China Insight
How China’s New Anti-Crime Policy Made a Hunt for Two Jailbreak Fugitives Go Viral
The CPC actively involves and rewards citizens in their new policy on combatting crimes.
Published
6 years agoon
By
Gabi Verberg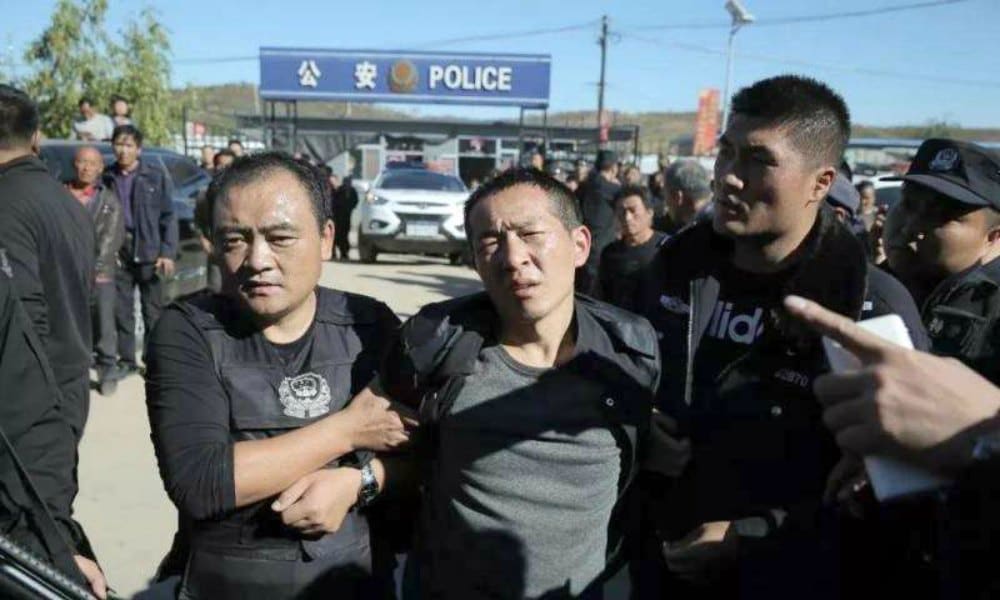
In early October of 2018, a major manhunt on two jailbreak fugitives from a Liaoning prison dominated the news for days and caused a sensation on the Chinese internet. With the 100,000 yuan (US$14,500) reward notice going viral, it marked the first grand online exposure of the Chinese government’s policy to involve its citizens in combatting crime actively, but many netizens question how safe it is for citizens to meddle in criminal affairs.
News about a prison escape of two convicted criminals captured the attention of netizens for days in the first week of October, with the fugitives’ background information, the thrilling chase, and the 100,000 yuan (US$14,500) reward notice all turning out to be the perfect ingredients to keep people hooked on the story, that also happened to occur during the National Day holiday.
The incident was extra special because it was the first major case in which the Chinese government’s ‘new’ method on battling crime by actively involving the public, received massive attention.
Timeline of the Chase
* Thursday, October 4th, morning:
News comes out that two prisoners have managed to escape from Lingyuan Third Prison in Liaoning province. According to the Beijing Youth Daily, the two criminals stole prison guards’ uniforms and used the attached security cards to get out of the building.
The fugitives, two men by the names of Zhang Guilin (33, 张贵林) and Wang Lei (39, 王磊), were both sentenced to life imprisonment for, respectively, armed robbery and the involvement in kidnapping and murder of an 11-year-old child. Zhang, also nicknamed “Flying Zhang,” gained a reputation for previous prison escapes in 2011 and 2012; the October jailbreak marks his third successful prison escape.
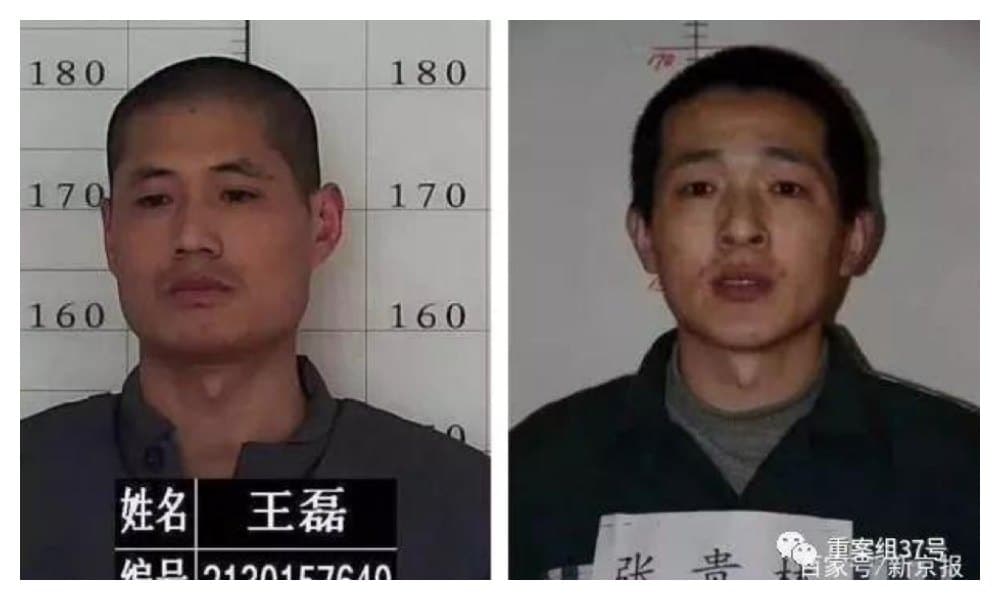

