China Digital
“Daddy Ma, Are You OK?” – Jack Ma’s Situation Discussed on Chinese Social Media
Public sentiments on Jack Ma have shifted, but the fans still defend their idol.
Published
4 years agoon

Chinese tech superhero Jack Ma has become a hot topic on international social media this month since he has been missing in action for weeks, while Alibaba is facing an anti-monopoly investigation. Ma seems to have fallen out of favor, not just with authorities but also with many Chinese web users.
This month, the alleged ‘disappearance’ of Alibaba founder Jack Ma made headlines in various English-language media, from Reuters to CNN and the Financial Times.
The direct reason for speculation about Jack Ma’s whereabouts was his absence at Africa’s Business Heroes, a talent show he helped create in which Ma was part of the finale judge panel. According to FT.com, the final – which won’t be broadcasted until spring – took place in November.
Although an Alibaba spokesperson explained Ma’s absence from the show as a “schedule conflict” that made it impossible for the tech tycoon to participate, many Twitter users directly tied his ‘suspected missing’ to a critical speech he gave at the Shanghai Bund Finance Summit on October 24 of 2020.
In this speech, Ma made critical remarks on how China’s financial market is regulated and supervised. Kevin Xu at Interconnected provides an English translation of this speech here.
On November 3rd, two days before Alibaba’s fintech subsidiary Ant Group was set to raise around $37 billion with the biggest initial public offering of all time, Chinese regulators abruptly suspended the process. A report by the Wall Street Journal claimed that Chinese President Xi Jinping personally made the decision to halt the IPO of Ant Group after years of rising tensions between Ma and the government.
Pressure on Jack Ma and Alibaba further increased in December when Chinese regulators launched an anti-monopoly investigation into Alibaba and the Ant Group.
Alibaba announced the investigation of its company on its official Weibo channel on December 25 of 2020.
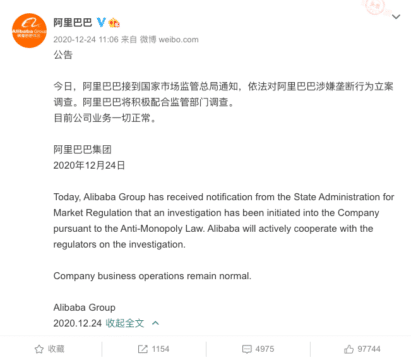
On December 25, People’s Daily also reported the anti-monopoly investigation. The state newspaper hosted a hashtag page about the matter on Sina Weibo (#人民日报再评阿里巴巴被调查#) which garnered over 240 million views. They wrote:
“Large Internet platform companies should take the lead in strengthening industry self-discipline, in further enhancing their sense of social responsibility, and in safeguarding a favorable Internet economic ecosystem. The Internet industry has never been, and should never become, a place that is outside the law for anti-monopoly. Regarding platform economy, reinforcing anti-monopoly regulations is never a “winter” for the industry – it is just a new starting point for better and healthier development.”
Although Chinese official media have since not reported much on the issue, and have not published about Ma’s alleged ‘disappearance’, Ma’s whereabouts and his situation has become a much-discussed topic on various Chinese social media platforms.
Jack Ma in Short
Being among the top 20 richest people in the world, Jack Ma is world-famous as the founder of Alibaba, a multinational tech company specializing in e-commerce that was founded in 1999.
Jack Ma, whose Chinese name is Ma Yun 马云, was born in Hangzhou in 1964 to a family of low status. His life story has been retold in many books. Ma was bullied at school, had poor math skills, and flunked the entrance exam twice before he was accepted into the Hangzhou Teacher’s Institute, where he graduated in 1988 with a Bachelor of Arts in English.
Ma had been interested in English since he was a young boy. He would cycle to the main hotel in his city to connect with foreign tourists, acting as their local tour guide in return for English classes. The name ‘Jack’ was given to him by one of the tourist friends he made at that time.

image via kknews.cc
Ma went on to become an English teacher and barely even touched a keyboard before he traveled to the US in 1995 as an interpreter. It was during this trip that he was first introduced to the internet, after which he became inspired to set up his own commercial web site in China – a web site named ‘China Pages’ for Chinese businesses.
Although that business flopped, Jack Ma founded Alibaba in 1999, which would turn into an internet giant influencing virtually all corners of China’s digital world. The Alibaba Group now operates numerous businesses, including Taobao, TMall, AliExpress, and the Ant Group.
Ma’s success is a source of inspiration to many, and his ‘crazy Jack’ energetic behavior and willingness to make fun of himself has only made him and his story all the more captivating.

