Over a year after China’s most popular car-hailing company Didi Chuxing took down its carpooling service, news of its relaunch – including a curfew for female passengers – became a huge topic of debate on Chinese social media this week.
Earlier this week, Didi Chuxing (滴滴出行) announced that it would be relaunching its carpooling service Hitch (滴滴顺风车 Didi Shunfengche) on November 20 in seven trial cities.
The announcement comes after more than a year of safety overhauls and periods of public discussion following the murder of two female passengers committed by Hitch drivers in 2018.
But the new safety guidelines, which included an 8 pm curfew for female riders, drew major outrage from online commenters.
Hitch is a carpooling app where riders and drivers heading in the same direction can team up and split the cost. The two murder cases in May and August of 2018, coupled with multiple reported cases of sexual assault, led to widespread criticism that Didi does not sufficiently vet drivers and ensure the safety of its (female) riders.
In response, Didi suspended the Hitch service indefinitely in the summer of 2018 and revamped its safety protocols across the entire platform.
“Hi, long time no see,” began a statement from Didi Hitch’s Weibo account announcing the relaunch on November 6: “After 435 days of hard work, we developed 18 iterations, optimized 330 functions, and received 300,000 user suggestions. Finally, we decided to move forward, hoping that Hitch can shoulder our responsibilities and create value for the public.”
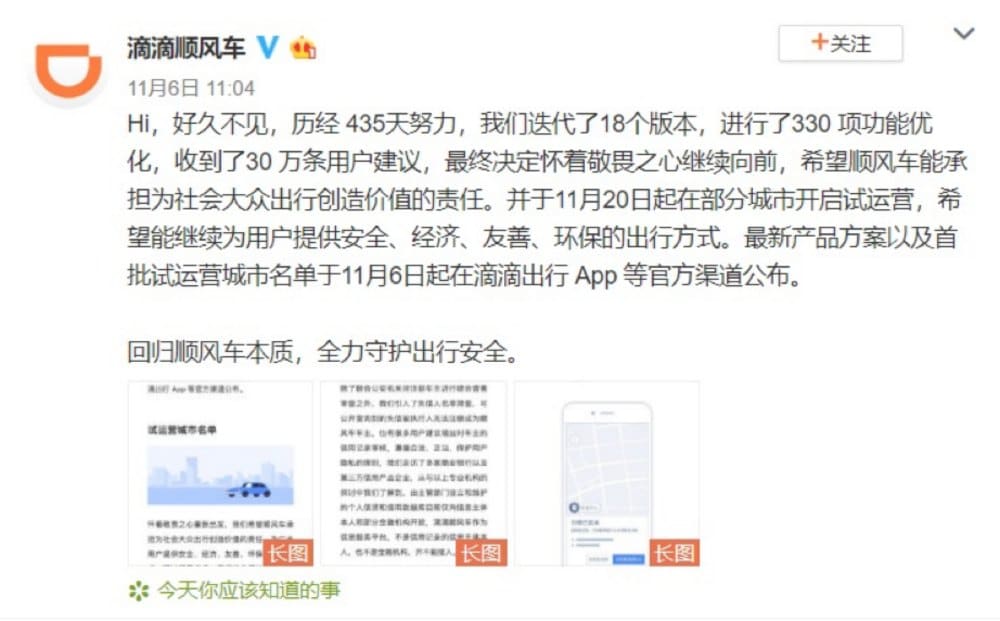
Didi’s announcement on Weibo.
The trial operations are set to begin in Harbin, Taiyuan, Shijiazhuang, and Changzhou on November 20 of this year, and expand to Shenyang, Beijing, and Nantong on November 29.
Didi further specified its trial operations, writing that services would be active from 5.00 in the morning until 23.00 at night, adding in between brackets that the services for women would end at 20.00 at night.

Many Weibo users were ecstatic at the news of the Hitch service starting again, but discussions were soon dominated by the question of whether or not Didi’s curfew for women was a sexist measure.
“What kind of protection is limiting the movement of women?! How about please restrict the damn criminals instead, okay?” one Weibo user commented on a popular news post about the story.
“After an entire year of discussion, this is your plan??” others asked: “Sure, I agree to the rule that women cannot ride after 8 pm, as long as men are also not allowed to leave home after 8 pm.”
One lawyer commented: “Stupid. Is this just a disclaimer from Didi? Self-protection? Or is it blatant discrimination against customers? In the face of a frequent and dangerous problem, rather than be concerned with prevention, protection, and response, they simply come up with strategies that refuse service to passengers.”
Didi responded that both the curfew and a 50km limit placed on rides were temporary safety measures during the trial relaunch period while the company continues to improve its services, but it did not help cool down discussions. Hashtags such as “Didi Hitch’s New Plan is Sex Discrimination” (#滴滴顺风车新方案被指性别歧视#) soon made their way across social media.
Besides the curfew, the relaunch announcement of Hitch also included an extensive range of other new safety features and regulations, including an entire program devoted to the safety of women. We have translated it below:
“PROTECTION PLAN FOR WOMEN”

1. Anti-single-picking mode: hide personal information and adopt a two-way confirmation mechanism to avoid the danger of drivers targeting single women.
2. Utilizing travel behavior records and other data, an algorithm will be integrated to find the most suitable fellow travelers for female users.
3. A customized “female safety assistant” includes the following features:
1 Rider can view relevant information such as the age of the car, the driver’s age, and the time of the most recent facial recognition verification of the driver
2 Reminder to share your route while traveling, availability of emergency contact services, real-time location protection, and other security functions.
3 Can check trip safety information and discover whether any abnormal behavior has taken place. In the case of abnormal behavior such as route deviation and long-term stopping, the emergency contact person will be informed immediately.
4. Special protections for women’s travel: long-distance trips require riders to undergo facial recognition, female users must set up emergency contacts, the driver will automatically audio record the trip (encrypted and uploaded to the platform).
5. Temporary restrictions: no cross-city trips or trips longer than 50 km will be allowed, and women will not be allowed as passengers from 8 pm to 5 am.
Although some of the new proposed policies above were met with online support*, as they were clearly designed to address the specific circumstances that led to the two murders in 2018, the curfew for women predominantly caused online anger.
Many commenters pointed out that one of the Didi murders was committed in broad daylight, not at night, which makes the curfew rule all the more confounding.
When big Weibo accounts such as the All-China’s Women Federation also started commenting on the issue, Didi Hitch apparently chose to avert further controversy; on November 7, Didi announced that during the trial period of its continued operations, services for all passengers, male and female, will now be limited to 8 pm.
“That’s right, we’re all equal as passengers,” some commented on the sudden policy change. Others, however, saw the change as a confirmation that Didi Hitch’s policies were indeed sexist.
Some commenters suggested something else to supposedly ensure Didi passengers’ safety: “Perhaps Didi should no longer allow male drivers to work after 8.00 pm instead.”
With 2018 being Didi’s toughest business year yet, this week’s controversy shows that the company still has to work hard this year and in the year to come to win back its customers’ trust, especially when it comes to its female passengers.
By Jessica Colwell
*(One of the more popular safety suggestions submitted to Didi during its period of public comment was the plan for all Hitch drivers’ information to be checked through a third-party credit data provider, although it is not sure when or if this proposed measure will be realized in the future.)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2019 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.


 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months ago
 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months ago
 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months ago
 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago