China and Covid19
Drug Shortages: Chinese Netizens Find New Ways to Access Medicines during Covid-19 Outbreak
From being creative to mutual aid platforms, Chinese netizens share multiple ways to get medicine to relieve Covid-19 symptoms.
Published
2 years agoon

Fears for a new strain of Covid-19 are causing another run on medicine in mainland China, where people are turning to alternative ways of getting popular medicine if the local (online) pharmacies have already sold out.
Lianhua Qingwen (连花清瘟), Paracetamol (对乙酰氨基酚), Ibuprofen (布洛芬), Paxlovid (奈玛特韦片), Diosmectite (蒙脱石散), and many more: these past weeks the various brand and generic names of analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antiviral pills, gastrointestinal medication, and cough-suppressants have been making their rounds on Chinese social media, where some seem to have become experts in getting their hands on popular medicines despite them often being sold-out or simply hard to get.
There are also many questions among netizens about which medications are the best to take when catching Covid, and how to get them.
Although various media report that major Chinese cities, including Shanghai, have now passed their Covid infection peaks, the Covid infections waves throughout China and all the problems that come with it are still dominating top trending lists on Chinese social media.
The topic “How To Guard Against the XBB Strain” (#如何防备XBB毒株#) received over 110 million views on Weibo on January 3rd.
The XBB.1.5 subvariant is part of a new class of Omicron that is taking hold in the U.S. and elsewhere. After news spread that XBB is known to cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, some feared that XBB could cause another round of infections (#XBB会在我国引起新一轮流行吗#) and Chinese consumers soon started buying Diosmectite (蒙脱石散), Norfloxacin (诺氟沙星), and other medicine in hopes of being prepared for a possible XBB infection.
The same thing happened in the early stages of the current wave, when the Lianhua Qingwen (连花清瘟) capsules, a traditional Chinese medicine that is believed to help alleviate COVID-19 symptoms, were sold out as so many people were stocking up on them.
Viral joke about everyone showing off the medication they were able to stock up on. Someone collected all the recommended medicine and asked what else he's missing…Friend replied: getting infected. pic.twitter.com/QpaDL2nUVw
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) December 8, 2022
At the time, a video went viral showing how one pharmacist in Baoding would only sell the popular medicine if patients would also buy additional medication.
Despite the run on medicines, Chinese health officials and health-related accounts on social media have repeatedly urged people to “buy medicine reasonably” (“合理备药”) instead of hoarding. But ever since the start of the nationwide wave of infections along with the easing of Covid measures, panic-buying and medicine shortages have become a problem all over the country.
At the moment, the antipyretic Ibuprofen (布洛芬) and Acetaminophen (Paracetamol/对乙酰氨基酚) are especially in high demand and harder to get. Many hospitals and pharmacies have run out of medicines, with people joking that doctors can only treat patients by “talking therapy” [话疗 huàliáo, ‘curing by taking,’ a homophone of 化疗 huàliáo, meaning chemotherapy).
In late December, one doctor working at the Huashan Hospital of Fudan University posted on social media that the hospital no longer had available medicines for fever relief, and also none for cough relief.
“Some pharmacies really have nothing left,” one Weibo commenter from Guangxi wrote: “Our pharmacy is empty and is not receiving new goods for two weeks. Ibuprofen, paracetamol, rectal acetaminophen, thermometers, masks, coughing syrup, medicine for colds, it’s all no longer available. Now we can’t even get Diosmectite.”
Despite the shortages, Chinese consumers are trying to find ways to still get their hands on medicine and self-tests.
Alternatives for Popular Medicine
One way in which people make sure they can still get medicine to relieve their symptoms is by finding alternative options for sold-out medications.
Recently, one public WeChat account under the online medical consultation platform Dingxiang Doctor (丁香医生, 丁香生活研究所) published an article titled “What To Do If You Cannot Find Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen?” (“买不到布洛芬、对乙酰氨基酚怎么办?“)
The article guides people in seeking alternatives for Ibuprofen and acetaminophen in situations when suitable pain and fever relief medicines are unavailable.
Alternatives include converting medicine doses so that adults can take children’s medications and vice versa (i.e. by calculating how many doses of children’s Ibuprofen an adult can take), using other kinds of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) than Ibuprofen or finding compound medication which still contain acetaminophen.
The article also reminds readers that these backup plans should only be used in times of emergency, as they might not be as efficient as Ibuprofen and acetaminophen and might cause other side effects.
Mutual Aid on WeChat
WeChat also helps people in finding the medicine they need. In December, Tencent launched the “Covid Medication Public Mutual Aid Platform” (新冠防护药物公益互助平台) mini-program on WeChat, through which people can place requests for medicines through the “I need medicines” (我需要药) tab, but can also share the medicine they no longer need under the “I have spare medicine” (我有多的药) tab.
These requests end up on the platform after users have filled in their personal information, including addresss and real-name authentication. Once a request or offer has ended, the users can mark it as completed.
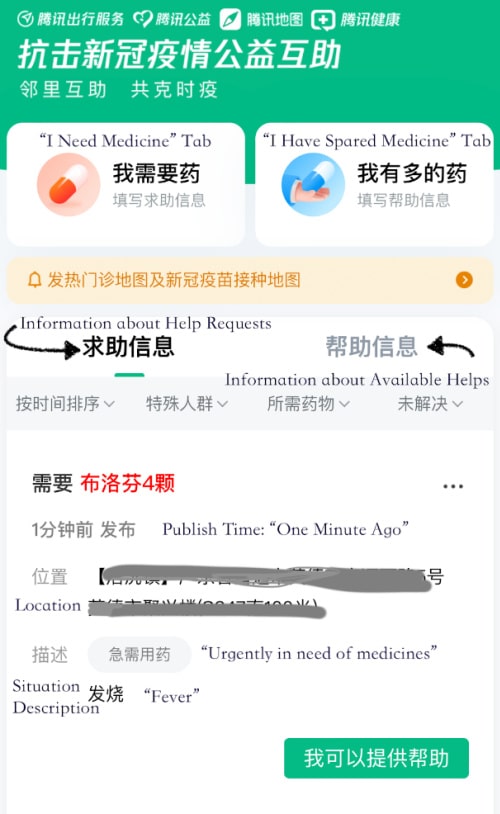
Featured above is a screenshot of the WeChat mutual aid platform. The bottom half of the image includes a request for four Ibuprofen capsules. Publish time, location, and situation description are available for the public (the location in the screenshot is blurred to protect privacy). Users can click the green bottom “I can offer help” (“我可以提供帮助”) to provide support if they can give away some spare Ibuprofen capsules.
Besides this service, many people also use their own WeChat community groups to exchange medicines between neighbors. According to a Weibo post by Zhejiang Daily, one woman in Hangzhou requested medication in the community WeChat group for her child, who had a fever of 41 celsius. The next morning, a bottle of Motrin appeared in front of her door, left for her by her next-door neighbor (#孩子发烧41℃第二天家门口出现一瓶美林#).
Amap Mutual Aid Function
Besides WeChat, the Chinese navigation/map platform Amap.com (高德地图) has now also introduced a function through which people can exchange medication and spare antigen tests.
Amap.com has joined forces with Alibaba’s Public Welfare platform in launching the Covid Medication Public Good Help Platform (新冠药物公益互助平台) through which people can find medication or surplus tests in their neighborhood, purely based on location, in times of emergency.
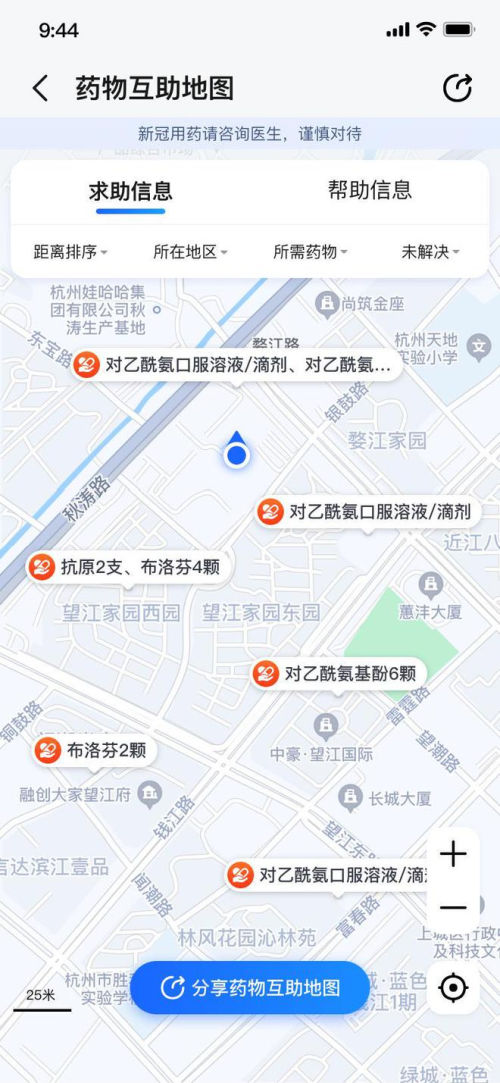
The function can be accessed by going to the “Medication Mutual Aid” (药物互助) from with the Amap app.
Saving Rapid Antigen Tests
While Chinese netizens are searching for new ways to get their hands on medicine and tests, there has also been a heightened focus on being careful with the resources people already have.
Given the limited access to Covid test kits these days, discussions on how to use test kits “wisely” to avoid wasting have popped up on social media.