Fugitives Wang (l) and Zhang (r).
*October 4th, morning:
Soon after the criminals escaped from prison, the Lingyuan Municipal Public Security Bureau issues a notice sharing the identity of the fugitives, asking the public to provide clues about their whereabouts. They also announce the clue leading to their arrest will be rewarded with a staggering US$14,500.
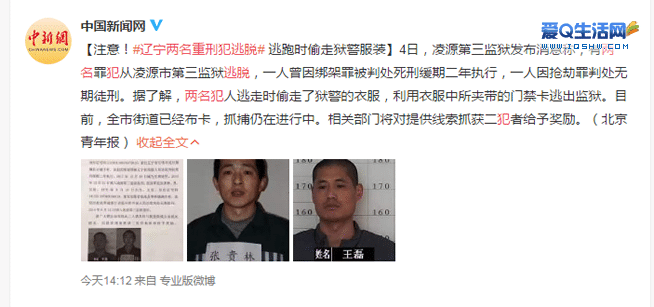
The news quickly spreads on Chinese social media, and within no time, the hashtag “Two heavy criminals escaped from prison” #两名重刑犯逃脱# goes viral and receives 170 million views.
*October 4th, 11 am:
The first tip-off: Beijing News publishes crucial surveillance camera footage that was given to police by a small shop in Songzhangzi, only 20 kilometers away from Lingyuan Third prison. It shows the two fugitives buying some food, beverages, and cigarettes, just hours after their escape from prison.

*October 4th, 5 pm:
Wang is spotted at another shop in a village in Pingquan County, in neighboring Hebei province, where he stays for about 10 minutes to buy liquor, beer, mineral water, and sausages.

Police rush to the kiosk shortly after. According to China Daily, about 800 police quickly arrive and nearly 1,000 villagers assist in the manhunt, searching the area from north to south.
*Friday, October 5th:
On the second day of the nationwide manhunt, a fatal crash occurs with a police car involved in the chase for the fugitives. The police car, with four police officers from the Hebei Police Department, was on its way to catch the breakers when it crashed into a tree. Two police officers did not survive the crash.
On Friday night, 430 officers are dispatched to Pingquan, along with 100 prison guards.
*Saturday afternoon, October 6th:
Within 50 hours of their escape, Wang and Zhang are captured. Police in the Hebei city of Chengde dispatch drones to scour the area and spot the convicts in the village of Taitoushan.
According to news reports, Zhang is arrested when he stops to ask a villager for directions. His fellow escapee is caught 20 minutes later.

The hashtags “Two escaped criminals from Liaoning are caught” #逃犯落网视频曝光# and “Video showing arrested fugitives” 逃犯落网视频曝光 are viewed millions of times.
Authorities in Liaoning launch an investigation, and the warden of Lingyuan Prison is dismissed from his position.
“Public Reporting on Crime”
The Lingyuan jailbreak fugitive case is the first example of a reward notice going viral since the PRC government launched a new trial policy in combatting corruption and other illegal practices earlier in 2018.
The ‘new’ policy is called “Public Reporting on Crime” (群众举报黑恶势力违法犯罪), and aims at actively involving and rewarding citizens in providing information about the whereabouts of criminals.

A state media illustration that propagates public reporting on criminal affairs.
The policy was featured in various media reports in summer of 2018, as a method introduced by the State Council of the People’s Republic of China, the Supreme’s People’s Court, Ministry of Public Security, and the Ministry of Justice.
The policy defines 11 categories in which citizens can report illegal practices, including the misuse of (political) power, illegal gambling practices, fraud in various industry sectors, and extortion.

