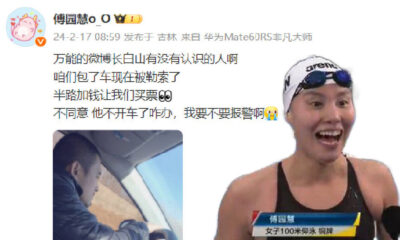
Featured
Pressured to get Married: For the Country and For Society
Every year, China’s bachelors and bachelorettes are dreading the return to their hometowns, as parents and family members will inescapably ask them that one question: “Why are you not married yet?”
Published
9 years agoon

WHAT’S ON WEIBO ARCHIVE | PREMIUM CONTENT ARTICLE
A creative protest against social marriage pressure has reignited online discussions about the status quo of China’s unmarried adults. While some support the choice of Chinese younger adults to be in charge of their own happiness, others suggest they are too focused on personal fulfillment.
Chinese New Year and the pressure to get married: it has already become an ‘old’ topic. Every year, China’s bachelors and bachelorettes are dreading the return to their hometowns, as parents and family members will inescapably ask them that one question: “Why are you not married yet?”
This year, a group of Chinese young women protested in Shanghai against their parents pressuring them to marry, holding signs saying: “Mum, please do not force me to get married during New Year, I’m in charge of my own happiness.”
 Protest in Shanghai against marriage pressure, February 4, 2015 (Qingdao News).
Protest in Shanghai against marriage pressure, February 4, 2015 (Qingdao News).
The women became a hot topic amongst netizens and authors, reigniting the online discussion about the status quo of China’s unmarried adults. “Coming back to your hometown saying you don’t want to be pressured into marriage is like going to the dog meat festival saying you don’t want to eat dog,” says writer Mao Li.
The Shengnü and Shengnan ‘problem’
The term ‘shengnü’ (剩女 ‘leftover woman’) has been a somewhat derogatory catch phrase in China’s media for years. It refers to women who are still single at the age of 27 or above; usually well-educated ladies who have difficulties in finding a partner that can live up to their expectations.
Their disadvantage in finding a partner relates to existing ideas in Chinese culture about the ‘ideal’ marriage age of women. A recent survey has pointed out that 50% of Chinese men already consider a women ‘left over’ when she is not married at the age of 25.
The male counterpart of the shengnü is the so-called ‘shengnan’ (剩男, ‘leftover man’). Chinese men face great difficulties in finding a bride, as Mainland China has been faced with an unbalanced male-female ratio since the 1980s. At the peak of disparity in 2004, more than 121 boys were born for every 100 girls. One explanation for this imbalance is the traditional preference for boys and sex-selective abortions since the one-child policy was introduced in 1978.
According to estimations, there currently are 20 million more men than women under the age of 30 (Luo & Sun 2014, 5; Chen 2011, 2).
The abundance of both single women and men in present-day China would suggest that there is hardly a problem: why don’t they just get married? Problematically, the majority of China’s unmarried women are twenty-somethings who live in urban areas and are at the ‘high end’ of the societal ladder (relatively high income and education), whereas the majority of the shengnan are based in rural areas and are at the ‘lower end’ (lower income/education).
Since Chinese women traditionally prefer to ‘marry up’ in terms of age, income and education, and the men usually ‘marry down’, the men and women find themselves at the wrong ends of the ladder (Ding & Xu 2015, 114).
China needs a babyboom
“Get married soon and have lots of babies,” says Huang Wenzheng, activist and one-child policy opponent (Qi 2014). China is currently facing a rapid decline in births. At the same time, the population is aging.
It is estimated that over 25% of Chinese people will be 65 years and older in 2050, leaving the burden of care to younger generations (BBC 2012). Getting Chinese bachelors and bachelorettes to marry and produce children has thus gone beyond the wish for a wedding banquet and cute grandchildren – it has become an important matter to society.
According to recent statistics, 80% of China’s bachelors and bachelorettes over the age of 24 experience pressure by their families to get married when they go home for the holiday period. The festival is now even nicknamed the “marriage pressure holiday” (催婚假期).
 Parents looking for a suitable partner for their single sons and daughter (Xinhua).
Parents looking for a suitable partner for their single sons and daughter (Xinhua).
After Chinese New Year, there generally is a 40% increase in blind dates. These meetings are often arranged by the parents, who attend ‘blind date events’ for their single sons or daughters. Many parents gather in public parks over the weekend, carrying banners with the picture and details of their unmarried child in the hopes of finding a suitable marriage partner for them.
“Don’t oppose to marriage pressure if you’re a loser”
