China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Why Is Want Want So Popular in China? The Remarkable Revival of an Iconic Brand
We explain why the 60-year-old Want Want brand became the ‘hot kid’ on the block on Chinese social media this year.
Published
2 years agoon
By
Tucker Jiang
Want Want – you probably know their rice crackers with the cute kid icon – is celebrating its 60th anniversary this year. How did this decades-old brand become all the rage recently in China? From Pelosi to pickles, there is more to it than nostalgia and its cute ‘Hot Kid’ alone.
Wang Wang (旺旺), better known as ‘Want Want’ in English, has become all the rage in China in recent months. In its September issue, the Chinese magazine China Marketing (销售与市场) listed Want Want as the number one brand on its marketing noticeboard hot brand list, referring to it as “‘Lonely Warrior’ Want Want” (‘孤勇者’旺旺).
The Want Want Group (旺旺集团) is the most well-known rice cracker maker in China and one of the largest food and beverage makers in the region.
Want Want is a brand that many Chinese millennials grew up with. The Taiwanese company behind Want Want has a history that dates back to 1962. After becoming the dominant rice cracker maker in Taiwan with a market share as high as 95%, founder Tsai Eng-meng (蔡衍明) looked across the Strait and officially ventured into the mainland market in 1992.
Why is the Want Want brand still so popular in mainland China today? The brand’s success directly goes back to Tsai Eng-meng, who undeniably is a marketing genius with a peculiar style. The Want Want company icon, officially named Wang Zai (旺仔) in Chinese and ‘Hot Kid’ in English, was created in 1979 and depicts a kid with wide open arms and legs, rolling his eyes (fun fact: Hot Kid never looks straight at you).
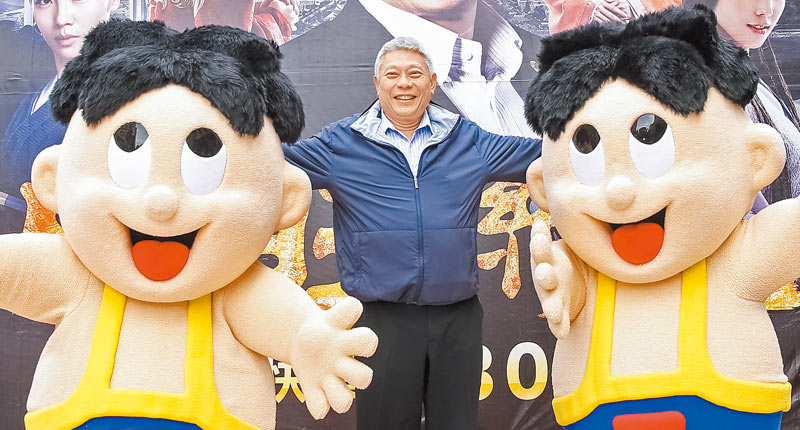

Want Want Group CEO Tsai with the Want Want icon ‘Hot Kid.’ Image via https://turnnewsapp.com/wd/74725.html.
With its catchy name and distinctive icon, Want Want soon became a household brand in China. Adding to the brand’s popularity are the many commercials throughout the years that show the brand’s style, standing out due to their simplicity and fun energy.
Some of these advertising campaigns have become part of the collective popular memory of Chinese millennials. On the Chinese video site Bilibili, old Want Want commercials bring up nostaligc feelings and still receive millions of views today (see this famous one, or see a collection of classic Want Want commercials on Bilibili here).

