China Insight
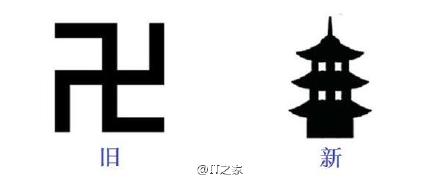
Pay Attention, Confused Foreigners: ‘Wan’ (卍) is Not a Nazi Symbol
Japan wants to get rid of the Buddhist manji-symbol (卍) on city maps, as foreigners associate it with the Nazi swastika. In China, where the symbol is known as the ‘wan’ character, some netizens seem to find the controversy entertaining.
Published
8 years agoon

Japan’s official map-making organization wants to get rid of the Buddhist manji symbol (卍) that marks the location of temples on city maps, as foreigners associate it with the Nazi swastika. In China, where the symbol is known as the ‘wan’ character, some netizens seem to find the controversy entertaining.
This week several international media, including
the BBC, wrote about the decision of the Japanese map-making association to change its manji symbol on tourist maps.
The 卍-symbol indicates the location of temples, but is often seen as the Nazi swastika by foreigners. With the Rugby World Cup and Olympics taking place in Japan in 2019 and 2020, Japanese authorities deem it is better to remove the symbol in order to avoid any misunderstanding amongst international visitors.
“Ignorant foreign travelers simply don’t understand Buddhist traditions”.
The news was also reported by Chinese media. The manji symbol is used in China as well, where it is a character pronounced as ‘wàn’.
China’s Sohu news writes that the Japanese manji is actually not the same as the Nazi swastika: the first has arms going anticlockwise (卍) whereas the arms of the Nazi symbol go clockwise (卐).
The article says that Hitler’s Nationalist Socialist Party designed the swastika that way because the German words for state and society both start with an S. This is allegedly why they designed the swastika in an S-shape.

Another difference, according to Sohu, is that the Buddhist swastika usually is gold, whereas the Nazi symbol is black.

The confusion between the two symbols is mostly created by foreigners, Sohu writes, who do not know the difference. Japanese netizens reportedly complain about “ignorant foreign travelers”, who simply “do not understand Buddhist traditions”. They should not protest its use – “When in Rome,” they say: “do as the Romans do.”
“By all means, don’t let them come to Chinese Buddhist temples. They’ll go crazy”.
On Chinese social media network Sina Weibo, a netizen called Wuguaixing seems entertained by the news. The micro-blogger, a PhD student at Tokyo University with over 100,000 Weibo followers, writes on his account:
“Ha ha! The much used Buddhist ‘wan’ (卍) character that marks temples on Japanese maps is opposed by foreigners, who think it is the Nazi ‘卐’ symbol. They now want to get rid of it.”
Other Weibo users commented on the post, saying: “Foreign tourists are just not culturally educated at all!” And: “By all means, don’t let them come to Chinese Buddhist temples. They’ll go crazy!”
The symbol can be found in many of China’s temples, either depicted on the Buddha or in ornaments.

The writer of one of the post’s most popular comments wonders why the manji symbol is a problem at all: “Does this centuries-old symbol really need to make way for the Nazi symbol, that is just some decades old?”
One Weibo user remarks: “If this was about any other Asian country, it would be no problem. But because of Japan’s past war crimes, the issue is very sensitive.”
“Where did everyone’s IQ go?!”
Some Weibo users address the history of the symbol: “Strictly speaking, this is an old Hindu symbol that was then used by Buddhism.” This comment is backed up by a netizen nicknamed Black & White, who writes: “The 卍 and the 卐 are two different characters, and they both read as ‘wàn’.”
According to Brittanica Academic, both symbols, either clockwise or anti-clockwise, are referred to as a swastika. It comes from the Sanskrit svastika meaning “conductive to well-being”, and is an ancient symbol of prosperity and good fortune. It represents the revolving sun, fire, or life, Buddhas Online explains.
According to the Encyclopedia Brittanica:
In the Buddhist tradition the swastika symbolizes the feet, or the footprints, of the Buddha. It is often placed at the beginning and end of inscriptions, and modern Tibetan Buddhists use it as a clothing decoration. With the spread of Buddhism, the swastika passed into the iconography of China and Japan, where it has been used to denote plurality, abundance, prosperity, and long life.
The swastika was used as a sign of ‘Aryan race’ in the 19th century, and was adopted by Nazism in the 20th century (Quinn 1994, x).
“Where did everyone’s IQ go?!” one Weibo user wonders.
China’s Ifeng news wrote an article about the swastika and the issue of the clockwise and anticlockwise arms. It explains that Buddhism actually uses the sign in both ways, and they both represent wisdom and compassion.