Well-known scholar Yang Zao (杨早) responds to this topic on Tencent’s Dajia (‘Everybody’, a media platform for authors), with an essay titled “Pressured to Get Married: For the Country, For Society” (为了国家,为了社会,逼你结婚). Yang is the third author to discuss the New Year’s marriage pressure and the Shanghai girls who want to take their love life into their own hands. The other two columns are by female writer Mao Li (毛利), who wrote an essay titled “Prove You’re Not a Loser Before Opposing Marriage Pressure” (想反逼婚,先证明你不是废物), and columnist Zhang Shi (张石), whose piece is called “China’s ‘Pressured-Married’ and Japan’s ‘Non-Married””(中国的“逼婚”和日本的“不婚”). Yang analyses the current debate on marriage, wondering if it is so controversial because society is pressuring it more or because unmarried adults are opposing it more.
Parents put more pressure on their children to get married, and children increasingly oppose it, says Mao Li. According to her, both sides make sense, but it is the children who have to explain their point-of-view; why would their parents understand them?
Those who were born in the 1980s and 1990s come from completely different times than their mothers and fathers, who suffered many hardships to get where they are today. Mao Li compares the way they raised their children to a farmer raising his crops: planting seeds, watering the fields and creating the right environment to grow. Now that the children are grown up and have left the family home, the logical step for them would be to get married – after all, their parents worked hard to build the right conditions for them to do so. They should not be surprised when their parents urge them to get settled.
“Coming back to your hometown saying you oppose to marriage pressure is like coming to the dog meat festival saying you oppose to eating dog,” Mao says: “You can’t expect people to comprehend it.” According to Mao, children can only oppose marriage pressure when they are completely independent. They cannot oppose marriage and still cling to their parents for financial support. “Prove you’re not a loser before opposing marriage pressure,” she says.
Writer Zhang Shi approaches the issue from another perspective; that of society. In Japan, fertility rates have sharply decreased. While society is ageing, the lack of young workers causes economic problems.
In order not to end up with the same problems as Japan, China has to get the marriages coming and birth rates going, argues Zhang. Parents who are forcing their children to get married are actually contributing to society, says Zhang: it is ‘warm advice’, not cold pressure. In an age of declining birthrates, urging people to have babies is a “social responsibility”.
“For the country, for society, for parents, can’t you let go a bit of ‘personal happiness’?”
The pressure to get married is ingrained in social ideology and China’s traditional family ethics, says Yang Zao. The problems that now emerge within society come from a clash between individualist and collectivist values.
Chinese society cannot be a perfect mix of both individualism and collectivism, according to Yang: “It is either one, and both will have downsides.” If China wants a liberal, individual-focused society, then its “evils” will have to be accepted too: some people will marry late, some will not marry at all, some will not have kids, others will go job-hopping, some people move from city to city and never settle down. Such a society will also generate low birth rates and an ageing society.
In a collective, family-focused society, the aging crisis and declining birth rates could be halted. Parents would not have to go to public parks to search for suitable partners for their unmarried kids. “For the country, for society, for parents, can’t you let go a bit of personal happiness’?”, says Yang. After all, isn’t marriage key to solving China’s present-day problems?
Since 1950, marriage officially is a ‘freedom of choice’ in Mainland China. Nevertheless, marriage in China still seems to involve more than two people: it is a get-together of two families with societal backing.
One Weibo user says: “The shengnü do not have an individual problem; they are a problem because society at large believes they have a problem – this is why it is a ‘problem’.”
No matter what the ‘nation’, ‘society’, or parents think, the protesting Shanghai girls are positive about their future: it is in their hands, and in their hands alone.
– by Manya Koetse
References
BBC. 2012. “Ageing China: Changes and Challenges.” BBC News, 19 September http://www.bbc.com/news/world-
Chen, Zhou. 2011. “The Embodiment of Transforming Gender and Class: Shengnü and Their Media Representations in Contemporary China.” Master’s thesis, University of Kansas.
Ding, Min and Jie Xu. 2015. The Chinese Way. Routledge: New York.
Luo, Wei, and Zhen Sun. 2014. “Are You the One? China’s TV Dating Shows and the Sheng Nü’s Predicament.” Feminist Media Studies, October: 1–18.
Mao Li 毛利. “想反逼婚,先证明你不是废物” [Prove You’re Not a Loser Before Opposing Marriage Pressure]. Dajia, 11 February http://dajia.qq.com/blog/466362096792665 [24.2.15].
Qi, 2014. “Baby Boom or Economy Bust.” The Wall Street Journal, 2 September http://blogs.wsj.com/chinarealtime/2014/09/02/baby-boom-or-economy-bust-stern-warnings-about-chinas-falling-fertility-rate/ [24.2.15].
Yang Zao 杨早. 2015. “为了国家,为了社会,逼你结婚” [Pressured to Get Married: For the Country, For Society]. Dajia, 17 February http://dajia.qq.com/blog/431261063359665 [24.2.15].
Zhang Shi 张石. 2015. “中国的“逼婚”和日本的“不婚” [China’s ‘Pressured-Married’ and Japan’s ‘Non-Married’]. Dajia, 16 February http://dajia.qq.com/blog/462372023502987 [24.2.15].
Image by Tencent Dajia, 2015.
©2014 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