A younger Ma in one of his fun song-and-dance appearances – as Snow White.
Ma officially stepped down as Alibaba’s CEO in 2019 but is still the company’s largest individual shareholder.
“What’s up with Ma Yun?”
Until recently, Jack Ma was one of the more popular Chinese celebrities on social media. Jack Ma quotes, memes, videos, or stories would frequently go viral.
As one of the most respected and powerful entrepreneurs of China, bookstores have entire sections dedicated to Jack Ma and his role as a business magnate, the richest man of China, and also as a welldoer and an inspiring influential.

Books about Jack Ma.
Whatever Ma would say or do would go trending, with many people praising what he did, what he said, or where he went.
In 2017, the meeting between US President Trump and Alibaba’s Ma was a big topic of discussion, with many Chinese web users taking pride in Ma’s meeting with Trump, calling him the perfect ambassador to China in their dealings with Trump. “Ma Yun [Jack Ma] for president!” was a much recurring phrase.
It is a phrase you won’t read as much, if at all, on Chinese social media these days anymore. The silence surrounding Jack Ma recently has led to speculation and reflections on his current situation.
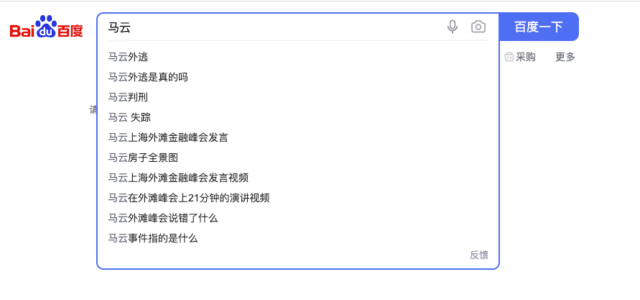
On Chinese search engine Baidu, the search prediction reflects web users’ confusion over his whereabouts; upon searching for ‘Ma Yun’ in the first week of January, the first five automatic predictions are the following:
– Jack Ma fled abroad
– Did Jack Ma really flee abroad?
– Jack Ma sentenced to prison
– Jack Ma disappeared
– Jack Ma Shanghai Bund speech
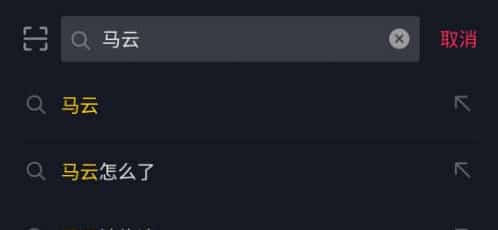
On Douyin (the Chinese TikTok), the first sentence to come up when searching for Ma Yun, is “What’s up with Ma Yun?”
On Weibo, where Jack Ma has over 26.4 million followers on his official account, there have not been any new posts since October 17. But Ma’s last post, which talks about an educational event, is still attracting new comments every few minutes.
“Daddy Ma, come on, ok? We’re rooting for you,” one commenter writes.
“We haven’t seen you in a long time, Brother Ma,” some write: “When will you come back into the public arena?”, with others saying: “Teacher Ma, what happened?”
But besides the messages from those who seem concerned about the well-being of the tech tycoon, there are many angry ones.
Some blame Ma for praising the ‘996’ work system (working from 9am-9pm, 6 days a week). In 2019, Ma called the 12-hour working day a “blessing,” causing much controversy online. Because the death of a young employee at Pinduoduo was also linked to her long working hours, the ‘996’ work system is a hot topic this week, with many condemning how Chinese tech companies are exploiting their employees and revisiting Ma’s 2019 comments.
Others also turn to Jack Ma’s Weibo page to complain about the shutdown of Alibaba’s music streaming app Xiami. Although Xiami only holds a small percentage of China’s music streaming market – apps such as QQ Music and KuGou are more popular – there are still many people who have been using the app for years and hate to see it go: “Why can’t you give it another chance, why can’t you take care of our Xiami!?”
And then there are those commenters who, in light of the recent developments and anti-monopoly investigations, call Ma a “greedy capitalist” and a “bloodsucker.” “Maybe he’ll be punished,” one person writes: “Is that a ‘blessing’ too?” “I went from being a fan to a hater,” another commenter writes, with others calling him an opportunist.
Changing Sentiments on Social Media
Jack Ma used to be an idol for many young people in China, but now it seems they have started to oppose him. On the Chinese video sharing site Bilibili, mainly used by younger generations, comments appearing in some videos featuring Ma are filled with anger and scolding.