“Reporting is Awarded” (image via sohu.com).
The official document in which the role of the public in the combat of illegal activities was especially stressed, was already issued by authorities in February of 2018 (“关于依法严厉打击黑恶势力违法犯罪的通告”, see Pkulaw.cn).
Amongst the first provinces to experiment with the police are, among others, Henan province, Hainan, and Liaoning province, where the method seems fruitful. In August, the Hainan Police department issued a notice asking for the public’s help in finding 17 fugitives. Attached to the notice where their names, addresses, and photographs. Within two days, 11 of these 17 fugitives were caught by the police.
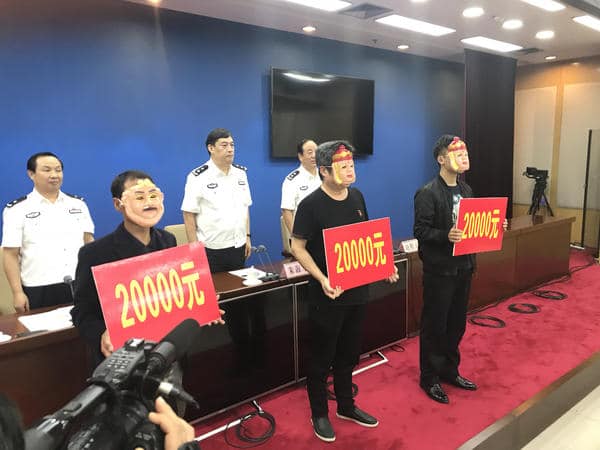

Award ceremony in Henan for people providing clues to police (https://www.henan100.com/news/2018/805020.shtml).
In Liaoning province, the police started a campaign providing digital and non-digital information about the new policy and the criminals they were looking for. According to local media, they soon received 300 clues and 158 fugitives who turned themselves in.
Possibly as a result of the first successes of the trial policy, the Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of China, wrote an extension on the policy concerning drugs. On the official website of the Ministry, they published a list of rewards for providing information about ‘drugs practices’. On the list, it says precisely what people can earn for providing clues about several kinds of drugs, where clues relating to soft drugs such as marihuana will receive a lower reward than those relating to hard drugs such as heroin.

Award ceremony (http://sc.people.com.cn/n2/2018/0706/c345167-31785050.html).
State media have been actively propagating the measure in 2018, also reporting on occasions where people are rewarded for giving clues to the police. To protect their identity, these people will commonly wear masks – sometimes even cute panda ones.
Scepticism on Safety
Wearing panda masks or not, there is ample skepticism online on whether or not providing information to the police is a dangerous move for those involved.
In the case of the Liaoning fugitives, many worried about the identity of the shopkeepers who provided the police with clues and security footage after the fugitives had visited their shops.
After the first sighting of the two criminals in the small store in Songzhangzi, Chinese media reported details on the shop and its owner, which led to much criticism on Weibo. Some commenters wrote: “You brain-dead media, how can you bring out information like this, and who is going to take responsibility when people retaliate against this man?”
Many others expressed their worries, saying: “Isn’t is dangerous to expose the boss [of the shop] like this?”, and “Please do protect this shop owner, thank you!”
Other netizens wrote: “After seeing this news, I know for sure, I will never report on crimes. It’s too dangerous, I don’t want to die.”
The public reporting policy states that the personal safety and confidentiality of ‘whistleblowers’ is guaranteed and that those who turn against these people will be punished severely. According to a post on Weibo by Beijing News, the small shopkeeper in question also received 24-hour police protection in front of his shop.
Concerning the case of the two escaped prisoners, so far, it is not yet clear if the main reward has been given out to citizens for giving the main clue that led to their recapture.
What does seem evident in this case, is that people, despite some worries about their safety, are more than willing to report illegal practices to the police when they know there might be a big reward waiting for them.
By Gabi Verberg and Manya Koetse
Follow @whatsonweibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us.
©2018 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Gabi Verberg is a Business graduate from the University of Amsterdam who has worked and studied in Shanghai and Beijing. She now lives in Amsterdam and works as a part-time translator, with a particular interest in Chinese modern culture and politics.