On December 27th, People’s Daily published a Weibo post titled “Nine Tips for Using Test Kits” suggesting people should test only on the second day of fever to confirm infection and then on the eighth day of fever to confirm recovery.
China News Service also posted a video titled “Do not waste it! When you will get an accurate test” (#抗原啥时候测才准#), discouraging people from using test kits when they suspect getting Covid-19 because of a close contact or headache because the timing might not be accurate and another rapid antigen test would go to waste.

Aside from advice released by official media, people also think of their own creative ways to save tests. One man in Hangzhou thought he was being smart by pulling the test strip out of the plastic test cover and cut it in half to use the same kit twice. Later, however, one test kit manufacturer warned people that tampering with the tests would affect the result (#业内人士评男子为节省抗原剪开试纸#).
Medicines from Overseas
Another way in which people are trying to get medicine during this Covid wave is by purchasing medicine overseas and sending it back to families and friends in mainland China.
One blogger posted on Xiaohongshu about Chinese in Australia overbuying Panadol. One image showed how a pharmacy in Australia had a notice up regarding purchase restrictions, which was written in Chinese: one person can buy a maximum of 100 Panadol tablets (which is one bigger package).

Similarly, various media outlets reported Chinese nationals panic-buying medicines in Singapore, Japan, Taiwan and Hongkong, leading to many countries also issuing purchase restrictions on fever-reducing and cold medicine.
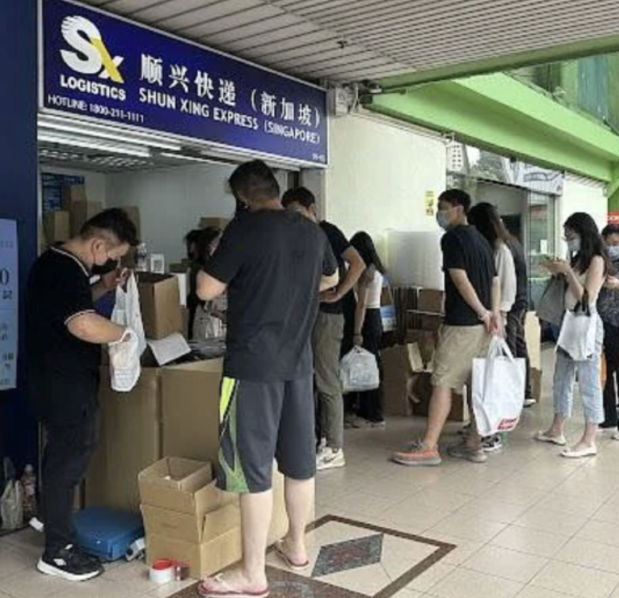

