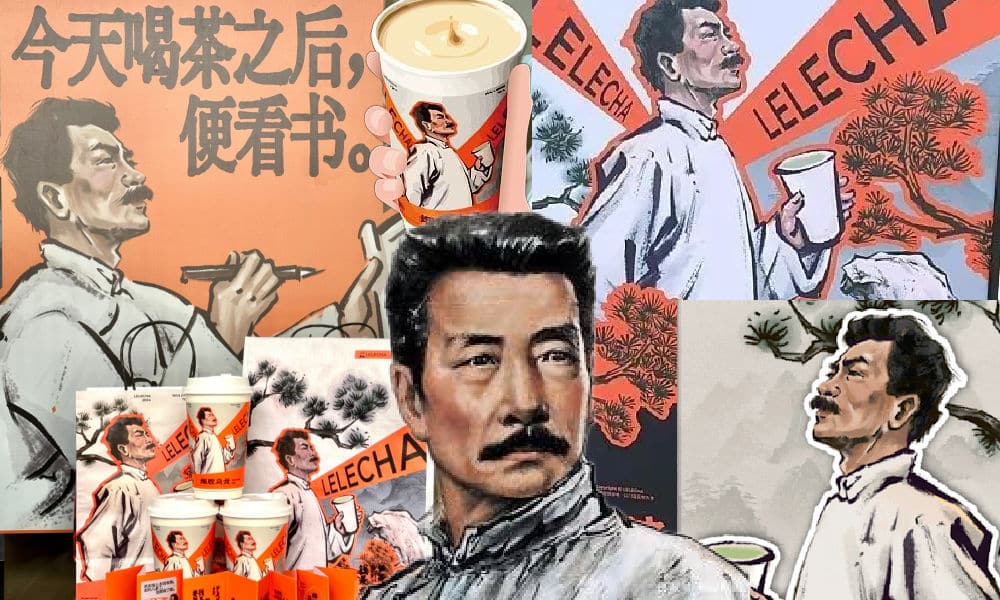
It seemed like such a good idea. For this year’s World Book Day, Chinese tea brand LELECHA (乐乐茶) put a spotlight on Lu Xun (鲁迅, 1881-1936), one of the most celebrated Chinese authors the 20th century and turned him into the the ‘brand ambassador’ of their special new “Smoky Oolong” (烟腔乌龙) milk tea.
LELECHA is a Chinese chain specializing in new-style tea beverages, including bubble tea and fruit tea. It debuted in Shanghai in 2016, and since then, it has expanded rapidly, opening dozens of new stores not only in Shanghai but also in other major cities across China.
Starting on April 23, not only did the LELECHA ‘Smoky Oolong” paper cups feature Lu Xun’s portrait, but also other promotional materials by LELECHA, such as menus and paper bags, accompanied by the slogan: “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” (“老烟腔,新青年”). The marketing campaign was a joint collaboration between LELECHA and publishing house Yilin Press.

Lu Xun featured on LELECHA products, image via Netease.
The slogan “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” is a play on the Chinese magazine ‘New Youth’ or ‘La Jeunesse’ (新青年), the influential literary magazine in which Lu’s famous short story, “Diary of a Madman,” was published in 1918.
The design of the tea featuring Lu Xun’s image, its colors, and painting style also pay homage to the era in which Lu Xun rose to prominence.
Lu Xun (pen name of Zhou Shuren) was a leading figure within China’s May Fourth Movement. The May Fourth Movement (1915-24) is also referred to as the Chinese Enlightenment or the Chinese Renaissance. It was the cultural revolution brought about by the political demonstrations on the fourth of May 1919 when citizens and students in Beijing paraded the streets to protest decisions made at the post-World War I Versailles Conference and called for the destruction of traditional culture[1].
In this historical context, Lu Xun emerged as a significant cultural figure, renowned for his critical and enlightened perspectives on Chinese society.
To this day, Lu Xun remains a highly respected figure. In the post-Mao era, some critics felt that Lu Xun was actually revered a bit too much, and called for efforts to ‘demystify’ him. In 1979, for example, writer Mao Dun called for a halt to the movement to turn Lu Xun into “a god-like figure”[2].
Perhaps LELECHA’s marketing team figured they could not go wrong by creating a milk tea product around China’s beloved Lu Xun. But for various reasons, the marketing campaign backfired, landing LELECHA in hot water. The topic went trending on Chinese social media, where many criticized the tea company.
Commodification of ‘Marxist’ Lu Xun
The first issue with LELECHA’s Lu Xun campaign is a legal one. It seems the tea chain used Lu Xun’s portrait without permission. Zhou Lingfei, Lu Xun’s great-grandson and president of the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation, quickly demanded an end to the unauthorized use of Lu Xun’s image on tea cups and other merchandise. He even hired a law firm to take legal action against the campaign.
Others noted that the image of Lu Xun that was used by LELECHA resembled a famous painting of Lu Xun by Yang Zhiguang (杨之光), potentially also infringing on Yang’s copyright.
But there are more reasons why people online are upset about the Lu Xun x LELECHA marketing campaign. One is how the use of the word “smoky” is seen as disrespectful towards Lu Xun. Lu Xun was known for his heavy smoking, which ultimately contributed to his early death.
It’s also ironic that Lu Xun, widely seen as a Marxist, is being used as a ‘brand ambassador’ for a commercial tea brand. This exploits Lu Xun’s image for profit, turning his legacy into a commodity with the ‘smoky oolong’ tea and related merchandise.
“Such blatant commercialization of Lu Xun, is there no bottom limit anymore?”, one Weibo user wrote. Another person commented: “If Lu Xun were still alive and knew he had become a tool for capitalists to make money, he’d probably scold you in an article. ”
On April 29, LELECHA finally issued an apology to Lu Xun’s relatives and the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation for neglecting the legal aspects of their marketing campaign. They claimed it was meant to promote reading among China’s youth. All Lu Xun materials have now been removed from LELECHA’s stores.