Also Read
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea
Chinese tea brand LELECHA faced backlash for using the iconic literary figure Lu Xun to promote their “Smoky Oolong” milk tea, sparking controversy over the exploitation of his legacy.
Published
4 days agoon
May 3, 2024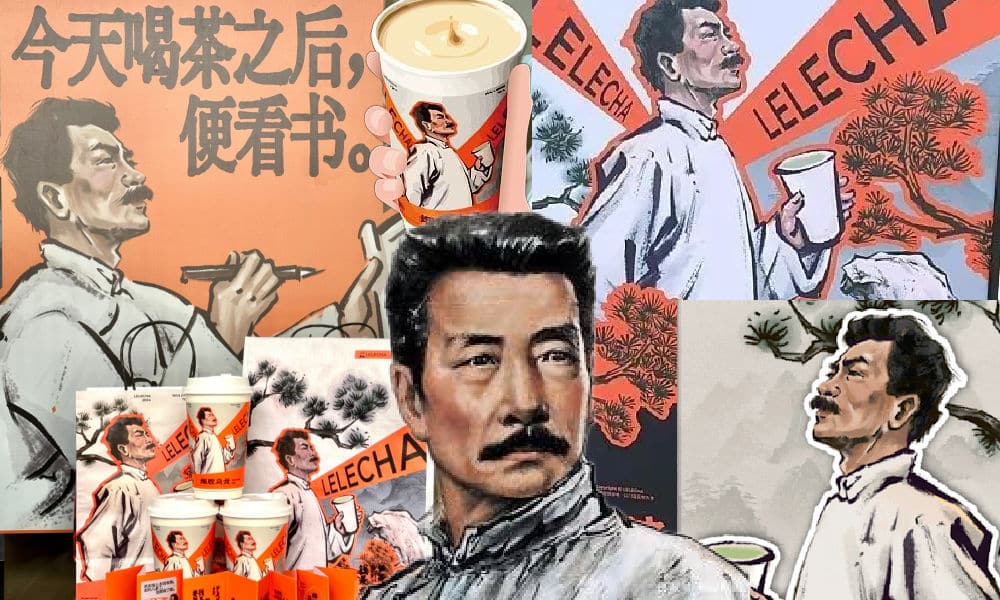
It seemed like such a good idea. For this year’s World Book Day, Chinese tea brand LELECHA (乐乐茶) put a spotlight on Lu Xun (鲁迅, 1881-1936), one of the most celebrated Chinese authors the 20th century and turned him into the the ‘brand ambassador’ of their special new “Smoky Oolong” (烟腔乌龙) milk tea.
LELECHA is a Chinese chain specializing in new-style tea beverages, including bubble tea and fruit tea. It debuted in Shanghai in 2016, and since then, it has expanded rapidly, opening dozens of new stores not only in Shanghai but also in other major cities across China.
Starting on April 23, not only did the LELECHA ‘Smoky Oolong” paper cups feature Lu Xun’s portrait, but also other promotional materials by LELECHA, such as menus and paper bags, accompanied by the slogan: “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” (“老烟腔,新青年”). The marketing campaign was a joint collaboration between LELECHA and publishing house Yilin Press.

Lu Xun featured on LELECHA products, image via Netease.
The slogan “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” is a play on the Chinese magazine ‘New Youth’ or ‘La Jeunesse’ (新青年), the influential literary magazine in which Lu’s famous short story, “Diary of a Madman,” was published in 1918.
The design of the tea featuring Lu Xun’s image, its colors, and painting style also pay homage to the era in which Lu Xun rose to prominence.
Lu Xun (pen name of Zhou Shuren) was a leading figure within China’s May Fourth Movement. The May Fourth Movement (1915-24) is also referred to as the Chinese Enlightenment or the Chinese Renaissance. It was the cultural revolution brought about by the political demonstrations on the fourth of May 1919 when citizens and students in Beijing paraded the streets to protest decisions made at the post-World War I Versailles Conference and called for the destruction of traditional culture[1].
In this historical context, Lu Xun emerged as a significant cultural figure, renowned for his critical and enlightened perspectives on Chinese society.
To this day, Lu Xun remains a highly respected figure. In the post-Mao era, some critics felt that Lu Xun was actually revered a bit too much, and called for efforts to ‘demystify’ him. In 1979, for example, writer Mao Dun called for a halt to the movement to turn Lu Xun into “a god-like figure”[2].
Perhaps LELECHA’s marketing team figured they could not go wrong by creating a milk tea product around China’s beloved Lu Xun. But for various reasons, the marketing campaign backfired, landing LELECHA in hot water. The topic went trending on Chinese social media, where many criticized the tea company.
Commodification of ‘Marxist’ Lu Xun
The first issue with LELECHA’s Lu Xun campaign is a legal one. It seems the tea chain used Lu Xun’s portrait without permission. Zhou Lingfei, Lu Xun’s great-grandson and president of the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation, quickly demanded an end to the unauthorized use of Lu Xun’s image on tea cups and other merchandise. He even hired a law firm to take legal action against the campaign.
Others noted that the image of Lu Xun that was used by LELECHA resembled a famous painting of Lu Xun by Yang Zhiguang (杨之光), potentially also infringing on Yang’s copyright.
But there are more reasons why people online are upset about the Lu Xun x LELECHA marketing campaign. One is how the use of the word “smoky” is seen as disrespectful towards Lu Xun. Lu Xun was known for his heavy smoking, which ultimately contributed to his early death.
It’s also ironic that Lu Xun, widely seen as a Marxist, is being used as a ‘brand ambassador’ for a commercial tea brand. This exploits Lu Xun’s image for profit, turning his legacy into a commodity with the ‘smoky oolong’ tea and related merchandise.
“Such blatant commercialization of Lu Xun, is there no bottom limit anymore?”, one Weibo user wrote. Another person commented: “If Lu Xun were still alive and knew he had become a tool for capitalists to make money, he’d probably scold you in an article. ”
On April 29, LELECHA finally issued an apology to Lu Xun’s relatives and the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation for neglecting the legal aspects of their marketing campaign. They claimed it was meant to promote reading among China’s youth. All Lu Xun materials have now been removed from LELECHA’s stores.

Statement by LELECHA.
On Chinese social media, where the hot tea became a hot potato, opinions on the issue are divided. While many netizens think it is unacceptable to infringe on Lu Xun’s portrait rights like that, there are others who appreciate the merchandise.
The LELECHA controversy is similar to another issue that went trending in late 2023, when the well-known Chinese tea chain HeyTea (喜茶) collaborated with the Jingdezhen Ceramics Museum to release a special ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ (佛喜) latte tea series adorned with Buddha images on the cups, along with other merchandise such as stickers and magnets. The series featured three customized “Buddha’s Happiness” cups modeled on the “Speechless Bodhisattva” (无语菩萨), which soon became popular among netizens.
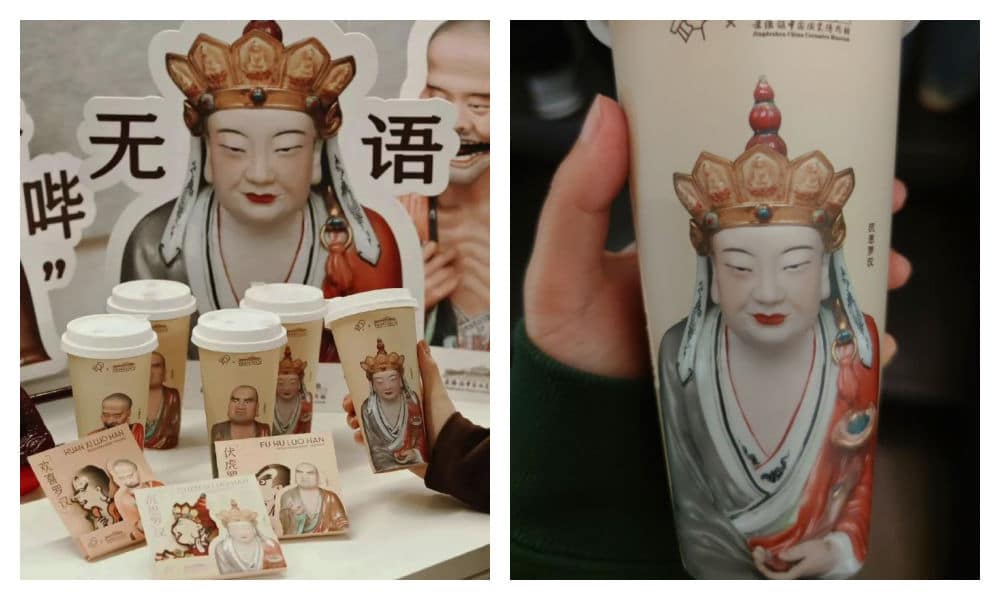