This shift in Ma’s popularity among young people was recently also explained by young Chinese vlogger Yu He in this video, who argues that young people do not adore Jack Ma in the same way older Chinese people do.
Ma’s vision of working really hard, praising the ‘996’ work culture, and “everybody can be successful if you really try hard” was an inspiration to previous generations, but many post-90s people in China today – who are struggling in a highly competitive job market – do not have a lot of faith in Ma’s work philosophy when their everyday lives are not about working to live, but about living to work. To them, Ma’s ideas about working around the clock to get further in life do not make sense, as some feel they are working themselves to death while others get rich.
There is also anger over consumer lending platform Huabei, a product of Alibaba’s Ant Group. Huabei previously encouraged users to spend more money in its ads, and its platform makes it very easy to spend money first and pay it back later – even for those who might not oversee the long-term consequences of excessive debt.
The question of why Jack Ma seems to have fallen out of favor with many Chinese people is also a topic of discussion on question-and-answer platform Zhihu.com.
One popular analysis by the e-commerce account Zhiser claims that Jack Ma used to be supported by the ordinary people because he made it possible for so many of them to make money through the Taobao marketplace platform, which started in 2003. Alibaba’s Alipay online payment platform made it possible for common people to conveniently transfer money without extra fees.
But over recent years, Zhiser argues, Alibaba’s business strategies have changed in such a way that its own profits are maximized and small sellers are negatively impacted.
With the arrival and growth of Alibaba’s Tmall, where only brand owners or authorized dealers can open an online store & where transaction commissions are much higher, the traffic of small sellers on the Taobao marketplace has been reduced. Alibaba’s activities are increasingly focused on benefiting the bigger companies – and itself -, while small entrepreneurs are increasingly struggling to be noticed and make money.
Without the means to open their own Tmall shop, without the capital to afford advertisement and paid promotions for their shops, the small sellers are watching helplessly how the big boys dominate the platform algorithms and take the money, Zhiser explains.
Alibaba is now also increasingly focusing on the fruit & vegetable market. There’s Alibaba’s Hema Fresh supermarket brand, for example, with big plans to open hundreds of stores nationwide in the upcoming years. The rise of Alibaba’s fresh food businesses directly impacts the livelihood of ten thousands of ordinary Chinese who have their own small vegetable shops or street stalls – exactly those people who are already in vulnerable social groups.
Although the rise of Alibaba was once a great opportunity for common people, the changing business strategies have now resulted in Jack Ma getting more enemies, including small entrepreneurs, small sellers and buyers, offline shops, offline vendors, etc.
For them, the ‘Alibaba dream’ of using the power of the Internet and technological advancement to enable small businesses and young people to share the benefits of free trade has lost credibility.
“These years, Jack Ma has played the role of the destroyer rather than the savior,” the author writes. His article received over 10,500 endorsements.
Zhiser’s article reflects a perspective that surfaces in many places. “We believed him, that he really was making things better for us,” another blogger writes.
Others think that Jack Ma was true about his intentions and dreams when he was a teacher and then started his business, but changed when he became surrounded by money-driven big investors, causing him to become alienated from his former ideas and philosophies, losing touch with China’s younger generation, the small shop owners he promised to serve and the ordinary people.
“He changed China, he changed the world”
Despite the recent criticism of Ma, many people still defend and support him. There are even those who criticize him but still express their admiration for him.