Chinese people lining up in front of Singapore’s logistic company Shun Xing to mail medicines back (image from Mothership.SG’s report).
While purchasing medicines overseas is easier for some than buying them in their own Chinese cities or towns, sending medicine to China can also pose a problem.
Some packages get lost in the shipping process, others are confiscated at customs or get turned down by couriers.
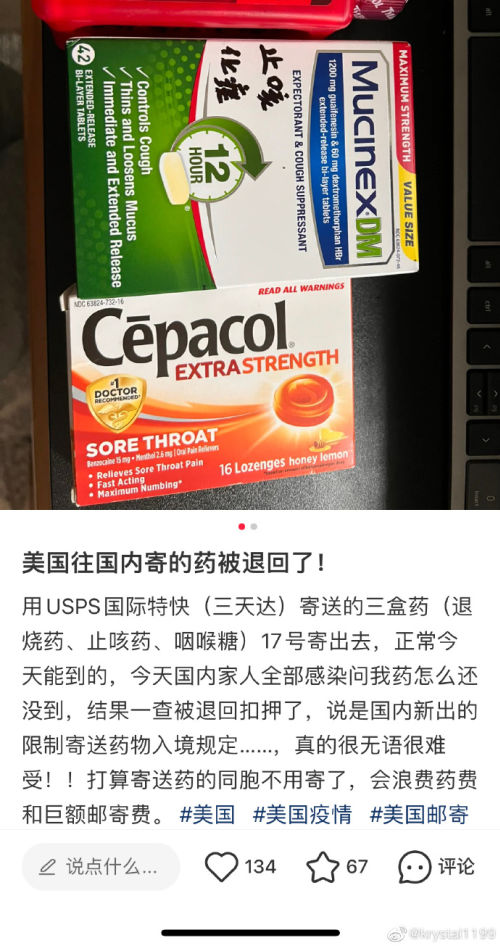
One Weibo user in the U.S. shared that her package was confiscated because of a new domestic policy limiting the international mailing of medicines. Similarly, a Xiaohongshu blogger from Singapore reported their cold relief medicines were turned down by the courier, who alleged that China’s new policy banned certain cold relief medicines from entering the country.
Despite the restrictions, people do not give up on trying. On Xiaohongshu, bloggers continue to share all kinds of tips and successful experiences of sending medicines back home to their friends and families, including what type of medicine to buy, what documentation to prepare, how many doses to send, and which courier company to use.
However, even if medicines can successfully arrive in China, custom clearance processes can takes a long time and sick family members may have already recovered when the medicines finally arrive.
Some people are also afraid that packages will be stolen upon arrival, as these kind of stories have also been surfacing on social media (#邮政局回应寄药被偷#).
“Enough Antigen Tests”
Over the past few days, there are have also been online discussions and news reports on antigen tests being back in stock at normal or even low prices (#抗原检测试剂遭甩卖#, #药店称抗原检测试剂特别充足#), leading some to hope that China’s medicine situation may turn around for the better in 2023.
Although experts now suggest that, in light of XXB, bulk buying Diosmectite is unnecessary, there are also those who no longer trust experts’ advice: “Once experts advised us not to bulk-buy, I know it is time to bulk-buy.”
Does a sufficient supply of antigen test kits mark a ‘return to normal’, or will new medication demands, such as Diosmectite, trigger another wave of medicine shortage?
On December 30, Health News (健康报) a publication under the National Health Commission, commented that the mutual aid medicine platforms may be here to stay.
While this message signals that the medicine shortage has not approached an end yet, people are tired of it: “I hope these [mutual aid] platforms will only blossom a short time,” one Weibo user writes: “I hope our lives can return to normal.”
By Zilan Qian, with contributions by Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Stories that are authored by the What's on Weibo Team are the stories that multiple authors contributed to. Please check the names at the end of the articles to see who the authors are.

Also Read
China and Covid19
Sick Kids, Worried Parents, Overcrowded Hospitals: China’s Peak Flu Season on the Way
“Besides Mycoplasma infections, cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
Published
8 months agoon
November 22, 2023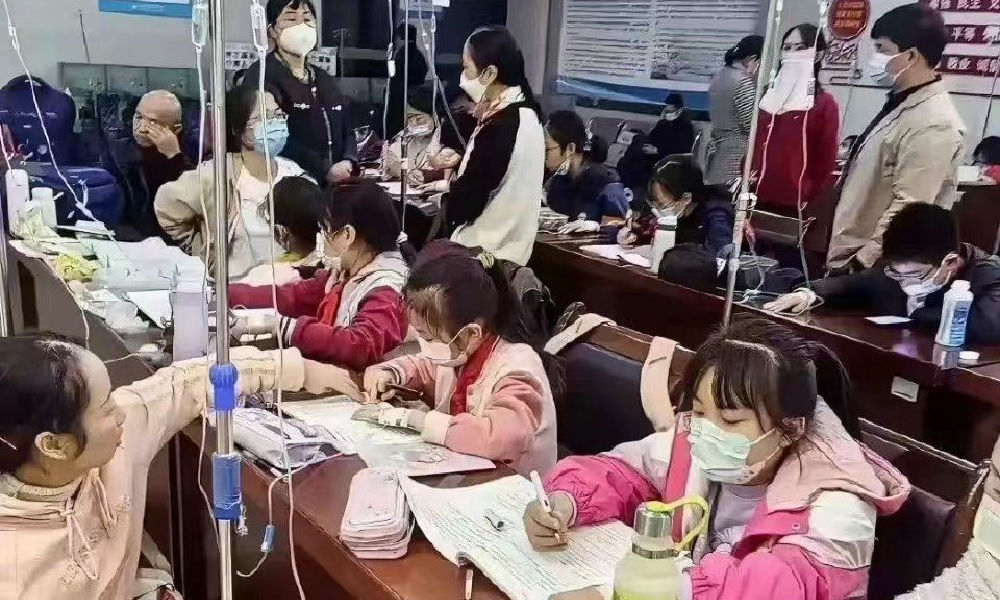
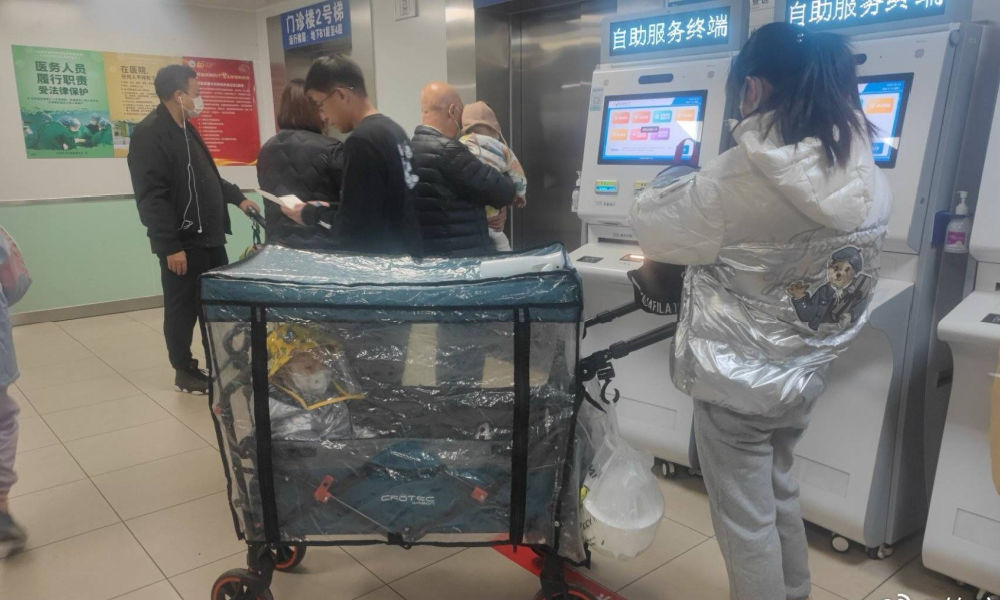
In the early morning of November 21, parents are already queuing up at Xi’an Children’s Hospital with their sons and daughters. It’s not even the line for a doctor’s appointment, but rather for the removal of IV needles.
The scene was captured in a recent video, only one among many videos and images that have been making their rounds on Chinese social media these days (#凌晨的儿童医院拔针也要排队#).