The HeyTea Buddha latte series, including merchandise, was pulled from shelves just three days after its launch.
However, the ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ success came to an abrupt halt when the Ethnic and Religious Affairs Bureau of Shenzhen intervened, citing regulations that prohibit commercial promotion of religion. HeyTea wasted no time challenging the objections made by the Bureau and promptly removed the tea series and all related merchandise from its stores, just three days after its initial launch.
Following the Happy Buddha and Lu Xun milk tea controversies, Chinese tea brands are bound to be more careful in the future when it comes to their collaborative marketing campaigns and whether or not they’re crossing any boundaries.
Some people couldn’t care less if they don’t launch another campaign at all. One Weibo user wrote: “Every day there’s a new collaboration here, another one there, but I’d just prefer a simple cup of tea.”
By Manya Koetse
[1]Schoppa, Keith. 2000. The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. New York: Columbia UP, 159.
[2]Zhong, Xueping. 2010. “Who Is Afraid Of Lu Xun? The Politics Of ‘Debates About Lu Xun’ (鲁迅论争lu Xun Lun Zheng) And The Question Of His Legacy In Post-Revolution China.” In Culture and Social Transformations in Reform Era China, 257–284, 262.
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Zibo had its BBQ moment. Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine with its special take on malatang. Tourism marketing in China will never be the same again.
Published
1 month agoon
April 1, 2024
Since the early post-pandemic days, Chinese cities have stepped up their game to attract more tourists. The dynamics of Chinese social media make it possible for smaller, lesser-known destinations to gain overnight fame as a ‘celebrity city.’ Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine.
During this Qingming Festival holiday, there is one Chinese city that will definitely welcome more visitors than usual. Tianshui, the second largest city in Gansu Province, has emerged as the latest travel hotspot among domestic tourists following its recent surge in popularity online.
Situated approximately halfway along the Lanzhou-Xi’an rail line, this ancient city wasn’t previously a top destination for tourists. Most travelers would typically pass through the industrial city to see the Maiji Shan Grottoes, the fourth largest Buddhist cave complex in China, renowned for its famous rock carvings along the Silk Road.
But now, there is another reason to visit Tianshui: malatang.
Gansu-Style Malatang
Málàtàng (麻辣烫), which literally means ‘numb spicy hot,’ is a popular Chinese street food dish featuring a diverse array of ingredients cooked in a soup base infused with Sichuan pepper and dried chili pepper. There are multiple ways to enjoy malatang.
When dining at smaller street stalls, it’s common to find a selection of skewered foods—ranging from meats to quail eggs and vegetables—simmering in a large vat of flavorful spicy broth. This communal dining experience is affordable and convenient for solo diners or smaller groups seeking a hotpot-style meal.
In malatang restaurants, patrons can usually choose from a selection of self-serve skewered ingredients. You have them weighed, pay, and then have it prepared and served in a bowl with a preferred soup base, often with the option to choose the level of spiciness, from super hot to mild.
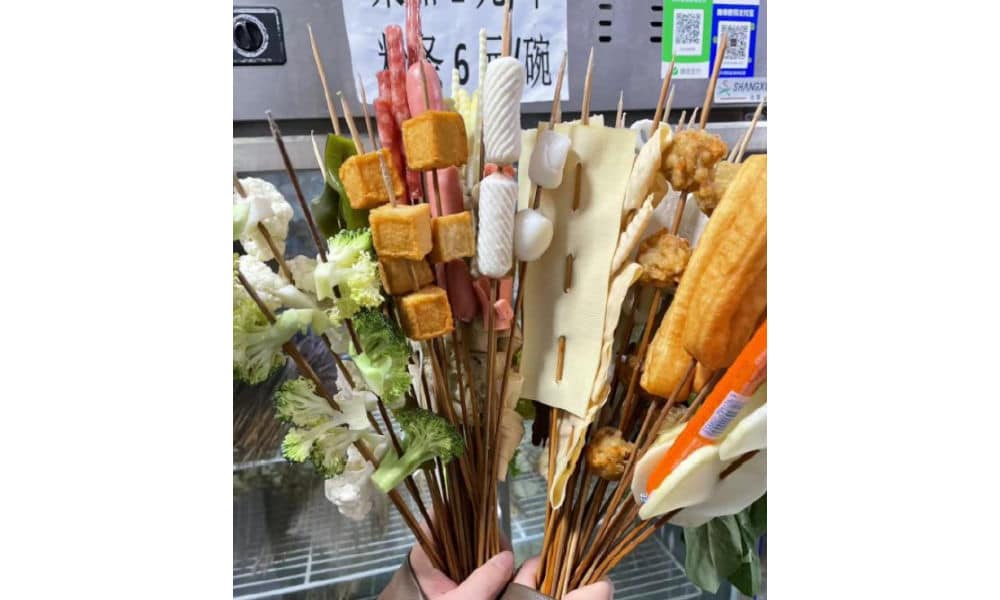