Regarding the criticism coming from post-90s generations, one Chinese web user commented:
“You have no idea what it was like before Jack Ma came around. You’re too young to know. If you want to go back [in that time], I suggest you go live on the moon.”
Discussing the changing sentiments regarding Ma, Zhihu author Qing Rui writes:
“Jack Ma is a great entrepreneur of this era. He changed China, he changed the world. A lot of nonsensical people scold him for damaging China’s real economy, while he’s actually worked hard to improve the efficiency of the business sector, which has not only greatly boosted the real economy, but also greatly improved the living standards of the Chinese people.”
It is a sentiment shared by many, who express that they think the recent shift in views on Ma is uncalled for, or reminding people of the positive effect Ma and his businesses have had on China’s development.
“Those who scold Jack Ma are brainless idiots,” some write.
“How is it possible for the public opinion on Daddy Ma shifting 180 degrees? It’s like throwing stones at someone who fell down,” one Weibo user from Shenyang writes.
Although perhaps less crowded than before, online ‘Ma Yun Fanclubs’ are still active. One Weibo fan writes: “Let’s all hope our favorite idol Ma Yun will smoothly sail through this crisis!”
As for the ‘disappearance’ of Jack Ma that has previously been reported – although Ma has not been out in public, it is highly unlikely that he is actually missing.
CNBC reported on January 5 that the Chinese billionaire is lying low, according to a person familiar with the matter.
When famous Chinese actress Fan Bingbing got caught up in a tax evasion scandal in 2018, her ‘disappearance’ also made headlines in international media. After months of silence and wild rumors, the actress returned to social media with a public apology. She was ordered to pay taxes and fines worth hundreds of millions of yuan.
Meanwhile, Jack Ma’s Weibo page is still receiving dozens of new messages. In between the “evil capitalist” scoldings, there are some who really hope Ma will come back to public life soon: “We’ll support you, teacher Ma, don’t give up!”
By Manya Koetse
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2021 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Books & Literature
Why Chinese Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Shopping Festival
Bookworms love to get a good deal on books, but when the deals are too good, it can actually harm the publishing industry.
Published
2 months agoon
June 8, 2024By
Ruixin Zhang
JD.com’s 618 shopping festival is driving down book prices to such an extent that it has prompted a boycott by Chinese publishers, who are concerned about the financial sustainability of their industry.
When June begins, promotional campaigns for China’s 618 Online Shopping Festival suddenly appear everywhere—it’s hard to ignore.
The 618 Festival is a product of China’s booming e-commerce culture. Taking place annually on June 18th, it is China’s largest mid-year shopping carnival. While Alibaba’s “Singles’ Day” shopping festival has been taking place on November 11th since 2009, the 618 Festival was launched by another Chinese e-commerce giant, JD.com (京东), to celebrate the company’s anniversary, boost its sales, and increase its brand value.
By now, other e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and Pinduoduo have joined the 618 Festival, and it has turned into another major nationwide shopping spree event.
For many book lovers in China, 618 has become the perfect opportunity to stock up on books. In previous years, e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Dangdang (当当) would roll out tempting offers during the festival, such as “300 RMB ($41) off for every 500 RMB ($69) spent” or “50 RMB ($7) off for every 100 RMB ($13.8) spent.”
Starting in May, about a month before 618, the largest bookworm community group on the Douban platform, nicknamed “Buying Like Landsliding, Reading Like Silk Spinning” (买书如山倒,看书如抽丝), would start buzzing with activity, discussing book sales, comparing shopping lists, or sharing views about different issues.