One photo shows a bulletin board at a local hospital warning parents that over 700 patients are waiting in line, estimating a waiting time of more than 13 hours to see a doctor.

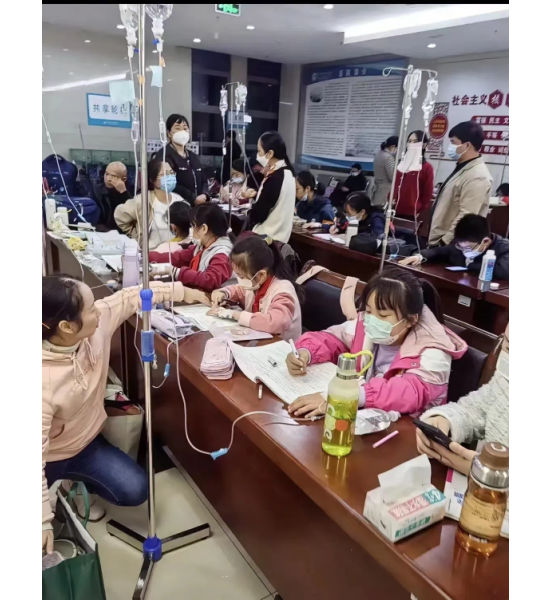
Another image shows children doing their homework while hooked up on an IV.

Recent discussions on Chinese social media platforms have highlighted a notable surge in flu cases. The ongoing flu season is particularly impacting children, with multiple viruses concurrently circulating and contributing to a high incidence of respiratory infections.
Among the prevalent respiratory infections affecting children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, influenza, and Adenovirus infection.
The spike in flu cases has resulted in overcrowded children’s hospitals in Beijing and other Chinese cities. Parents sometimes have to wait in line for hours to get an appointment or pick up medication.
According to one reporter at Haibao News (海报新闻), there were so many patients at the Children’s Hospital of Capital Institute of Pediatrics (首都儿科研究所) on November 21st that the outpatient desk stopped accepting new patients by the afternoon. Meanwhile, 628 people were waiting in line to see a doctor at the emergency department.
Reflecting on the past few years, the current flu season marks China’s first ‘normal’ flu peak season since the outbreak of Covid-19 in late 2019 / early 2020 and the end of its stringent zero-Covid policies in December 2022. Compared to many other countries, wearing masks was also commonplace for much longer following the relaxation of Covid policies.
Hu Xijin, the well-known political commentator, noted on Weibo that this year’s flu season seems to be far worse than that of the years before. He also shared that his own granddaughter was suffering from a 40 degrees fever.
“We’re all running a fever in our home. But I didn’t dare to go to the hospital today, although I want my child to go to the hospital tomorrow. I heard waiting times are up to five hours now,” one Weibo user wrote.
“Half of the kids in my child’s class are sick now. The hospital is overflowing with people,” another person commented.
One mother described how her 7-year-old child had been running a fever for eight days already. Seeking medical attention on the first day, the initial diagnosis was a cold. As the fever persisted, daily visits to the hospital ensued, involving multiple hours for IV fluid administration.
While this account stems from a single Weibo post within a fever-advice community, it highlights a broader trend: many parents swiftly resort to hospital visits at the first signs of flu or fever. Several factors contribute to this, including a lack of General Practitioners in China, making hospitals the primary choice for medical consultations also in non-urgent cases.
There is also a strong belief in the efficacy of IV infusion therapy, whether fluid-based or containing medication, as the quickest path to recovery. Multiple factors contribute to the widespread and sometimes irrational use of IV infusions in China. Some clinics are profit-driven and see IV infusions as a way to make more money. Widespread expectations among Chinese patients that IV infusions will make them feel better also play a role, along with some physicians’ lacking knowledge of IV therapy or their uncertainty to distinguish bacterial from viral infections (read more here)
To prevent an overwhelming influx of patients to hospitals, Chinese state media, citing specialists, advise parents to seek medical attention at the hospital only for sick infants under three months old displaying clear signs of fever (with or without cough). For older children, it is recommended to consult a doctor if a high fever persists for 3 to 5 days or if there is a deterioration in respiratory symptoms. Children dealing with fever and (mild) respiratory symptoms can otherwise recover at home.
One Weibo blogger (@奶霸知道) warned parents that taking their child straight to the hospital on the first day of them getting sick could actually be a bad idea. They write:
“(..) pediatric departments are already packed with patients, and it’s not just Mycoplasma infections anymore. Cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. And then, of course, those with bad luck are cross-infected with multiple viruses at the same time, leading to endless cycles. Therefore, if your child experiences mild coughing or a slight fever, consider observing at home first. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
The hashtag for “fever” saw over 350 million clicks on Weibo within one day on November 22.
Meanwhile, there are also other ongoing discussions on Weibo surrounding the current flu season. One topic revolves around whether children should continue doing their homework while receiving IV fluids in the hospital. Some hospitals have designated special desks and study areas for children.
Although some commenters commend the hospitals for being so considerate, others also remind the parents not to pressure their kids too much and to let them rest when they are not feeling well.
Opinions vary: although some on Chinese social media say it's very thoughtful for hospitals to set up areas where kids can study and read, others blame parents for pressuring their kids to do homework at the hospital instead of resting when not feeling well. pic.twitter.com/gnQD9tFW2c
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) November 22, 2023
By Manya Koetse, with contributions from Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China and Covid19
Repurposing China’s Abandoned Nucleic Acid Booths: 10 Innovative Transformations
Abandoned nucleic acid booths are getting a second life through these new initiatives.
Published
1 year agoon
May 19, 2023
During the pandemic, nucleic acid testing booths in Chinese cities were primarily focused on maintaining physical distance. Now, empty booths are being repurposed to bring people together, serving as new spaces to serve the community and promote social engagement.
Just months ago, nucleic acid testing booths were the most lively spots of some Chinese cities. During the 2022 Shanghai summer, for example, there were massive queues in front of the city’s nucleic acid booths, as people needed a negative PCR test no older than 72 hours for accessing public transport, going to work, or visiting markets and malls.
The word ‘hésuān tíng‘ (核酸亭), nucleic acid booth (also:核酸采样小屋), became a part of China’s pandemic lexicon, just like hésuān dìtú (核酸地图), the nucleic acid test map lauched in May 2022 that would show where you can get a nucleic test.
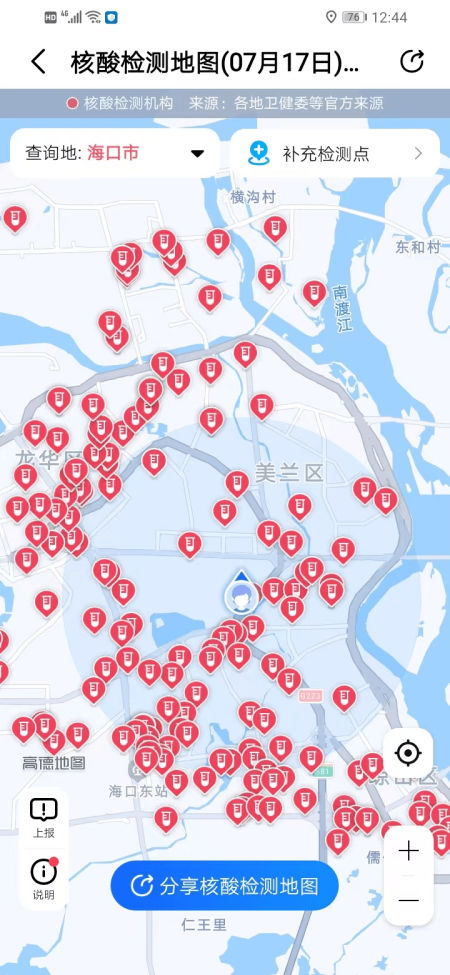
Example of nucleic acid test map.
During Halloween parties in Shanghai in 2022, some people even came dressed up as nucleic test booths – although local authorities could not appreciate the creative costume.

Halloween 2022: dressed up as nucliec acid booths. Via @manyapan twitter.
In December 2022, along with the announced changed rules in China’s ‘zero Covid’ approach, nucleic acid booths were suddenly left dismantled and empty.
With many cities spending millions to set up these booths in central locations, the question soon arose: what should they do with the abandoned booths?
This question also relates to who actually owns them, since the ownership is mixed. Some booths were purchased by authorities, others were bought by companies, and there are also local communities owning their own testing booths. Depending on the contracts and legal implications, not all booths are able to get a new function or be removed yet (Worker’s Daily).
In Tianjin, a total of 266 nucleic acid booths located in Jinghai District were listed for public acquisition earlier this month, and they were acquired for 4.78 million yuan (US$683.300) by a local food and beverage company which will transform the booths into convenience service points, selling snacks or providing other services.
Tianjin is not the only city where old nucleic acid testing booths are being repurposed. While some booths have been discarded, some companies and/or local governments – in cooperation with local communities – have demonstrated creativity by transforming the booths into new landmarks. Since the start of 2023, different cities and districts across China have already begun to repurpose testing booths. Here, we will explore ten different way in which China’s abandoned nucleic test booths get a second chance at a meaningful existence.
1: Pharmacy/Medical Booths
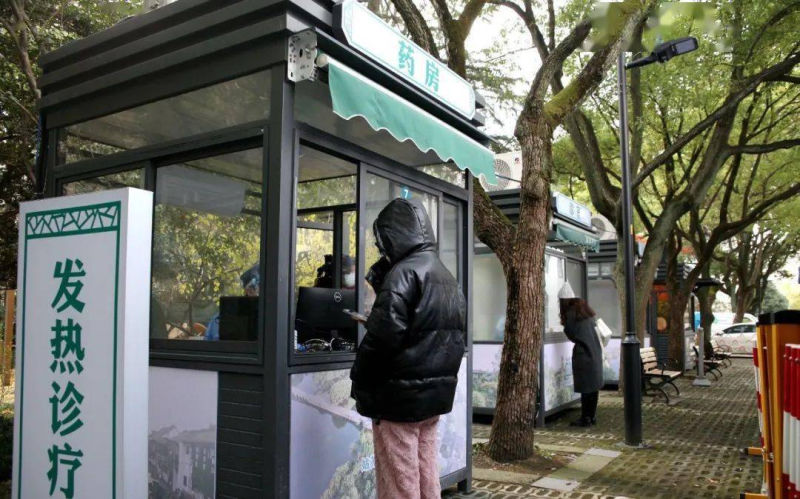