From one of Want Want’s iconic commercials.
Ingenious strategies brought great success to the company from the start and subsequently ushered in “the golden decade” for Want Want from 2004 to 2013, making Tsai the richest man in Taiwan for three consecutive years.
Apart from Want Want’s signature rice cracker products, products such as Hot Kid Milk (旺仔牛奶), Lonely God Potato Chips (浪味仙), and QQ Gummies (旺仔QQ糖) also became household names in the mainland.
However, facing more competition and failing to keep up with Chinese customers’ evolving consumption habits and preferences, Want Want was stuck in a bottleneck period and its sales slowed down after 2014. Its recent comeback and sudden social media success have everything to do with Nancy Pelosi’s controversial Taiwan visit in August of 2021.
A ‘GOOD’ TAIWANESE COMPANY
On July 28, Tsai Wang-Chia (蔡旺家), Tsai Eng-meng’s second son and Want Want’s Chief Operating Officer and executive director, posted three single words on his Weibo account (@Matt旺家): “YOU GO AWAY.”
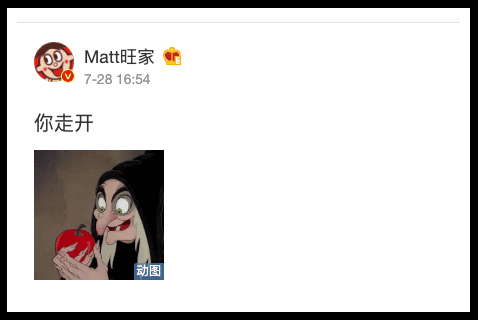
The text was accompanied by a photo of an old witch, which just so happens to be the nickname Chinese netizens gave to Pelosi, and the timing of the post was right when reports about the U.S. House Speaker’s potential Taiwan visit were coming out. Want Want soon became a hot topic afterward.
People had already been paying more attention to Tsai Wang-chia’s Weibo account in light of the then-ongoing calls to boycott Taiwanese companies on Chinese social media following rumors regarding Pelosi’s controversial visit.
Someone claiming to be an employee at Want Want then posted on the popular Red (Xiaohongshu) app, defending Want Want for being a “good Taiwanese company,” asking people to “please don’t hurt us by mistake.” This triggered a public campaign of digging into Tsai’s previous posts, and netizens soon discovered that the Want Want executive director had published similar posts before.
In March of 2022, when a U.S. delegation visited Taiwan, Tsai bluntly posted: “The American pigs have arrived in Taiwan” (“美国猪到台湾了“).
Because of his consistent patriotic and pro-unification stance, coupled with a down-to-earth personality and plain-spoken style despite being an heir of a multibillion dollar family, Tsai Wang-chia soon won the hearts of millions of Chinese netizens.
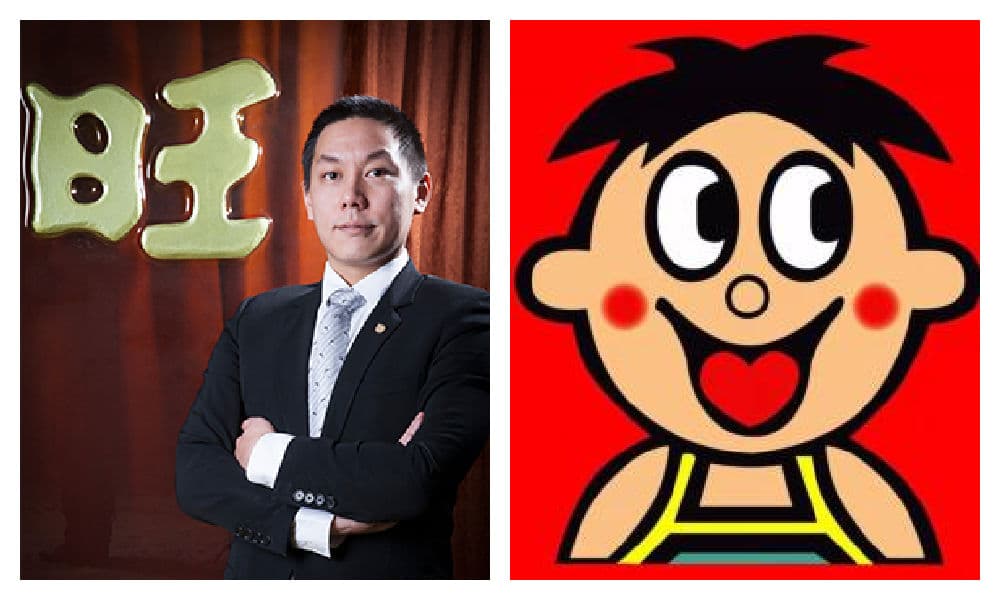

Tsai Wang-Chia (蔡旺家) and ‘Hot Kid’ (旺仔)
The hype got so so big that people started claiming that the figure of Want Want, the iconic Hot Kid, was actually based on Tsai Wang-chia as a child – despite the fact that ‘Hot Kid’ was created in 1979 while Tsai Wang-Chia was born in 1984.
PATRIOTIC ‘PRESIDENT WANT’
Tsai’s pro-unification sentiments seem to run in the family. Want Want founder Tsai Eng-meng, who is also commonly referred to as ‘President Want’ (旺董), has long been a unification supporter. This is also reflected in his business empire, which includes the Want Want China Times Group (旺旺中时媒体集团) that owns dominant pan-Blue (pro-China) media outlets in Taiwan.
Various videos, which soon widely circulated online, also showed ‘President Want’ expressing gratitude for the “great market of the mainland” (“因为有大陆这个伟大的市场,才造就了我旺旺的今天”) and proudly declaring that all Want Want employees are “impressive and dignified Chinese people” (堂堂正正的中国人).
To the delight of many Chinese netizens, more events and incidents showing Want Want’s patriotic stance were brought to light one after another.
The company filed for IPO on the HK Stock Exchange in 2008 with the name “Want Want China Holdings Limited” (中国旺旺控股有限公司); its Want Want Hospital in Hunan (湖南旺旺医院) was among the first private institutions to send a medical aid team to Wuhan during the initial COVID outbreak in the city; in 2019, when a Taiwanese celebrity mockingly said on a local program that “mainlanders cannot afford to eat pickles”, its newspaper Want Daily (旺报) published a conspicuous headline on its August 18 frontpage saying “MAINLANDERS CAN AFFORD TO EAT PICKLES!” (“大陆人吃得起榨菜!”), noting on the side: “Taiwanese are Chinese. We are from the same country and therefore should support each other.” (“台湾人就是中国人. 我们都是同一国的,所以当然要相挺.”)

In early August of this year, Want Want soared to the top of Weibo’s trending list, and netizens swarmed its live stream channel on Taobao, vowing to “consume wildly” (“野性消费”) and “empty their stock” (“清空库存”) in support of the brand.
According to the Time Weekly (时代周报), a government-owned newspaper from Guangzhou, the number of viewers on the channel that day reached almost 100,000 – up to ten times more than what the channel usually received in viewers, – and sales of its online shop spiked as many new customers came in after following the trending hashtag.
THE OTHER SIDE OF THE COIN
In contrast to Want Want’s fervent popularity in mainland China, the brand has become more controversial on the other side of the Taiwan Strait, especially in light of its ownership of multiple leading media outlets, with many expressing worries that its dominant position might impact press freedom.
In June of 2019, a predominantly young mass rallied against so-called “red media” (Taiwanese media in favor of Beijing), with Want Want-owned newspapers (China Times 中国时报 and Want Daily 旺报) and TV channels (China Television 中国电视公司 and CTiTV 中天电视台) being among the main targets.

Protesting against Want Want and other ‘pro-China’ companies in Taiwan, image via https://news.ltn.com.tw/news/life/breakingnews/2859708
The following month, the Financial Times published an article, quoting anonymous journalists working for these outlets, saying that their editorial managers took direct instructions from Beijing’s Taiwan Affairs Office, a claim that the Want Want China Times Group later responded to as “malicious slander.”
In late 2020, the Tsai Ing-wen administration stripped CTiTV of its broadcast license upon renewal out of concerns about editorial interference by President Want Tsai Eng-meng. Such a ruling was a first since the founding of Taiwan’s National Communications Commission in 2006, a government body that regulates the industry, and evoked opposition from the ‘Blue Camp’ and controversy among the public.
SUCCESSFUL ON ALL FRONTS
Despite receiving criticism in Taiwan, Want Want has continued its success in mainland China. This year, Want Want is celebrating the company’s 60th anniversary, as well as the 30th year anniversary of the opening of its first factory in mainland China.
China Marketing wrote about Want Want’s 2022 success that “consistency is key” in marketing. Not only did the brand stick with its original logo and traditional products such as rice crackers and its dairy drink, it has also focused on nostalgic or playful ad campaigns throughout the years (think of its successful slogan “You Want, I Want, Everyone Wants” “你旺、我旺、大家旺.”)
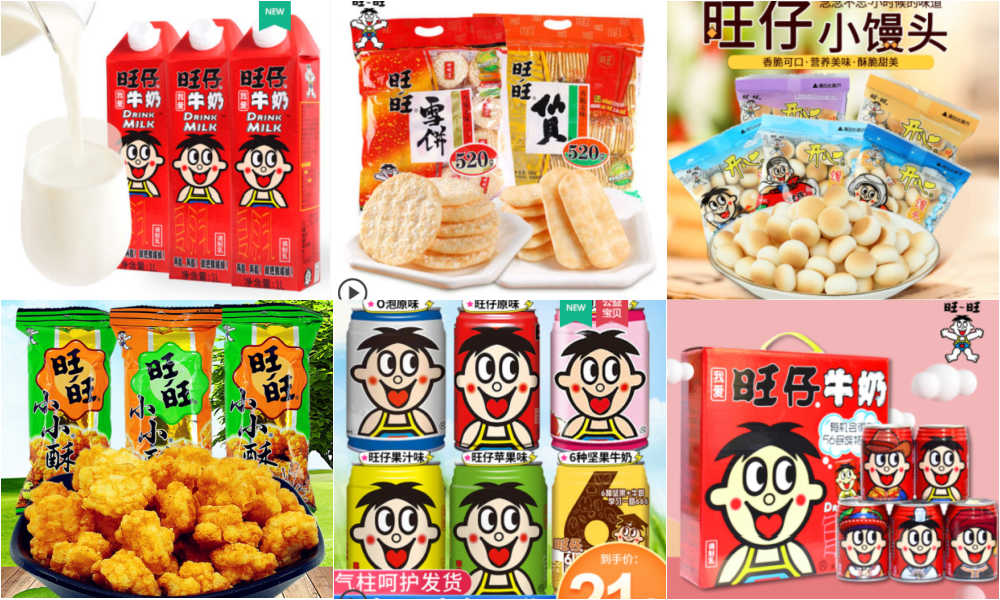

Want Want products for sale on Taobao.
At the same time, the company is not afraid to launch new products and stay active in the world of Chinese social media and e-commerce.
But what has really become an essential point in its regained success this year is the brand’s consistency in delivering a patriotic message through multiple channels that resonated with Chinese consumers at a time of deteriorating US-China relations and more focus on cross-strait relations.
Erke, the Chinese sportswear brand by Hongxing Erke Group (鸿星尔克), was also brought back into the limelight in 2021 after they donated 50 million yuan ($7.7 million) to the Henan flood efforts. When people found out that the relatively low-profile brand donated such a high amount of money to help the people in Henan despite its own losses, its online sales went through the roof – everyone wanted to support this generous ‘patriotic brand.’
While nationalistic consumer sentiments matter, being a ‘patriotic brand’ alone is not enough; it eventually is the combination of being consistent and authentic, delivering popular products, and having a strong marketing campaign. When it comes to the mainland market, Want Want tackled all fronts this year.
In October of 2022, Want Want celebrated China’s National Day by using drones to project netizens’ hopes and wishes for the future all over the Great Wall, including a projection of a giant Want Want drink (#旺旺把爱国刻进了DNA#).