Social media users share lists of which books to buy during the 618 shopping festivities.
This year, however, the mood within the group was different. Many members posted that before the 618 season began, books from various publishers were suddenly taken down from e-commerce platforms, disappearing from their online shopping carts. This unusual occurrence sparked discussions among book lovers, with speculations arising about a potential conflict between Chinese publishers and e-commerce platforms.
A joint statement posted in May provided clarity. According to Chinese media outlet The Paper (@澎湃新闻), eight publishers in Beijing and the Shanghai Publishing and Distribution Association, which represent 46 publishing units in Shanghai, issued a statement indicating they refuse to participate in this year’s 618 promotional campaign as proposed by JD.com.
The collective industry boycott has a clear motivation: during JD’s 618 promotional campaign, which offers all books at steep discounts (e.g., 60-70% off) for eight days, publishers lose money on each book sold. Meanwhile, JD.com continues to profit by forcing publishers to sell books at significantly reduced prices (e.g., 80% off). For many publishers, it is simply not sustainable to sell books at 20% of the original price.
One person who has openly spoken out against JD.com’s practices is Shen Haobo (沈浩波), founder and CEO of Chinese book publisher Motie Group (磨铁集团). Shen shared a post on WeChat Moments on May 31st, stating that Motie has completely stopped shipping to JD.com as it opposes the company’s low-price promotions. Shen said it felt like JD.com is “repeatedly rubbing our faces into the ground.”
Nevertheless, many netizens expressed confusion over the situation. Under the hashtag topic “Multiple Publishers Are Boycotting the 618 Book Promotions” (#多家出版社抵制618图书大促#), people complained about the relatively high cost of physical books.
With a single legitimate copy often costing 50-60 RMB ($7-$8.3), and children’s books often costing much more, many Chinese readers can only afford to buy books during big sales. They question the justification for these rising prices, as books used to be much more affordable.
Book blogger TaoLangGe (@陶朗歌) argues that for ordinary readers in China, the removal of discounted books is not good news. As consumers, most people are not concerned with the “life and death of the publishing industry” and naturally prefer cheaper books.
However, industry insiders argue that a “price war” on books may not truly benefit buyers in the end, as it is actually driving up the prices as a forced response to the frequent discount promotions by e-commerce platforms.
China News (@中国新闻网) interviewed publisher San Shi (三石), who noted that people’s expectations of book prices can be easily influenced by promotional activities, leading to a subconscious belief that purchasing books at such low prices is normal. Publishers, therefore, feel compelled to reduce costs and adopt price competition to attract buyers. However, the space for cost reduction in paper and printing is limited.
Eventually, this pressure could affect the quality and layout of books, including their binding, design, and editing. In the long run, if a vicious cycle develops, it would be detrimental to the production and publication of high-quality books, ultimately disappointing book lovers who will struggle to find the books they want, in the format they prefer.
This debate temporarily resolved with JD.com’s compromise. According to The Paper, JD.com has started to abandon its previous strategy of offering extreme discounts across all book categories. Publishers now have a certain degree of autonomy, able to decide the types of books and discount rates for platform promotions.
While most previously delisted books have returned for sale, JD.com’s silence on their official social media channels leaves people worried about the future of China’s publishing industry in an era dominated by e-commerce platforms, especially at a time when online shops and livestreamers keep competing over who has the best book deals, hyping up promotional campaigns like ‘9.9 RMB ($1.4) per book with free shipping’ to ‘1 RMB ($0.15) books.’
This year’s developments surrounding the publishing industry and 618 has led to some discussions that have created more awareness among Chinese consumers about the true price of books. “I was planning to bulk buy books this year,” one commenter wrote: “But then I looked at my bookshelf and saw that some of last year’s books haven’t even been unwrapped yet.”
Another commenter wrote: “Although I’m just an ordinary reader, I still feel very sad about this situation. It’s reasonable to say that lower prices are good for readers, but what I see is an unfavorable outlook for publishers and the book market. If this continues, no one will want to work in this industry, and for readers who do not like e-books and only prefer physical books, this is definitely not a good thing at all!”
By Ruixin Zhang, edited with further input by Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Digital
China’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