Also Read
Featured
Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed
“The battle for the lower bunk beds” (“下铺之争”) is a reflection of society and generational difference in China, touching upon expectations regarding the respect younger individuals should show the elderly.
Published
2 days agoon
April 24, 2024
PREMIUM NEWSLETTER | ISSUE #27
This week’s newsletter:
◼︎ 1. Editor’s Note – Battle for the Bottom Bed
◼︎ 2. What’s Been Trending – A closer look at the featured stories
◼︎ 3. What More to Know – Five bit-sized trends
◼︎ 4. What’s the Drama – Top TV to watch
◼︎ 5. What’s Noteworthy – Zara x Haidilao
◼︎ 6. What’s Popular – Martin Garrix x Huang Zitao
◼︎ 7. What’s Memorable – Social media in times of flood
◼︎ 8. Weibo Word of the Week – Coffin rooms
Dear Reader,
Sometime around last summer, a significant debate about train etiquette began trending on Chinese social media. Central to the discussion was a question that attracted over 190 million views on Weibo: Can passengers bring their own “bed curtains”?
The curtains in question (床帘 chuánglián, also 火车遮挡帘 huǒchē zhēdǎnglián) are often used in the cheapest class of sleeper cabins on Chinese trains, known as hard sleepers (硬卧 yìngwò). In these cabins, each compartment features six bunk beds, with three beds on each side separated by a small table. Only the bottom bunk offers sufficient space for seating and is also the most expensive among the three.
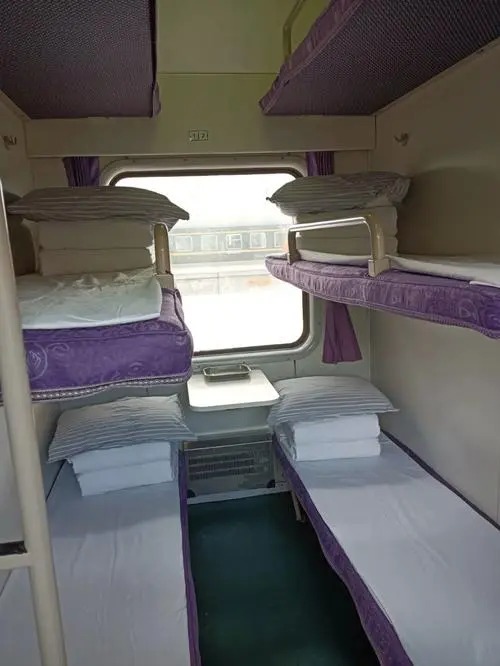

Example of Chinese hard sleeper train compartment, image via Sohu.
Train carriages usually comprise 11 semi-open compartments, each featuring a corridor and two foldable seats per cubicle. With so many people in one carriage, noise can become an issue, and privacy can be hard to come by.
“Bed curtains” have emerged as a popular strategy to combat these nuisances, creating a somewhat private and quiet space on trains without disturbance from fellow travelers. Essentially, they are pieces of fabric that can be easily secured above or on the sides of the bunk bed using clips or ropes. These days, Taobao sells them in various colors and patterns.