Although the issue seems more nuanced than a simple (anti)clockwise explanation, for some netizens, it’s not complicated at all: “The 卍 is a Buddhist symbol, and the 卐 is a Nazi symbol, please don’t mix them up.”
– By Manya Koetse
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
References
Quinn, Malcolm. 1994. The Swastika: Constructing the Symbol. London/New York: Routledge.
Featured image from Flickr: https://c2.staticflickr.com/6/5179/5435812352_e2578ba5b8.jpg
©2016 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya Koetse is the founder and editor-in-chief of whatsonweibo.com. She is a writer, public speaker, and researcher (Sinologist, MPhil) on social trends, digital developments, and new media in an ever-changing China, with a focus on Chinese society, pop culture, and gender issues. She shares her love for hotpot on hotpotambassador.com. Contact at manya@whatsonweibo.com, or follow on Twitter.

China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea
Chinese tea brand LELECHA faced backlash for using the iconic literary figure Lu Xun to promote their “Smoky Oolong” milk tea, sparking controversy over the exploitation of his legacy.
Published
20 hours agoon
May 3, 2024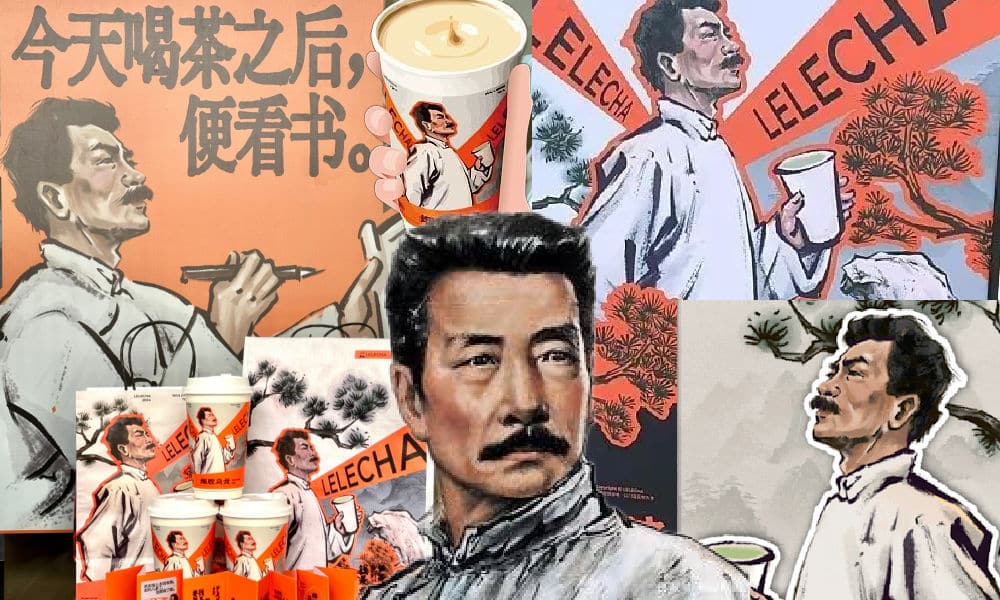
It seemed like such a good idea. For this year’s World Book Day, Chinese tea brand LELECHA (乐乐茶) put a spotlight on Lu Xun (鲁迅, 1881-1936), one of the most celebrated Chinese authors the 20th century and turned him into the the ‘brand ambassador’ of their special new “Smoky Oolong” (烟腔乌龙) milk tea.
LELECHA is a Chinese chain specializing in new-style tea beverages, including bubble tea and fruit tea. It debuted in Shanghai in 2016, and since then, it has expanded rapidly, opening dozens of new stores not only in Shanghai but also in other major cities across China.
Starting on April 23, not only did the LELECHA ‘Smoky Oolong” paper cups feature Lu Xun’s portrait, but also other promotional materials by LELECHA, such as menus and paper bags, accompanied by the slogan: “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” (“老烟腔,新青年”). The marketing campaign was a joint collaboration between LELECHA and publishing house Yilin Press.