It’s Gaokao time! For the first time, China’s Gaokao essay topic was about the latest AI developments, triggering discussions on social media.
Published
2 months agoon
June 7, 2024
This week, China’s National College Entrance Exams, better known as the “Gaokao” (高考), became one of the most-discussed topics on Chinese social media. ‘Gaokao,’ ‘AI,’ and ‘Gaokao essay’ were the hottest words on Weibo by the end of the week.
The Gaokao (literally: ‘higher exams’) are a prerequisite for entering China’s higher education institutions and are usually taken by students in their last year of senior high school. June 7th marked the first day of the Gaokao, which will continue until June 9th.
For the over 13.4 million participating students, the Gaokao week is a pivotal moment. Scoring high on this exam can grant access to better colleges, significantly improving their chances of obtaining a good job after graduation. Given the potentially life-changing results, the Gaokao period is a stressful time for both students and their parents.
The Gaokao essay (高考作文) is a significant component of the Chinese language exam, testing students’ writing skills, critical thinking, and ability to express ideas coherently. The essay, which must be completed within a limited time, requires students to discuss given topics.
These topics are generally related to Chinese society and culture, consistently attracting attention on social media. This year, multiple essay questions were related to AI and social media.
Those taking the Beijing exam (北京卷), for example, received a question related to the “like” function on WeChat, suggesting that some people feel strongly about the number of “likes” they receive and give, asking students to reflect on the phenomenon of receiving and giving “likes” on social media.
But the question receiving the most attention on social media was part of the New Curriculum Standard Test I (新课标I卷), which is distributed among different provinces.
Students vs. Chatbots: Letting AI Write an Essay on AI
Students received the following topic prompt for their Gaokao essay, which should be at least 800 characters long:
“With the spread of the internet and AI applications, we can quickly get answers to more and more questions. Will this also lead to us having fewer problems?” (随着互联网的普及、人工智能的应用,越来越多的问题能很快得到答案。那么,我们的问题是否会越来越少?)
The question sparked discussions because it was the first time a Gaokao essay question focused on AI applications designed to interact with users, like ChatGPT.
Although many thought the essay question was easy—unlike this year’s math exam—it still generated some interesting reflections.
Some Weibo users responded that the answer to the question was within the question itself. One Weibo blogger answered: “If there were no AI, we wouldn’t have this question, so problems/questions related to AI will only increase. The emergence of new things will inevitably be accompanied by new problems.”
Others commented on the concerns brought by the emergence of AI applications like ChatGPT. In early 2023, hashtags such as “Ten Professions That Could be Replaced by ChatGPT” (#可能被ChatGPT取代的10大职业#) gained a lot of attention on Chinese social media, where many were concerned that jobs from various industries, including customer service, programming, media, education, market research, finance, etc., would soon be done by AI chatbots instead of humans.
In line with this thought and the AI theme of this year’s Gaokao essay, netizens and some Chinese media outlets decided to let various language models take the exam and see how they would perform: could AI actually do better in writing an essay about AI than Chinese students? (Related hashtags: #让AI写高考作文#, #假如AI写高考语文作文#; #ChatGPT来交卷了#).
Xinhua, for example, asked Open AI’s ChatGPT to answer various questions. Sina Tech (新浪科技) also asked OpenAI’s ChatGPT to answer the AI-related essay question, along with Chinese chatbots, like Baidu’s Erniebot (文心一言), Tencent’s Yuanbao (元宝), iFlytek’s Sparkdesk (星火), and Alibaba’s Tongyi Qianwen (通义千问). Toutiao News did the same, letting three chatbots (ChatGPT, Erniebot, Tongyi Qianwen) compete against each other.
There is no general consensus on how well these AI chatbots can write a Gaokao essay. Although compared to last year, there are now more and better domestic AI models, OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4 is generally still seen as the best chatbot out there.
This was its answer (originally in Chinese, translated to English with ChatGPT):
New Issues and Thoughts Brought by Technological Progress
With the popularization of the internet and the application of artificial intelligence, we can quickly obtain a large amount of information, and many questions can be answered in a short time. However, does this mean that we will have fewer questions? I believe the answer is no.
Firstly, although technology provides us with convenience, new technologies also bring new problems. The popularization of the internet has made information dissemination faster, but at the same time, the authenticity and accuracy of information have become new concerns. Fake news, information overload, and privacy breaches are increasingly prominent issues. These new problems need to be identified, understood, and resolved by us.