For now, Want Want has practically made ‘loving China’ a part of its brand. Mixing rice crackers with some nationalism is turning out to be a recipe for success – at least in the mainland.
By Tucker Jiang, with contributions by Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our weekly newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Books & Literature
Why Chinese Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Shopping Festival
Bookworms love to get a good deal on books, but when the deals are too good, it can actually harm the publishing industry.
Published
2 months agoon
June 8, 2024By
Ruixin Zhang
JD.com’s 618 shopping festival is driving down book prices to such an extent that it has prompted a boycott by Chinese publishers, who are concerned about the financial sustainability of their industry.
When June begins, promotional campaigns for China’s 618 Online Shopping Festival suddenly appear everywhere—it’s hard to ignore.
The 618 Festival is a product of China’s booming e-commerce culture. Taking place annually on June 18th, it is China’s largest mid-year shopping carnival. While Alibaba’s “Singles’ Day” shopping festival has been taking place on November 11th since 2009, the 618 Festival was launched by another Chinese e-commerce giant, JD.com (京东), to celebrate the company’s anniversary, boost its sales, and increase its brand value.
By now, other e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and Pinduoduo have joined the 618 Festival, and it has turned into another major nationwide shopping spree event.
For many book lovers in China, 618 has become the perfect opportunity to stock up on books. In previous years, e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Dangdang (当当) would roll out tempting offers during the festival, such as “300 RMB ($41) off for every 500 RMB ($69) spent” or “50 RMB ($7) off for every 100 RMB ($13.8) spent.”
Starting in May, about a month before 618, the largest bookworm community group on the Douban platform, nicknamed “Buying Like Landsliding, Reading Like Silk Spinning” (买书如山倒,看书如抽丝), would start buzzing with activity, discussing book sales, comparing shopping lists, or sharing views about different issues.

Social media users share lists of which books to buy during the 618 shopping festivities.
This year, however, the mood within the group was different. Many members posted that before the 618 season began, books from various publishers were suddenly taken down from e-commerce platforms, disappearing from their online shopping carts. This unusual occurrence sparked discussions among book lovers, with speculations arising about a potential conflict between Chinese publishers and e-commerce platforms.
A joint statement posted in May provided clarity. According to Chinese media outlet The Paper (@澎湃新闻), eight publishers in Beijing and the Shanghai Publishing and Distribution Association, which represent 46 publishing units in Shanghai, issued a statement indicating they refuse to participate in this year’s 618 promotional campaign as proposed by JD.com.
The collective industry boycott has a clear motivation: during JD’s 618 promotional campaign, which offers all books at steep discounts (e.g., 60-70% off) for eight days, publishers lose money on each book sold. Meanwhile, JD.com continues to profit by forcing publishers to sell books at significantly reduced prices (e.g., 80% off). For many publishers, it is simply not sustainable to sell books at 20% of the original price.
One person who has openly spoken out against JD.com’s practices is Shen Haobo (沈浩波), founder and CEO of Chinese book publisher Motie Group (磨铁集团). Shen shared a post on WeChat Moments on May 31st, stating that Motie has completely stopped shipping to JD.com as it opposes the company’s low-price promotions. Shen said it felt like JD.com is “repeatedly rubbing our faces into the ground.”
Nevertheless, many netizens expressed confusion over the situation. Under the hashtag topic “Multiple Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Book Promotions” (#多家出版社抵制618图书大促#), people complained about the relatively high cost of physical books.
With a single legitimate copy often costing 50-60 RMB ($7-$8.3), and children’s books often costing much more, many Chinese readers can only afford to buy books during big sales. They question the justification for these rising prices, as books used to be much more affordable.
Book blogger TaoLangGe (@陶朗歌) argues that for ordinary readers in China, the removal of discounted books is not good news. As consumers, most people are not concerned with the “life and death of the publishing industry” and naturally prefer cheaper books.
However, industry insiders argue that a “price war” on books may not truly benefit buyers in the end, as it is actually driving up the prices as a forced response to the frequent discount promotions by e-commerce platforms.
China News (@中国新闻网) interviewed publisher San Shi (三石), who noted that people’s expectations of book prices can be easily influenced by promotional activities, leading to a subconscious belief that purchasing books at such low prices is normal. Publishers, therefore, feel compelled to reduce costs and adopt price competition to attract buyers. However, the space for cost reduction in paper and printing is limited.
Eventually, this pressure could affect the quality and layout of books, including their binding, design, and editing. In the long run, if a vicious cycle develops, it would be detrimental to the production and publication of high-quality books, ultimately disappointing book lovers who will struggle to find the books they want, in the format they prefer.
This debate temporarily resolved with JD.com’s compromise. According to The Paper, JD.com has started to abandon its previous strategy of offering extreme discounts across all book categories. Publishers now have a certain degree of autonomy, able to decide the types of books and discount rates for platform promotions.
While most previously delisted books have returned for sale, JD.com’s silence on their official social media channels leaves people worried about the future of China’s publishing industry in an era dominated by e-commerce platforms, especially at a time when online shops and livestreamers keep competing over who has the best book deals, hyping up promotional campaigns like ‘9.9 RMB ($1.4) per book with free shipping’ to ‘1 RMB ($0.15) books.’
This year’s developments surrounding the publishing industry and 618 has led to some discussions that have created more awareness among Chinese consumers about the true price of books. “I was planning to bulk buy books this year,” one commenter wrote: “But then I looked at my bookshelf and saw that some of last year’s books haven’t even been unwrapped yet.”
Another commenter wrote: “Although I’m just an ordinary reader, I still feel very sad about this situation. It’s reasonable to say that lower prices are good for readers, but what I see is an unfavorable outlook for publishers and the book market. If this continues, no one will want to work in this industry, and for readers who do not like e-books and only prefer physical books, this is definitely not a good thing at all!”
By Ruixin Zhang, edited with further input by Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Chinese Sun Protection Fashion: Move over Facekini, Here’s the Peek-a-Boo Polo
From facekini to no-face hoodie: China’s anti-tan fashion continues to evolve.
Published
2 months agoon
June 6, 2024
It has been ten years since the Chinese “facekini”—a head garment worn by Chinese ‘aunties’ at the beach or swimming pool to prevent sunburn—went international.
Although the facekini’s debut in French fashion magazines did not lead to an international craze, it did turn the term “facekini” (脸基尼), coined in 2012, into an internationally recognized word.

The facekini went viral in 2014.
In recent years, China has seen a rise in anti-tan, sun-protection garments. More than just preventing sunburn, these garments aim to prevent any tanning at all, helping Chinese women—and some men—maintain as pale a complexion as possible, as fair skin is deemed aesthetically ideal.
As temperatures are soaring across China, online fashion stores on Taobao and other platforms are offering all kinds of fashion solutions to prevent the skin, mainly the face, from being exposed to the sun.

One of these solutions is the reversed no-face sun protection hoodie, or the ‘peek-a-boo polo,’ a dress shirt with a reverse hoodie featuring eye holes and a zipper for the mouth area.

This sun-protective garment is available in various sizes and models, with some inspired by or made by the Japanese NOTHOMME brand. These garments can be worn in two ways—hoodie front or hoodie back. Prices range from 100 to 280 yuan ($13-$38) per shirt/jacket.

The no-face hoodie sun protection shirt is sold in various colors and variations on Chinese e-commerce sites.
Some shops on Taobao joke about the extreme sun-protective fashion, writing: “During the day, you don’t know which one is your wife. At night they’ll return to normal and you’ll see it’s your wife.”