Lu Xun featured on LELECHA products, image via Netease.
The slogan “Old Smoky Oolong, New Youth” is a play on the Chinese magazine ‘New Youth’ or ‘La Jeunesse’ (新青年), the influential literary magazine in which Lu’s famous short story, “Diary of a Madman,” was published in 1918.
The design of the tea featuring Lu Xun’s image, its colors, and painting style also pay homage to the era in which Lu Xun rose to prominence.
Lu Xun (pen name of Zhou Shuren) was a leading figure within China’s May Fourth Movement. The May Fourth Movement (1915-24) is also referred to as the Chinese Enlightenment or the Chinese Renaissance. It was the cultural revolution brought about by the political demonstrations on the fourth of May 1919 when citizens and students in Beijing paraded the streets to protest decisions made at the post-World War I Versailles Conference and called for the destruction of traditional culture[1].
In this historical context, Lu Xun emerged as a significant cultural figure, renowned for his critical and enlightened perspectives on Chinese society.
To this day, Lu Xun remains a highly respected figure. In the post-Mao era, some critics felt that Lu Xun was actually revered a bit too much, and called for efforts to ‘demystify’ him. In 1979, for example, writer Mao Dun called for a halt to the movement to turn Lu Xun into “a god-like figure”[2].
Perhaps LELECHA’s marketing team figured they could not go wrong by creating a milk tea product around China’s beloved Lu Xun. But for various reasons, the marketing campaign backfired, landing LELECHA in hot water. The topic went trending on Chinese social media, where many criticized the tea company.
Commodification of ‘Marxist’ Lu Xun
The first issue with LELECHA’s Lu Xun campaign is a legal one. It seems the tea chain used Lu Xun’s portrait without permission. Zhou Lingfei, Lu Xun’s great-grandson and president of the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation, quickly demanded an end to the unauthorized use of Lu Xun’s image on tea cups and other merchandise. He even hired a law firm to take legal action against the campaign.
Others noted that the image of Lu Xun that was used by LELECHA resembled a famous painting of Lu Xun by Yang Zhiguang (杨之光), potentially also infringing on Yang’s copyright.
But there are more reasons why people online are upset about the Lu Xun x LELECHA marketing campaign. One is how the use of the word “smoky” is seen as disrespectful towards Lu Xun. Lu Xun was known for his heavy smoking, which ultimately contributed to his early death.
It’s also ironic that Lu Xun, widely seen as a Marxist, is being used as a ‘brand ambassador’ for a commercial tea brand. This exploits Lu Xun’s image for profit, turning his legacy into a commodity with the ‘smoky oolong’ tea and related merchandise.
“Such blatant commercialization of Lu Xun, is there no bottom limit anymore?”, one Weibo user wrote. Another person commented: “If Lu Xun were still alive and knew he had become a tool for capitalists to make money, he’d probably scold you in an article. ”
On April 29, LELECHA finally issued an apology to Lu Xun’s relatives and the Lu Xun Cultural Foundation for neglecting the legal aspects of their marketing campaign. They claimed it was meant to promote reading among China’s youth. All Lu Xun materials have now been removed from LELECHA’s stores.

Statement by LELECHA.
On Chinese social media, where the hot tea became a hot potato, opinions on the issue are divided. While many netizens think it is unacceptable to infringe on Lu Xun’s portrait rights like that, there are others who appreciate the merchandise.
The LELECHA controversy is similar to another issue that went trending in late 2023, when the well-known Chinese tea chain HeyTea (喜茶) collaborated with the Jingdezhen Ceramics Museum to release a special ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ (佛喜) latte tea series adorned with Buddha images on the cups, along with other merchandise such as stickers and magnets. The series featured three customized “Buddha’s Happiness” cups modeled on the “Speechless Bodhisattva” (无语菩萨), which soon became popular among netizens.
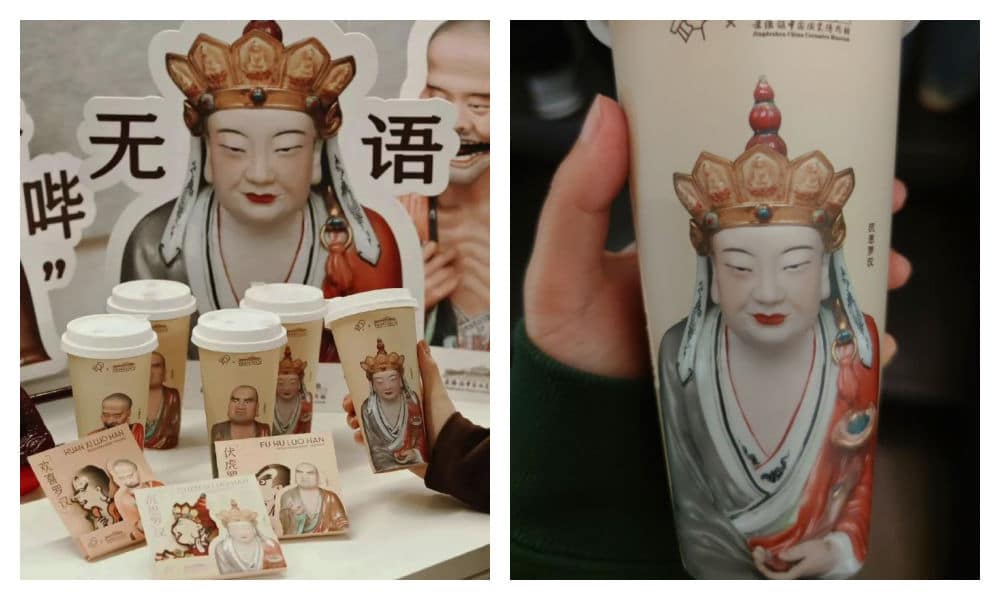