Secondly, the application of artificial intelligence, although it improves efficiency, also brings ethical and social issues. The transparency of AI decision-making, algorithmic bias, and the impact on the job market are all urgent issues that society needs to address. People need to constantly raise new questions to ensure a balance between technological progress and social welfare.
Furthermore, the development of technology prompts us to reflect more deeply on humanity itself. We need to rethink the relationship between humans and technology and consider the role and boundaries of technology in our lives. These philosophical issues are more important than ever.
Therefore, technological progress does not reduce our questions but rather prompts more new questions and reflections. It is these constantly emerging questions that drive social progress and human thought. We need to embrace the challenges brought by technology with a more open and critical attitude and actively seek solutions.
Although the domestic chatbots gave somewhat different answers, the overall tone was similar, though some commenters argued that ChatGPT was still the strongest, along with iFlytek’s Sparkdesk.
An online poll asking Weibo users to grade the ChatGPT essay from lower than 20 points up to the full 60 points saw divided responses, though a majority rated it as lower than 20 points.
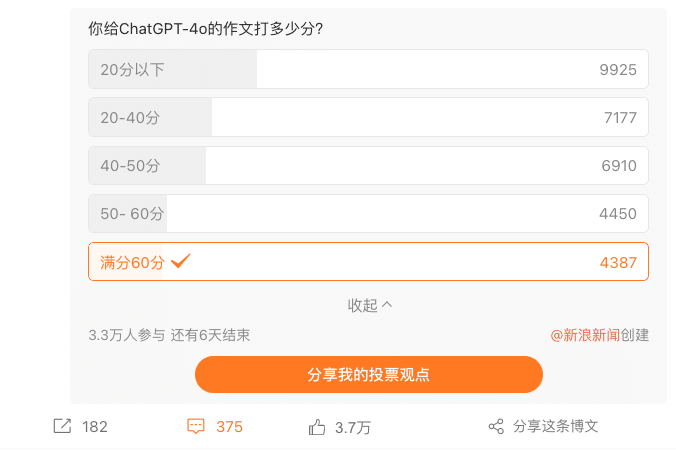
How well can ChatGPT write an essay about AI? Opinions are divided.
This shows that many commenters think that AI chatbots are still not able to beat humans when it comes to writing Gaokao essays.
Commenters reacted to the various AI-generated essays in various ways, including:
• “Actually, none of them are very good. They are too formulaic and standardized, lacking the natural creativity and originality that humans possess.”
• “They just give soulless standard answers.”
• “It’s all about ‘firstly,’ ‘secondly,’ ‘furthermore.'”
• “There are no examples, no points proven; it should be a low grade.”
• “It’s just too stiff.”
• “This is like reading reports, not essays.”
• “AI places more emphasis on logic, which aligns with the writing style of foreigners.”
• “There’s no feeling in these essays; there’s a certain kind of AI feeling to AI.”
Meanwhile, some bloggers are taking up the challenge and are publishing their own online essays in response to the Gaokao question.
Some of them are not worried that chatbots will take over their critical tasks: “AI will be AI. There’s no connection to the social realities, and it’s as cold as ice.”
“Their words might make sense, but they lack feeling.”
But for some discussing the topic, they have come to realize that they are already depending too much on digital tools and AI applications for their everyday tasks, writing: “I made an attempt to write an essay, but discovered I already forgot how to do it!” For them, the discussion itself is a wake-up call that writing an essay from scratch is a skill that requires practice and cannot be fully replaced by chatbots, making personal creativity essential to score points and avoid the ‘AI-fication’ of texts.
PS:
In his book China’s Millennials, Eric Fish describes the limits on Chinese students’ answers; taboo responses, such as those containing harsh criticisms of the Chinese government or society, could potentially lead to failure. Although the essay is purportedly meant to showcase the student’s creativity, it must adhere to the unwritten rules of what is socially acceptable.
By Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Future is Here

“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese

Enjoying the ‘Sea’ in Beijing’s Ditan Park

A Triumph for “Comrade Trump”: Chinese Social Media Reactions to Trump Rally Shooting

Weibo Watch: Get Up, Stand Up

The Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Singing Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

About the “AI Chatbot Based on Xi Jinping” Story

China’s Intensified Social Media Propaganda: “Taiwan Must Return to Motherland”

Weibo Watch: Telling China’s Stories Wrong

Saying Goodbye to “Uncle Wang”: Wang Wenbin Becomes Chinese Ambassador to Cambodia
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight3 months ago
China Insight3 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music4 months ago
China Music4 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoToo Sexy for Weibo? Online Discussions on the Concept of ‘Cābiān’
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months agoBehind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?







Chin CKit
January 10, 2021 at 7:04 am
Jack Ma the Chinese Mr. Bean.
Olivier VEROT
January 11, 2021 at 1:09 pm
great post @Manya.
Very interesting to see the fight between nationalist (and army of the propaganda) and the true fan of Jack Ma.
Jack is a real leader and inspire hundred of thousand of business men in China.
He is missing creating a real problem in the society…
The fight between billionaires and state.
slitherio
January 27, 2021 at 5:09 am
We’ll support you, teacher Ma, don’t give up!