Via ‘copyquan’ republished on Sohu.
Blogger ‘copyquan’ recently explored various ways in which abandoned PCR testing points are being repurposed.
One way in which they are used is as small pharmacies or as medical service points for local residents (居民医疗点). Alleviating the strain on hospitals and pharmacies, this was one of the earliest ways in which the booths were repurposed back in December of 2022 and January of 2023.
Chongqing, Tianjin, and Suzhou were among earlier cities where some testing booths were transformed into convenient medical facilities.
2: Market Stalls
In Suzhou, Jiangsu province, the local government transformed vacant nucleic acid booths into market stalls for the Spring Festival in January 2022, offering them free of charge to businesses to sell local products, snacks, and traditional New Year goods.
The idea was not just meant as a way for small businesses to conveniently sell to local residents, it was also meant as a way to attract more shoppers and promote other businesses in the neighborhood.
3: Community Service Center
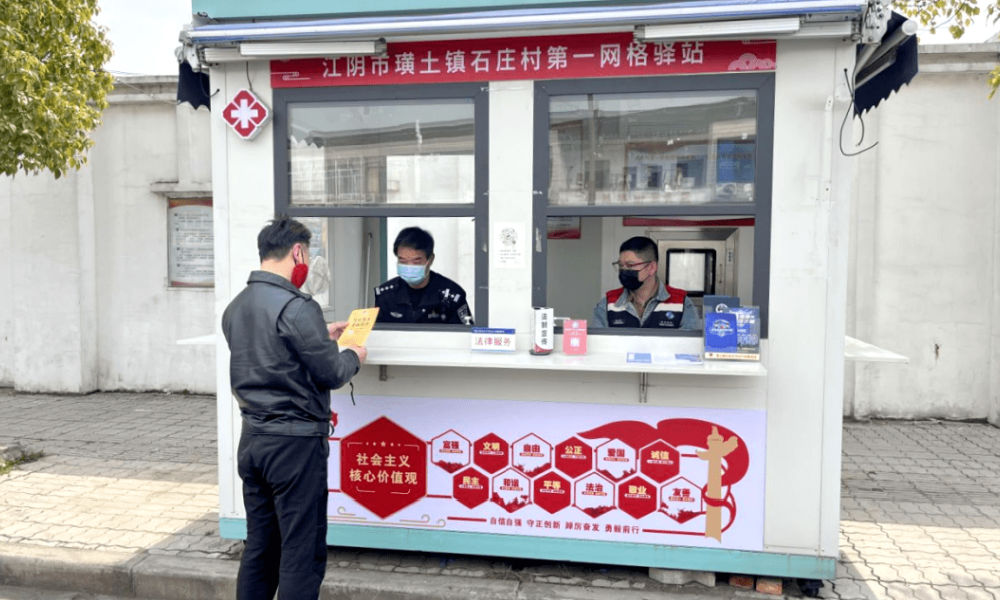

Small grid community center in Shizhuang Village, image via Sohu.
Some residential areas have transformed their local nucleic acid testing booths into community service centers, offering all kinds of convenient services to neighborhood residents.
These little station are called wǎnggé yìzhàn (网格驿站) or “grid service stations,” and they can serve as small community centers where residents can get various kinds of care and support.
4: “Refuel” Stations
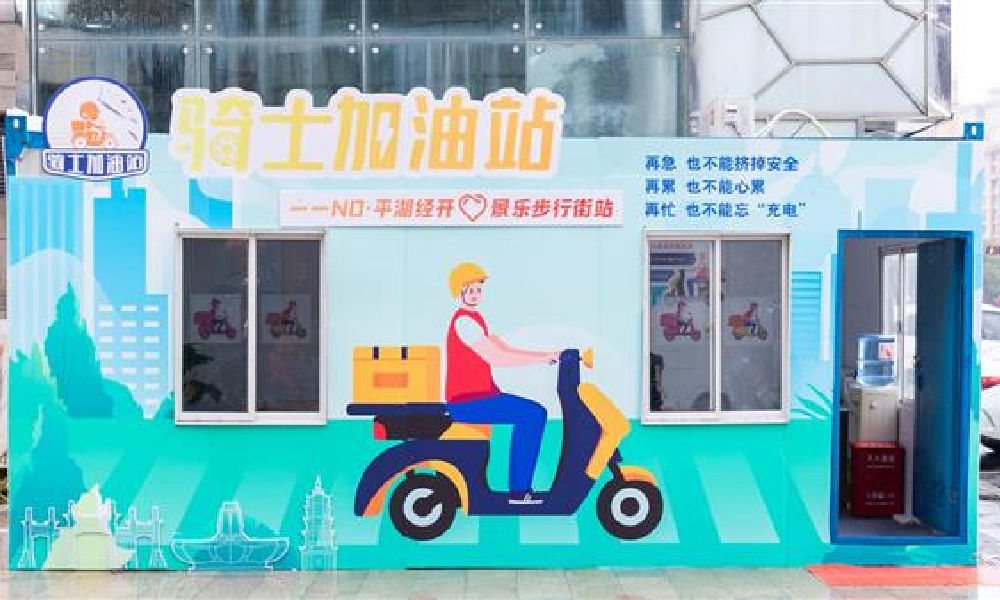

In February of this year, 100 idle nucleic acid sampling booths were transformed into so-called “Rider Refuel Stations” (骑士加油站) in Zhejiang’s Pinghu. Although it initially sounds like a place where delivery riders can fill up their fuel tanks, it is actually meant as a place where they themselves can recharge.
Delivery riders and other outdoor workers can come to the ‘refuel’ station to drink some water or tea, warm their hands, warm up some food and take a quick nap.
5: Free Libraries
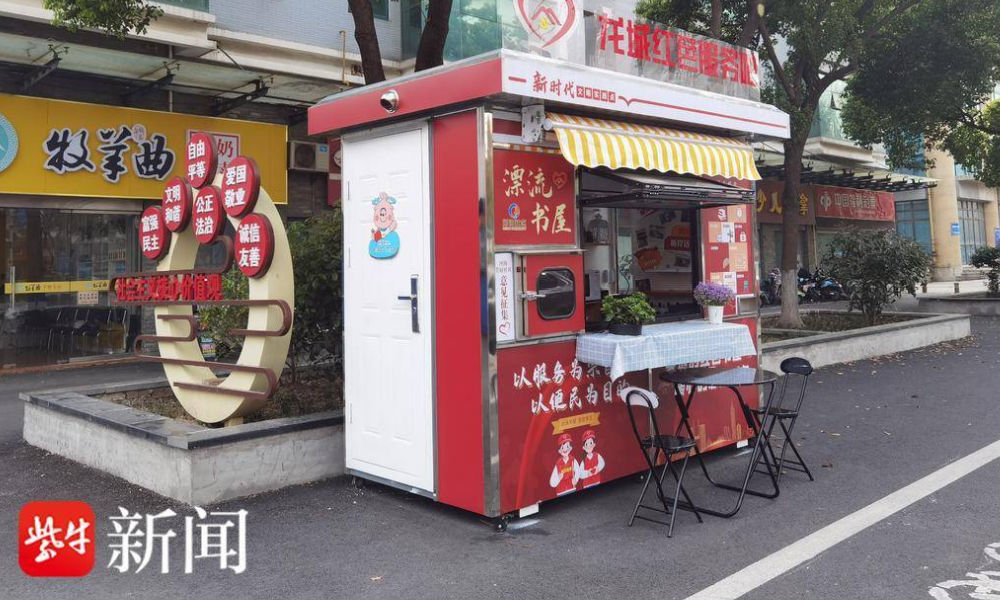