The HeyTea Buddha latte series, including merchandise, was pulled from shelves just three days after its launch.
However, the ‘Buddha’s Happiness’ success came to an abrupt halt when the Ethnic and Religious Affairs Bureau of Shenzhen intervened, citing regulations that prohibit commercial promotion of religion. HeyTea wasted no time challenging the objections made by the Bureau and promptly removed the tea series and all related merchandise from its stores, just three days after its initial launch.
Following the Happy Buddha and Lu Xun milk tea controversies, Chinese tea brands are bound to be more careful in the future when it comes to their collaborative marketing campaigns and whether or not they’re crossing any boundaries.
Some people couldn’t care less if they don’t launch another campaign at all. One Weibo user wrote: “Every day there’s a new collaboration here, another one there, but I’d just prefer a simple cup of tea.”
By Manya Koetse
[1]Schoppa, Keith. 2000. The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. New York: Columbia UP, 159.
[2]Zhong, Xueping. 2010. “Who Is Afraid Of Lu Xun? The Politics Of ‘Debates About Lu Xun’ (鲁迅论争lu Xun Lun Zheng) And The Question Of His Legacy In Post-Revolution China.” In Culture and Social Transformations in Reform Era China, 257–284, 262.
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Brands, Marketing & Consumers
More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success
Zibo had its BBQ moment. Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine with its special take on malatang. Tourism marketing in China will never be the same again.
Published
1 month agoon
April 1, 2024
Since the early post-pandemic days, Chinese cities have stepped up their game to attract more tourists. The dynamics of Chinese social media make it possible for smaller, lesser-known destinations to gain overnight fame as a ‘celebrity city.’ Now, it’s Tianshui’s turn to shine.
During this Qingming Festival holiday, there is one Chinese city that will definitely welcome more visitors than usual. Tianshui, the second largest city in Gansu Province, has emerged as the latest travel hotspot among domestic tourists following its recent surge in popularity online.
Situated approximately halfway along the Lanzhou-Xi’an rail line, this ancient city wasn’t previously a top destination for tourists. Most travelers would typically pass through the industrial city to see the Maiji Shan Grottoes, the fourth largest Buddhist cave complex in China, renowned for its famous rock carvings along the Silk Road.
But now, there is another reason to visit Tianshui: malatang.
Gansu-Style Malatang
Málàtàng (麻辣烫), which literally means ‘numb spicy hot,’ is a popular Chinese street food dish featuring a diverse array of ingredients cooked in a soup base infused with Sichuan pepper and dried chili pepper. There are multiple ways to enjoy malatang.
When dining at smaller street stalls, it’s common to find a selection of skewered foods—ranging from meats to quail eggs and vegetables—simmering in a large vat of flavorful spicy broth. This communal dining experience is affordable and convenient for solo diners or smaller groups seeking a hotpot-style meal.
In malatang restaurants, patrons can usually choose from a selection of self-serve skewered ingredients. You have them weighed, pay, and then have it prepared and served in a bowl with a preferred soup base, often with the option to choose the level of spiciness, from super hot to mild.
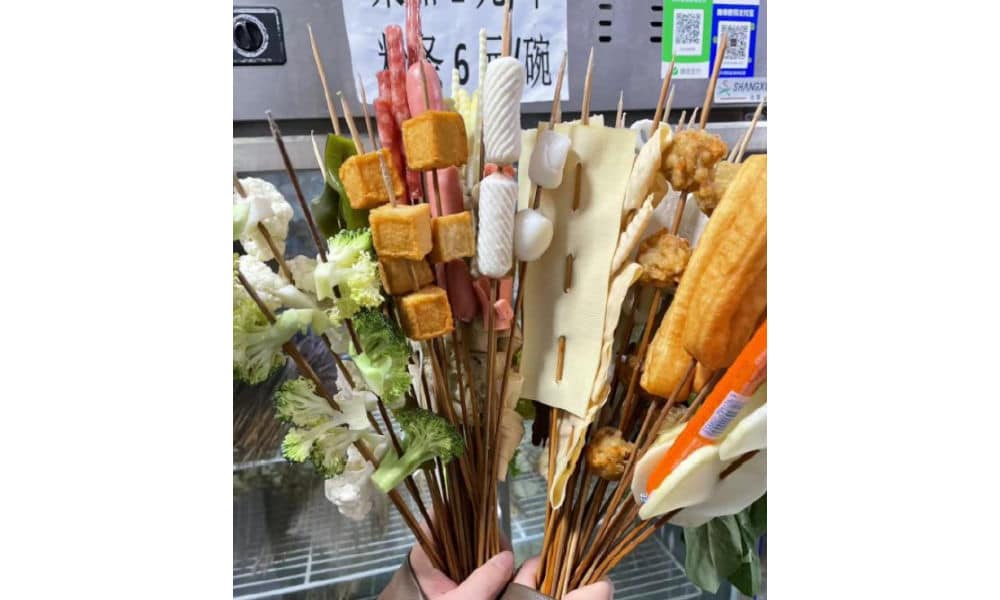