Bunk bed curtains, sold on e-commerce sites likes Taobao, turn lower bunk beds in a more private space.
Recently, the debate over these curtains reignited on Chinese social media, particularly focusing on how their use creates an additional barrier for other passengers, especially the elderly, to sit on the lower beds. This sparked discussions about whether younger passengers should consider swapping their lower bunk beds with senior passengers, who may find it difficult to access the middle and upper berths, where it’s often impossible for them to sit up straight.
The catalyst for these discussions was a viral video featuring an elderly lady confronting two young people who had hung covers on their bottom bunk beds. She accused them of selfishness for not allowing older passengers with upper bunk tickets to sit on their beds.
Many commenters expressed support for the young passengers in the video, emphasizing that they are not obliged to let other passengers sit on their bed. The topic unleashed a flood of stories of train annoyances about strangers sitting on people’s bottom beds, depriving them of privacy.
The topic further popularized the use of bed curtains, with commenters writing: “I dislike others sitting on my bed but find it difficult to confront them; this is such a clever solution!”
There are currently no explicit regulations prohibiting or allowing these bed curtains, as long as they do not cause inconvenience or block access to other bunks, but many people view them as “uncivilized” and “impolite.”
The online critics of bed curtains often fondly recall their experiences traveling on China’s sleeper trains in past decades. They reminisce about meeting strangers, sharing snacks, playing cards, and forming friendships—experiences characterized by less privacy, but more camaraderie.
As this discussion has been dubbed “the battle for the lower bunk beds” (“下铺之争”), it’s evident that it encompasses more than just seating arrangements. Some say it is a reflection of the current society. It touches upon societal shifts, traditional/cultural expectations regarding the respect younger individuals should show the elderly, and mostly, generational differences.
Unlike the older generations preceding them, Chinese younger generations, products of the one-child policy and growing up amid increasing prosperity, have undergone a significant transformation in their familial roles over the past decades. Not only were they both pampered and pressured to succeed, they also often enjoyed having their own rooms from a young age. Their upbringing has fostered a more individualistic perspective, a heightened emphasis on personal happiness, and a greater value placed on privacy.
Additionally, while previous generations typically ‘served’ their parents, you see that parents often prioritize ‘serving’ their children of younger generations, treating them as equals within the household. This has also led to different views on the interaction between younger and older members of society. Many younger people won’t accept Chinese seniors acting rude or entitled simply because of their age.
The “battle for the bottom bed” essentially symbolizes clashes between different generations. While older generations value communal experiences and respect for elders, younger generations assert their individual rights and prioritize personal space. Given the insufficient seating for all six passengers in current hard sleepers, they argue that it’s China Railways’ responsibility to adapt the layout to better cater to passengers’ needs.
Meanwhile, some Chinese ‘experts’ are cited by media, encouraging young people who have bought lower berths to be understanding and swap with the elderly for their convenience. A related hashtag on the matter was viewed more than 400 million times on Weibo, and the most popular replies basically told the experts to shove their suggestion up theirs. “I have the right to what I pay for,” some said: “If they need a lower bed, let them pay for a lower bed.”
Some bloggers comment that the very fact that this seemingly trivial topic has become such a major topic of debate on Chinese social media is a sign of a “regression in morality.” Some propaganda accounts raise the example of the humble PLA soldier Lei Feng, who would help out other passengers and train staff while traveling, instead of occupying a seat. While most do not expect the same of modern-day travelers, they do think that people, young and old, should show a little more understanding for each other.
In this light, another video garnered attention. It showed an elderly woman on a train politely requesting to swap a top bunk with a young passenger occupying a bottom bunk. The request was made on behalf of her 83-year-old travel companion, and they were happy to compensate for the price difference. That video received praise from netizens, who expressed that it’s the attitude that matters. The young passenger swapped beds with the older lady and did not accept payment for it.
In the end, it’s clear that kindness and empathy are cross-generational, and that communication always helps bridging differences.
In case you don’t feel like bridging differences on your next hard sleeper train, however, here’s the link to the bed curtains.
Warm regards,
– Manya Koetse & Miranda Barnes
What’s Been Trending

1: Chengdu Disneyland | Chengdu Disney is the latest viral hotspot on Chinese social media, and it’s probably unlike anything you’d imagine. How did an ordinary outdoor senior gym in a local Chengdu neighborhood become nationally known as ‘Chengdu Disney’? By mixing online trends with real-life fun, blending foreign styles with local charm, and adding a dash of humor and absurdity, Chengdu now boasts its very own ‘Chengdu Disney.’ We explain the trend here👇🏼

2: Unleashing Flood of Stories | The recent marriage announcement of the renowned Chinese calligrapher/painter Fan Zeng and Xu Meng, a Beijing TV presenter 50 years his junior, has sparked online discussions about the life and work of the esteemed Chinese artist. Some netizens think Fan lacks the integrity expected of a Chinese scholar-artist.