Although malatang originated in Sichuan, it is now common all over China. What makes Tianshui malatang stand out is its “Gansu-style” take, with a special focus on hand-pulled noodles, potato, and spicy oil.
An important ingredient for the soup base is the somewhat sweet and fragrant Gangu chili, produced in Tianshui’s Gangu County, known as “the hometown of peppers.”
Another ingredient is Maiji peppercorns (used in the sauce), and there are more locally produced ingredients, such as the black fungi from Qingshui County.
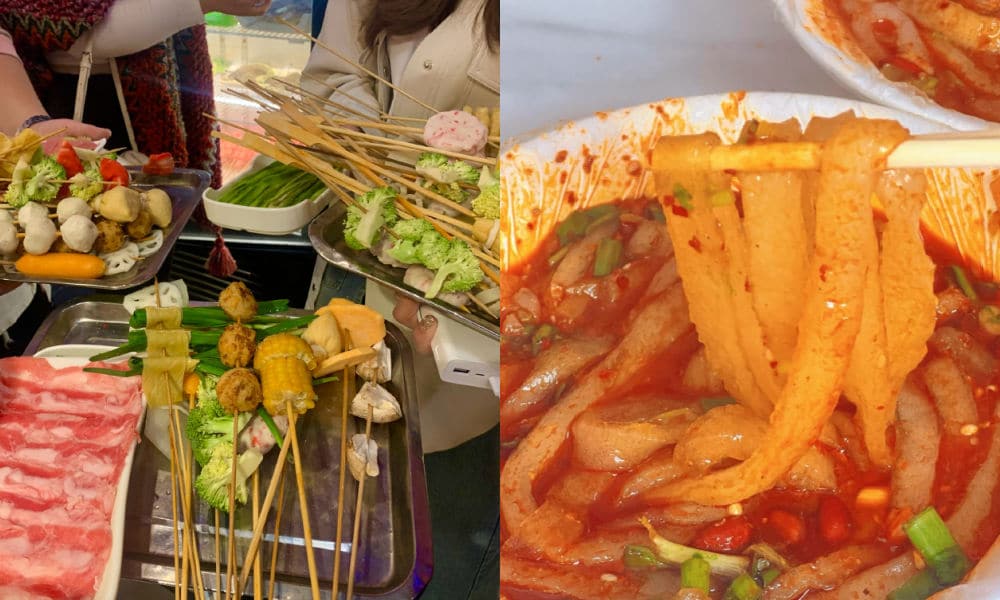

One restaurant that made Tianshui’s malatang particularly famous is Haiying Malatang (海英麻辣烫) in the city’s Qinzhou District. On February 13, the tiny restaurant, which has been around for three decades, welcomed an online influencer (@一杯梁白开) who posted about her visit.
The vlogger was so enthusiastic about her taste of “Gansu-style malatang,” that she urged her followers to try it out. It was the start of something much bigger than she could have imagined.
Replicating Zibo
Tianshui isn’t the first city to capture the spotlight on Chinese social media. Cities such as Zibo and Harbin have previously surged in popularity, becoming overnight sensations on platforms like Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin.
This phenomenon of Chinese cities transforming into hot travel destinations due to social media frenzy became particularly noteworthy in early 2023.
During the Covid years, various factors sparked a friendly competition among Chinese cities, each competing to attract the most visitors and to promote their city in the best way possible.
The Covid pandemic had diverse impacts on the Chinese domestic tourism industry. On one hand, domestic tourism flourished due to the pandemic, as Chinese travelers opted for destinations closer to home amid travel restrictions. On the other hand, the zero-Covid policy, with its lockdowns and the absence of foreign visitors, posed significant challenges to the tourism sector.
Following the abolition of the zero-Covid policy, tourism and marketing departments across China swung into action to revitalize their local economy. China’s social media platforms became battlegrounds to capture the attention of Chinese netizens. Local government officials dressed up in traditional outfits and created original videos to convince tourists to visit their hometowns.
Zibo was the first city to become an absolute social media sensation in the post-Covid era. The old industrial and mining city was not exactly known as a trendy tourist destination, but saw its hotel bookings going up 800% in 2023 compared to pre-Covid year 2019. Among others factors contributing to its success, the city’s online marketing campaign and how it turned its local BBQ culture into a unique selling point were both critical.