Although malatang originated in Sichuan, it is now common all over China. What makes Tianshui malatang stand out is its “Gansu-style” take, with a special focus on hand-pulled noodles, potato, and spicy oil.
An important ingredient for the soup base is the somewhat sweet and fragrant Gangu chili, produced in Tianshui’s Gangu County, known as “the hometown of peppers.”
Another ingredient is Maiji peppercorns (used in the sauce), and there are more locally produced ingredients, such as the black fungi from Qingshui County.
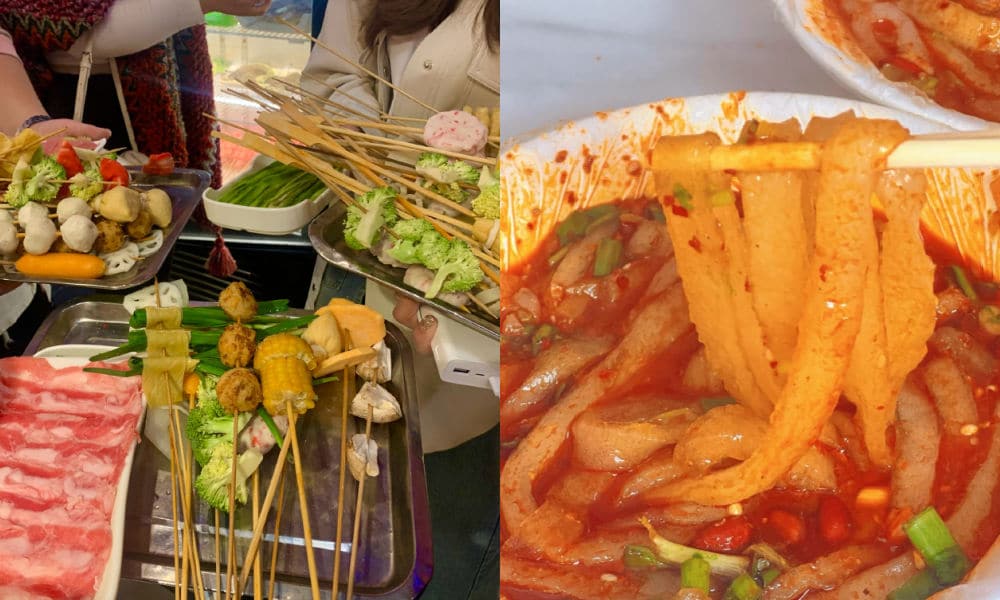