3: Yellen’s Favorites | Earlier in April, Yellen concluded her second trip to Beijing within a year, and once again, it’s not her official talks but rather her choices in food and drink venues that are sparking discussion on social media. From Yunnan classics to fusion cuisine, these are Janet Yellen’s picks for dining and drinking in Beijing.
What More to Know
◼︎ 🌧️ Guangdong Floods | Flooding, landslides, power outages. It’s been a rough few days in Guangdong. From the provincial capital Guangzhou to smaller cities like Shaoguan, Zhaoqing, and Qingyuan, exceptionally heavy rainfall since April 18 has brought significant problems to various areas. At least 4 deaths have been reported, with 10 people still missing. More than 100,000 people have been evacuated. The regions hardest hit are along the Beijiang River, which flooded on April 21. This marks the second flood of the river this year, with the first occurring on April 7, marking the earliest date in the season since floods in major Chinese rivers began being numbered in 1998. As with previous floods, social media is used as a channel to warn people about the ongoing situation, with further rainfall expected. Meanwhile, state media are honoring rescue workers as local heroes, or ‘those going against the tide’ (nìxíngzhě 逆行者).
◼︎ 🌋 Ijen Crater Death | A 31-year-old Chinese tourist tragically lost her life after falling from the edge of Indonesia’s Ijen volcano while attempting to take a photo. She tripped over her own long skirt, plummeting from a height of 75 meters early on the morning of April 20, while the tourists were there to witness the sunrise. With the May 1st holiday approaching, Chinese authorities, through social media, are using this incident as a cautionary tale to warn tourists of the hazards of prioritizing that ‘perfect social media photo’ over personal safety.
◼︎ 💀 Another University Poisoning Case | One recurring case that surfaces on Weibo is that of Zhu Ling, the female victim in the notorious 1995 thallium poisoning incident at Beijing’s Tsinghua University. Although Zhu Ling survived, she was left paralyzed and reliant on her parents for care for the rest of her life. The case remains unsolved, with many pointing to her roommate as the primary suspect. Now, a new suspected poisoning incident at a university has gained attention, following the death of a 25-year-old male student at Xiangtan University due to organ failure after seeking medical treatment. His 27-year-old roommate is currently under suspicion and has been detained. This is a case that is likely to draw further scrutiny in the time to come.
◼︎ 🏃♂️ Marathon Controversy | There was something fishy about the conclusion of the Beijing Half Marathon and the four runners at the finish line. In a video clip that went viral on Chinese social media (see here), viewers observed that three African runners seemed to intentionally slow down to allow Chinese competitor He Jie (何杰) to win the gold medal. Now, the Beijing Half Marathon Organizing Committee has announced the disqualification of all four runners for “breaching the rules of the competition,” nullifying their results, and reclaiming their trophies and medals. The Chinese Athletics Association has also introduced new regulations for discipline management in national events. It appears that the three African runners were “pace setters” who were not intended to be competing athletes, and sponsor/partner Xtep (特步), a sports equipment company, was responsible for not properly identifying them. Consequently, the company has been terminated as a partner. Marathon fraud and the importance of properly regulating major sports events has become a recurring topic on Chinese social media. Last October, the Chinese Athletics Association issued an emergency notice to standardize and regulate China’s national marathon and running events more effectively after Chinese marathon runner Yin Shunjin appeared to be intentionally obstructed by a support vehicle, forcing him to navigate around it and costing him valuable time in the crucial final two minutes of the marathon.
◼︎ 🎲 Little Tuan Tuan Goes to Jail | Popular Chinese influencer “Little Tuan Tuan” (一条小团团), who has millions of followers on the Douyu livestreaming app, became a top trending topic on Chinese social media on April 23 after news came out that she had been arrested. The famous game livestreamer had already stopped airing since last month, but it only now became known that she is suspected of engaging in large-scale illegal gambling activities. In late 2023, Douyu’s chairman and CEO Chen Shaojie was also arrested for allegedly hosting online gambling, which is illegal in mainland China. At the time, state media already reported that the arrest of Chen may lead to a group of top game anchors being implicated due to their involvement in gambling and money laundering. After the earlier arrest of four other anchors, Tuan Tuan is the latest livestream host to be arrested, signaling a zero tolerance approach towards gambling activities in China’s game-focused livestreaming world. Little Tuan Tuan could face up to five years in prison.
What’s the Drama