Zibo crowds, image via 163.com.
Since 2023, multiple cities have tried to replicate the success of Zibo. Although not all have achieved similar results, Harbin has done very well by becoming a meme-worthy tourist attraction earlier in 2024, emphasizing its snow spectacle and friendly local culture.
By promoting its distinctive take on malatang, Tianshui has emerged as the next city to captivate online audiences, leading to a surge in visitor numbers.
Like with Zibo and Harbin, one particular important strategy used by these tourist offices is to swiftly respond to content created by travel bloggers or food vloggers about their cities, boosting the online attention and immediately seizing the opportunity to turn online success into offline visits.
A Timeline
What does it take to become a Chinese ‘celebrity city’? Since late February and early March of this year, various Douyin accounts started posting about Tianshui and its malatang.
They initially were the main reason driving tourists to the city to try out malatang, but they were not the only reason – city marketing and state media coverage also played a role in how the success of Tianshui played out.
Here’s a timeline of how its (online) frenzy unfolded:
- July 25, 2023: First video on Douyin about Tianshui’s malatang, after which 45 more videos by various accounts followed in the following six months.
- Feb 5, 2024: Douyin account ‘Chuanshuo Zhong de Bozi’ (传说中的波仔) posts a video about malatang streetfood in Gansu
- Feb 13, 2024: Douyin account ‘Yibei Liangbaikai’ (一杯梁白开) posts a video suggesting the “nationwide popularization of Gansu-style malatang.” This video is an important breakthrough moment in the success of Tianshui as a malatang city.
- Feb – March ~, 2024: The Tianshui Culture & Tourism Bureau is visiting sites, conducting research, and organizing meetings with different departments to establish the “Tianshui city + malatang” brand (文旅+天水麻辣烫”品牌) as the city’s new “business card.”
- March 11, 2024: Tianshui city launches a dedicated ‘spicy and hot’ bus line to cater to visitors who want to quickly reach the city’s renowned malatang spots.
- March 13-14, 2024: China’s Baidu search engine witnesses exponential growth in online searches for Tianshui malatang.
- March 14-15, 2024: The boss of Tianshui’s popular Haiying restaurant goes viral after videos show him overwhelmed and worried he can’t keep up. His facial expression becomes a meme, with netizens dubbing it the “can’t keep up-expression” (“烫不完表情”).

The worried and stressed expression of this malatang diner boss went viral overnight.
- March 17, 2024: Chinese media report about free ‘Tianshui malatang’ wifi being offered to visitors as a special service while they’re standing in line at malatang restaurants.
- March 18, 2024: Tianshui opens its first ‘Malatang Street’ where about 40 stalls sell malatang.
- March 18, 2024: Chinese local media report that one Tianshui hair salon (Tony) has changed its shop into a malatang shop overnight, showing just how big the hype has become.
- March 21, 2024: A dedicated ‘Tianshui malatang’ train started riding from Lanzhou West Station to Tianshui (#天水麻辣烫专列开行#).
- March 21, 2024: Chinese actor Jia Nailiang (贾乃亮) makes a video about having Tianshui malatang, further adding to its online success.
- March 30, 2024: A rare occurrence: as the main attraction near Tianshui, the Maiji Mountain Scenic Area announces that they’ve reached the maximum number of visitors and don’t have the capacity to welcome any more visitors, suspending all ticket sales for the day.
- April 1, 2024: Chinese presenter Zhang Dada was spotted making malatang in a local Tianshui restaurant, drawing in even more crowds.
A New Moment to Shine
Fame attracts criticism, and that also holds true for China’s ‘celebrity cities.’
Some argue that Tianshui’s malatang is overrated, considering the richness of Gansu cuisine, which offers much more than just malatang alone.
When Zibo reached hype status, it also faced scrutiny, with some commenters suggesting that the popularity of Zibo BBQ was a symptom of a society that’s all about consumerism and “empty social spectacle.”
There is a lot to say about the downsides of suddenly becoming a ‘celebrity city’ and the superficiality and fleetingness that comes with these kinds of trends. But for many locals, it is seen as an important moment as they see their businesses and cities thrive.
Even after the hype fades, local businesses can maintain their success by branding themselves as previously viral restaurants. When I visited Zibo a few months after its initial buzz, many once-popular spots marketed themselves as ‘wanghong’ (网红) or viral celebrity restaurants.
For the city itself, being in the spotlight holds its own value in the long run. Even after the hype has peaked and subsided, the gained national recognition ensures that these “trendy” places will continue to attract visitors in the future.
According to data from Ctrip, Tianshui experienced a 40% increase in tourism spending since March (specifically from March 1st to March 16th). State media reports claim that the city saw 2.3 million visitors in the first three weeks of March, with total tourism revenue reaching nearly 1.4 billion yuan ($193.7 million).
There are more ripple effects of Tianshui’s success: Maiji Shan Grottoes are witnessing a surge in visitors, and local e-commerce companies are experiencing a spike in orders from outside the city. Even when they’re not in Tianshui, people still want a piece of Tianshui.
By now, it’s clear that tourism marketing in China will never be the same again. Zibo, Harbin, and Tianshui exemplify a new era of destination hype, requiring a unique selling point, social media success, strong city marketing, and a friendly and fair business culture at the grassroots level.
While Zibo’s success was largely organic, Harbin’s was more orchestrated, and Tianshui learned from both. Now, other potential ‘celebrity’ cities are preparing to go viral, learning from the successes and failures of their predecessors to shine when their time comes.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

The Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight2 months ago
China Insight2 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 weeks ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 weeks ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng
-

 China Media2 months ago
China Media2 months agoParty Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”