On Xiaohongshu, fashion commenters note how Chinese sun protective clothing has become more extreme over the past few years, with “sunburn protection warriors” (防晒战士) thinking of all kinds of solutions to avoid a tan.
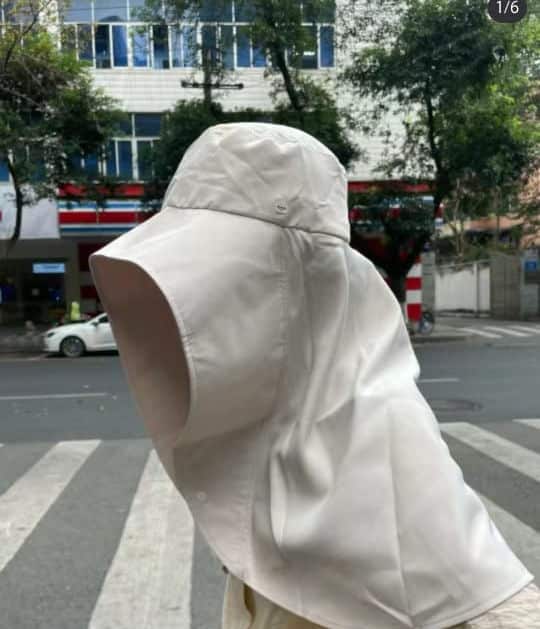




Although there are many jokes surrounding China’s “sun protection warriors,” some people believe they are taking it too far, even comparing them to Muslim women dressed in burqas.
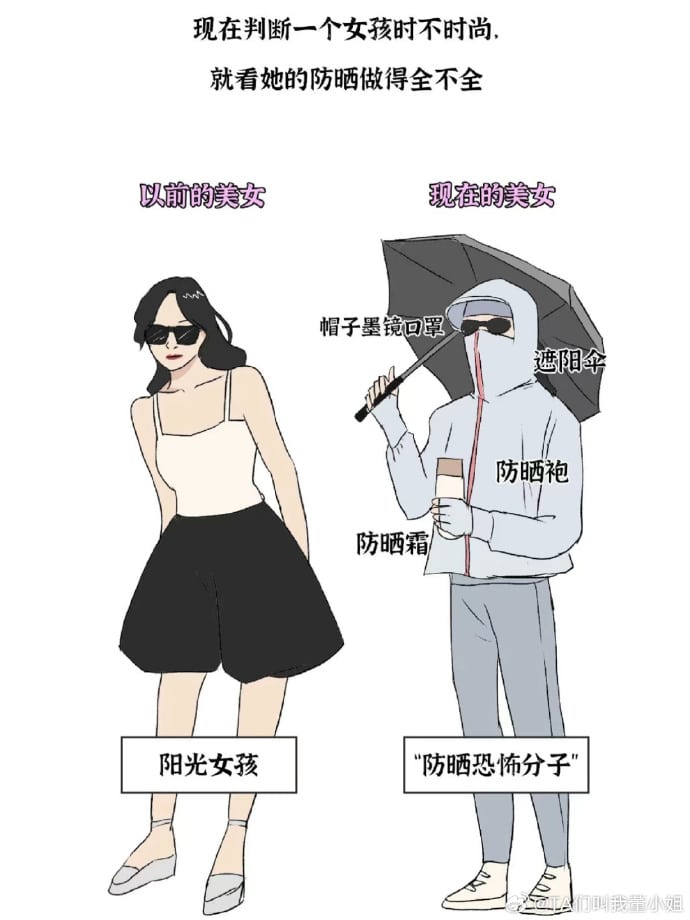
Image shared on Weibo by @TA们叫我董小姐, comparing pretty girls before (left) and nowadays (right), also labeled “sunscreen terrorists.”
Some Xiaohongshu influencers argue that instead of wrapping themselves up like mummies, people should pay more attention to the UV index, suggesting that applying sunscreen and using a parasol or hat usually offers enough protection.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?






mmmm_crackers
November 1, 2022 at 11:06 pm
insightful. i am an old man born and raised in the you.ess.ayy but i have fond memories of want want. i appreciate teh article. (y)