One restaurant that made Tianshui’s malatang particularly famous is Haiying Malatang (海英麻辣烫) in the city’s Qinzhou District. On February 13, the tiny restaurant, which has been around for three decades, welcomed an online influencer (@一杯梁白开) who posted about her visit.
The vlogger was so enthusiastic about her taste of “Gansu-style malatang,” that she urged her followers to try it out. It was the start of something much bigger than she could have imagined.
Replicating Zibo
Tianshui isn’t the first city to capture the spotlight on Chinese social media. Cities such as Zibo and Harbin have previously surged in popularity, becoming overnight sensations on platforms like Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin.
This phenomenon of Chinese cities transforming into hot travel destinations due to social media frenzy became particularly noteworthy in early 2023.
During the Covid years, various factors sparked a friendly competition among Chinese cities, each competing to attract the most visitors and to promote their city in the best way possible.
The Covid pandemic had diverse impacts on the Chinese domestic tourism industry. On one hand, domestic tourism flourished due to the pandemic, as Chinese travelers opted for destinations closer to home amid travel restrictions. On the other hand, the zero-Covid policy, with its lockdowns and the absence of foreign visitors, posed significant challenges to the tourism sector.
Following the abolition of the zero-Covid policy, tourism and marketing departments across China swung into action to revitalize their local economy. China’s social media platforms became battlegrounds to capture the attention of Chinese netizens. Local government officials dressed up in traditional outfits and created original videos to convince tourists to visit their hometowns.
Zibo was the first city to become an absolute social media sensation in the post-Covid era. The old industrial and mining city was not exactly known as a trendy tourist destination, but saw its hotel bookings going up 800% in 2023 compared to pre-Covid year 2019. Among others factors contributing to its success, the city’s online marketing campaign and how it turned its local BBQ culture into a unique selling point were both critical.

Zibo crowds, image via 163.com.
Since 2023, multiple cities have tried to replicate the success of Zibo. Although not all have achieved similar results, Harbin has done very well by becoming a meme-worthy tourist attraction earlier in 2024, emphasizing its snow spectacle and friendly local culture.
By promoting its distinctive take on malatang, Tianshui has emerged as the next city to captivate online audiences, leading to a surge in visitor numbers.
Like with Zibo and Harbin, one particular important strategy used by these tourist offices is to swiftly respond to content created by travel bloggers or food vloggers about their cities, boosting the online attention and immediately seizing the opportunity to turn online success into offline visits.
A Timeline
What does it take to become a Chinese ‘celebrity city’? Since late February and early March of this year, various Douyin accounts started posting about Tianshui and its malatang.
They initially were the main reason driving tourists to the city to try out malatang, but they were not the only reason – city marketing and state media coverage also played a role in how the success of Tianshui played out.
Here’s a timeline of how its (online) frenzy unfolded:
- July 25, 2023: First video on Douyin about Tianshui’s malatang, after which 45 more videos by various accounts followed in the following six months.
- Feb 5, 2024: Douyin account ‘Chuanshuo Zhong de Bozi’ (传说中的波仔) posts a video about malatang streetfood in Gansu
- Feb 13, 2024: Douyin account ‘Yibei Liangbaikai’ (一杯梁白开) posts a video suggesting the “nationwide popularization of Gansu-style malatang.” This video is an important breakthrough moment in the success of Tianshui as a malatang city.
- Feb – March ~, 2024: The Tianshui Culture & Tourism Bureau is visiting sites, conducting research, and organizing meetings with different departments to establish the “Tianshui city + malatang” brand (文旅+天水麻辣烫”品牌) as the city’s new “business card.”
- March 11, 2024: Tianshui city launches a dedicated ‘spicy and hot’ bus line to cater to visitors who want to quickly reach the city’s renowned malatang spots.
- March 13-14, 2024: China’s Baidu search engine witnesses exponential growth in online searches for Tianshui malatang.
- March 14-15, 2024: The boss of Tianshui’s popular Haiying restaurant goes viral after videos show him overwhelmed and worried he can’t keep up. His facial expression becomes a meme, with netizens dubbing it the “can’t keep up-expression” (“烫不完表情”).