Best Choice Ever (Chéng Huān Jì 承欢记) is the latest Chinese TV drama hit. Produced by CCTV and simultaneously broadcasted on CCTV-8 and Tencent, it premiered on April 9, and some are already calling it the best romcom drama of the year. This urban family/romance drama centers around the story of Mai Chenghuan (麦承欢), a post-95 young woman living in Shanghai, who is preparing to marry her boyfriend Xin Jialiang (辛家亮), who comes from a wealthy family. However, when Chenghuan’s mum is doing all she can to meddle in their relationship, Mai Chenghuan must break free from her mother’s overbearing influence and focus on her own personal growth.
Noteworthy:
▶️ This drama is based on a book by the same name by Hong Kong writer Yi Shu or Isabel Nee Yeh-su, who is known for the strong, intelligent female characters in her stories.
▶️ The main protagonist is played by the super popular Chinese actress Yang Zi (杨紫), who previously starred in hit series such as Ode to Joy (欢乐颂) and The Oath of Love (余生).
▶️ This series is also airing in Thailand starting from April 29, but you won’t hear Yang Zi speaking Chinese there; the entire show will be dubbed in Thai.
▶️ The Shanghai Culture and Tourism office has also been involved in this production, that features some pretty scenes from around Shanghai, which is drawing in young visitors wanting to visit film locations like the Zhapu Road Bridge and Huaihuai Mansion.
You can watch Best Choice Ever online here (with English subtitles) via YouTube.
What’s Noteworthy

A short dress sold by Zara has gone viral in China for looking like the aprons used by the popular Chinese hotpot chain Haidilao. “I really thought it was a Zara x Haidialo collab,” some customers commented. Others also agree that the first thing they thought about when seeing the Zara dress was the Haidilao apron.
What’s Popular

Dutch DJ Martin Garrix found himself embroiled in controversy following the first F1 China Grand Prix Music Festival in Shanghai, which took place from Friday to Sunday. Garrix was allegedly supposed to perform together with Chinese singer Huang Zitao (黄子韬), who initially complained via livestream that the DJ did not show up to their joint rehearsal, and then claimed the DJ showed disrespect by performing his song without him being present on stage. On Weibo, one hashtag about the incident attracted over 160 million views.
Both Huang and Garrix are popular on Weibo, where the Chinese singer has over 66 million fans while the Dutch DJ has more than 360,000 followers.
In response, Garrix promptly posted a video on Weibo refuting what he called “misinformation and lies,” asserting that he and Huang Zitao were never scheduled to perform together. Hearing about Huang’s complaints, he still invited him up on stage, but he never showed up (Garrix claimed he was hiding in the bathroom). Following this, the event organizers issued an apology for the confusion.
Online, opinions remain divided, with some defending Garrix and labeling Huang a “crybaby,” while others support Huang, arguing that Garrix was rude for not wanting to share the stage with the Chinese singer. Either way, it seems the two performers won’t be sharing a beer, nor a stage, anytime soon.
What’s Memorable

This pick from our archive – in light of the current floods – revisits the flood of three years ago. The social media trends during China’s heavy rainfall and floods in Henan in July of 2021 show the multidimensionality of online communication in times of disaster. Facing the devastating downpours, Weibo became a site for participation, propaganda, and some controversial profiting.👇
Weibo Word of the Week