image via sohu.
In various Chinese cities, abandoned nucleic acid booths have been transformed into little free libraries where people can grab some books to read, donate or return other books, and sit down for some reading.
Changzhou is one of the places where you’ll find such “drifting bookstores” (漂流书屋) (see video), but similar initiatives have also been launched in other places, including Suzhou.
6: Study Space
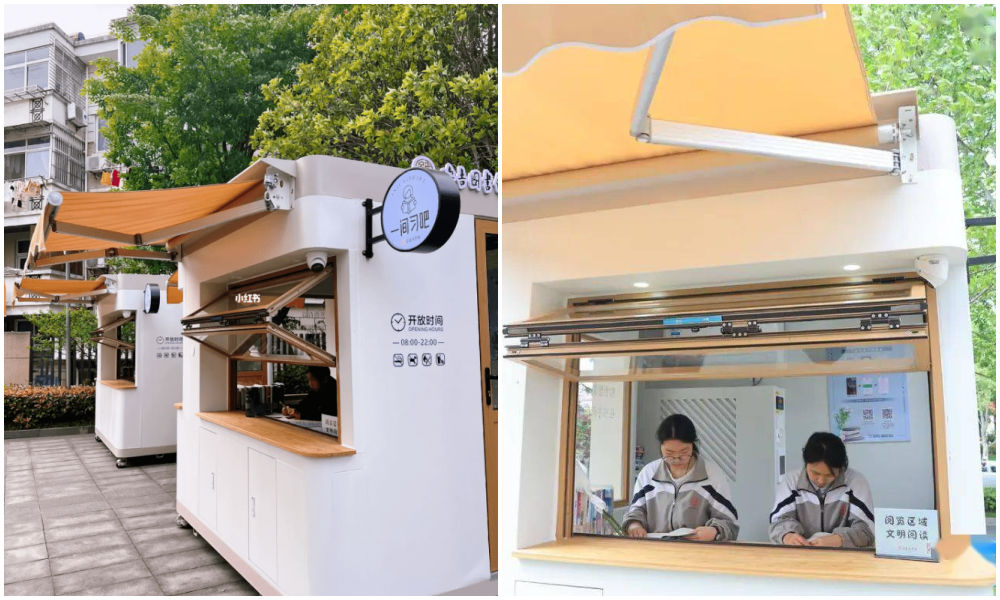

Photos via Copyquan’s article on Sohu.
Another innovative way in which old testing points are being repurposed is by turning them into places where students can sit together to study. The so-called “Let’s Study Space” (一间习吧), fully airconditioned, are opened from 8 in the morning until 22:00 at night.
Students – or any citizens who would like a nice place to study – can make online reservations with their ID cards and scan a QR code to enter the study rooms.
There are currently ten study booths in Anji, and the popular project is an initiative by the Anji County Library in Zhejiang (see video).
7: Beer Kiosk
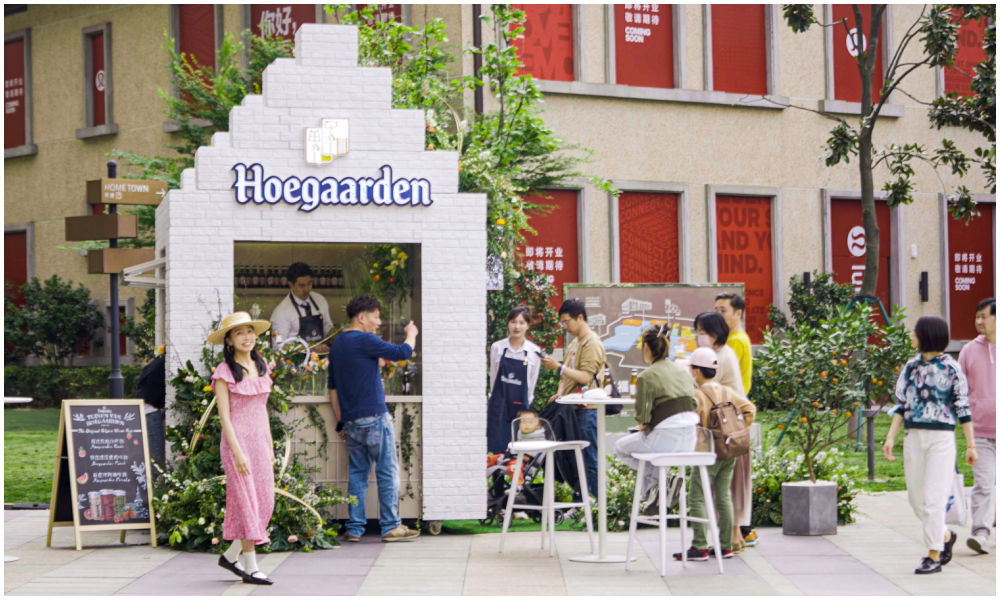