The worried and stressed expression of this malatang diner boss went viral overnight.
- March 17, 2024: Chinese media report about free ‘Tianshui malatang’ wifi being offered to visitors as a special service while they’re standing in line at malatang restaurants.
- March 18, 2024: Tianshui opens its first ‘Malatang Street’ where about 40 stalls sell malatang.
- March 18, 2024: Chinese local media report that one Tianshui hair salon (Tony) has changed its shop into a malatang shop overnight, showing just how big the hype has become.
- March 21, 2024: A dedicated ‘Tianshui malatang’ train started riding from Lanzhou West Station to Tianshui (#天水麻辣烫专列开行#).
- March 21, 2024: Chinese actor Jia Nailiang (贾乃亮) makes a video about having Tianshui malatang, further adding to its online success.
- March 30, 2024: A rare occurrence: as the main attraction near Tianshui, the Maiji Mountain Scenic Area announces that they’ve reached the maximum number of visitors and don’t have the capacity to welcome any more visitors, suspending all ticket sales for the day.
- April 1, 2024: Chinese presenter Zhang Dada was spotted making malatang in a local Tianshui restaurant, drawing in even more crowds.
A New Moment to Shine
Fame attracts criticism, and that also holds true for China’s ‘celebrity cities.’
Some argue that Tianshui’s malatang is overrated, considering the richness of Gansu cuisine, which offers much more than just malatang alone.
When Zibo reached hype status, it also faced scrutiny, with some commenters suggesting that the popularity of Zibo BBQ was a symptom of a society that’s all about consumerism and “empty social spectacle.”
There is a lot to say about the downsides of suddenly becoming a ‘celebrity city’ and the superficiality and fleetingness that comes with these kinds of trends. But for many locals, it is seen as an important moment as they see their businesses and cities thrive.
Even after the hype fades, local businesses can maintain their success by branding themselves as previously viral restaurants. When I visited Zibo a few months after its initial buzz, many once-popular spots marketed themselves as ‘wanghong’ (网红) or viral celebrity restaurants.
For the city itself, being in the spotlight holds its own value in the long run. Even after the hype has peaked and subsided, the gained national recognition ensures that these “trendy” places will continue to attract visitors in the future.
According to data from Ctrip, Tianshui experienced a 40% increase in tourism spending since March (specifically from March 1st to March 16th). State media reports claim that the city saw 2.3 million visitors in the first three weeks of March, with total tourism revenue reaching nearly 1.4 billion yuan ($193.7 million).
There are more ripple effects of Tianshui’s success: Maiji Shan Grottoes are witnessing a surge in visitors, and local e-commerce companies are experiencing a spike in orders from outside the city. Even when they’re not in Tianshui, people still want a piece of Tianshui.
By now, it’s clear that tourism marketing in China will never be the same again. Zibo, Harbin, and Tianshui exemplify a new era of destination hype, requiring a unique selling point, social media success, strong city marketing, and a friendly and fair business culture at the grassroots level.
While Zibo’s success was largely organic, Harbin’s was more orchestrated, and Tianshui learned from both. Now, other potential ‘celebrity’ cities are preparing to go viral, learning from the successes and failures of their predecessors to shine when their time comes.
By Manya Koetse
Independently reporting China trends for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

A Brew of Controversy: Lu Xun and LELECHA’s ‘Smoky’ Oolong Tea

Weibo Watch: The Battle for the Bottom Bed

Zara Dress Goes Viral in China for Resemblance to Haidilao Apron

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

The ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions

Top 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday

“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng

Party Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”

From Pitch to Politics: About the Messy Messi Affair in Hong Kong (Updated)

Looking Back on the 2024 CMG Spring Festival Gala: Highs, Lows, and Noteworthy Moments

Chengdu Disney: The Quirkiest Hotspot in China

More than Malatang: Tianshui’s Recipe for Success

Two Years After MU5735 Crash: New Report Finds “Nothing Abnormal” Surrounding Deadly Nose Dive

The Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight2 months ago
China Insight2 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Arts & Entertainment3 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment3 months agoTop 9 Chinese Movies to Watch This Spring Festival Holiday
-

 China Arts & Entertainment2 weeks ago
China Arts & Entertainment2 weeks ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng
-

 China Media2 months ago
China Media2 months agoParty Slogan, Weibo Hashtag: “The Next China Will Still Be China”