“Coffin Room” | Our Weibo Word of the Week is “Coffin Room” (guāncái fáng 棺材房), or even “Mini Coffin Room” (mínǐ guāncái fáng 迷你棺材房), referring to extremely tiny spaces being rented out at rooms.
The term “coffin room” isn’t new; it previously appeared in mainstream media to describe small cubicles rented out in Hong Kong to people who couldn’t afford larger spaces in the exorbitantly expensive housing market. However, it has recently resurfaced on Chinese social media to describe similarly cramped spaces in Shanghai.
One viral video showcased a rental room of about 5m² (approximately 53.82 square feet) with a makeshift sleeping space right behind a toilet, measuring about two meters long and one meter wide (approximately 6.56 feet long and 3.28 feet wide), all for a monthly rent of 300 yuan ($41). This so-called “coffin room” sparked controversy, with many deeming it absurd and a testament to Shanghai’s overheated housing market. However, the landlord mentioned that the room was already rented out to a Didi driver the day it was posted. See video here.
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron
Who’s gonna buy this Zara dress in China? “I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”
Published
7 days agoon
April 19, 2024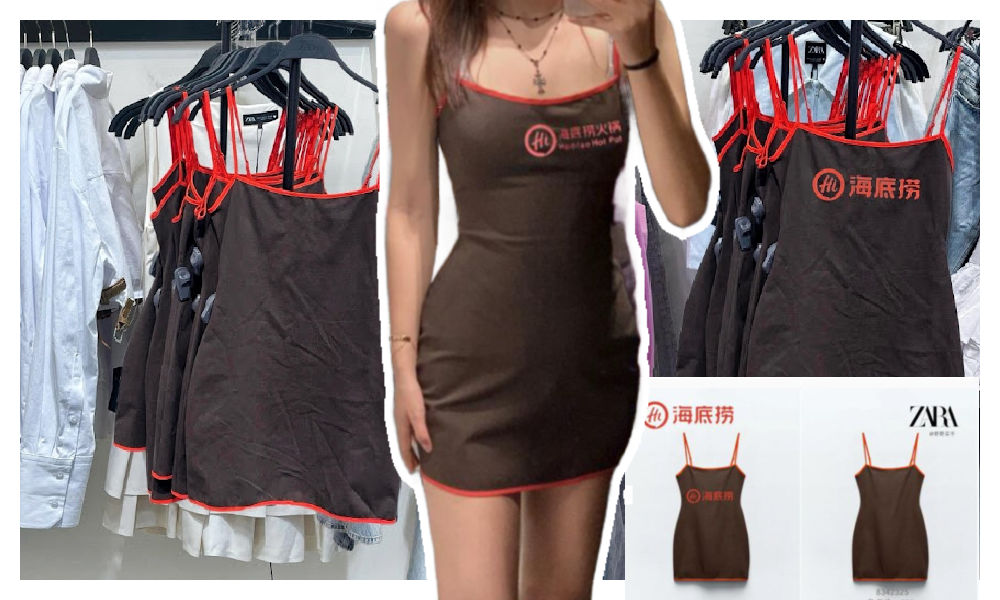
A short dress sold by Zara has gone viral in China for looking like the aprons used by the popular Chinese hotpot chain Haidilao.
“I really thought it was a Zara x Haidialo collab,” some customers commented. Others also agree that the first thing they thought about when seeing the Zara dress was the Haidilao apron.
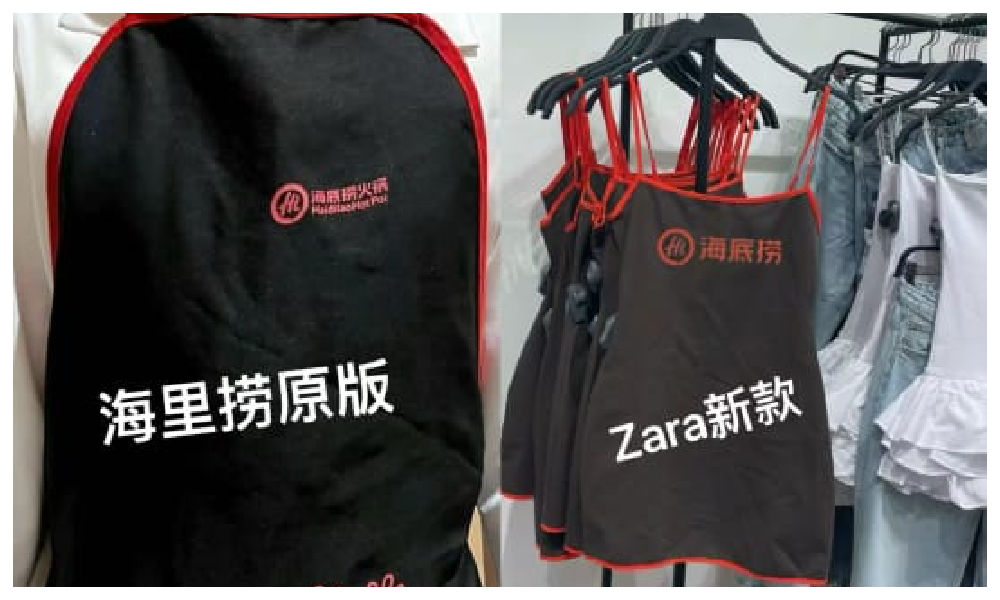

The “original” vs the Zara dress.
The dress has become a popular topic on Xiaohongshu and other social media, where some images show the dress with the Haidilao logo photoshopped on it to emphasize the similarity.