Hoegaarden beer shop, image via Creative Adquan.
Changing an old nucleic acid testing booth into a beer bar is a marketing initiative by the Shanghai McCann ad agency for the Belgium beer brand Hoegaarden.
The idea behind the bar is to celebrate a new spring after the pandemic. The ad agency has revamped a total of six formr nucleic acid booths into small Hoegaarden ‘beer gardens.’
8: Police Box
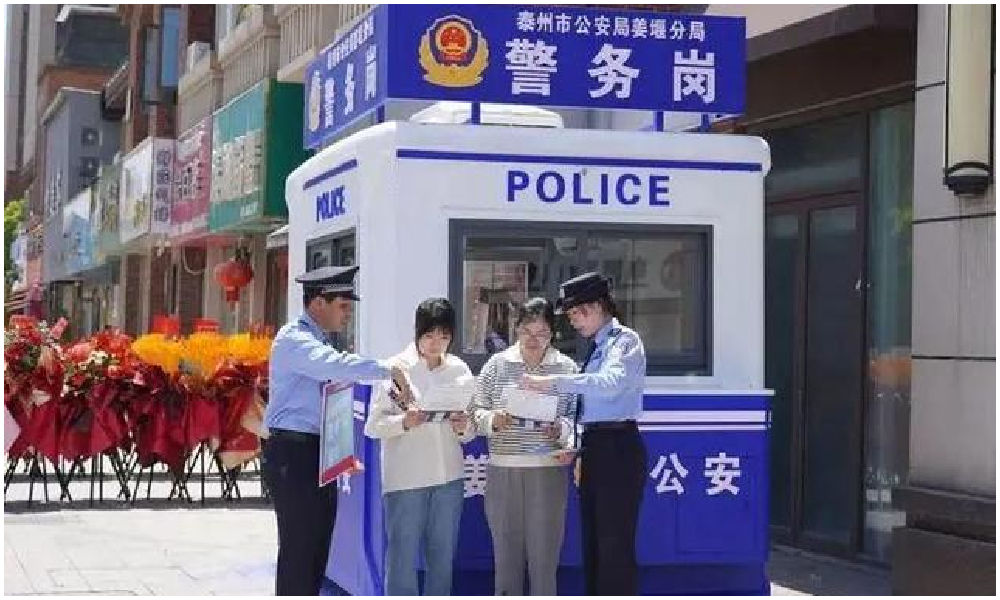

In Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province, authorities have repurposed old testing booths and transformed them into ‘police boxes’ (警务岗亭) to enhance security and improve the visibility of city police among the public.
Currently, a total of eight vacant nucleic acid booths have been renovated into modern police stations, serving as key points for police presence and interaction with the community.
9: Lottery Ticket Booths
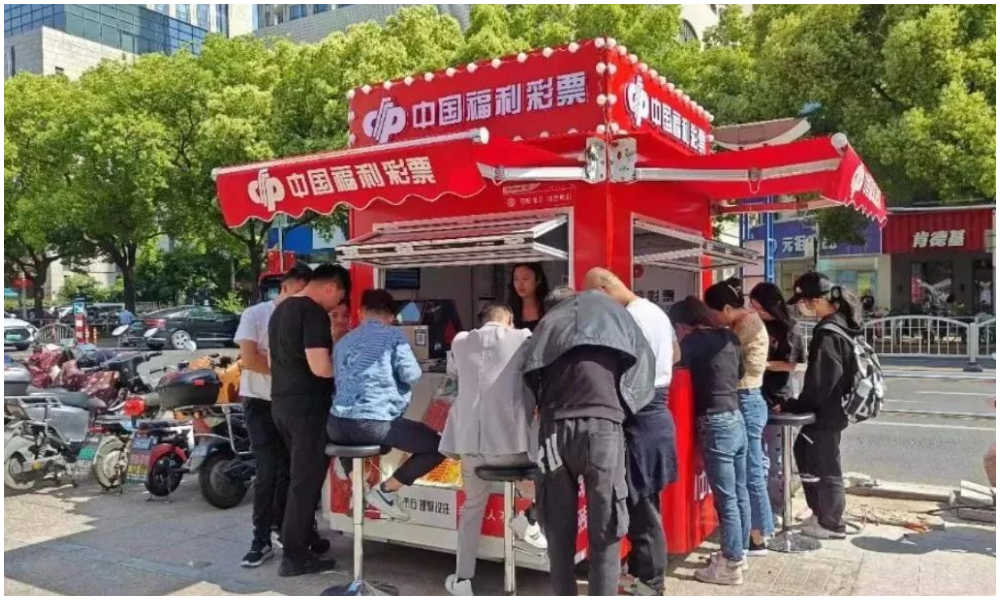

Image via The Paper
Some nucleic acid booths have now been turned into small shops selling lottery tickets for the China Welfare Lottery. One such place turning the kiosks into lottery shops is Songjiang in Shanghai.
Using the booths like this is a win-win situation: they are placed in central locations so it is more convenient for locals to get their lottery tickets, and on the other hand, the sales also help the community, as the profits are used for welfare projects, including care for the elderly.
10: Mini Fire Stations
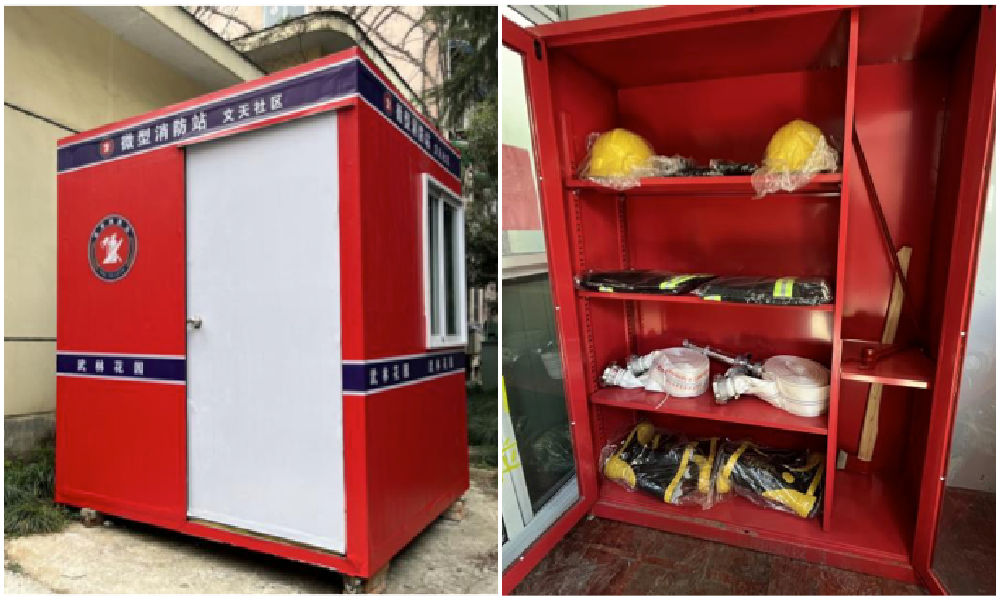

Micro fire stations, images via ZjNews.
Some communities decided that it would be useful to repurpose the testing points and turn them into mini fire kiosks, just allowing enough space for the necessary equipment to quickly respond to fire emergencies.
Want to read more about the end of ‘zero Covid’ in China? Check our other articles here.
By Manya Koetse,
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?