Roger Guindon
January 22, 2016 at 5:14 pm
Being a foreigner in another country I certainly would not want a country to change ay any cost, a symbol that has thousands of years of history.. History is history that’s why we travel to educate ourselves on other cultures. :O)
Charuko Nakamachi
January 23, 2016 at 8:05 pm
I find this article to be interesting. So much angst over a symbol used for thousands of years with benevolent intent, usurped by one malevolent group a mere ninety four years ago, and troubled over today.
I find myself both torn and mystified by this symbol. It seems harsh to me in it’s appearance with it’s sharp angles, but the Buddhist usage is one of benevolence. My sense is that the NAZI usurpation of this symbol has taken it out of its context, and stolen it from kinder hearts.
Beyond that, it’s a very Japanese decision to remove it from maps that visitors would be using. The idea is to promote harmony and to make visitors as comfortable as possible. I believe that’s an exceptionally benevolent and laudable thing to do.
Domonique Brown
May 28, 2019 at 4:51 pm
That’s ignorant. Stop defending white supremacy. You should check your privilege. You probably think the “okay” hand gesture is safe to use. #BLM
Peter Herz
August 17, 2016 at 6:26 pm
I am an American who is 1/2 Central European Jewish. My father, God rest him, knew of family who perished in the Shoah. But it did not take me long to recognize the wanzi as a symbol of Buddhism, not Naziism, when I lived in Taiwan. I would tell Japan to keep the wanzi, or however the Japanese pronounce it, to mark temples on their maps, and I would tell the rest of the world to learn some history other than that of Europe over the past three centuries.
Andy Tithesis
August 27, 2018 at 4:37 pm
Most westerners have a Pavlovian response to anything relatable to the Nazi regime. We in America are taught very little of history outside a handful of our own believed victories. Few pay attention to even that I am afraid. As with most humans if you give them a cultural green light to despise and condemn something they will do so without a thought. Nobody wants to learn the details when they can act aggressively and spew venom as it is much more fun for most. Mankind will always have is beast not far from his heart but separated almost completely from his brain. I consider myself a Buddhist even though I am said to be tainted by my upbringing in western culture. I actually agree with that. Eastern thought is a rare thing these days worldwide. If you are on the computer reading this you to are more than likely tainted by the western influence. Still though there is redemption for those who can take it all in and turn something new and benevolent outwards. This symbol should never be taken down if put up for non radical reasons related to ignorance and racism. You should not be upset with the foreshadowed foreigners you should be upset with your own powers bowing to the almighty currency they greedily see coming. Your map company is a traitor to it’s own roots and you should let them know how you feel. Shall everything be made for sale to outside influence? It seems the way of the world as of late and it is sad and depressing. I have every religion in my heart and consider myself a student to them all if they will teach me wisdom beyond what our current world has to offer. Which really sets the bar pretty low actually but I shall remain hopeful that we as a species and a single race, the human race, can rise above the capitalist swindle and put a stop to such moronic and shameful sell out tactics such as this. This bewilders me and there should really be more articles like these on our side of the pond but sadly there is not. This is my opinion anyways. I thank you for your time. All are my brothers and sisters. Good luck to you all always. ♥
jamey james
January 6, 2019 at 9:32 pm
I am in agreement that one should respect traditional history. I have watched a lot of showlin stuff and had worked the fact out for myself of the difference between the two symbols being clockwise and anticlockwise. This also includes the colours gold and or black. I think that one should educate them self and learn the proper history before condemnation application.
Laura
January 25, 2019 at 6:10 pm
You MUST keep your traditions and wanzi. Don’t let the Occident tell you what you have to do. If the foreigners don’t like that, they can go back home ! Both Swastika have NOTHING to do with Nazism. We must stop this propaganda and protect the culture all over the world.
In Europe it becomes also very difficult. For example in Latvia, where the swastika is a very old worshiped symbol.
A french friend
Rancid Boar
July 9, 2020 at 7:58 am
This article doesn’t do a great job representing the Swastika.. The Swastika is clockwise and Suawstika is counterclockwise. Both were used since ancient times… The first person to use the Sanskrit word swastika and describe it was the Sage Panini. Su=Good Astik=To be, therefore the swastika means to be good… Nazis didn’t design thiers since they just bastardized the design and meaning. Still it isn’t an anti-Semitic, ignore that aspect. Your selective attention and cognitive dissonance has already let you ignore the Christian Cross and Sword of Islam as anti-Semitic symbols, despite the fact that those were actually used to crucify and kill Jews. Only Western mf with identity crisis can make a auspicious symbol a hate symbol, and a torture device a ‘holy’ cross… Makes perfect sense… The Swastika is eternal and will be used as long as humanity exists.
salesh Prasad Mishra
October 9, 2021 at 7:02 am
Oh wonderful This again.. You know folks, if you happen to one day read media not made by the west, or controlled by the west? Maybe you will open your eyes one day.
and for the rest of you you should stop actually swallowing whole would Western media is shoving down your throat.
it must also concern you that there are religions and even Nations that are older than your Bible but of course that doesn’t matter to you does it I know it’s a shocker.
even everything that you read on Wikipedia has a very Western vibe to it and by that you know exactly what I mean they’re always talking about our lease to them. You have to start learning how other people and other cultures actually work once you do you realize exactly what kind of mind virus has been implanted in your brain.
think freely