Statement by LELECHA.
On Chinese social media, where the hot tea became a hot potato, opinions on the issue are divided. While many netizens think it is unacceptable to infringe on Lu Xun’s portrait rights like that, there are others who appreciate the merchandise.
The LELECHA controversy is similar to another issue that went trending in late 2023, when the well-known Chinese tea chain HeyTea (喜茶) collaborated with the Jingdezhen Ceramics Museum to release a special ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ (佛喜) latte tea series adorned with Buddha images on the cups, along with other merchandise such as stickers and magnets. The series featured three customized “Buddha’s Happiness” cups modeled on the “Speechless Bodhisattva” (无语菩萨), which soon became popular among netizens.
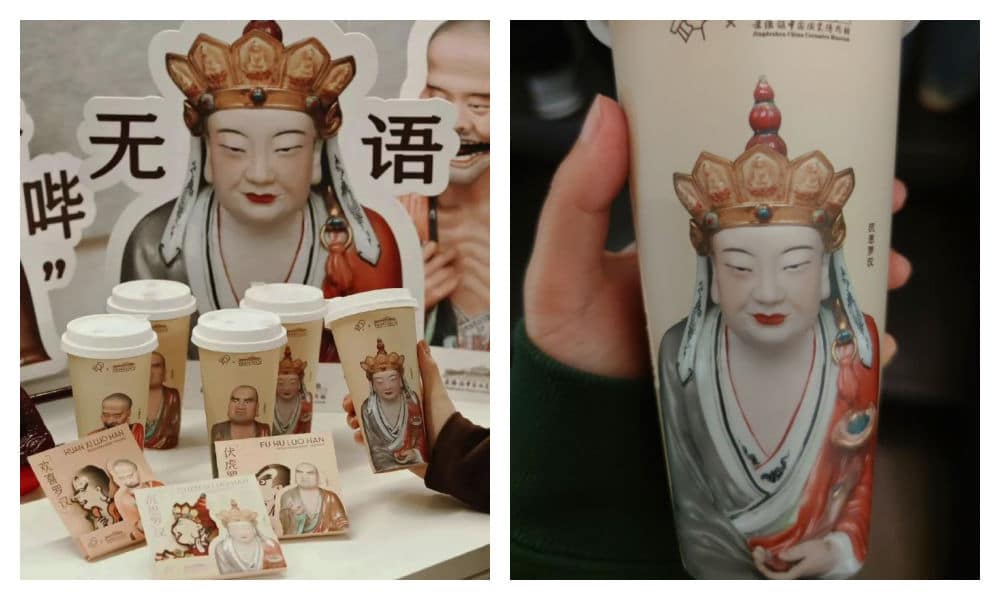

The HeyTea Buddha latte series, including merchandise, was pulled from shelves just three days after its launch.
However, the ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ success came to an abrupt halt when the Ethnic and Religious Affairs Bureau of Shenzhen intervened, citing regulations that prohibit commercial promotion of religion. HeyTea wasted no time challenging the objections made by the Bureau and promptly removed the tea series and all related merchandise from its stores, just three days after its initial launch.
Following the Happy Buddha and Lu Xun milk tea controversies, Chinese tea brands are bound to be more careful in the future when it comes to their collaborative marketing campaigns and whether or not they’re crossing any boundaries.
Some people couldn’t care less if they don’t launch another campaign at all. One Weibo user wrote: “Every day there’s a new collaboration here, another one there, but I’d just prefer a simple cup of tea.”
By Manya Koetse
[1]Schoppa, Keith. 2000. The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. New York: Columbia UP, 159.
[2]Zhong, Xueping. 2010. “Who Is Afraid Of Lu Xun? The Politics Of ‘Debates About Lu Xun’ (鲁迅论争lu Xun Lun Zheng) And The Question Of His Legacy In Post-Revolution China.” In Culture and Social Transformations in Reform Era China, 257–284, 262.
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?