One post on Xiaohongshu discussing the dress, with the caption “Curious about the inspiration behind Zara’s design,” garnered over 28,000 replies.
Haidilao, with its numerous restaurants across China, is renowned for its hospitality and exceptional customer service. Anyone who has ever dined at their restaurants is familiar with the Haidilao apron provided to diners for protecting their clothes from food or oil stains while enjoying hotpot.
These aprons are meant for use during the meal and should be returned to the staff afterward, rather than taken home.
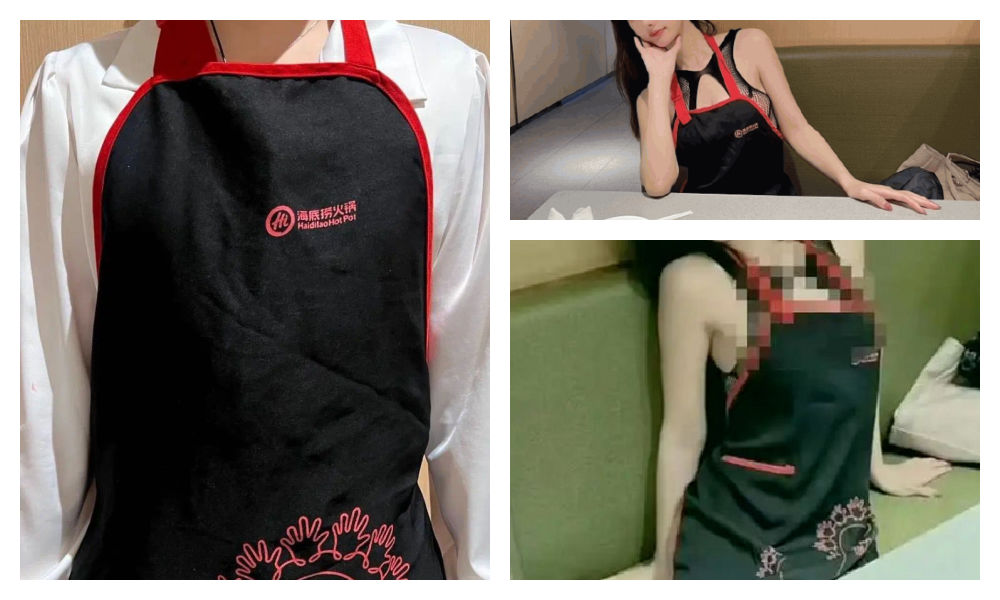

The Haidilao apron.
However, many people who have dined at Haidilao may have encountered the following scenario: after indulging in drinks and hotpot, they realize they are still wearing a Haidilao apron upon leaving the restaurant. Consequently, many hotpot enthusiasts may have an ‘accidental’ Haidilao apron tucked away at home somewhere.
This only adds to the humor of the latest Zara dress looking like the apron. The similarity between the Zara dress and the Haidilao apron is actually so striking, that some people are afraid to be accused of being a thief if they would wear it.
One Weibo commenter wrote: “The most confusing item of this season from Zara has come out. It’s like a Zara x Haidilao collaboration apron… This… I can’t wear it: I’m afraid that someone will say I stole the apron from Haidilao.”

Funnily enough, the Haidilao apron similarity seems to have set off a trend of girls trying on the Zara dress and posting photos of themselves wearing it.

It’s doubtful that they’re actually purchasing the dress. Although some commenters say the dress is not bad, most people associate it too closely with the Haidilao brand: it just makes them hungry for hotpot.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

Where to Eat and Drink in Beijing: Yellen’s Picks

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

In Hot Water: The Nongfu Spring Controversy Explained

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight2 months ago
China Insight2 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday
-

 China Media2 months ago
China Media2 months agoParty Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”
-

 China World2 months ago
China World2 months agoFrom Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)